On Campus Information Sessions & Tours
Registration instructions.
- Registration for a campus visit is required .
- To sign up, please select an available date from the calendar below. Multiple events may pop up when you select an available date. Click on the event labeled "On-Campus Visit" at the time that works for you, and then complete the registration form on a new page.
- Once your registration is complete, we will be in touch via email with helpful information to plan your visit and visit reminders.
- If you arrive on campus without registering, a member of our visitor team will help you to determine your best options including providing information about a self-guided tour and helping you to register for an open tour date and time.
- Sign up for an online session here - this is a 1 hour live session with an admissions officer.
- Click here to do a self-paced virtual tour of Harvard's campus.
- If you are in the area, you may stop by our office at 5 James Street from 9am-5pm Monday to Friday (11am-5pm on Wednesdays) and pick up a self-guided tour map and ask questions of the Visitor Center staff.

COVID-19 Precautions
Group visits/tours, important information for your visit.
- Special Accommodations - there will be space on the registration form to request special accommodations. Please note that we require 21 days advance notice in order to secure ASL interpreters. We cannot provide interpreters for other languages at this current time. Those requesting the use of a wheelchair must leave a current driver’s license or state ID with our Visitor Center personnel until the chair is returned.
- Most buildings are closed to the public. Public restrooms will be available in the Elizabeth Cary Agassiz House before/after the information session, and at the end of the tour at Smith Campus Center.
- At this time, it is not possible to store luggage or other personal property during your visit. We apologize for any inconvenience this may cause, especially for families who have traveled long distances to join us.
- Your registration and attendance have no bearing on the admissions process should you decide to apply.
- Guests are not permitted to record any part of the information session and/or tour.
On-Campus Visit Calendar & Registration
- Utility Menu
GA4 Tracking Code

Stay updated on news & events
1a999a828aff8a8659722cf3eb28e635
Introducing the visit harvard mobile app.

By Amy Kamosa
The Harvard Visitor's Center has launched a new Visit Harvard mobile app that will provide free, self-guided, self-paced themed walking tours of the University. The first tour released on the app is a historic walking tour of the Cambridge Campus. It incorporates 14 locations throughout campus that highlight some of the most important buildings and events of the University's nearly 400-year history.
In 2019, approximately 8 million people visited Harvard Square, and more than 35,000 visitors took part in public and private tours of the Harvard Campus. When the campus shut down in early 2020 due to the pandemic, Robin Parker, Associate Director of Harvard's Visitor Center, worked with colleagues and a small team of undergraduate tour guides led by Fari Mbaye '22 and Madi Fabber '22, to create a series of live, student-led online virtual tours as an option for would-be visitors who were no longer able to come to the Square.
The mobile app tour builds on the content developed for those virtual offerings, but provides a more accessible option that visitors can use to guide themselves while they visit campus in-person, or from the comfort of their own couch anywhere in the world.
"Our student tour guides really led the charge on the creation of these tours. Some of the images they've included have never been seen before, and the content weaves a really compelling story through Harvard's history," said Parker.
It was that storytelling aspect of the mobile tour that Mbaye said was the most challenging and important aspect of translating the live tour content to the app. "When we, as tour guides, give live tours, we're really just working off bullet points and we weave our own details and jokes in as we go. With the app, we had to turn the content into a complete story that people would want to read and listen to," she explained.
If app users choose to visit the campus, they can follow the geo-location tags on the app to travel point-to-point. The total distance of the tour is approximately one mile and should take approximately one hour to complete—including travel between stops, but the self-guided nature of the app means that users can complete this circuit at their own pace.
According to Visitor Center Manager Maggie Dawson, the ease of use and simplicity of design was an intentional choice to ensure that the app was as accessible as possible. Additional features like geo-location tagging, audio tracks with transcript, and image alternative text for visually-impaired users, all enable a large range of users to interact with the app in their own way, and according to Dawson, inclusion will continue to be a priority as more content is added. "Our hope is to tell many parts of the Harvard story to as many audiences as possible. Not only are additional tours in development, including a Black History Tour, and Arts Walk, and a Women's History tour, but we are expanding the tour languages as well," she explained.
