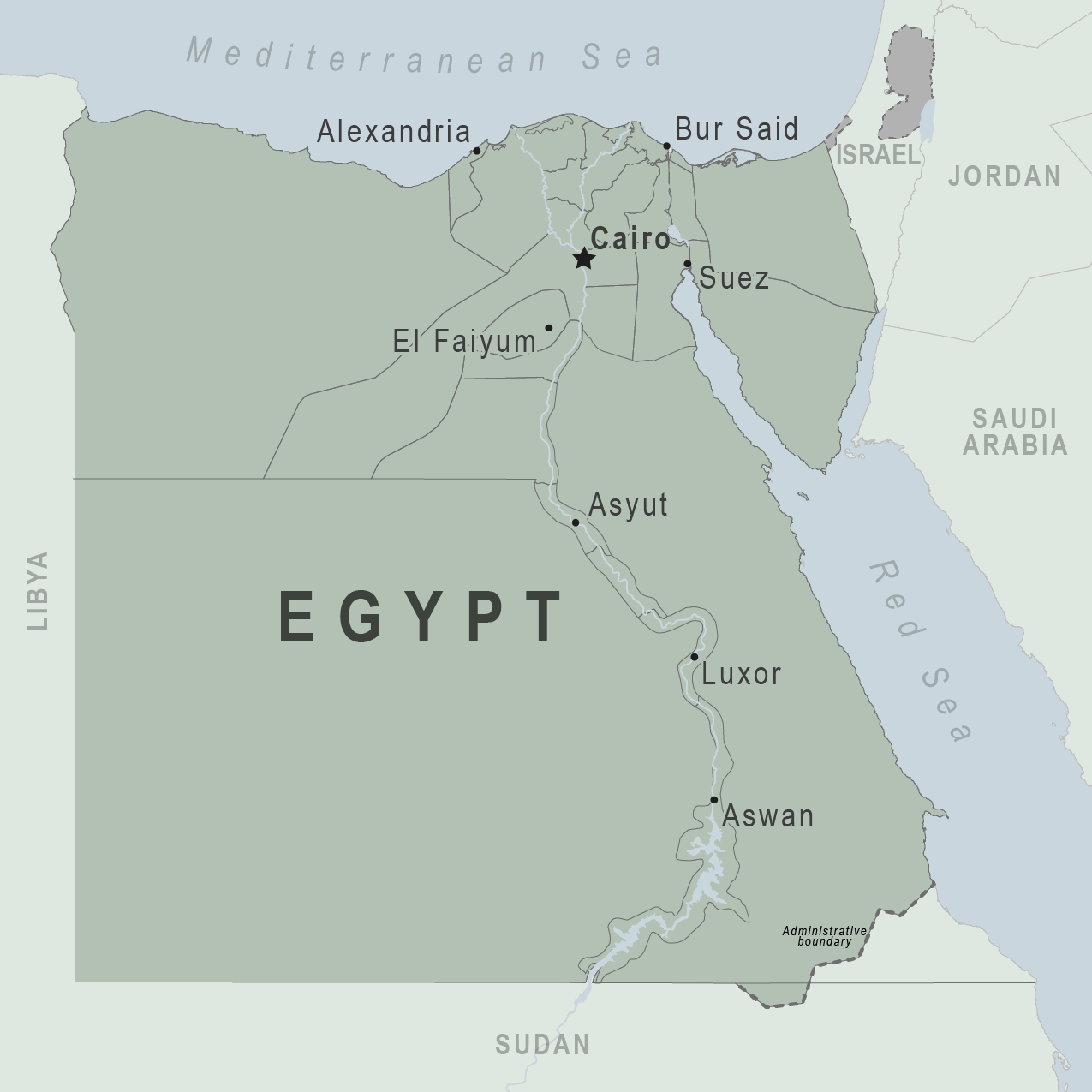
Egypt Travel Restrictions
Traveler's COVID-19 vaccination status

Traveling from the United States to Egypt
Open for vaccinated visitors
COVID-19 testing
Not required
Not required for vaccinated visitors
Restaurants
Required in enclosed environments and public transportation.
Egypt entry details and exceptions
Ready to travel, find flights to egypt, find stays in egypt, explore more countries on travel restrictions map, destinations you can travel to now, dominican republic, netherlands, philippines, puerto rico, switzerland, united arab emirates, united kingdom, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Can I travel to Egypt from the United States?
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Egypt.
Can I travel to Egypt if I am vaccinated?
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Egypt without restrictions.
Can I travel to Egypt without being vaccinated?
Unvaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Egypt without restrictions.
Do I need a COVID test to enter Egypt?
Visitors from the United States are not required to present a negative COVID-19 PCR test or antigen result upon entering Egypt.
Can I travel to Egypt without quarantine?
Travelers from the United States are not required to quarantine.
Do I need to wear a mask in Egypt?
Mask usage in Egypt is required in enclosed environments and public transportation.
Are the restaurants and bars open in Egypt?
Restaurants in Egypt are open. Bars in Egypt are .
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Egypt Travel Advisory
Travel advisory july 13, 2023, egypt - level 3: reconsider travel.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed.
Reconsider travel to Egypt due to terrorism . Exercise increased caution in Egypt due to the Embassy’s limited ability to assist dual national U.S.-Egyptian citizens who are arrested or detained.
Do not travel to:
- The Sinai Peninsula (with the exception of travel to Sharm El-Sheikh by air) due to terrorism .
- The Western Desert due to terrorism .
- Egyptian border areas due to military zones .
Country Summary: Terrorist groups continue plotting attacks in Egypt. Terrorists may attack with little or no warning, and have targeted diplomatic facilities, tourist locations, transportation hubs, markets/shopping malls, western businesses, restaurants, resorts, and local government facilities. Terrorists have conducted attacks in urban areas, including in Cairo, despite the heavy security presence. Terrorists have targeted religious sites, to include mosques, churches, monasteries, and buses traveling to these locations.
Due to risks to civil aviation operating within or in the vicinity of Egypt, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has issued a Notice to Air Missions (NOTAM) and/or a Special Federal Aviation Regulation (SFAR). For more information U.S. citizens should consult the Federal Aviation Administration’s Prohibitions, Restrictions and Notices .
Local law prohibits protesting or demonstrating without a permit. Being near anti-government protests can draw scrutiny from Egyptian police and security forces. U.S. citizens have been detained for participating in protests and for posting content on social media perceived as critical of Egypt or its allies.
The U.S. Embassy may have a limited ability to provide consular services to dual U.S.-Egyptian citizens. Egyptian law considers dual citizens to be Egyptian citizens.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Egypt.
If you decide to travel to Egypt:
- Stay alert in locations frequented by Westerners.
- Avoid demonstrations and crowds.
- Obtain comprehensive medical insurance that includes medical evacuation.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Egypt.
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Sinai Peninsula – Level 4: Do Not Travel The Sinai Peninsula remains a particularly dangerous area, with frequent attacks on security forces and civilians.
The U.S. government has limited ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens anywhere in the Sinai Peninsula as U.S. government employees are not authorized to travel to these areas (with the exception of the beach resort of Sharm El-Sheikh; travel to Sharm El-Sheikh is only permitted by air). Visit our website for Travel to High-Risk Areas .
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, search for travel advisories, external link.
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Egypt Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
Be aware of current health issues in Egypt. Learn how to protect yourself.
Level 2 Practice Enhanced Precautions
- Updated Global Polio August 20, 2024 Some international destinations have circulating poliovirus. Before any international travel, make sure you are up to date on your polio vaccines. Destination List: Afghanistan, Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Guinea, Indonesia, Kenya, Liberia, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Pakistan, Republic of South Sudan, Republic of the Congo, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, Sudan, Tanzania, including Zanzibar, The Gambia, Uganda, Yemen, Zambia, Zimbabwe
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
- Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
- Avoid floodwater
Clinical Guidance
Schistosomiasis
- Wading, swimming, bathing, or washing in contaminated freshwater streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, or untreated pools.
Avoid bug bites
African tick-bite fever.
- Avoid Bug Bites
African Tick-bite fever
Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic fever
- Tick bite
- Touching the body fluids of a person or animal infected with CCHF
- Mosquito bite
Leishmaniasis
- Sand fly bite
- An infected pregnant woman can spread it to her unborn baby
- Avoid animals
Rift Valley Fever
- Touching blood, body fluids, or tissue of infected livestock
Rift Valley fever
Airborne & droplet
Avian/bird flu.
- Being around, touching, or working with infected poultry, such as visiting poultry farms or live-animal markets
- Avoid domestic and wild poultry
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Egypt, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH)
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Egypt. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Egypt include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Schistosomiasis, a parasitic infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Egypt. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Egypt’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Egypt may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Egypt, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Egypt for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
- May we help you? Customer service 24 hours a day:
- +34 91 524 33 66
- [email protected]
- Requirements for travel to Egypt
- Plan your trip to Egypt
Egypt remains a tourist destination that captivates millions of people for its history , archaeological wealth and landscapes. If you are planning a trip to the country, in this article we tell you what is needed to travel to Egypt, so that you can organize your vacation in the best possible way.
Documentation for travel to Egypt
For residents of the european union.
To enter Egypt traveling from any of the EU member countries, the documentation you will need is a valid passport with a minimum validity of 6 months and, in addition, you will need to apply for a visa.
How to obtain a visa to Egypt?
It can be obtained directly upon arrival at the airport in the easiest way, or online from the Egyptian Ministry of Foreign Affairs website.

For citizens from non-European Union countries
The best option is to inquire at the relevant Egyptian embassy or consulate. In both cases, especially if you have contracted a trip through an agency, it is advisable to ask the same company that organizes the trip to also arrange visas for tourists.
With the exception of some Arab countries, all persons wishing to visit Egypt must apply for a tourist visa, which costs US$25 and is valid for 30 days. For longer stays, a special visa can be requested in advance or extended within the country. How to pay for a visa to Egypt? Payment can be made in dollars and also in euros or pounds sterling.
Vaccinations and health insurance
In these times of COVID-19 pandemic, to enter Egypt it is mandatory to present the complete vaccination schedule.
Visit the Egypt travel recommendations page of your country’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs .
Other diseases
No other vaccinations are mandatory for entry into Egypt , although it is recommended to check the status of standard vaccinations in case a booster against mumps, rubella, measles, diphtheria, typhoid or tetanus is necessary.
It should be noted that, for a Western traveler, the level of hygiene in Egypt may be low or insufficient, so it is recommended to wash your hands thoroughly before and after eating in each restaurant. And avoid drinking tap water, always opt for bottled water. In the capital, Cairo , it is the only place where there is no risk from drinking tap water, as it is treated with a lot of chlorine. In the rest of the country, tap water should be avoided at all costs. The good news is that bottled water is very cheap in Egypt.
Take out travel medical insurance
Regarding medical insurance for travelers, it is essential to contract one before traveling to Egypt because it is usually a requirement to enter the country and to be treated within the private health system. The recommended travel insurance for travel to Egypt is any insurance that covers not only medical problems but also theft and loss, to travel with more peace of mind.
If you go to Alexandria or to the shores of the Red Sea If you go scuba diving, or travel to Egypt for hiking or motorcycle riding, all of these are classified as “dangerous activities” and many health insurances do not cover them, so you should pay close attention and if you are going to do any of these activities, try to take out an insurance policy that covers them. You should also check or ask if the policy covers medications or ambulance transfers.
Internet connection in Egypt
It is becoming easier and easier to find free WiFi connection in hotels, cruise ships and restaurants in Egypt, especially since it is the second country in the world with the largest number of undersea fiber optic cables. This is due to its strategic geographical position as the main route connecting Asia, the Middle East and East Africa with Europe. However, there is still a long way to go before all historical sites, monuments and archaeological sites have a good free public WiFi connection. So, if you need constant internet during your trip to Egypt, the best options for mobile data are SIM cards or eSIM cards.
There is also the option of activating the international roaming service or carrying Pocket WiFi (small portable routers that you carry in your pocket and provide internet connection) but both services are usually much more expensive than the cards.
The average price of a SIM card for Egypt with 3G or 4G for 15 days ranges between 35€ and 47€, a price range similar to that of an eSIM card for 8 days. Vodafone’s roaming service costs 105€ for 14GB for 7 days, while Orange’s 700 MB for one week costs 49€. The rental of Pocket WiFi for 7 days costs between 60€ and 70€, excluding shipping costs which can be between 20€ and 25€.
How to manage money in Egypt
The currency of Egypt is the Egyptian pound (EGP). The average daily expenditure per tourist per day is estimated at around 600 EGP , including lodging, food, internal transportation and excursions, although this may vary slightly depending on the type of services contracted.
It is recommended to always have enough change on hand to pay for cabs and tipping. There are a good number of ATMs in almost all Egyptian cities, with the exception of areas in the interior of Middle Egypt and in the oases. Mid- and high-priced hotels and restaurants accept credit cards, with a sales rate ranging from 3% to 10%.
If you need to change currency in Egypt, you can do it officially at Amex and Travel Choice Egypt offices, and also in commercial banks, exchange offices (Forex) and even in some hotels. Rates are generally similar in all establishments, although some places may charge commissions.
We have more information about the Egyptian pound and various indicative prices of the most typical products and purchases that you will make on your trip.
What is required to enter and exit Egypt
Entry to egypt via airport.
To enter Egypt as a tourist, two basic requirements are necessary: a valid passport and a visa.
Passengers are also usually checked to see if they have any supporting documentation from the lodging establishment, as well as confirmation of an organized tour reservation with the corresponding itinerary and return ticket date.
Airport round trip
To leave Egypt and return to your country of origin, the airport control is similar to the entry control, with the addition of the customs check of products purchased by the tourist as souvenirs The products must not violate any international standard of suspected smuggling or infringe bromatology laws, in the case of edible products.
Covid-19 Pandemic Specific Measures and Restrictions
During the Covid-19 pandemic, some specific rules for entry and exit were added. And although prevention measures in Egypt were carried out with considerable discipline, the various waves of contagion could not be avoided. Therefore, we recommend you to travel with an FPP2 mask during your trip to Egypt, at least in situations of higher risk (if you decide to move by yourself and travel by metro or cab, for example), although it is not mandatory to do so. Current medical insurances usually include expenses derived from complications, tests or any other incident involving Covid-19.
Previously, upon arrival in the country, the temperature of each tourist was checked and a certificate of vaccination against Covid-19 was requested, and a negative PCR test was not mandatory for entry. However, as of June 17, 2022, Egypt lifted all restrictions for any international traveler, no vaccination certificate or PCR or antigen test is required .
As always, we recommend that you check a few days before your trip in case conditions change.
Other articles that may interest you...
If you are interested in what to buy in Egypt, the first thing we will tell you is that there
Traveling with children
It is very rare that the most touristic countries in the world are not prepared to receive children traveling with
Utilizamos cookies y otras tecnologías
Selecciona la configuración de privacidad.
Do you need a visa to go to Egypt?