The Visit Harvard App is available for download through the Apple Store and Google Play . There is also a desktop version of the app you can access here .
Blog posts by month
- March 2024 (2)
- February 2024 (2)
- May 2023 (1)
- March 2023 (1)
- August 2022 (4)
- Utility Menu
72a1f7f6e071e66b3c32803c6a42b3cb

- Classifieds
- Training Portal
- Contingent Workforce
573afce095134b6b933403ff00bbab3c
Where can i find a tour of harvard’s campus.
A tour is a great way to get to know the campus! Harvard Information Center, located in the Smith Campus Center, offers free student-led walking tours through Harvard Yard. Tours are one hour and provide a general overview of the main Cambridge camps and University history. The Information Center also has maps for self-guided walking tours. For details and schedule, as well as links to tour information at the graduate schools go here . The Admissions Office offers separate tours for prospective students.
FAQs by department
- Administrative Fellows Program
- Center for Workplace Development
- Compensation
- Harvard Bridge Program
- Labor and Employee Relations
- Learning & Development
- Our Workplace
- Recognition
- Recruitment Office
- Total Rewards
Virtual Tour
Https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/allston/1/science-and-engineering-complex-sec, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/allston/2/114-western-avenue, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/allston/3/east-atrium, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/allston/4/main-atrium, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/allston/10/engineering-yard, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/allston/5/lower-level-1, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/allston/6/lower-level-2, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/allston/9/library, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/allston/9/upper-floors, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/allston/11/classrooms, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/allston/12/allston-neighborhood, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/allston/8/sustainability, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/allston/7/active-learning-labs, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/cambridge/1/harvard-yard, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/cambridge/2/science-center-and-seas-history, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/cambridge/3/labs-cruft-lise-mckay, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/cambridge/4/pierce-hall, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/cambridge/5/maxwell-dworkin, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/cambridge/6/northwest-building, https://seas.harvard.edu/tour/cambridge/7/engineering-sciences-lab.
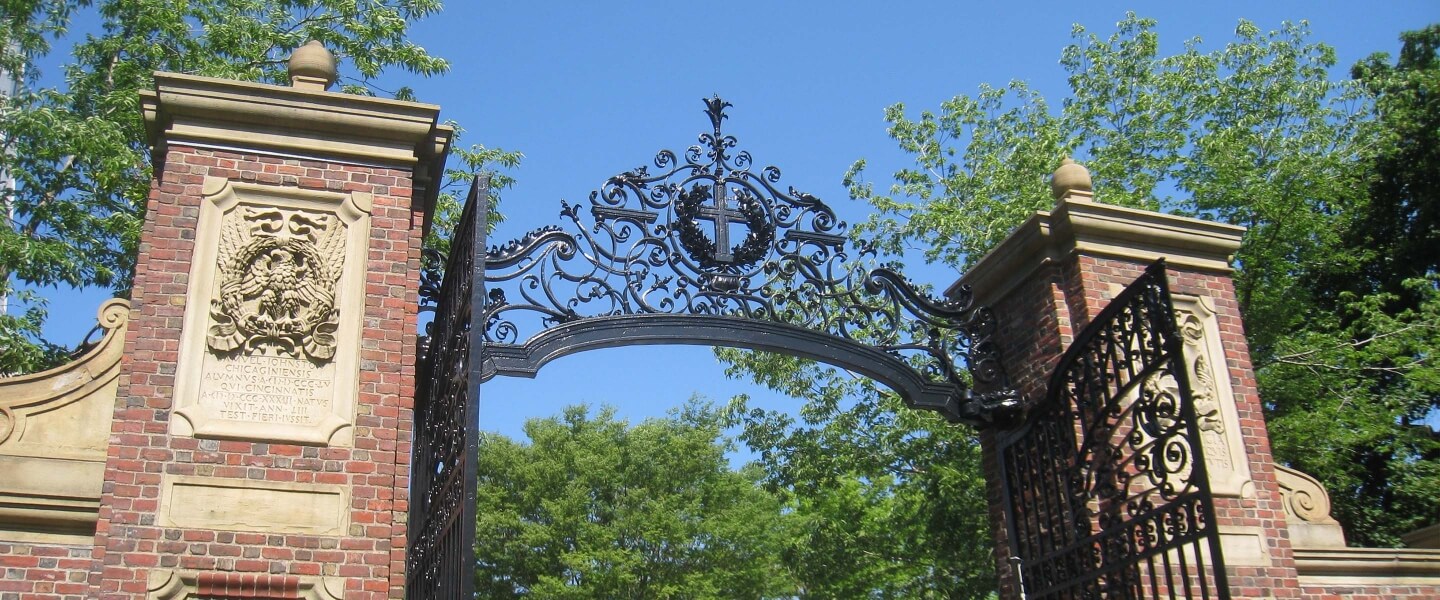

1. Harvard Yard
Harvard Yard , in Cambridge, Massachusetts, is a grassy area enclosed by fences with twenty-seven gates. It is the oldest part of the Harvard University campus, its historic center, and its modern crossroads. Harvard Yard contains most of the freshman dormitories; Harvard's most important libraries; Memorial Church; several classroom and departmental buildings; and the offices of the Dean of the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, the Dean of Harvard College, and President of Harvard University.
Find out more about Harvard Yard and other areas of the University as a whole by taking an in-person, virtual, or audio tour of Harvard .
An introduction to Harvard SEAS
To address current and future societal challenges, knowledge from fundamental science, art, and the humanities must all be linked through the application of engineering principles with the professions of law, medicine, public policy, design and business practice.
In other words, solving important issues requires a multidisciplinary approach. With the combined strengths of SEAS, FAS, and the professional schools, Harvard is ideally positioned to both broadly educate the next generation of leaders who understand the complexities of technology and society and to use its intellectual resources and innovative thinking to meet the challenges of the 21st century.
Private tour group providers
This information is for private tour providers not associated with Harvard University. If you are an individual looking for a tour, please visit our Tours page.
At this time, Cambridge and Boston tour companies who wish to lead tours of visitors through Harvard Yard are required to register with the Harvard University Visitor Center.
For further inquiry, please contact: [email protected]
Registration process
Apply to be a registered Harvard Yard Tour Provider
To register:
- Fill out the application.
- Submit a copy of a business license (in Cambridge or Boston) and proof of insurance.
- Allow up two weeks for the authorization process.
Once approved:
- The Harvard University Visitor Center will provide a physical “Welcome Packet” to the tour company.
- Sign the Harvard Yard Use Agreement.
- The tour company will be directed to the online payment system, where tour passes must be purchased at least three days in advance for the desired tour date (currently through the end of the semester).
Before the tour:
- Prior to coming to campus, the tour company must review the Harvard Yard Guidelines and go to Visit Harvard for any updated campus information.
- The tour company will use Touchnet, the online payment system, to purchases passes for the current semester at least three days in advance of the desired tour date.
- A Harvard Yard Tour Pass purchase requires a non-refundable payment of $1.50 per tour attendee.
- The tour company will receive a PDF file of the Harvard Yard Tour Pass within three business days.
- The tour company must print the Harvard Yard Tour Pass in color and it must be visibly worn on the tour group leader at all times while in Harvard Yard. Lanyards and other tour materials may be found in the “Welcome Packet.”
Keep in mind:
- Occasionally the Yard closes for University activities. If this conflicts with a tour you have sign up for, your payment will be refunded.
- Tour groups can include up to 35 people.
- The tour company may offer up to one tour per day in Harvard Yard, as space is available.
- The tour company may offer tours in Harvard Yard between 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. daily.