Sep 3, 2023 • 4 min read

Most travelers need a visa to visit Egypt, but you'll soon get to see the Pyramids of Giza © SrdjanPav / Getty Images
Almost all travelers require a visa to enter Egypt, but fortunately, the process is pretty simple, and a little advance planning goes a long way.
This guide will walk you through the entry requirements for visiting the land of pyramids on a tourist visa.
Who needs a visa to visit Egypt?
Most nationalities need a visa to enter Egypt, but citizens of many countries can apply for an e-Visa in advance or obtain a visa on arrival at Egypt’s international airports. Both cost US$25.
Getting an e-Visa is generally a smoother process than getting a visa at the airport. Apply for a tourist visa online in advance on the Egyptian Government's official e-Visa website . All you have to do is fill out the online application form and pay.
If you decide to get a visa at the airport when you land in Egypt, be prepared to wait in line – bring your own pen to fill out the paperwork in line or on the plane – and pay in cash (US dollars, euros or British pounds only, not Egyptian pounds).
Citizens of Bahrain, Hong Kong, Kuwait, Macau, Oman, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates can enter Egypt visa-free for up to 90 days. Citizens of Malaysia can enter for up to 14 days.
If you're not eligible to get a visa on arrival or an e-Visa, head to the Egyptian embassy or consulate in your home country and apply in person. The visa process can take several weeks.
How to get an e-Visa for Egypt
To save time, apply for an e-Visa before your trip to Egypt. Citizens of these countries are eligible for Egypt’s e-Visa and can apply on the Egyptian government's official website . Your passport must be valid for at least six months before the date you intend to arrive.
The process is simple: sign up for an account, fill the form and pay the US$25 using a credit or debit card. You’ll receive email notifications as the application is processed.
If you’re issued a visa, you’ll be emailed a link to your e-Visa to download and print the document. When you land in Egypt, present the e-Visa to the Egyptian border patrol with your passport. Have a copy of your accommodation details or tour booking in case you’re asked to show them at the airport.
Egypt’s e-Visa can be single or multiple entry. The single-entry visa allows visitors one entry into the country for stays of up to 30 days. The multiple-entry visa allows travelers to come into Egypt an unlimited number of times over a period of 180 days and for up to 30 days at a time. Apply for a multi-entry visa at least seven days before your trip.
Visa on arrival in Egypt
If you don’t have time to apply for an e-Visa, you can still get a visa on arrival at the airport if you’re eligible. Visas are available for purchase (US$25) at a kiosk in the arrivals hall before the immigration counters.
Have the correct amount in cash in a major foreign currency (US dollars, euros or British pounds) to avoid delays.
The visa comes in the form of a stamp that you’ll need to put into your passport to present at the immigration counters and passport control.
If you opt for a visa on arrival, you’ll need a passport that’s valid for at least six months from your arrival date, a travel itinerary and documentation to show you've booked accommodations or tours.
Visa on arrival is available at all of Egypt’s international airports. The downsides are that you can be issued a single entry visa only, and the lines at the airport can be long.

You don't need a visa to stay in Sinai on short trips
If you are visiting the resort towns on the Gulf of Aqaba coast and won’t be going to mainland Egypt, you can stay in Sinai for 14 days without buying an Egyptian visa. The Sinai-only visa allows travellers to visit Sharm El Sheikh , Dahab , Nuweiba , Taba and St Catherine, but you cannot go to Ras Muhammad National Park.
The Sinai-only visa is available at the airport in Sharm El Sheikh and the Egypt–Israel border crossing at Taba. If you arrive at Taba and plan to visit mainland Egypt, you must purchase a visa online in advance or at an Egyptian embassy abroad.
This article was first published Jun 26, 2022 and updated Sep 3, 2023.
Explore related stories

Destination Practicalities
Sep 5, 2024 • 9 min read
Plan the perfect trip to Egypt with these essential tips on etiquette, health and safety.

Sep 4, 2024 • 5 min read

Jun 26, 2024 • 6 min read

Mar 12, 2024 • 4 min read

Mar 4, 2024 • 4 min read

Jan 11, 2024 • 4 min read

Jan 2, 2024 • 11 min read

Dec 8, 2023 • 7 min read

Dec 5, 2023 • 4 min read

Nov 5, 2023 • 6 min read

Covid-19 Travel
Egypt lifts Covid-19 restrictions for all in-bound travellers
Daily infection rates have been steadily declining in the country since a peak in february.
June 17, 2022
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on WhatsApp
Traveling to Egypt during Covid-19: What you need to know before you go
What’s on offer
Entry requirements, us cdc travel advisory:, related articles.

Giza Governor orders to develop area surrounding Grand Egyptian Museum

Man kills wife and daughter, injures 4 others in Giza family massacre

Antiquities Ministry to develop entrance to pyramids area at Fayoum Governorate

Egypt’s first underwater military museum to be established in the Red Sea

What Are The Requirements To Travel To Egypt?
There are 3 main entry requirements for travel to Egypt: a valid passport with at least two blank pages and at least 6 months validity remaining. Additionally, you also need a valid entry visa.

Now that the worst of the Covid-19 pandemic has passed, Egypt is once again open to tourists, as are the country’s many world-famous tourist sites. So, what are the requirements to travel to Egypt? Let’s take a look:
Valid Entry Visa
In addition to a valid passport, you will also need a visa. The citizens of approximately 70 countries can get a visa on arrival at any international Egyptian airport or they can apply online for an Egypt e-Visa prior to travelling to Egypt . For the citizens of these 70+ countries there is no need to visit an Egyptian embassy. This only applies in the case of tourist visas.
Those who are able to obtain a visa-on-arrival should note that a visa-on-arrival is a single entry 30-day visa. If applying online for an Egypt e-Visa, you have the choice between a single-entry and multi-entry visa. As of the time of writing, the visa fee for a single-entry visa was $25 while the visa fee for a multi-entry visa $60.
If you require a visa other than a tourist visa, such as a business visa, you will need to visit an Egyptian embassy or consular office.
People who come from countries whose citizens are not illegible for a visa-on-arrival or an e-Visa must also apply for their visas at an embassy or consular office. In addition to your passport and application form, you may be asked for additional documentation.
The number of documents required tends to differ from one nationality to the next, and can include things like bank statements, pay slips, and even a letter from your employer stating that you will be granted leave and that you will return to your job after you trip to Egypt.
Anyone who needs to apply for a visa at an Egyptian embassy should do so well in advance of their planned departure day because visa processing can take several weeks. It takes at least two to four weeks, or even longer, to find out if your application has been successful or not.
South Sinai Resorts
The citizens of many countries can visit Egypt’s South Sinai resorts, such as Sharm El-Sheikh, without the need for a visa. Instead, you are given a free “permission to enter” stamp in your passport that serves as your visa. This allows you to remain in the country for up to 15 days. However, you are not allowed to leave the Sinai Peninsula.
According to the U.S. State Department, all travel in North Sinai should be avoided, while all non-essential travel in South Sinai should also be avoided. The government of Canada has similar warnings in place due to the unpredictable security situation.
If you plan on taking advantage of this 15-day visa-free option, it is best that you travel directly to a coastal resort like Sharm El-Sheikh where additional security measures have long been in place in order to protect the area’s thriving tourism industry.
Detailed Guide: Egypt Visa Requirements
Design Your Custom Egypt Tour
Explore Egypt your way by selecting only the attractions you want to visit
Immunization for Egypt
What are the requirements to travel to Egypt in terms of immunization? There are no mandatory vaccines needed in order to visit Egypt. However, it is recommended that all travellers get vaccinated for Hepatitis A and Typhoid.
Hepatitis A can spread by means of contaminated food or water. No matter where you stay while you are in Egypt, you will be at risk of getting Hepatitis A if you have not been vaccinated.
Typhoid can also be spread by contaminated food and water but tends to be more prevalent in the smaller cities and in rural areas. If your travel plans include being in contact with animals, you should also consider getting vaccinated against Rabies.
Last but not least, if you are from a country where Yellow Fever is prevalent, or if you have recently traveled to or through such a country, you will need to show proof of Yellow Fever immunization on arrival in Egypt.
If you have concerns about whether you need a particular vaccine or not, you should consult with a travel health professional prior to travelling to Egypt.
Detailed Guide: What Vaccines Are Required To Travel To Egypt?
Covid-19 Requirements
What are the requirements to travel to Egypt in terms Covid? The good news is that the Egyptian government has lifted all Covid-19 travel restrictions. Visitors are no longer required to show proof of Covid-19 vaccination. There is also no longer any mandatory Covid-19 test on arrival in the country. The last remaining travel restrictions were lifted on the 17th of June, 2022.
Detailed Guide: Do You Need Covid Vaccine to Travel to Egypt?
Your Dream Trip to Egypt is only a Few Clicks Away!
Now that you know what are the requirements to travel to Egypt, it’s time to start planning your Egypt itinerary . We’re sure you want to see everything Egypt has to offer, including the pyramids, the Sphinx, the Valley of the Kings , and more. But where should you go? Which tour company offers the best value? How many days should you spend touring? What about accommodations? These questions and more can make planning a dream vacation a little overwhelming. Luckily, we’ve got all the answers for you!
Don’t miss out on seeing the most amazing sights in Egypt! Book a high-quality Egypt tour and/or Nile cruise today!
Explore Egypt and the Middle East your way by selecting only the attractions you want to visit

12-Day Cairo, Nile Cruise And Red Sea Stay

10-Day Luxury Nile Cruise and Cairo Tours

10-Day Egypt and Jordan Luxury Tours

8-Day Cairo to Abu Simbel Tour w/ Nile Cruise

8-Day Egypt Holiday Tour – Cairo and Nile Cruise [By Train]

8-Day Best of Egypt Tour – Cairo and Nile Cruise [By Air]
Egypt travel information.

Full Safety Guide: Is It Safe to Travel to Egypt?

What are the Must Visit Places in Egypt?

Egypt Travel Tips: This You Need to Know

How to Plan a Trip to Egypt – Start Here!

Best Time to Visit Egypt: Weather & Tourism Insights

What to Pack for Egypt (Simple Packing List)
Last Updated on June 21, 2024
You might also like

We Don't Just Sell Amazing Tours, We Make Dreams Come True!
Private tours since 1955.

Award-Winning Service
Create your dream trip.
Design Your Custom Tour
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
Entry requirements
This advice reflects the UK government’s understanding of current rules for people travelling on a full ‘British citizen’ passport from the UK, for the most common types of travel.
The authorities in Egypt set and enforce entry rules. If you’re not sure how these requirements apply to you, contact the Consulate General for Egypt in the UK .
Passport validity requirements
Your passport must be valid for 6 months from the date you arrive. Check with your travel provider to make sure your passport and other travel documents meet their requirements. Renew your passport if you need to.
Visa requirements
British passport holders travelling to Egypt normally need a visa. Visa processing fees are non-refundable.
We advise you to get a visa before you travel, particularly if travelling for work or business. You can apply for a visa from the official Visa2Egypt portal or at your nearest Egyptian Consulate . Tourist visas granted using the e-visa system are valid for a maximum of 3 months.
The online e-visa portal (Visa2Egypt) does not currently accept applications from variant British passport holders (those from British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies).
All British passport holders can get a visa in advance by submitting an application in person or by post to the Egyptian Consulate in London . The specific requirements for the visa are listed on the website.
Alternatively, if you wish to get a visa on arrival, you can do so at approved bank kiosks within airport arrival halls, before reaching immigration counters. The visa fee is 25 US dollars, payable in dollars as the preferred currency, although you may also be able to pay in pounds sterling or euros. Visas granted on arrival are valid for a maximum of 30 days. There’s no need to buy a visa from an agent. In many cases agents will charge more than US$25 for a visa. If you’re harassed by an agent, report the incident to the tourist police in the airport terminal.
If you’re travelling to Sharm el Sheikh, Dahab, Nuweiba and Taba resorts for up to 15 days, you will receive a free entry permission stamp on arrival. If you intend to travel out of these areas or stay longer than 15 days, you must get a visa.
If you have travelled to one of the South Sinai Red Sea resorts, entered without a visa and your plans have changed, you can normally purchase a visa at Sharm el Sheikh airport to allow you to travel elsewhere.
Applications for visa extensions should be made at Egyptian Passport and Immigration Offices. You may have difficulties leaving Egypt with an out of date visa. You will normally have to pay a fine if your visa is out of date by more than 14 days.
For further information and enquiries, contact the Egyptian Consulate in London .
Visa extensions
Apply for visa extensions at the Egyptian Passport and Immigration Offices. You may face difficulties if you try to leave Egypt on an expired visa. You may be fined if your visa has expired by more than 14 days.
Contact the Egyptian Consulate in London for more information.
Visas at the Egypt-Sudan Border Crossing
If you’re crossing the border from Sudan, the Egyptian authorities have advised it is still possible to get a visa on arrival for the regular cost of 25 US dollars.
HIV test for work permits
You will need to show your result from a HIV test to apply for a work permit.
Vaccination requirements
At least 8 weeks before your trip, check the vaccinations and certificates you need on TravelHealthPro’s Egypt guide . Depending on the country you’re arriving from, this may include a yellow fever vaccination certificate.
Customs rules
There are strict rules about goods that can be brought into and taken out of Egypt . You must declare anything that may be prohibited or subject to tax or duty.
You’re allowed to bring in or take out up to 5,000 Egyptian pounds. There is no limit to the amount of hard currency that you can bring in, but you must declare it when you arrive if it’s worth more than 10,000 US dollars.
You must also declare certain valuables, including electrical equipment or video cameras, when you arrive. These will be noted in your passport. You may be asked to show these items again when you leave the country. If you do not have them on you, you may have to pay a high rate of customs duty.
Officials are likely to confiscate satellite phones or radio communications equipment unless you have prior clearance from the Ministry of Telecommunications.
Contact the Egyptian embassy in your country of residence for further information on customs requirements
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Egypt travel advice
Latest updates: The Need help? section was updated.
Last updated: August 22, 2024 10:14 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, egypt - exercise a high degree of caution.
Exercise a high degree of caution in Egypt due to the unpredictable security situation and the threat of terrorism.
Northern Sinai - Avoid all travel
This advisory excludes the Al Qantra Shark – Ras Sedr road between the border of the Governorate of South Sinai and Al-Ganayen, in Suez Governorate, on which you should exercise a high degree of caution.
The Western desert and Libyan border area - Avoid all travel
- within 50 kilometres of the border with Libya
- the Western Desert, west of the Giza-Luxor-Aswan-Abu Simbel road, including the oasis of Dakhla
This advisory excludes the following areas where you should exercise a high degree of caution:
- Marsa Matruh via the Marsa Matruh Road only
- The White and Black deserts via the Oasis Road only
- The oases of:
- Siwa via the Masra Matruh-Siwa Road only
- Bahariya, Farafra and Bawati via the Oasis and the Farafra-Dairut Roads only
Northern part of the Governorate of South Sinai - Avoid non-essential travel
This advisory excludes the following locations, where you should exercise a high degree of caution:
- the Dahab – Nuweiba – Taba road
- the towns of Nuweiba and Taba
- the Al Qantra Shark – Ras Sedr road up to the border with the Governorate of Suez
- cities between Ras Sedr and El Tor
Back to top
Situation in Israel, the West Bank and the Gaza Strip
Following recent developments in Israel, the West Bank and the Gaza Strip, the security situation in neighbouring Sinai could deteriorate suddenly. Local authorities could impose movement restrictions on short notice.
If you are in or near affected areas:
- monitor local and international media to stay informed of the rapidly evolving situation
- follow the advice of local authorities
The security situation in Egypt is unpredictable and certain regions of the country (for instance, North Sinai, Western Desert, etc.) are particularly volatile and should be avoided. There is a significant risk of terrorist attacks throughout the country. Attacks can be indiscriminate and occur with no warning, including in Cairo. While attacks in the North Sinai are frequent and mainly target security forces, terrorists have also targeted popular tourist destinations, places of worship, and other places frequented by foreigners throughout Egypt.
Terrorists have targeted Coptic Christians and their places of worship, in both urban and isolated areas. Terrorists also attacked a mosque in the North Sinai on November 24, 2017, killing over 300 people. Avoid all religious institutions in Egypt.
There is a significant presence of armed security forces and police in most governorates throughout the country. Curfews may be imposed on very short notice.
On May 19, 2019 and December 28, 2018, attacks on buses carrying tourists took place near the pyramids of Giza. The explosions resulted in multiple casualties.
There is an increased risk of incidents and attacks on and around dates of national significance, including:
- January 25, the anniversary of the 2011 Egyptian revolution;
- The week of Orthodox Easter;
- June 30 to July 3, the anniversary of the removal of former president Mohamed Morsi in 2013;
- August 14, the anniversary of clearing protesters from Rabaa and al-Nahda squares in 2013; and
- Other religious observances and holidays.
Exercise increased caution during these periods.
Be particularly cautious in commercial establishments, government facilities, public areas, tourist sites, the vicinity of churches and mosques at the time of religious services and any other areas frequented by foreigners. Avoid police stations, security installations and government buildings, as well as all crowds and demonstrations.
Western Desert
Borders with Sudan and Libya are porous, and bandits and armed groups are active in these areas. Attacks on security checkpoints and forces are expected to continue. Egyptian military and security personnel are also engaged in security operations in the area. If you intend to travel to these areas, consider the risks to your personal safety and ensure you have made appropriate security arrangements. Travel to these areas requires a permit from the Travel Permits Department at the Egyptian Ministry of Interior Affairs.
To visit the isolated oasis town of Siwa, take the Marsa Matruh-Siwa road. Access to essential services such as medical care, ATMs, fuel and mobile phone coverage is limited on the Marsa Matruh-Siwa Road and in Siwa itself. There is only one gas station on the 300km road between Marsa Matruh and Siwa. The road is poorly lit, unpaved in some areas and has a number of significant potholes. Traffic accidents are common.
If you are travelling to Siwa:
• carefully plan all road travel in advance • fill up in Marsa Matruh and make sure to have enough fuel to reach your destination • be sure to have sufficient water and cash with you • travel during daylight hours only • consider renting a vehicle with four-wheel-drive • expect military checkpoints along the way • do not travel off-road outside of the Oasis
North Sinai Governorate
The security situation in North Sinai Governorate, particularly the areas bordering Israel and the Gaza Strip, is extremely unpredictable. Terrorist groups regularly carry out attacks against Egyptian security forces. A curfew is in effect from 5 p.m. to 7 a.m., due to ongoing Egyptian military operations against terrorist groups in the region. Road blockades by unsanctioned groups, kidnappings, robberies and carjackings by armed groups and terrorists occur.
South Sinai Governorate
While attacks are significantly less frequent than in North Sinai, terrorists have carried out attacks in South Sinai Governorate, targeting both security forces and tourists. Terrorist groups may expand targeted areas to include coastal resorts such as Sharm el-Sheikh. While enhanced security measures are in place to protect the tourism infrastructure in Sharm el-Sheikh, the area may be seen as a high-value target by terrorists.
Coastal resorts in Sinai, including Dahab, Nuweiba and Sharm el-Sheikh, have seen incidents of petty theft.
Tensions between security authorities and local Bedouin tribes may rise unexpectedly, affecting tourism.
There are several police checkpoints along the highways in South Sinai.
You need a permit from the Ministry of the Interior to travel in a 4x4 vehicle from mainland Egypt to South Sinai through the Suez crossing.
Local authorities may ask for identification and search your vehicle.
When travelling in the area:
- always use main highways
- avoid uncontrolled and poorly maintained roads
- stop at designated checkpoints and comply with authorities’ requests
- be aware of your surroundings at all times
Red Sea resorts and Upper Egypt
Exercise a high degree of caution when travelling to Red Sea coastal resorts (such as Ain el-Sokhna, el-Gouna Bay, Hurghada, Marsa Alam, Safaga and Soma Bay) and to the Upper Egypt cities of Aswan and Luxor. While the beach resort areas are generally considered safe, sporadic terrorist attacks have targeted foreign tourists in recent years. Pay particular attention to local conditions if you are visiting Upper Egypt and the historic sites of the Nile Valley. Sectarian, economic and family-related disputes have occurred and can quickly become violent. Travel in large groups and by organized transportation, and follow the advice of local authorities, hotels and tour guides if you are travelling to rural areas.
Demonstrations and Civil unrest
While the size and frequency of demonstrations has decreased significantly in recent years, they can still occur anywhere at any time without warning, but are most likely to occur on Fridays following noon prayers.
Be extremely vigilant. Avoid all demonstrations or large public gatherings. Keep well informed of developing situations by monitoring local news reports and follow the advice of local authorities. Women should take particular care, as there is a serious risk of sexual assault during demonstrations; once surrounded by a group, it can be difficult to escape.
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Rates of violent and petty crime have historically been low in Egypt, although there are reports that such crime has been on the rise given the economic downturn since 2011. Crimes such as pickpocketing, bag and purse snatching and home invasion, while rare, have become more common. Purse snatching and pickpocketing occur most often in tourist locations and on the metro. Be aware of your surroundings and vigilant for thieves using different strategies to distract and rob you.
Reports of carjackings are extremely rare, however they do occur. They generally target sports utility or other high-value vehicles. Although isolated areas and night driving present the greatest threat, there have been reported incidents in daylight hours and in busy areas of Cairo. Assailants are usually armed, and a variety of tactics may be used to get vehicles to stop, including throwing objects at the windshield, feigning a traffic accident or minor collision with the target vehicle, or “sandwiching” the target vehicle to force it off the road. If you find yourself in such a situation, do not resist as carjackers are typically after the vehicle and, if the carjacking is successful, will leave the driver unharmed.
If you are a victim of crime, report it to the Tourist Police or at a nearby police station as soon as possible. Request a copy of the police report at the time the report is made. Failure to report the crime while in Egypt makes it much more difficult to seek prosecution.
Women’s safety
Women, particularly foreigners, are frequently subject to unpleasant male attention, sexual harassment and verbal abuse. This often takes the form of staring, inappropriate remarks, catcalls and touching. The risks increase around public holidays, when more men are in the streets.
Advice for women travellers
Unexploded landmines remain a risk in some desert and coastal areas, notably the Mediterranean shore, the Western Desert, the Sinai Peninsula and the western shore of the Gulf of Suez. Known minefields are not marked by signs, but may be enclosed by barbed wire. Seek local advice, especially if travelling off-road.
Road safety
Road conditions are often poor and the rate of vehicular accidents is one of the highest in the world. Drivers generally have little regard for traffic regulations and do not follow safe driving practices. Be cautious when crossing streets as drivers do not give pedestrians the right of way.
In the event of an accident, do not move the vehicle until the police arrive, unless you are in immediate danger, such as from a crowd and need to move to safety. Exercise caution when using taxis and the metro. There have been robberies and accidents involving both. Many taxis do not have working metres, and back seats are rarely equipped with seat belts. Women should not sit in the front seat, as this could be misinterpreted by the driver. The metro can be overcrowded and is not climate controlled but does have cars for women only on most lines.
Use vehicles and hire drivers from reputable travel agencies.
Public transportation
Safety standards for rail travel vary throughout Egypt. There have been major accidents in recent years, attributed to aging infrastructure, poor maintenance and human error. Exercise a high degree of caution.
Avoid microbuses because of hazardous driving habits.
Overcrowding and poor safety standards on ferries have caused accidents. Use reputable ferry operators.
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Scuba diving / aquatic activities
Sharks and other potentially dangerous aquatic animals are present in the waters off Egypt. Certain beaches and dive areas may be subject to temporary closures. Exercise caution and seek advice from local authorities, and ensure to dive with reputable and licensed operators.
Water safety abroad
Israeli Border
Due to recent events in Israel, West Bank and the Gaza Strip, the land borders could close with little notice.
Crossing at the Taba land border between Egypt and Israel is possible at this time. Cross-border movement regulations and restrictions are subject to change at any time and are the prerogative of the responsible authorities.
The Rafah border crossing point to the Gaza Strip, which is controlled by border authorities in both Egypt and Gaza, opens and closes intermittently due to the ongoing armed conflict in Israel. Global Affairs Canada continues to advise against all travel in this area due to ongoing military operations against terrorists. Consult local authorities and refer to the travel advice for Israel, the West Bank, and the Gaza Strip for further information.
Beyond the provision of a travel document (the passport), the Canadian government does not facilitate the crossing of borders by private citizens. It is the citizen’s responsibility to meet the entry requirements of the country where they wish to travel, in most cases either through application for a visa or simply by going to a point of entry. Authorities at the Rafah border crossing from Egypt to Gaza have sometimes requested a letter or witnessed declaration from the Embassy of Canada to Egypt as a requirement to cross the border. The Canadian embassy is unable to provide such a letter or declaration. You should avoid all travel to Gaza. Furthermore, the Canadian government has very limited ability to provide consular services to Canadians in the Gaza Strip and once there, it may be difficult to leave.
General safety information
Although most tourist sites are open, the situation across Egypt remains unpredictable and less consistently safe than it was before January 2011. There is a potential for rapid escalation into violence where large groups of people are assembled
Egypt has a special police force to assist tourists. Officers wearing a distinctive arm band saying “Tourism Police,” can be found in hotels and at tourist sites.
Carry identification at all times. Photocopy your passport and other identification in case of loss or seizure.
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Egyptian authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave Egypt.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Diplomatic and Special passport holders are required to have visas before arrival in Egypt.
Travelers attempting to enter Egypt with diplomatic or official passports who do not have visas will be required to remain, at their own expense, in the airport transit area until their immediate departure from Egypt can be arranged. The Embassy of Canada in Egypt cannot intervene in such matters.
Tourist visa: required Business visa: required Student visa: required
You must obtain a visa from an Egyptian embassy or consulate near you before your departure. Electronic visas issued before October 1, 2023, remain valid until their expiry date.
If you wish to extend your stay in Egypt, contact the Immigration Authority of Egypt. You may be fined upon departure if you overstay your 30-day visa period without proper authorization.
Foreign Representatives in Canada
Entry and exit stamps
You must show proof of an entry stamp in your passport when you leave Egypt. If you cannot provide proof of entry, you cannot obtain an exit stamp and will be denied exit.
If you have entered the country with a Canadian passport and have obtained a new one while in Egypt, you must have the entry stamp transferred to the new passport by the Egyptian Immigration Authority.This requirement also applies to newborns and dual citizens.
If a child is born in Egypt to a Canadian parent, a data stamp proving that the child was born in Egypt must be added to the child’s Canadian passport before the child can exit the country. Since there will be no entry stamp in the child’s passport, you must submit both the child’s birth certificate and Canadian passport to the Egyptian Immigration Authority to obtain what Egyptian authorities term the “data stamp.” Parents are advised to contact the Embassy of Canada as soon as possible to apply for citizenship and a passport for their child, so as not to further delay what can be a lengthy process.
Regional travel
If you are contemplating onward travel to other Arab countries, bear in mind that Canadians have been denied entry because their passports bore an Israeli visa, an Israeli border stamp or an Egyptian or Jordanian border stamp issued by an office bordering Israel, which would indicate they entered from Israel.
Medication and cosmetics
Egyptian authorities consider some prescription and over-the-counter medicines medications controlled substances. They will seize all narcotic and psychotropic medications, even if you have the original prescription. For all other prescription and over-the-counter medications:
- Carry the original prescription
- Ensure the medication is in its original packaging
- Don’t attempt to enter with more than 3 months’ supply.
Authorities also regulate the import of cosmetics and veterinary products.
Health entry requirements
All foreigners planning to study, work or train in Egypt for longer than one month may be required to undergo testing for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Egyptian immigration authorities in Cairo’s Mogamma building provide information on this procedure upon application.
When entering from another country you may be required to provide proof of immunizations. Please verify with the Egyptian Embassy nearest to you before travelling.
- Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
- Polio: Advice for travellers - 20 August, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.

Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is no risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is required if you are coming from or have transited through an airport of a country where yellow fever occurs.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is not recommended.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada * It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
In this destination, rabies is commonly carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. In this destination, rabies treatment may be limited or may not be available, therefore you may need to return to Canada for treatment.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
The World Health Organization (WHO), at the time of their last report, identified this country as no longer poliovirus-infected, but as having been previously infected within the last 24 months.
Polio is spread from person to person and through contaminated food and water. Infection with polio virus can cause paralysis and death in individuals of any age who are not immune.
Polio can be preventeed by vaccination.
Recommendations:
- Be sure that your polio vaccinations are up to date before travelling. Polio is part of the routine vaccine schedule for children in Canada.
- One booster dose of the polio vaccine is recommended as an adult .
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
There is a risk of schistosomiasis in this destination. Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by tiny worms (blood flukes) which can be found in freshwater (lakes, rivers, ponds, and wetlands). The worms can break the skin, and their eggs can cause stomach pain, diarrhea, flu-like symptoms, or urinary problems. Schistosomiasis mostly affects underdeveloped and r ural communities, particularly agricultural and fishing communities.
Most travellers are at low risk. Travellers should avoid contact with untreated freshwater such as lakes, rivers, and ponds (e.g., swimming, bathing, wading, ingesting). There is no vaccine or medication available to prevent infection.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The level of risk may vary by:
The virus that causes chikungunya is spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can cause fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times.
Learn more:
Insect bite and pest prevention Chikungunya
- In this country, risk of dengue is sporadic. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue fever.
Rift Valley fever is a viral disease that can cause severe flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can be fatal. It is spread to humans through contact with infected animal blood or tissues, from the bite of an infected mosquito, or eating or drinking unpasteurized dairy. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from insect bites and avoid animals, particularly livestock, and unpasteurized dairy. There is no vaccine available for Rift Valley fever.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Human cases of avian influenza have been reported in this destination. Avian influenza is a viral infection that can spread quickly and easily among birds and in rare cases it can infect mammals, including people. The risk is low for most travellers.
Avoid contact with birds, including wild, farm, and backyard birds (alive or dead) and surfaces that may have bird droppings on them. Ensure all poultry dishes, including eggs and wild game, are properly cooked.
Travellers with a higher risk of exposure include those:
- visiting live bird/animal markets or poultry farms
- working with poultry (such as chickens, turkeys, domestic ducks)
- hunting, de-feathering, field dressing and butchering wild birds and wild mammals
- working with wild birds for activities such as research, conservation, or rehabilitation
- working with wild mammals, especially those that eat wild birds (e.g., foxes)
All eligible people are encouraged to get the seasonal influenza shot, which will protect them against human influenza viruses. While the seasonal influenza shot does not prevent infection with avian influenza, it can reduce the chance of getting sick with human and avian influenza viruses at the same time.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Medical services and facilities
Medical facilities are below Canadian standards.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Health and safety outside Canada
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
You should carry an international driving permit.
International Driving Permit
The use of drugs and open consumption of alcohol (other than in licensed facilities such as hotels and restaurants) are prohibited. Transgressions could be punished by detention or other penalties.
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are strict. Convicted offenders can expect jail sentences and heavy fines. Capital punishment is a sentencing option for certain drug-related crimes.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
Demonstrations
Local law prohibits protests without a permit.
Being near anti-government protests may subject you to scrutiny from Egyptian police and security forces.
Drones are strictly prohibited in Egypt; anyone convicted of unauthorized import or use of drone technology could be subject to lengthy jail terms and deportation. Unauthorized possession and usage of drones in Egypt may carry similar charges to espionage.
Electronic devices
Egyptian officials will likely confiscate electronic devices upon entry if you did not obtain prior approval to import them. This includes:
- large video cameras
- filming equipment
- satellite phones
- certain equipment like binoculars
You may face interrogation on the intended use of your devices due to their potential use for military and surveillance purposes.
Contact the nearest Embassy of the Arab Republic of Egypt for further information on regulations and requirements on electronic devices.
Photography
Photography of bridges, canals (including the Suez Canal), government, police and embassy buildings and vehicles, as well as military personnel and establishments is prohibited.
Social media
Publishing or posting social media or other content that could be perceived as critical of Egyptian society, government, security forces or the President may be considered illegal under Egyptian law. Convictions can carry heavy fines and lengthy prison sentences. There is a high risk of arrest in connection to social media posts considered critical of Egypt.
Due to the current security context and political sensitivities, be conscious of your behaviour and how it may be interpreted by Egyptian authorities. Visitors including researchers, journalists, activists and development workers could encounter problems with authorities, if their activities are perceived as suspicious. Meeting with members of or expressing support for organizations banned in Egypt could be perceived as criminal behaviour.
Suspects may be detained without charges or access to immediate legal counsel during investigative stages of a criminal case.
Strict duties apply on the importation of expensive electronics, including video and photographic equipment, laptops, and computer software and hardware. Such equipment should be for personal use and you should list it (model and serial number) and check it upon arrival and departure, in which case no duty will be collected. Appropriate permits and authorizations are required for the commercial importation of any type of electronics.
It is prohibited to export any antiquity or any item older than 100 years without a licence. Contact the Embassy of the Arab Republic of Egypt in Ottawa for further information regarding customs requirements.
The currency is the Egyptian pound (EGP, E£).
A maximum of E£5,000 can be brought into or taken out of Egypt. You must declare any amount of currency equivalent to US$10,000 or more.
Traveller’s cheques and foreign currency are easily exchanged in hotels and banks. U.S. dollars are preferred, particularly at tourist sites. Some travel agents and tour operators request payment in U.S. cash only.
Major credit cards are accepted in larger stores and for larger purchases, but many merchants will only accept cash or may charge a fee for payment by credit card.
Forced marriages
There are reports of Canadian citizens being forced into marriage without their prior knowledge or consent.
Marriage Overseas
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is legally recognized in Egypt.
If you are a Canadian citizen, but also a citizen of Egypt, our ability to offer you consular services may be limited while you're there. You may also be subject to different entry/exit requirements .
Dual citizens
The Egyptian government considers Canadians who also hold Egyptian citizenship to be Egyptian while in Egypt, therefore our ability to offer consular services may be limited. You may be considered an Egyptian citizen if you were born to an Egyptian father, regardless of birth place.
Egyptian-Canadian men may be subject to military service when in Egypt. In order to be exempted, dual citizens are required to present many documents before leaving Egypt, including a document of discharge due to dual citizenship. This document does not necessarily provide an exemption, and obtaining it may be a lengthy process that could affect your departure date. The Government of Canada has no jurisdiction in the process, as the decision on military service rests solely with the Egyptian government. You should contact the Egyptian embassy or consulate in Canada before travelling.
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and Egypt.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Egypt by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Egypt to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children's Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country's judicial affairs.
- International Child Abductions: A guide for affected parents
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Request emergency assistance
The work week is Sunday through Thursday. Egypt’s customs, laws and regulations adhere closely to Islamic practices and beliefs. Exercise common sense and discretion in dress and behaviour.
Dress conservatively: for women, knee-length or longer dresses and long sleeves are preferable, and men should not wear shorts outside tourist areas. Respect religious and social traditions to avoid offending local sensitivities. Overt public displays of intimate affection are frowned upon in Egyptian culture.
In 2025, the lunar month of Ramadan is expected to begin on or around February 28.
In public, between sunrise and sunset, be discreet when:
2SLGBTQI+ persons
Egyptian laws doesn’t criminalize sexual acts or relationships between persons of the same sex.
However, 2SLGBTQI+ travellers could be discriminated against based on their sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression or sex characteristics.
You could be arrested for indecent exposure, public nuisance or scandalous acts.
The Egyptian police target apps and websites popular within the 2SLGBTQI+ community. They have used fake and legitimate accounts from community members who had their phones confiscated. Assaults and arrests by the police have occurred as a result of encounters set up through dating apps.
2SLGBTQI+ travellers should carefully consider the risks of travelling to Egypt.
Travel and your sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics
Egypt, particularly Cairo and Eastern Sinai, is located in an active seismic zone. The country is also subject to sand and dust storms.
Local services
In case of emergency, dial:
- police: 112
- medical assistance: 113
- firefighters: 110
- COVID-19 inquiries: 105
Consular assistance
For emergency consular assistance, call the embassy of Canada in Cairo and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.
Přejít k obsahu | Přejít k hlavnímu menu | Přejít k vyhledávání

- COVID-19 travel restrictions: Egypt
- < Travel restrictions
Travel restrictions
By Kiwi.com March 29, 2022
By Kiwi.com | March 29, 2022
This article was published on March 29, 2022, and all the information in the article is correct as of this time. Before you book your trip, we highly recommend that you also check official sources for the most up-to-date travel requirements, as they are subject to constant change.
Can I enter Egypt?
All foreign travelers can enter Egypt as long as they follow the local COVID-19 requirements presented below.
Please note that all foreign visitors must complete an Egyptian Declaration Form and E-Visa before departing for Egypt.

Can I enter Egypt if I am vaccinated?
You can enter Egypt if you are vaccinated. You are considered fully vaccinated if you have completed the vaccination course at least 14 days before arriving in Egypt.
As of February 2022, seven vaccines are approved in Egypt:
- AstraZeneca
- Sinopharm
- Johnson & Johnson
Travel documents if I am vaccinated
- A printed certificate confirming vaccination in English or Arabic
Can I enter Egypt if I am unvaccinated?
You can enter Egypt if you are unvaccinated.
Travel documents if I am unvaccinated
- A negative PCR test taken no more than 72 hours or a rapid antigen test taken no more than 24 hours before departure in English or Arabic
Please note the validity of your PCR test is extended to 96 hours if you are traveling from the following countries (or airports):
- France (Paris)
- Germany (Frankfurt)
- Italy (Rome)
- Republic of Korea
- New Zealand
- The UK (London Heathrow)
In addition, be aware that you can enter Egypt on a direct flight without tests with certain further requirements through the following airports:
- Hurghada (HRG)
- Marsa Alam (RMF)
- Sharm El Sheikh (SSH)
Upon arrival, you must be tested with a rapid antigen test and stay in your hotel room until you receive the result (12 -24 hours after arrival). Children under the age of 12 are exempt from this entry requirement.
As of February 2022, Egypt is open to all countries. However, there are special requirements for travelers coming from the following countries:
- South Africa
Upon arrival in Egypt, they have to:
- Take a PCR test
- Self-isolate for 14 days
Can I leave Egypt?
You can leave Egypt. However, please learn the requirements concerning COVID-19 tests and other documents of the destination country in advance.
- A certificate of full vaccination against COVID-19 in paper or electronic format
If you are unvaccinated, please present one of the following documents:
- A certificate of recovery from COVID-19 (no more than 180 days old before the day of crossing the border of a particular country)
- A negative COVID-19 test result (the relevant period and kind of test may vary, please check the requirements of the destination country)
COVID-19 situation in Egypt currently
Currently, the COVID-19 situation in Egypt is moderate as compared to the previous months.

Frequently asked questions
Is it safe to travel to egypt right now.
International travel to Egypt is possible and safe now as long as you follow basic rules:
- Wear masks at public
- Maintain a 1.5-meter social distance
Is Cairo open for travel?
Currently, Cairo is open for travelers. Please abide by all COVID-19 regulations that are the same as in the rest of the country.
Do I have to quarantine if I go to Egypt?
Travelers are obliged to undergo a 14-day mandatory self-isolation if they are arriving from the following countries:
In addition, unvaccinated travelers who fail to present a COVID-19 test at boarding have to self-isolate until they receive a result of a rapid antigen test taken at the airport upon arrival.
All other categories of travelers are exempt from self-isolation.
How do I get a health pass to travel to Egypt?
At present, there is no digital health pass for foreign arrivals in Egypt. Please print out copies of your COVID-19 documents and carry them with you.
What are the biggest international airports in Egypt?
Here is a list of the biggest international airports in Egypt:
- Cairo International airport (CAI)
- Luxor International airport (LXR)
- Hurghada International airport (HRG)
- Sharm el-Sheikh International airport (SSH)
Useful links:
- Egyptian Declaration Form
- Egypt Travel Restrictions Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic
Visit our Travel Restriction section at Kiwi.com Stories to read more travel restrictions articles
COVID-19 Egypt
Popular routes on Kiwi.com
- Cheap flights from Dubai to London
- Cheap flights from Vilnius to Tenerife
- Cheap flights from Nairobi to Eldoret
- Cheap flights from Tenerife to Vilnius
- Cheap flights from London to Prague
- Cheap flights from Barcelona to Tenerife
- Cheap flights from London to Athens
- Cheap flights from Cairo to Dubai
- Cheap flights from Berlin to Istanbul
- Cheap flights from Istanbul to Baku
- Cheap flights from London to Warsaw
- Cheap flights from London to Lisbon

The best, tastiest, and most interesting pasta dishes from around the world
Everyone loves pasta, right? In all its forms it’s a simple, delicious meal, so for #WorldPastaDay we look at some facts of the finest pasta dishes from different food cultures

Australia to reopen to vaccinated tourists
For the first time in nearly two years, most of Australia is set to welcome tourists again, under certain conditions

6 essentials on your travel checklist during the pandemic
All you need from COVID-19 tests through to flexible booking options and your own toilet paper

No quarantine in Estonia for recovered or vaccinated travelers
Those who recovered from COVID-19 in the past six months won’t have to self-isolate

Latest developments: COVID-19 and travel
SIA aims to vaccinate employees while large companies help with the development of digital vaccination passport

Etihad and Emirates to trial COVID-19 digital passport in world first
The IATA Travel Pass mobile app should be available on iOS and Android by March 2021
Hack the system, fly for less