- The tour company must remain in good standing in order to annually renew the Harvard Yard Use Agreement.
Frequently asked question
Who has to register to provide tours in harvard yard.
At this time, Cambridge and Boston Tour Companies who wish to lead tours of visitors through Harvard Yard are required to register with the Harvard University Visitor Center.
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.
Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

An Olympics first
University Disability Resources celebrates Disability Pride

Brian Lee to step down as VP for alumni affairs and development
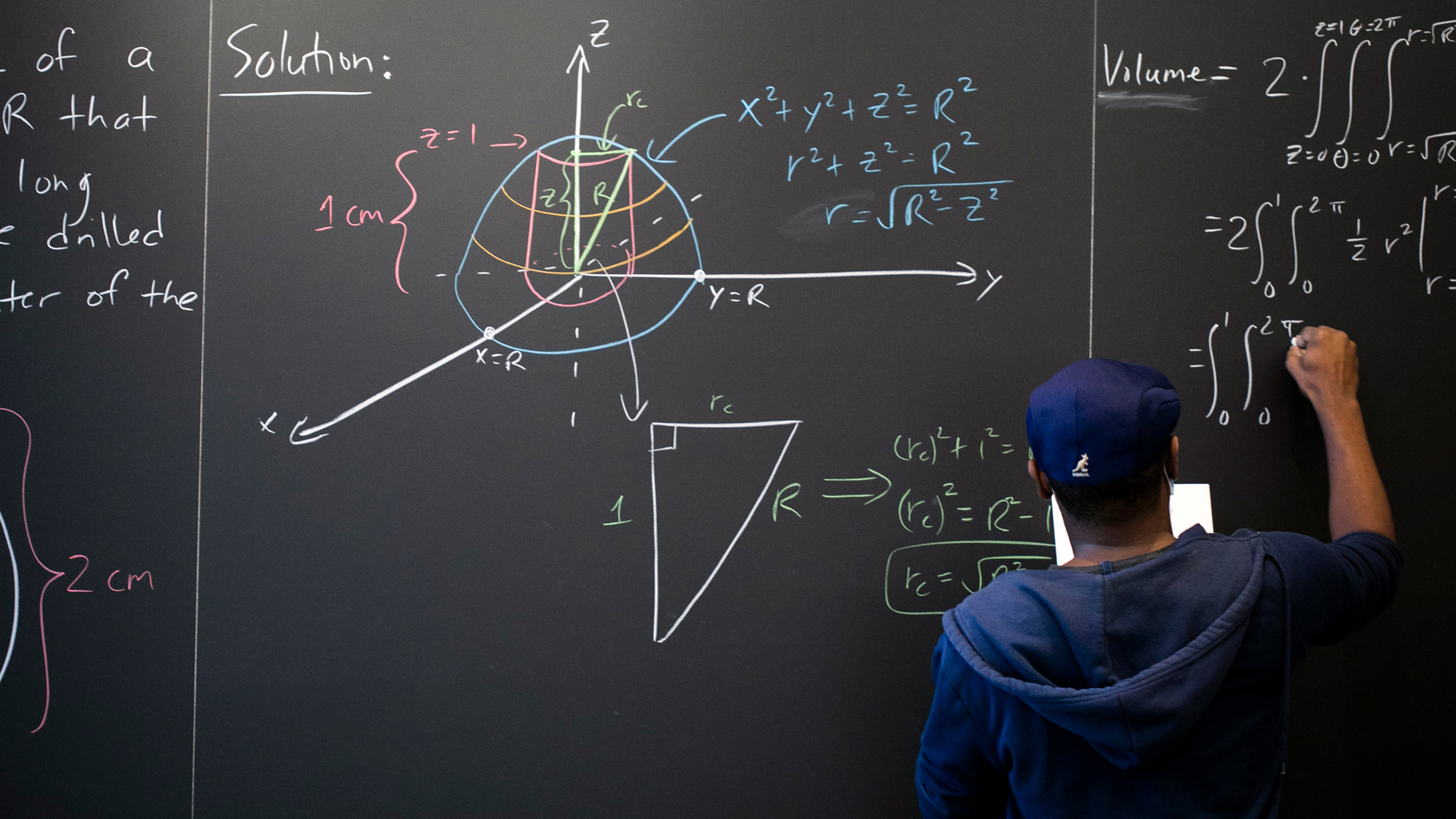
Hakim Walker, preceptor of mathematics, uses the chalkboard in the Science Center math lounge to try to solve a problem: finding the volume of a ball with a 2-centimeter-long cylindrical hole drilled through it.