Chiapas: The Warm Heart of Mexico

Belleville: A Part of Paris Rated AAA – Actually Almost Affordable

Best Locations to Fly to in September in North America

Egypt Entry and Travel Requirements
- Evisa.Express
- Egypt Entry Requirements
Egypt Entry Requirements are the set of rules determining the procedures to enter Egypt without any issues. These rules also include the necessary documents that travelers must prepare for the planned trip.
Some of the most important documents required for Egypt are a valid visa and passport. Visa requirements may vary depending on the traveler's nationality.
The Egyptian Government has facilitated entry to Egypt for travelers from most countries around the world introducing the electronic visa system. Currently, the list of eVisa eligible countries includes over 180 nationalities. Travelers whose nationality is not included on the list as well as those who need to visit Egypt for non-tourist purposes or for a longer period of time will need to obtain an embassy visa. Moreover, a few visa-exempt countries' citizens, mostly members of the Gulf Cooperation Council , can enter Egypt visa-free for short-term stays.
Egypt welcomes all international tourists, as well as Egyptian citizens and residents, wishing to stay in Egypt. Amid the ongoing coronavirus pandemic, the country introduced some protective measures aiming at controlling the spread of the new Covid-19 cases. Before your trip, make sure to check the recent entry rules to access Egypt smoothly.
The Egyptian health authorities may perform random health and temperature checks and require all travelers to wear face coverings while at the airport.
Important Update : In June 2022, the Egyptian authorities decided to lift all Covid-19 restrictions for travelers arriving in Egypt, regardless of their vaccination status.
Documents check-list for entering Egypt
- valid passport/ID
- valid visa or eVisa (depending on eligibility)
- valid travel insurance with Covid-19 coverage
Egypt Travel Requirements
Egypt welcomes back all foreign travelers and Egyptian citizens and residents coming back to Egypt, with minimal entry and travel requirements remaining in place.
Not fully vaccinated travelers must present a negative PCR test certificate in paper form with the traveler's unique QR code. Children under the age of six, as well as all fully vaccinated travelers, can skip the testing requirement.
Another requirement that all travelers must meet, despite their vaccination status is to have a completed Egypt Health Declaration and travel insurance with Covid-19 coverage for the whole duration of the stay.
Travelers arriving from high-risk countries and those who develop Covid-19 symptoms during their stay may be subject to a quarantine while in Egypt (depending on their vaccination status).
Besides the remaining Covid-19 entry requirements in place, Egypt requires certain travelers to have a travel authorization in the form of a regular visa, eVisa, or a Visa on Arrival. Moreover, travelers arriving from 10 specified countries need State Security approval in addition to their visas.
Egypt restaurants, cafes, and tourist attractions operate as usual and masks are required in all closed public spaces.
Testing, vaccination, and quarantine requirements
Testing requirements.
Non-vaccinated travelers, including Egyptian citizens and residents, must take a PCR Covid-19 test within 72 hours of the planned arrival in Egypt.
Children under the age of 6 are exempt from the testing requirement.
Please note ! Travelers arriving from the following countries can present PCR tests taken within 96 hours of their arrival considering the long travel and transit periods:
- North America,
- South America,
- London Heathrow,
- and Frankfurt
The Egyptian Government has stipulated that only paper forms of the taken PCR tests will be accepted upon arrival. Make sure to print out the result of your test and take the printed copy with your unique QR code with you to the airport.
Vaccination requirements
The Egyptian Government does not require incoming travelers to be fully vaccinated to enter. However, fully vaccinated visitors can skip all testing and quarantine requirements currently in place.
To be considered fully vaccinated by the Egyptian authorities you must have taken the last vaccination dose no earlier than 14 days of the planned arrival. The vaccination should be taken via one of the accepted vaccines:
- AstraZeneca,
- Johnson and Johnson,
- Moderna, Pfizer,
- Sinovac or Sputnik V
Quarantine requirements
Travelers arriving in Egypt from high-risk areas or areas of variants of concern may need to take a PCR test on arrival. If the test comes back positive, such travelers will need to undergo a quarantine period in Egypt.
Vaccinated travelers arriving in Egypt from high-risk countries may skip the additional quarantine and testing requirements in place.
Traveling from Egypt
Egyptian citizens and residents traveling abroad from Egypt to other countries should adhere to the entry rules applied by foreign governments.
Make sure to check what are the entry requirements of the country you plan on visiting and prepare all the required documents to cross the border without any issues.
The applicable entry rules may include the need to complete a Health Declaration, get tested for Covid-19, have a vaccination certificate, and more.
Traveling to Egypt
Traveling to Egypt requires having the following documents:
- a valid passport or ID*
- valid health insurance with Covid-19 coverage for the whole duration of the stay
- a negative PCR test result or a vaccination certificate
- a completed Egypt health declaration
*depending on the nationality of the traveler
Entry rules for Children
Children under the age of six entering Egypt can skip the current testing requirements in place. However, unvaccinated underage travelers aged six and older must comply with the testing requirements of Egypt and take a PCR test within 72 hours of their arrival in Egypt.
Entry rules for arriving to Red Sea (Hurghada and Marsa Alam), South Sinai (Sharm El Sheikh), and Marsa Matrouh
Travelers arriving directly to the Red Sea (Hurghada and Marsa Alam), South Sinai (Sharm El Sheikh), and Marsa Matrouh have the option to choose after arrival testing for a fee of 30 USD.
After taking the PCR test, travelers are requested to self-isolate at their hotel and wait for test results, which should arrive up to 24 hours.
Egypt visa policy
10 countries can enter Egypt for up to three months on a visa-free basis without the need to meet any special conditions.
Citizens of the following countries may enter Egypt visa-free:
- Saudi Arabia
- The United Arab Emirates
*Travelers from these countries are allowed to enter Egypt visa-free for 14 days.
Travelers from the following countries can enter Egypt on a visa-free basis, as long as they meet a few additional requirements, such as being of a specified by the Egyptian Government age or providing additional supporting documents, such as a return ticket or proof of hotel booking for the stay:
- Afghanistan
- South Sudan
Regular visa
Travelers from the following countries must apply for a regular visa at the Egyptian Embassy or Consulate:
- Afghanistan,
- Bangladesh,
- Mauritania,
- The Philippines,
- Sierra Leone,
47 countries are eligible to visit the contry with an Egypt eVisa obtained online that comes in two types:
- single-entry for a 30-day stay with a three-month validity period
- multiple-entry for numerous 30-day visits in Egypt; valid for six months
Two main requirements to meet to apply for the Egypt eVisa are as follows:
- a valid passport that won't expire for the next six months
- a face photo of the applicant
Visa on Arrival is available to citizens of most countries, except 84 specified ones. A Visa on Arrival is a travel authorization that's issued upon completing the process of applying at one of the border crossing points in Egypt.
State Security Approval
Travelers planning to visit Egypt from the following countries need to get special approval from the Egyptian State Security Authorities before departure (in addition to having a valid visa for entry):
Please note that this requirement may apply to more travelers depending on their specific situation, e.g., female citizens of Moldova aged between 15 and 35 also need to get approval from the Egyptian State Security Authorities prior to their visit to Egypt.
Egypt Passenger Locator Form
The Egyptian Government requires all incoming travelers, including Egyptian nationals and residents, to fill out a health declaration answering questions relating to their health status, personal details, contact details, flight information, and travel to Egypt information.
The form can be easily accessed online here and can be either completed using a laptop/phone or on paper. However, the completed with the required data form must be printed out and signed to be presented at the border in paper form.
Underage travelers also need to present a completed Health Declaration. If underage travelers are not able to complete the form on their own, their parents or legal guardians should do it on their behalf.
Travel Insurance
The Egyptian Government has made it mandatory for all arriving travelers to have travel insurance.
The requirement of having a valid health insurance has been implemented because of the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic to make sure all travelers visiting Egypt will have the possible Covid-19 costs, such as quarantine or testing, covered.
Your travel insurance must cover the entire period of your stay in Egypt and must cover Covid-19-related costs.
International Air Transport Association (IATA) represents and serves air travel industry with advocacy and global standards for safety, security, efficiency.
trusted by over 800,000+ travellers, and partners including:

Evisa Express uses cookies and similar technologies for statistical and analytical purposes to optimize usage. By continuing to browse the site, you are agreeing to our use of cookies. If you do not change the settings, cookies will be saved in your device's memory. Cookie Policy and Terms of Service.
Travel Vaccines and Advice for Egypt

Egypt’s 3,000 year history is rich and complex, filled with more than just mummies and pyramids. This land has ties to people and places that existed millenniums ago.
There are many sights to see in Egypt. The pyramids of Giza, the oldest of the original seven wonders of the world, remain still largely intact. The life-giving Nile River. The legendary tomb of King Tut.
But, as many sights as there are in Egypt, recent conflict in and around the country has increased the risks of travel there.
On This Page: Do I Need Vaccines for Egypt? Other Ways to Stay Healthy in Egypt Health Notices and Outbreaks in Egypt Do I Need a Visa or Passport for Egypt? What Is the Climate Like in Egypt? Is It Safe to Travel to Egypt? Egyptian Rules, Customs and Laws Suggestions for Women Traveling in Egypt What Should I Take to Egypt? U.S. Embassy in Egypt
Do I Need Vaccines for Egypt?
Yes, some vaccines are recommended or required for Egypt. The CDC and WHO recommend the following vaccinations for Egypt: typhoid , hepatitis A , polio , yellow fever , rabies , hepatitis B , influenza , COVID-19 , pneumonia , meningitis , chickenpox , shingles , Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis) and measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) .
See the bullets below to learn more about some of these key immunizations:
- Typhoid – Food & Water – Shot lasts 2 years. Oral vaccine lasts 5 years, must be able to swallow pills. Oral doses must be kept in refrigerator.
- Hepatitis A – Food & Water – Recommended for most travelers.
- Polio – Food & Water – Required if arriving from a country with polio transmission. Considered a routine vaccination for most travel itineraries. Single adult booster recommended.
- Yellow Fever – Mosquito – Required if traveling from a country with risk of yellow fever transmission.
- Rabies – Saliva of Infected Animals – High risk country. Vaccine recommended for long-term travelers and those who may come in contact with animals.
- Hepatitis B – Blood & Body Fluids – Recommended for travelers to most regions.
- Influenza – Airborne – Vaccine components change annually.
- COVID-19 – Airborne – Recommended for travel to all regions, both foreign and domestic.
- Pneumonia – Airborne – Two vaccines given separately. All 65+ or immunocompromised should receive both.
- Meningitis – Direct Contact & Airborne – Given to anyone unvaccinated or at an increased risk, especially students.
- Chickenpox – Direct Contact & Airborne – Given to those unvaccinated that did not have chickenpox.
- Shingles – Direct Contact – Vaccine can still be given if you have had shingles.
- Polio – Food & Water – Considered a routine vaccination for most travel itineraries. Single adult booster recommended.
- TDAP (Tetanus, Diphtheria & Pertussis) – Wounds & Airborne – Only one adult booster of pertussis required.
- Measles Mumps Rubella (MMR) – Various Vectors – Given to anyone unvaccinated and/or born after 1957. One time adult booster recommended.
See the table below for more information:
Specific Vaccine Information
- Typhoid – Salmonella Typhi causes typhoid, a severe infection transmitted via contaminated food and water. Vaccination is recommended for travelers and those with elevated infection risks. Practicing proper hygiene and safe food handling can also reduce the likelihood of contracting typhoid.
- Hepatitis A – Hepatitis A spreads through contaminated food, water, and close contact. Protect yourself by getting vaccinated with the hepatitis A vaccine and maintaining proper hygiene. Vaccination is a critical step in preventing this contagious liver infection, according to health authorities.
- Polio – Polio, a viral disease impacting the nervous system, is primarily transmitted through fecal-oral contact. Vaccination is the primary safeguard against polio. The vaccine triggers immune responses that build immunity and form a vital part of the global strategy to eliminate this debilitating disease.
- Rabies – Preventing rabies involves avoiding contact with infected animals and ensuring timely vaccination. The rabies vaccine is a critical tool, offering protection through post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) and preemptive vaccination for high-risk individuals like travelers.
- Hepatitis B – Hepatitis B, a liver infection, is transmitted through contact with infected bodily fluids. Prevention includes practicing safe behaviors, but the cornerstone of protection is hepatitis B vaccination. This vaccine activates the immune system, generating antibodies that offer potent and enduring defense against the virus.
- Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR) – Measles, mumps, and rubella are highly contagious diseases with potentially severe consequences. Preventing their transmission is possible through vaccination with the MMR vaccine. This two-dose vaccine not only safeguards individuals but also helps create herd immunity, reducing the risk of outbreaks within communities.
Decisions should be made based on travel plans and whether there is an increased personal risk for contracting certain diseases.
Other Ways to Stay Healthy in Egypt
Prevent bug bites in egypt.
Safeguard against bug bites by following CDC-recommended practices like donning long attire and using EPA-registered repellents like DEET or picaridin. Be mindful of bug activity times and bolster your sleeping space with nets and screens. In the event of bug bites, clean the area, resist itching, and use over-the-counter treatments to help with itching. Be sure to seek medical help for severe reactions.
Food and Water Safety in Egypt
Safeguard your health during international travels by eating fully cooked, hot meals, at reliable dining establishments. To minimize the chances of travelers’ diarrhea , follow these precautions: choose safe foods, avoid untreated water, practice frequent hand-washing, consider probiotics, and exercise caution when indulging in unfamiliar cuisines.
Altitude Sickness in Egypt
At high altitudes, altitude sickness can strike, causing symptoms like headaches and nausea due to oxygen deprivation. Preventive measures include gradual ascent, hydration, and medication like acetazolamide. If symptoms develop, swift descent to lower altitudes, rest, and medical evaluation if necessary are crucial for recovery and safety.
Infections To Be Aware of in Egypt
- African Tick-Bite Fever – Protect against African Tick-Bite Fever (ATBF) by wearing long sleeves, applying insect repellent, and regularly inspecting for ticks. Consult healthcare experts for guidance when planning trips to affected regions.
- Avian/Bird Flu – Avian flu, a virus that affects birds and can transmit to humans, can be prevented through vaccination of poultry, strict biosecurity, safe poultry handling and cooking, outbreak surveillance, and public awareness campaigns highlighting preventive measures.
- Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever – Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever is a tick-borne disease that can be transmitted between humans through bodily fluids. Preventive strategies comprise tick avoidance, healthcare worker safety measures, and research efforts towards a vaccine to halt its transmission.
- Dengue – Dengue fever, transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes, significantly impacts global health, affecting up to 400 million people yearly. Without specific antiviral treatments, prevention through avoiding mosquito bites is key. Repellents and nettings are recommended.
- Leishmaniasis – Leishmaniasis spreads via sand fly bites but can also be transmitted through other means. Prevention includes using insect repellents, covering up, and staying indoors during sand fly activity.
- Rift Valley Fever – Rift Valley Fever (RVF) is a zoonotic virus transmitted by mosquitoes and contact with infected animals. Preventing RVF involves mosquito control, safe animal handling, and vaccination of livestock, along with public health education to raise awareness.
- Schistosomiasis – Schistosomiasis is a parasitic infection transmitted through contaminated water. Avoiding contact with infected water sources and using protective clothing can reduce the risk of infection. Seeking medical evaluation promptly if symptoms such as fever and fatigue manifest enables timely diagnosis and treatment, preventing complications and promoting recovery.
- Zika – Zika virus, transmitted mainly by Aedes mosquitoes, can have serious consequences, especially for pregnant women and their babies. To prevent Zika, individuals should protect themselves from mosquito bites, practice safe sex, and eliminate breeding sites.
Health Notices and Outbreaks in Egypt
- Polio – Polio cases have been reported in Egypt over the last 12 months. Vaccination is considered the best form of protection against the virus. Make sure your polio vaccine history is up-to-date. If you have received the polio vaccine in the past, a single, lifetime booster may be needed.
Do I Need a Visa or Passport for Egypt?
US Citizens must have a visa to travel to Egypt as well as a valid passport.
Single and multiple entry visas are available that permit a stay in Egypt of up to 30 days.
If you attempt to leave Egypt after the end date noted on your visa, you will be fined. Should you find yourself in this situation, be sure to arrive at the airport well before your flight and with plenty of Egyptian currency.
Sources: Embassy of Egypt and U.S. State Department
What Is the Climate Like in Egypt?
Egypt only has two seasons – a hot summer and a moderate winter. In general, Egyptian days are warm or hot and nights are cool or even cold. While the majority of Egypt is desert, there are four unique physical regions with different climates.
The Nile Region
- Nile Delta – The ancient city Alexandria is located in the Nile Delta. This area was created by the world’s longest river and is the most expansive oasis in the world. The delta begins north of Cairo and extends farther north to the Mediterranean Sea. This region has a hot desert climate. But, the most northern part closest to the sea is the wettest region in the country. It has higher humidity and more moderate temperatures, reaching no higher than 90 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Nile Valley – This region includes the two major Egyptian cities Luxor and Aswan. The Nile Valley is hot and dry, with very little precipitation. The summer months get especially hot, with daytime temperatures reaching highs of up to 105 degrees Fahrenheit at the peak of the summer. Nighttime temperatures dip down to around 70 degrees Fahrenheit at the lowest points. The winter months are much more moderate with less fluctuation from night to day.
Western Desert
The Pyramids of Giza are located in the northeast corner of this region.
This region is one of the driest areas in the Sahara Desert. It spans from the Mediterranean Sea south to the Sudanese Border, and from the Libyan border east to the Nile River Valley. The area rarely sees any rain. Hot, dry sandstorms, called khamsins, are common in the spring months and can be dangerous.
Temperatures vary greatly. In summer months, temperatures can get up to 110 degrees Fahrenheit during the day and 45 degrees Fahrenheit at night. In winter months, temperatures fluctuate less, but the desert can get to 65 degrees Celsius during the day and as low as 30 degrees Celsius at night.
Eastern Desert
The Eastern Desert is mountainous. The topography increases east of the Nile to become dry, rocky hills, the Red Sea Mountains, at elevations around 1,900 meters or higher. This is a dry, desolate area that is isolated from the rest of the country. There is not much in this part of the country because it is not suitable for agriculture or other sustained settlements.
Sinai Peninsula
This is a triangular peninsula that connects Asia with Africa. It is also known as the Sinai Desert because of its arid climate. The rest of Egypt is to the West, Israel and the Gaza Strip to the east. The Mediterranean Sea is to the north and the Red Sea is to the south.
The peninsula has two distinctly different climates. The northern part of the peninsula, closer to the Mediterranean, is dry and intensely hot during the summer and sees more rain during the winter. The southern part, closer to the Red Sea, is at higher elevation and is more prone to clouds, especially near the tops of the hills. The temperatures fluctuate a little more, getting cooler at night. Humidity is higher near the coasts on the peninsula.
Is It Safe to Travel to Egypt?
Avoid an embarrassing stop, over 70% of travelers will have diarrhea., get protected with passport health’s travelers’ diarrhea kit .
Non-essential travel to Egypt is not recommended. The U.S. Department of State has issued travel warnings to Egypt.
Travelers should avoid going to the Western Desert toward the Libyan border and the Sinai Peninsula due to an unpredictable security situation.
When traveling to coastal resorts, exercise a high degree of caution.
Travelers should use reputable Egyptian travel agencies if they still decide to make the trip. Those agencies are informed about the security issues and will know how to best advise.
Egyptian Rules, Customs and Laws
Public Behavior
- Intimate behavior and any sort of public displays of affection including cuddling, kissing and even hand-holding are seen as inappropriate.
- When visiting a home, it is customary to bring a small gift and remove shoes before entering.
- Egyptians have unique functions for the two hands. The left hand is to be used for “unclean” functions, like putting on shoes or wiping in the bathroom. It’s is seen as unhygienic to put food into the mouth or into a communal food bowl with that hand. The right hand should be used for greetings and eating.
Conversation
- Egyptians are passionate about certain subjects and conversations about those subjects, including Israel, Islam and Palestine, should be treated carefully. There is potential for serious offense if careful consideration is not taken, especially when expressing opinions about religion.
- Dress should be modest. Shorts are considered acceptable only near the coastal resorts, and shirts for both men and women should cover the shoulders. Immodest clothing encourages disapproval from the Egyptians as well as gropers.
- Be conscious of dress when visiting mosques or other sacred places. Travelers should be especially modest, with women covered from wrist to ankle and men covered from below the shoulder to below the knee. Travelers should also remove their shoes or wear overshoes.
Suggestions for Women Traveling in Egypt
- Wear loose, opaque clothes that cover all immodest areas (chest, thighs, upper arms)
- When traveling alone on public transportation, sit with other women or, when offered, sit in carriages reserved for women
- When traveling with a man, wear a wedding ring. It is more respectable to appear to be married than “just friends”
- Appear confident and travel with purpose
- Avoid eye-contact with Egyptian men and appear standoffish rather than overly friendly
- When swimming in pools or open-air springs, wear a t-shirt and leggings
- If hassling or groping does occur, call out and make a scene
What Should I Take to Egypt?
- Travel Documents – Make sure to have copies of all important travel documents, including your passport, visa, travel insurance, etc.
- Protection from the Sun – Be ready to prevent sunburns. Don’t forget sunscreen of SPF 30 or higher, a hat and sunglasses.
- Light, breathable cotton clothing – Bring clothing that is easy to wash. Whether in Egypt’s coastal regions or arid desert areas, light clothing will help with comfort in the heat, even in winter months.
- Jacket – This will help protect against potential summer windstorms and also provide backup for when indoors get chilly from heavy air conditioning.
- Comfortable shoes – Many of Egypt’s most exciting sites require at least some walking and sightseeing. In general, it is best to go with comfortable shoes.
- Health and Hygiene – Pack a basic medical kit filled with items that may not be readily available in parts of Egypt. Kits should include things like: bandages, antibacterial hand gel, pain relievers, anti-diarrhea drugs and re-hydration salts.
- Egyptian travel adapter – To charge your phone, you will need a travel adapter made for Egypt.
U.S. Embassy in Egypt
All Americans visiting Egypt should register online with the US State Department before departure. This will inform the office of your travel plans within the country and will allow them to reach out in the case of an emergency or evacuation.
If you plan to purchase a local SIM card you can also enter your phone number to receive SMS updates from the office.
U.S. Embassy Cairo 5 Tawfik Diab Street Garden City, Cairo Egypt Telephone: (20-2) 2797 3300 Fax: (20-2) 2797 3200
Visit the Embassy of the United States to Egypt website prior to your departure to confirm correct contact details for the office.
If you have any questions about traveling to Egypt or are wondering what shots you may need for your trip, schedule an appointment by calling or book online now!
Customer Reviews
Passport health – travel vaccines for egypt.