Photos by Stephanie Mitchell/Harvard Staff Photographer
Ideas captured in chalk on slate
Manisha Aggarwal-Schifellite and Juan Siliezar
Harvard Staff Writers
Blackboards and whiteboards offer windows into the questions, problems, theories, and arguments students are taking on this semester
Since its invention in the early 1800s, the chalkboard has been a classroom fixture and an essential visual tool for learning. Despite advances in technology, the appeal of chalk and slate endures, although some prefer markers and whiteboards (a mid-20th-century addition). Across the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, students, researchers, and faculty use these boards to aid collaboration, harness creativity, make the abstract concrete, and work out big questions. Here’s a sampling.

On his glass board, Mihnea Popa , a professor of mathematics (pictured above), writes out ideas, theories, and arguments that become abstract very fast. “It is essentially impossible to have a discussion without writing things down and going back to earlier thoughts if needed,” he said. “Writing things on the board makes it easier to discover mistakes as well, for which the eraser provides a first solution.”
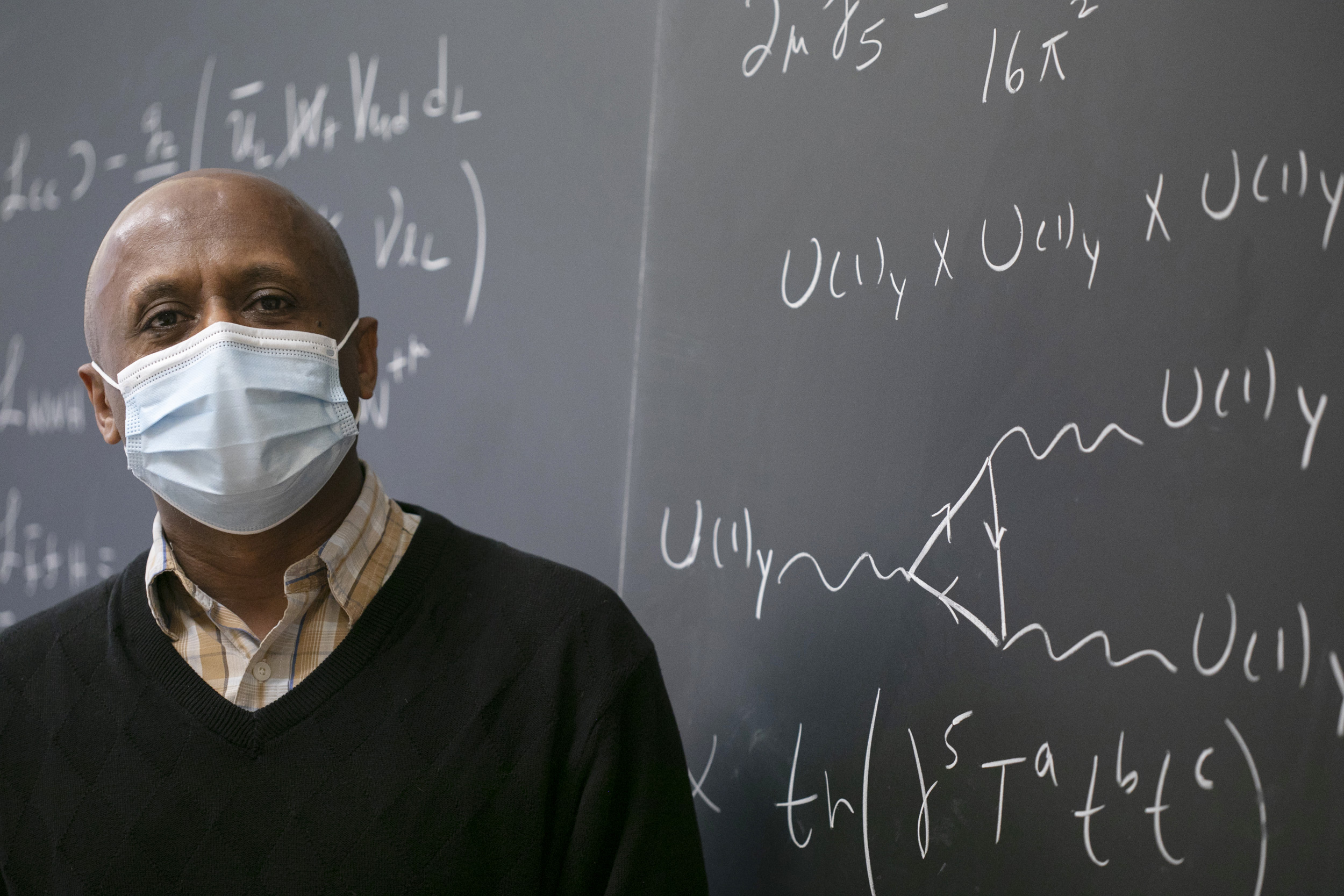

Girma Hailu , a senior preceptor in physics (pictured above), enlists chalkboards in lectures, office hours, and discussions. “The process of writing on the chalkboard gives everyone time to pause, think, assimilate information, and raise questions.”
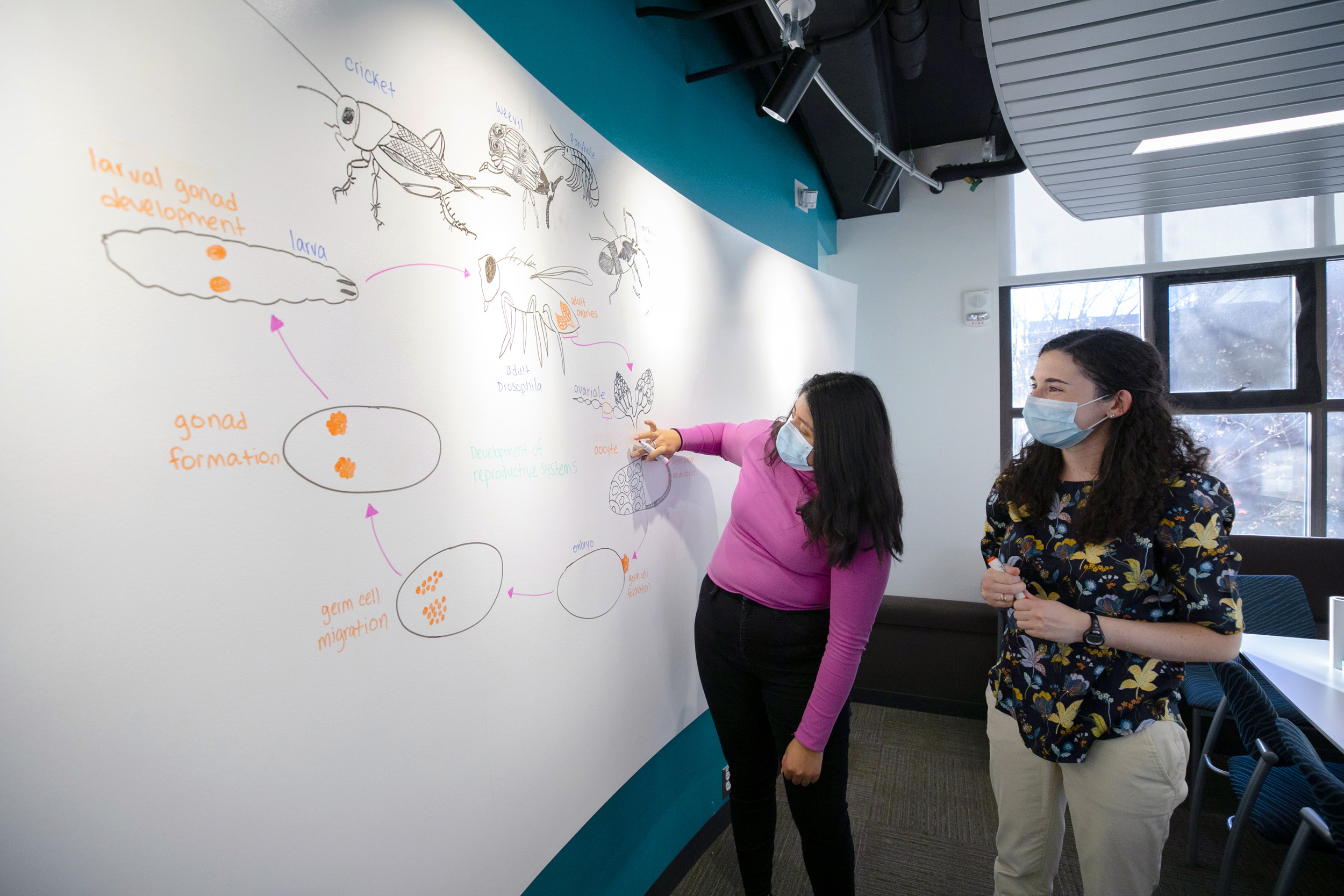

Drawings of animal embryos and other tissues fill the whiteboards of the Extavour Lab , whose researchers study the ancient origins of germ cells to understand their evolution. “We frequently draw on the boards to plan and discuss our experiments, which include genetic crosses, dissections, and microscopy,” said graduate student researcher Emily Rivard (pictured above with Adriana Aguilar-Maldonado ).

Hakim Walker (pictured above) has students practice solving problems in groups on the blackboard. “I firmly believe that students do not truly learn math by just copying it down or watching someone else do it; they only learn math by actively doing math themselves,” said the preceptor of mathematics and first-year proctor in Matthews Hall.

The idea to hang whiteboards along the halls of the Institute for Quantitative Social Science came from Director Gary King . “Instead of people peeking at photos as they walk by, they pour out of their offices and work on real problems together in the hallways,” said King, the Weatherhead University Professor. “These hallways are not merely connectors of different spaces; they are integral parts of the building. They help us build, house, and improve our community.”