- Records Requests
- Passport Health App
- Privacy Center
- Online Store

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
We now advise:
Exercise a high degree of caution in Egypt overall due to the threat of terrorism.
Other levels apply in some areas.
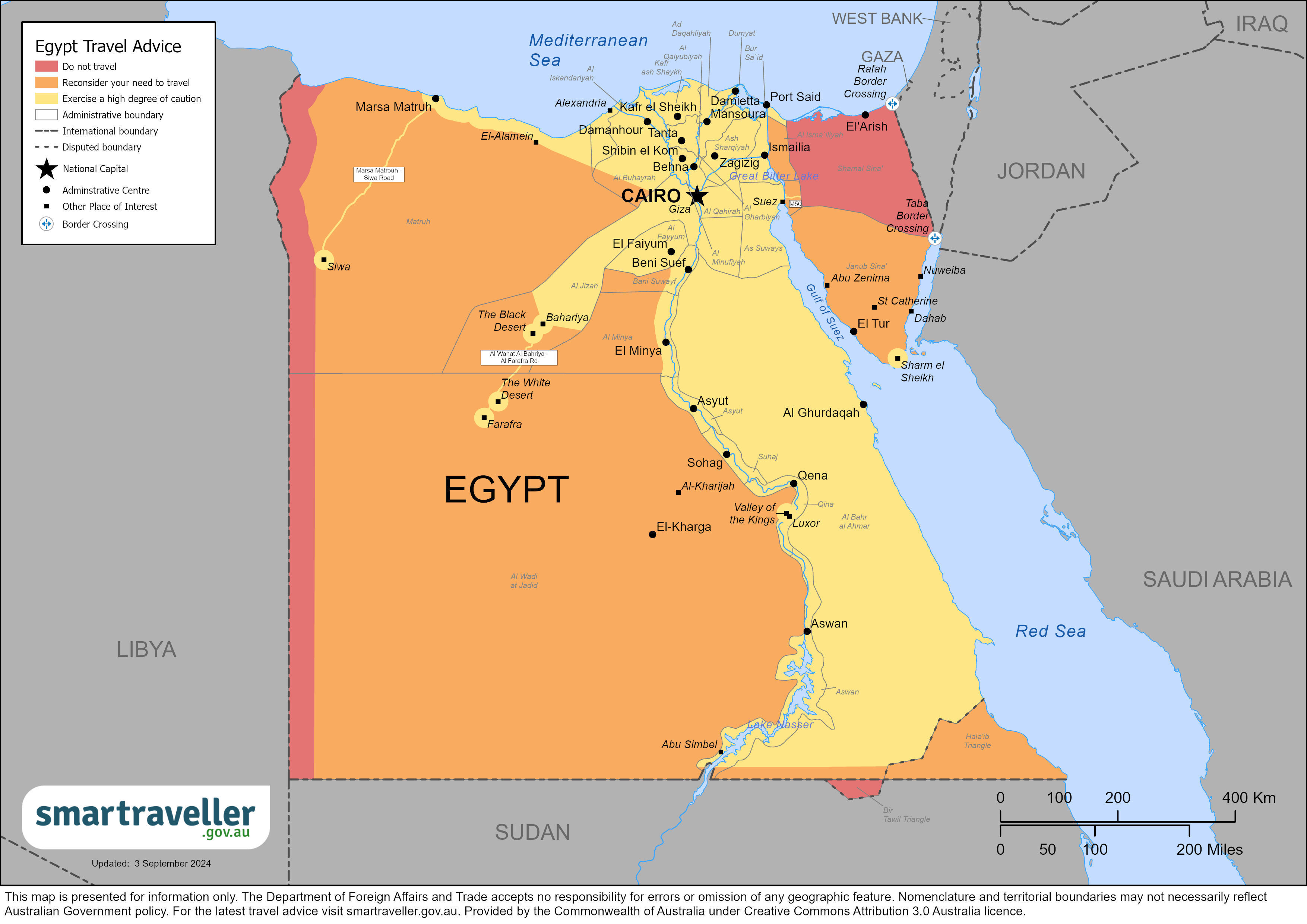
Egypt (PDF 781.32 KB)
Africa (PDF 1.77 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire and rescue services.
Call 180 or 123.
Medical emergencies
Call 122, 123 or contact the local police.
Advice levels
Exercise a high degree of caution in Egypt overall.
Do not travel within 40km of Egypt's border with Libya or to the Governorate of North Sinai, including the Taba-Suez Road.
Do not travel to:
- within 40km of Egypt's border with Libya due to the high threat of terrorist attack
- the Governorate of North Sinai, including the Taba-Suez Road due to the high threat of terrorist attack and violent crime.
Reconsider your need to travel to North of the St Catherine-Nuweiba Road in South Sinai, the Ismailiyah Governorate east of the Suez Canal, West of the Nile Valley and Nile Delta regions except for the areas listed under ‘Exercise a high degree of caution and the Haila’ib Triangle and Bir Tawil Trapezoid and within 20km of the border with Sudan.
Reconsider your need to travel to the following locations due to the threat of terrorism:
- North of the St Catherine-Nuweiba Road in South Sinai except for the coast
- the Ismailiyah Governorate east of the Suez Canal
- West of the Nile Valley and Nile Delta regions except for the areas listed under ‘Exercise a high degree of caution’
- the Haila’ib Triangle and Bir Tawil Trapezoid and within 20km of the border with Sudan.
- Ongoing military action in the Occupied Palestinian Territories could lead to increased tensions in other locations in the Middle East. Demonstration and protest activity may occur, and localised security situations could deteriorate with little notice. Avoid all demonstrations and protests. Follow the advice of local authorities and monitor local media for updates.
- Increased tensions in the Middle East may result in airspace closures, flight cancellations and diversions, and other travel disruptions.
There's a high threat of terrorist attacks and violent crime in the Governorate of North Sinai.
- The Rafah crossing between Gaza and Egypt may be closed or have highly restricted access which is subject to change at short notice. It has been subject to air strikes during the current conflict.
- Terrorists have attacked popular tourist locations, resulting in deaths and injuries. More attacks are likely. Be alert to possible threats.
- Terrorist groups in Egypt have targeted Christians in the past. Take care, particularly during major religious periods and at religious sites.
- You're at risk of kidnapping in Egypt. Take extra precautions.
- Violent crime can happen. Take extra care if you're a woman and alone. Don't leave valuables unsecured in your hotel room or unattended in a public place.
- Women, particularly foreigners, are frequently subject to unwelcome male attention.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Infectious diseases are common. These include hepatitis, filariasis and rabies. Only drink boiled or bottled water. Avoid contact with dogs and cats.
- Don't swim in fresh water, including the Nile River, to avoid waterborne diseases such as bilharzia (schistosomiasis).
- Dengue and malaria are present. Use insect repellent and make sure your accommodation is insect-proof.
- Cairo can have very high levels of pollution and dust. If you suffer from breathing difficulties or a lung condition, seek medical advice before travel.
Full travel advice: Health
- Making public comments that criticise the Egyptian government, security forces, or Islam can be illegal. Police have arrested foreign visitors who posted critical social media.
- There are severe consequences for carrying illegal drugs, including the death penalty, long prison sentences or deportation.
- You need approval to bring satellite phones and radio communications equipment into Egypt. Apply to the Ministry of Communications and Information Technology before you leave. The use of drones is illegal.
- Egyptian family law differs significantly from Australian law. Before you become involved in a local legal matter, get legal advice, including on family and business legal matters.
- Although same-sex relationships are not explicitly criminalised in Egypt, the charge of 'debauchery' has been used to prosecute LGBTQIA+ people. There is little public acceptance of homosexuality in Egypt. Avoid any public displays of affection.
- Sex outside of marriage is illegal. Dress standards are very conservative, particularly for women. Wear modest clothes that cover your legs and upper arms.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. You should contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Egypt for the latest details.
- Foreign journalists need accreditation from the Egyptian Press Centre before arrival. There are severe punishments for journalists working without accreditation.
- There are landmines in some areas. Get advice from local authorities before you travel.
- Australian-Egyptian dual nationals are treated as Egyptian. This will limit your access to consular assistance. Always travel on your Australian passport if possible. This doesn't mean you will receive special treatment in terms of local law.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter tells you what the Australian government can and can't do to help when you're overseas.
- For consular help, contact the Australian Embassy in Cairo .
- To stay up to date with local information, follow the Embassy’s social media accounts.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Although the greatest terrorist threat is in North Sinai, terrorist attacks could occur anywhere in Egypt. Potential targets include:
- religious sites
- tourist locations
The last major attacks occurred in 2019, but more attacks could happen at any time without warning.
To reduce your risks from terrorism:
- consider the level of security at places you plan to visit
- have a clear exit plan in case of a security incident
- report suspicious activity or items to the police
- monitor the media for new or emerging threats
- take official warnings seriously
- follow the advice of local authorities
If there's an attack, leave the affected area as soon as it's safe to. Continue to avoid the area in case of secondary attacks.
Terrorism is a threat worldwide.
Governorate of North Sinai
There's a high threat of terrorist attacks and violent crime in the Governorate of North Sinai, including the Taba-Suez Road. Do not travel to North Sinai.
Terrorists or criminals could target you, or you might be included in violence directed at others.
North Sinai is under a long-term state of emergency.
The Rafah crossing between Gaza and Egypt may be closed or have highly restricted access for long periods and is subject to change at short notice. It has been subject to air strikes during the current conflict.
If, despite our advice, you decide to travel to North Sinai:
- seek professional security advice
- arrange contingency plans and personal security measures
- note that our ability to provide consular assistance may be extremely limited
More information:
Security Situation
The situation in Israel and the Occupied Palestinian Territories could lead to increased tensions and the security situation could deteriorate with little notice. Avoid all demonstrations and protests. Peaceful protests and rallies can turn violent at short notice. Be aware, follow the advice of local authorities and monitor local media for updates.
On 8 October 2023, an Egyptian police officer is reported to have shot and killed two Israeli tourists and an Egyptian tour guide in Alexandria. A third tourist was injured.
The Rafah crossing between Gaza and Egypt may be closed or have highly restricted access for long periods and is subject to change at short notice. It has been subject to air strikes during the current conflict.
Since October 2023, suspected drones and projectiles have impacted areas along the Gulf of Aqaba, including in Taba, close to Egypt's border with Israel's Red Sea port of Eilat, and in the Red Sea resort town of Nuweiba, north of Dahab. Be alert to possible strikes. Monitor local media and follow the advice of local authorities.
Civil unrest and political tension
The security situation in the region remains unpredictable and could deteriorate with little or no warning.
Be alert and monitor local media for updates.
Demonstrations and protests
Protests can occur across Egypt.
Clashes between rival protesters or security forces have resulted in many deaths and injuries. Foreigners, including journalists, have been among the victims. Serious sexual assaults on women, including foreigners, have occurred during demonstrations.
Security forces have targeted foreign journalists. Egyptian authorities have arrested, detained or questioned journalists.
Protest hotspots
Protests can happen anywhere and at any time, although strict security clampdowns have been preventing protests in recent years. However, the following places and times are common focal points for demonstrations:
- Tahrir Square and surrounding streets, including the nearby British and US Embassies and Garden City area, in Cairo
- the al-Ittihadiya Presidential Palace in Heliopolis, Giza
- the area of the Raba Al-Adawiya Square in Nasr City
- Fridays following midday prayers
- the anniversary of the 2011 revolution on 25 January and the days leading up to this public holiday
Under Egyptian law, it's illegal for:
- more than 10 people to gather without notice
- foreigners to participate in protests and demonstrations
Authorities may arrest foreigners who participate in protests.
Egyptian authorities may impose curfews and restrictions on movement at short notice.
Public protests and events that draw large groups of people can turn violent. To protect yourself during periods of unrest:
- avoid demonstrations, rallies and large crowds
- monitor the media for possible unrest and avoid those areas
- obey any curfews and respect local laws
- be prepared to change your travel plans
Protests may disrupt transport. Contact your airline or travel agent to check.
- Demonstrations and civil unrest
Violent crime
Violent crime is rare but can occur, including armed robbery , sexual assault , incidents involving minors, carjacking and burglary.
Petty crime remains low in Cairo, although the declining economy and ensuing financial hardship have seen reports of increased crime.
Take extra care if you're a woman and alone. Women may be physically and verbally harassed or assaulted , including when using public transport and walking in public areas.
Ensure children and young people are always accompanied by known or trusted people and not left alone with hotel or entertainment/excursion staff. If you feel uncomfortable, leave the area and seek help from the hotel or local authorities. The Tourist Police can be contacted on 126 or 122 if you're a resident of Egypt.
Taxi and rideshare drivers have assaulted passengers, including foreigners. See Travel
To protect yourself from violent crime:
- don't leave valuables outside a safe in your hotel room or unattended in a public place
- be alert to pickpockets and bag snatchers in tourist areas, particularly after dark
- read reducing the risk of sexual assault before you go
If you're the victim of a crime, report the incident to the tourist police immediately.
If you don't report a crime before you leave, you may not be able to seek prosecution later.
- Advice for women
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you're connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
More information:
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
Kidnapping occurs across the world with political, ideological, and criminal motives. Foreigners, including Australians, have been kidnapped overseas whilst travelling. Kidnaps can happen anywhere, anytime, including in destinations that are typically at lower risk.
Kidnapping is a risk in Egypt. Terrorists have targeted foreign nationals. There is a high threat of terrorist kidnappings in South and North Sinai. Terrorist attacks occur frequently in these areas.
If, despite our advice, you travel to an area with a high risk of kidnapping, our ability to provide consular assistance in these destinations will be limited.
To reduce the risk of kidnapping:
- always be alert to your personal security and surroundings
- get professional security advice for travel in locations with a heightened kidnap risk
- check your accommodation has appropriate security measures
- avoid isolated locations, particularly when travelling alone
- notify family or friends of planned travel and share your location
- avoid talking about your money or business affairs
- use ATMs in public places and during daylight hours
- avoid giving personal details to strangers online or over the phone
The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it doesn't make payments or concessions to kidnappers. Ransom payments to kidnappers have funded further terrorist attacks and criminal activity. Paying a ransom to terrorist groups will likely break Australian counter-terrorism financing laws.
More information:
Tours and adventure activities
Transport and tour operators don't always follow safety and maintenance standards.
If you plan to do an adventure activity :
- check if your travel insurance policy covers it
- check tours are well equipped with food, medical supplies and emergency communications
- ask about and insist on minimum safety requirements
- always use available safety gear, such as life jackets or seatbelts
If proper safety equipment isn't available, use another provider.
Safaris and camping
Authorities have banned safaris and camping in the area near Bahariya Oasis until further notice. This includes the western and southern parts of Oases–Siwa and Oases Road.
It doesn't include the White Desert in Farafra. However, restrictions applying to Bahriya Oasis may disrupt access.
Climate and natural disasters
Egypt, particularly Cairo, experiences earthquakes . Find out about local safety procedures in case one strikes.
Sand and dust storms occur between March and May.
If a natural disaster occurs, follow the advice of local authorities.
Find out about emerging natural disasters from the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System .
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away
Physical and mental health
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
If you plan to bring medication, check if it's legal in Egypt. Take enough legal medicine for your trip.
Carry a copy of your prescription or a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medication is
- your required dosage
- that it's for personal use
Health risks
- Infectious diseases
Waterborne, foodborne and other infectious diseases are common, including these listed by the World Health Organization:
Serious outbreaks sometimes occur.
To protect yourself from illness:
- drink boiled water or bottled water with sealed lids
- don't swim in fresh water, including the Nile River, to avoid waterborne diseases, such as bilharzia (schistosomiasis) (World Health Organization)
- avoid contact with dogs and cats
Get urgent medical attention if bitten by an animal.
Insect-borne diseases
There's a risk of malaria (World Health Organization) in El Faiyum Governorate from June through to October.
To protect yourself from disease:
- make sure your accommodation is insect-proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
Air pollution
Cairo regularly experiences very high levels of air pollution and dust.
Get medical advice if you suffer from breathing difficulties or a lung condition.
- Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency Air Quality Forecast
Medical care
Medical facilities.
The standard of medical facilities in Cairo is enough for routine illnesses. Elsewhere, facilities can be very basic. Treatment can also be costly. Many require up-front payment.
If you become seriously ill or injured, you'll need to be evacuated to a place with better facilities. Medical evacuation can be very expensive and hard to organise. Ensure you have sufficient travel insurance to cover the costs.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
Criticising authority
Authorities may treat public comments that criticise the Egyptian Government, security forces or Islam as illegal. Police have arrested foreigners who published critical social media posts, including 'liking' pages.
Possessing illegal drugs can lead to the death penalty, long prison sentences or deportation.
- Carrying or using drugs
Egyptian family law differs significantly from Australian law, particularly in relation to divorce, child custody and support.
Before you become involved in a local legal matter, get legal advice, including for family and business legal matters.
It's important to know your rights and responsibilities under Egyptian law. See Travel
Marriage laws
If you want to get married in Egypt, check the legal requirements before you travel. You can do this either through the Australian Embassy in Cairo or the Egyptian Embassy in Canberra .
In Egypt, it's illegal to:
- have sexual relations outside marriage
- take photos of bridges and canals, including the Suez Canal
- take photos of military personnel, buildings or equipment
The Egyptian Government doesn't interfere with the practice of Christianity, but preaching is illegal. If you're considering preaching in Egypt, seek local legal advice beforehand. Follow the advice of local authorities.
LGBTQIA+ laws
LGBTQIA+ individuals face significant social stigma and discrimination in Egypt. Egyptian law does not explicitly criminalise same-sex relationships, however, people have been charged with 'committing an indecent act in public and breaching public morality' and penalised with imprisonment.
LGBTQIA+ people and advocacy groups have reported harassment, intimidation, arrests, and other forms of abuse, including by police.
There are also reports that authorities have used social media, dating websites, and mobile phone apps to entrap people suspected of being gay or transgender in the act of 'debauchery,' which is a criminal offence that carries severe sentences.
There is little public acceptance of homosexuality in Egypt.
- Advice for LGBTQIA+ travellers
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
Staying within the law and respecting customs
Dual citizenship
If you're an Australian-Egyptian dual national, local authorities will treat you as an Egyptian, even if you travel on an Australian passport.
This limits our consular services if you're arrested or detained.
If possible, always travel on your Australian passport .
Dual nationals living in Egypt for long periods need proof of Egyptian citizenship, such as a national identification card.
Male dual nationals who haven't completed military service usually don't need to enlist. However, they must get an exemption certificate before they can leave Egypt. Get one from the nearest Egyptian embassy, consulate , or Ministry of Defence Draft Office.
If you're arrested, request local authorities inform the Australian Embassy.
Dual nationals
Local customs
The Islamic holiday month of Ramadan is observed in Egypt. Respect religious and cultural customs and laws during this time.
Avoid eating, drinking or smoking in public or in front of people who are fasting.
Orthodox Easter is observed by the Christian community, as is Christmas Day, which is celebrated on 7 January in Egypt.
The work week is Sunday to Thursday. Egypt's customs, laws, and regulations follow Islamic practices and beliefs. Exercise common sense and discretion in dress and behaviour.
Dress conservatively. Knee-length or longer dresses and long sleeves are preferable for women, and men should not wear shorts outside tourist areas. Respect religious and social traditions to avoid offending local sensitivities. Overt public displays of intimate affection are frowned upon in Egyptian culture.
If in doubt, seek local advice.
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Egypt for the latest details. To pay for a tourist visa on entry, you must have a non-Egyptian credit card or US dollars in cash. Bring the required amount, as ATMs may not disperse USD or other foreign currency.
Check with your travel provider for the latest information and monitor the travel advice of the country you're planning to transit through. There are no direct flights to Australia, but there are flights via a transit hub to Australia.
- Egypt Electronic Visa Portal
Children of Egyptian fathers must have their father's approval to leave Egypt. Authorities may ask for proof of this approval before allowing the children to leave.
Other formalities
Journalist accreditation.
Foreign journalists must get accreditation from the Egyptian Press Centre before arrival. You need this if your visit is for work purposes. The Press Centre is part of the Egyptian State Information Service.
Punishments are severe for journalists working without accreditation.
Communications equipment and drones
You need approval to bring satellite phones and radio communications equipment into Egypt.
Apply to Egypt's Ministry of Communications and Information Technology well in advance of your trip. Authorities are likely to confiscate equipment brought in without clearance.
The use of drones, for any purpose, is illegal. Authorities will confiscate drones on arrival.
Pest control
If you arrive in Egypt by road, officials may check your car for pests. Follow the advice of local authorities.
Yellow fever vaccination
You need a valid yellow fever vaccination certificate to enter Egypt if you arrive from a country where yellow fever is widespread.
Countries where yellow fever is a risk
Some countries won't let you enter unless your passport is valid for 6 months after you plan to leave that country. This can apply even if you're just transiting or stopping over.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
You can end up stranded if your passport is not valid for more than 6 months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
Passport with ‘X’ gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can’t guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
- LGBTQIA+ travellers
The local currency is the Egyptian Pound (EGP).
You can take up to EGP 5000 in cash when travelling to or from Egypt.
You must declare all foreign currency amounts over $US 10,000 or equivalent. This covers all forms of currency, not only cash.
If you're visiting as a tourist, you may need to pay $US or euros for your accommodation. Most well-established hotels and resorts accept card payments. ATMs are available in most established areas.
Consult your financial institution prior to your travel.
Embassy or Consulate of Egypt
Local travel
Consider the security situation and risks to your safety in different locations. See Safety
There are landmines in some areas, notably:
- the desert areas around El Alamein
- stretches of coastline near Marsa Matruh
- the western shore of the Gulf of Suez
- the Sinai Peninsula
Before you go, tell local authorities of your planned travel. Ask them about current risks and precautions for your route and destination.
Travel restrictions and disruptions
If you travel around Egypt, you may be stopped at military and civilian checkpoints. Officials at checkpoints have detained and harassed foreigners.
Rules apply to people entering the Sinai, including via the Ahmed Hamdi tunnel. When you enter, you must present one of the following:
- a valid form of ID with a Sinai address
- proof of ownership or rental contracts of property in the Sinai
- hard copy evidence of hotel reservations
Travel to the Sinai in a 4WD vehicle may be restricted if you don't hold a valid permit. Check the advice of local authorities before travel.
Land borders
Egypt's borders are under military control.
The military restricts and, in some cases, bans the movement of civilians and vehicles.
You need permission to cross borders on the main sealed roads, including at the borders with Libya, Sudan, Israel and parts of the Sinai. Get permission from the Travel Permits Department of the Egyptian Ministry of the Interior.
If, despite our advice, you plan to cross from Egypt into the Gaza strip:
- read our advice on Israel, the Gaza Strip and the West Bank
- check border crossing requirements with your nearest Egyptian embassy or the Ministry of the Interior in Cairo
You must get permission from Egyptian authorities to enter and exit the Gaza Strip using the Rafah border crossing.
If you enter the Gaza Strip through this border, you must leave the same way.
You may be delayed in the Gaza Strip for a long time, possibly weeks while waiting for approval to return.
The Australian Government can't influence the granting of approval or when the crossing will open. Our ability to provide consular help in Gaza is extremely limited.
Other borders
Road travel to Abu Simbel, 40km north of the Sudanese border, can be dangerous. If you do, go on an organised tour guarded by police escorts.
There's a high threat of terrorist attacks within 50km of Egypt's border with Libya. Deadly attacks have occurred in the area.
Driving permit
You can't drive in Egypt on your Australian driver's licence.
Before arriving in Egypt, get an international driver's permit and get an embassy or consulate of Egypt to certify it.
Road travel
Road travel can be dangerous.
Road conditions are very poor. Cars, buses and trucks frequently drive at high speed and without headlights at night.
Road accidents occur often.
Where possible, avoid travelling by road. Visit regional places, including Luxor, by other means.
- Driving or riding
Motorcycles
Take extra care if you plan to ride a motorbike. Be alert to the different road conditions.
Always wear a helmet.
Taxis and Rideshare
Cairo and Alexandria have a lot of taxis. Rideshare services are available in Cairo and Alexandria.
In Cairo, taxis are white. In Alexandria, taxis are black and yellow.
All taxis should have a meter. The law requires drivers to use their meters. However, many taxi drivers will claim that the meter is broken and try to negotiate a fare.
Taxis rarely have seatbelts, especially in the back seats.
Sexual harassment of women by taxi drivers is common.
Avoid taxis, especially if you're a woman and on your own. Ride share apps may be safer as you can track your driver's details and share the trip details with others.
If you use a taxi, travel with people you know or advise others of your planned travel and destination.
Public transport
The Cairo Metro subway system is generally reliable.
Maintenance and safety standards of other public road and rail transport are very poor.
- Transport and getting around safely
Rail travel
Train travel is generally safe, but accidents do occur.
In March and April 2021, two train accidents occurred in North and South Egypt. The accidents caused many deaths and injuries.
There have been a number of train derailments on the Cairo-Aswan line. Several people were injured when a train derailed between Aswan and Luxor in 2016.
Piracy and armed robbery are risks in the southern Red Sea and Gulf of Aden.
All forms of shipping are attractive targets for pirates. This includes commercial vessels, pleasure craft and luxury cruise liners.
The International Maritime Bureau issues piracy reports.
If you plan to travel by boat , be highly alert and cautious in the southern Red Sea and Gulf of Aden.
Scuba diving / aquatic activities
Sharks and other potentially dangerous aquatic animals are in Egyptian waters. Certain beaches and dive areas may be subject to temporary closures. Exercise caution and seek advice from local authorities. Ensure you dive with reputable and licensed operators.
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Egypt's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
For consular help, contact:
Australian Embassy, Cairo
11th floor, World Trade Centre 1191 Corniche el Nil Boulac, Cairo, Egypt
Phone: +20 2 2770 6600 Fax: +20 2 2770 6650 Website: egypt.embassy.gov.au Facebook: Australia in Egypt X: @AusAmbEGY
The Australian Embassy in Cairo operates on Sunday – Thursday.
The security situation may affect Embassy opening hours.
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Egypt?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.

Egypt .css-pelz90{font-weight:400;} Travel Restrictions
Fill in the "Passport" and "From" sections above for personalised results
Set Up Alerts
Still confused?

GET THE LATEST NEWS
Download our Android App
GET IN TOUCH
Business Enquiries: [email protected]
Press: [email protected]
©2022 Canitravel.net - All rights reserved.
My People are Stranded: Bearing Witness to the Struggle of Sudanese Refugees in Egypt
By Wedad Osman | September 4, 2024
The war in Sudan has marked more than 500 days, a grim milestone for many Sudanese people. The conflict shows no signs of abating, and has resulted in the world’s largest displacement crisis forcing more than 10 million people to confront the harsh reality that their displacement may be more permanent than they once believed. As the war continues to rage on, I often find myself thinking back to my childhood and the streets of Khartoum, which I called home until the age of 12.
Khartoum, Sudan, was a beautiful city nestled along the banks of the River Nile, alive with the warmth of its people and the vibrant energy of a capital that united individuals from every corner of a vast and diverse nation. Every Friday morning, my family and I would savor tea and zalabieh (a Sudanese donut) from the street vendors on Al Balabil Street before heading to my grandparents’ home in the Arkaweet neighborhood. Now, I often find myself wondering if those street stalls and my grandparents’ house still stand.
Once home to approximately 6 million people, Khartoum has now been reduced to rubble due to a military conflict between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and a paramilitary group known as the Rapid Support Forces (RSF). The war, which began on April 15, 2023, has resulted in the displacement of around 10.7 million people within Sudan, with over 2.1 million fleeing to neighboring countries. As a result, many have no hope of returning to the only home they’ve ever known.
Over the past year, watching my family and friends flee Khartoum to less than welcoming host countries has been incredibly painful. Due to its geographical proximity and long-standing cultural ties, Egypt is a primary destination for Sudanese refugees escaping the conflict with the latest estimates ranging around 500,000 people. However, the journey to Egypt has been anything but smooth or easy for those seeking refuge. This summer, I spent time in Egypt interviewing Sudanese refugees and hearing firsthand the many challenges they face.
At the Border
In the early days of the conflict, the border was open to Sudanese women, children, and the elderly, allowing them to enter without visa requirements. However, as the months passed, visas became mandatory for everyone , and the associated costs and accessibility challenges grew increasingly complex.
Despite the Four Freedoms Agreement signed by Egypt and Sudan in 2004, which guarantees freedom of movement, residency, work, and property ownership for citizens across both countries, Sudanese refugees now face overwhelming challenges as the Egyptian government effectively disregards these commitments. While American citizens can obtain a visa to Egypt for just $25 at the airport , Sudanese refugees face costs between $1,500 and $2,500—an impossible amount for families who fled with nothing but the clothes on their backs. For context, the annual salary for Sudanese government employees in 2021, based on the minimum wage for civil servants, was only $80.64—making these visa fees unattainable for most.
Accessibility challenges are also significant. For those departing by land from northern Sudan, transportation to and from the border crossings at Wadi Halfa and Argeen en route to Cairo is both costly and perilous, with significant time required. The ongoing war has made traveling throughout Sudan dangerous due to random stops by militia members or thugs. Mandatory curfews across the country force people to find shelter wherever they are stopped, adding to the difficulty of reaching the border.
Renting a private vehicle from Dongola, the capital of Sudan’s Northern State, to Aswan in southern Egypt costs around $650. In comparison, bus and plane fares combined with various fees required to travel to Cairo total approximately $250 per person. These fees are collected by Sudanese and Egyptian officials at numerous checkpoints before exiting Sudan or entering Egypt. However, these estimates do not account for the significant costs and logistical challenges associated with reaching Northern Sudan from other regions. Frequent checkpoint stops by both Sudanese security officers and Egyptian border authorities can stretch the journey into Egypt to nearly a full day. The only alternative to land transport is an hour-long flight from Port Sudan to Cairo, which costs $500 one-way.
The situation at the Sudan-Egypt border is dire. Every day, hundreds of Sudanese gather, waiting for visas, only to be stranded for days amidst disorganization, erratic operating hours, and frequent closures. Even with valid paperwork, many are turned away and forced to sleep unsheltered in the desert.The combination of high costs, dangerous travel conditions, and chaotic border management has created an unbearable ordeal for those seeking safety.
Inside Egypt
For those able to enter Egypt, the situation is becoming increasingly unstable as Egyptian authorities roll out new laws that threaten the way of life for Sudanese refugees by targeting their residential status and sources of income and limiting their freedom of movement. One such law included a decree setting a deadline for June 30th, by which all refugees who entered Egypt “illegally” (including those who entered before visa requirements) and those with expired residency must pay a $1,000 fine, in addition to “other fees,” and find sponsorship from an Egyptian host.
While I was in Egypt interviewing Sudanese refugees I witnessed firsthand the pervasive fear within the community. Deportations are frequent , with abrupt changes to visa statuses leaving refugees vulnerable to being sent back to Sudan. Refugees now carry their visas and passports constantly to avoid random checks by Egyptian authorities. I was told that anyone caught without proper documentation—regardless of their immigration status—could be deported to Wadi Halfa, a grueling 25-hour journey covering over 1,200 miles, within the same day.
Exacerbating this situation is a secretive campaign aimed at detaining and deporting thousands of Sudanese refugees, largely to reduce migration to Europe and tighten control over refugee populations. The New Humanitarian and the Refugees Platform in Egypt uncovered evidence of this campaign through interviews with refugees, lawyers, and rights groups, as well as by obtaining internal documents, satellite images, and videos. They found that refugees are being detained in overcrowded, unsanitary military facilities where they face abuse and are often coerced into signing documents authorizing their own deportation. These deportations, often carried out suddenly in the dead of night, leave refugees no chance to contest their removal. Children, elderly people, and even those registered with the UN are not spared. The appalling conditions in these detention centers include rat infestations, overflowing sewage, and lack of shelter.
This crackdown has remained largely hidden from public view, bolstered by EU funding intended to curb migration, despite blatant violations of international humanitarian law. In Egypt, refugees now face mounting hostility from authorities, leaving them trapped in fear and uncertainty with no clear way forward.
Risk of Return
Sudanese refugees, with limited access to legal employment in Egypt, are often forced to rely on support from family members abroad. However, refugees I interviewed told me that the Egyptian government is cracking down on this by arresting anyone found with U.S. dollars or foreign currency not “lawfully obtained.” Since opening bank accounts is becoming increasingly difficult for Sudanese people, traditional methods of wire transfer and monetary transactions are limited, with cash exchanges being the only – now potentially dangerous – option.
Sudanese who sought refuge in Egypt after the war have lived at their own expense without receiving state aid. Meanwhile, the UN Refugee Agency (UNHCR) in Egypt has been slowly processing the paperwork and interviews required to register Sudanese people as refugees, making deportation still a very real possibility for a large majority unable to travel to Cairo or still waiting for an interview.
Currently, returning Sudanese citizens to Sudan is tantamount to a death sentence. At least 20,000 people have been killed since the war began, and atrocities including widespread sexual violence continue to be committed. Two of the countries largest cities, Khartoum and Wad Madani have been destroyed by the conflict with houses, schools, and hospitals leveled. In Darfur whole villages are pillaged and mass killings are organized by the RSF. Many cities on Sudan’s periphery have become more expensive to live in than Egypt due to a shortage of residential properties, leading to high rent costs, and resource scarcity, which has caused food prices to triple . With the swell of diseases sweeping the country as the health system is near collapse , findings of famine in Darfur and warnings of its spread, the odds of survival for many of those who are returned are bleak.
Meanwhile in Egypt, Sudanese people are being scapegoated to distract from the country’s own crises: the ailing Egyptian economy has increased the cost of living for everyone, with most jobs remaining low-paying and new opportunities scarce. Additionally, rising rent prices are being blamed on the Sudanese community , leading to heightened tensions between the country’s citizens and their fellow residents.
Communal Solidarity
Regardless, I have seen the Sudanese community in Egypt find solace in each other. Many of them live close together in the Giza governorate, with a large population residing in the Faisal neighborhood, where a sizable Sudanese minority had lived for years before the war. With Sudanese businesses lining the streets and men crowded in the outdoor coffee shops chatting and watching football, it paints a picture reminiscent of the countless nights I spent walking the streets of Khartoum.
The Sudanese community has also held on to their communal nature while displaced in Egypt, with Sudanese-led charitable organizations like Sudan Cairo Aid providing services such as accommodation support, mental health recommendations, food and basic supplies, hygiene products, and medical supplies to anyone who reaches out to them for help. The people of Sudan are an incredibly resilient community. While they always search for ways to lift each other, they need the international community’s attention and assistance.
The Sudanese population in Egypt is currently living at the mercy of a hostile government that does not care for them and is unlawfully arresting and deporting them. This situation is unjust and unfathomably dangerous for people who have already suffered so much.
The war has been deemed as an inevitability due to Sudan’s turbulent political state post-revolution, and the country’s plight has primarily gone ignored as such. Suffering on such a large scale should never be seen as inevitable, and expedient support is vital to ensure that Sudanese people can retain their right to refuge in countries like Egypt without fear of deportation and arbitrary arrest.
Since the revolution in 2018, the Sudanese people have endured a pandemic, a failed democratic transition, a military coup, and now a devastating war—all within just five years. Many Sudanese youths have not attended school consistently during this period, leaving their education in limbo. Friends I once went to school with are now uncertain if they will ever complete their studies or afford to restart their education abroad.
The futures of Sudanese people have been stolen by a war and conflict they did not choose, and now, as they strive to regain a semblance of normalcy, they are being targeted. While my family and the Sudanese refugees I spoke with in Egypt may never return to the pre-war Sudan I remember, they at least deserve the opportunity to safely rebuild their lives and community in a place of refuge.
Wedad Osman is a summer 2024 intern at Refugees International and a student at Georgetown University. She is originally from Sudan.
Sign up for our updates on the most pressing displacement and humanitarian issues.
Mobile Menu Overlay

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The U.S. government advises to reconsider travel to Egypt due to terrorism and limited consular assistance for dual U.S.-Egyptian citizens. Learn about visa requirements, health risks, safety tips, and other travel information for Egypt.
Find out if you can travel to Egypt from the United States and what entry requirements you need. Learn about COVID-19 testing, quarantine, mask rules, and more for Egypt.
The U.S. Department of State advises against traveling to Egypt due to terrorism and limited consular assistance. Avoid the Sinai Peninsula, the Western Desert, and border areas, and enroll in STEP for alerts and emergency services.
COVID-19 Testing Entry Requirements. Most travelers heading to Egypt must show a negative PCR or antigen test certificate, with results in either English or Arabic. The certificate must be issued no more than 72 hours (24 hours for antigen tests) before the flight to Egypt. However, for those coming from Japan, China, Thailand, North America ...
Learn about the vaccines and medicines you may need before traveling to Egypt, including COVID-19, hepatitis A, hepatitis B, measles, polio, rabies, typhoid, and yellow fever. Also find out how to protect yourself from non-vaccine-preventable diseases such as leptospirosis, schistosomiasis, and malaria.
Cairo's long-awaited Grand Egyptian Museum is now scheduled for opening in November 2022. Who can go All travelers can enter Egypt providing they can show proof of a negative Covid-19 test.
Learn about travel requirements prior to your trip to Egypt. Find out about the necessary documentation to travel to Egypt, visas, vaccinations and medical insurance. ... and a negative PCR test was not mandatory for entry. However, as of June 17, 2022, Egypt lifted all restrictions for any international traveler, no vaccination certificate or ...
Note: this post was originally published on August 18, 2021, updated on October 1, 2021, updated on December 17, 2021, and updated again on January 27, 2022. It will continue to be updated with the latest requirements. In January, 2022, Egypt's Ministry of Health announced 3 major updates to their Covid-19 entry requirements.
Most travelers need a visa to enter Egypt, but citizens of some countries can apply for an e-Visa or get a visa on arrival. The visa costs US$25 and is valid for 30 days for single entry or 180 days for multiple entry.
The Egyptian government has announced it is lifting all Covid-19 restrictions for travellers into the country, whether citizens or visitors. The decision was announced on Thursday, after a meeting between Prime Minister Mostafa Madbouly and the Egyptian Supreme Committee for the Management of the Epidemiology and Health Pandemic Crisis.
Find out the latest FCDO advice on travel to Egypt, including areas where travel is not recommended or advised against. Learn about safety and security, entry requirements, health and consular ...
Entry requirements. Travelers who can show acceptable proof of full vaccination, or a negative PCR test obtained within 72 hours of departure, can enter. They must submit details of vaccination or negative test digitally a t least two days before starting their trip. Those arriving in the coastal governorates of South Sinai, Red Sea and Marsa ...
Learn what you need to know before travelling to Egypt in 2024, including visa, immunization, and Covid-19 rules. Find out how to get a visa on arrival, online, or for free, and which vaccines are recommended or required.
The UK government advises against all travel to parts of Egypt due to high threat of terrorist attack, political turmoil and crime. Cairo is one of the areas affected by the security alert, along ...
Find out how to get a visa for Egypt, including tourist visas, visa extensions and visa fees. If you're travelling to Sharm el Sheikh, Dahab, Nuweiba and Taba resorts, you may not need a visa for ...
COVID-19 Testing Entry Requirements. Most travelers heading to Egypt must show a negative PCR or antigen test certificate, with results in either English or Arabic. The certificate must be issued no more than 72 hours (24 hours for antigen tests) before the flight to Egypt. However, for those coming from Japan, China, Thailand, North America ...
Learn about the security situation, entry and exit requirements, health risks and natural disasters in Egypt. Exercise a high degree of caution and avoid all travel to some regions due to terrorism, armed groups and military operations.
All foreign travelers can enter Egypt as long as they follow the local COVID-19 requirements presented below. Please note that all foreign visitors must complete an Egyptian Declaration Form and E-Visa before departing for Egypt. Egypt welcomes travelers from all around the world, but visitors need to be familiar with the current entry ...
Learn about the documents and procedures to enter Egypt from different countries, including visa-free, eVisa, and Visa on Arrival options. Find out the latest Covid-19 rules, testing, vaccination, and quarantine requirements for travelers to Egypt.
Learn about the recommended and required vaccines for Egypt, as well as other health precautions and travel tips. Find out how to protect yourself from diseases like polio, typhoid, hepatitis, rabies, and more.
Countries General Travel Requirements. 9/2/2021. EGYPTAIR is committed as always to delivering a safe and pleasant travel experience. -Due to the spread of Covid-19, Passengers are requested to review the latest Governments published travelling restrictions, which can be found on Travel Regulations Map page provided by IATA for details.
The Australian Government advises reconsidering your need to travel to Egypt overall due to the threat of terrorism. Other levels apply in some areas, such as North Sinai and Sharm El Sheikh. Check the latest updates, health risks, local laws and travel contacts before you go.
Up to date travel restrictions for Egypt, including travel information concerning quarantine, vaccine, lockdown, Covid test, face mask and much more.
I'm always asked what to pack for Egypt, so I decided to create a comprehensive Egypt packing guide, including: 1. What clothes to pack for a trip to Egypt 2. What toiletries to take to Egypt 3. What electronics to bring to Egypt 4. Egypt travel essentials you didn't know about 5. What NOT to bring to Egypt 6.
The war in Sudan has marked more than 500 days, a grim milestone for many Sudanese people. The conflict shows no signs of abating, and has resulted in the world's largest displacement crisis forcing more than 10 million people to confront the harsh reality that their displacement may be more permanent than they once believed. As the war continues to rage on, I often find myself thinking back ...