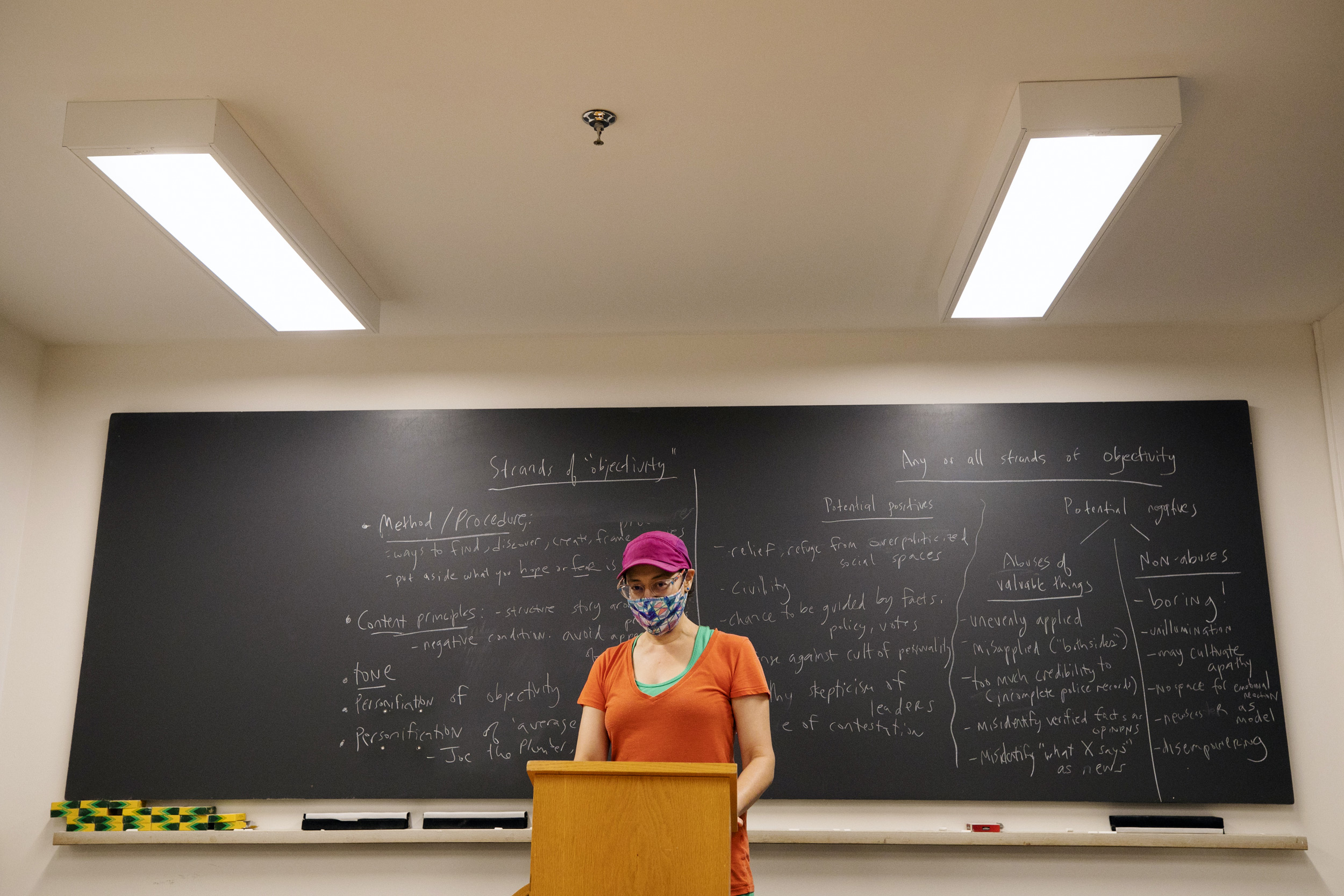
In her course “Truth, Lies, and the Press,” Edgar Pierce Professor of Philosophy Susanna Siegel (pictured above) and her students investigate the philosophy of journalism. “This board work is from our discussions of one of the thorniest notions in philosophy: objectivity,” said Siegel. “It’s thorny because there are so many things it can mean. Throughout the semester we kept a running list of different principles and practices that the word is used to refer to, so students can more clearly assess whether they are possible or impossible, worthwhile or unproductive, used or abused.”

Visiting lecturer in English Alan Niles focuses on highlighting the work of women in “English Literature: The First 1000 Years.” “To read past literature historically means recognizing the ways women have always participated in the world of letters, alongside and in dialogue with men,” he said. “And the difficulties of writing as a woman are themselves something we should study, and that students can find interesting.”
A debate about Mary, Queen of Scots, and questions of authorship, as seen in this board, “not only taught them the surprising and volatile history behind Mary, whose poetry is rarely covered, but it also showed them how literature invites us to consider perspectives other than our own, and that we disagree more constructively as a society when we seek to understand different points of view,” said Vanessa “V.M.” Braganza (pictured above), the course’s teaching fellow and a Ph.D. candidate studying Renaissance literature.
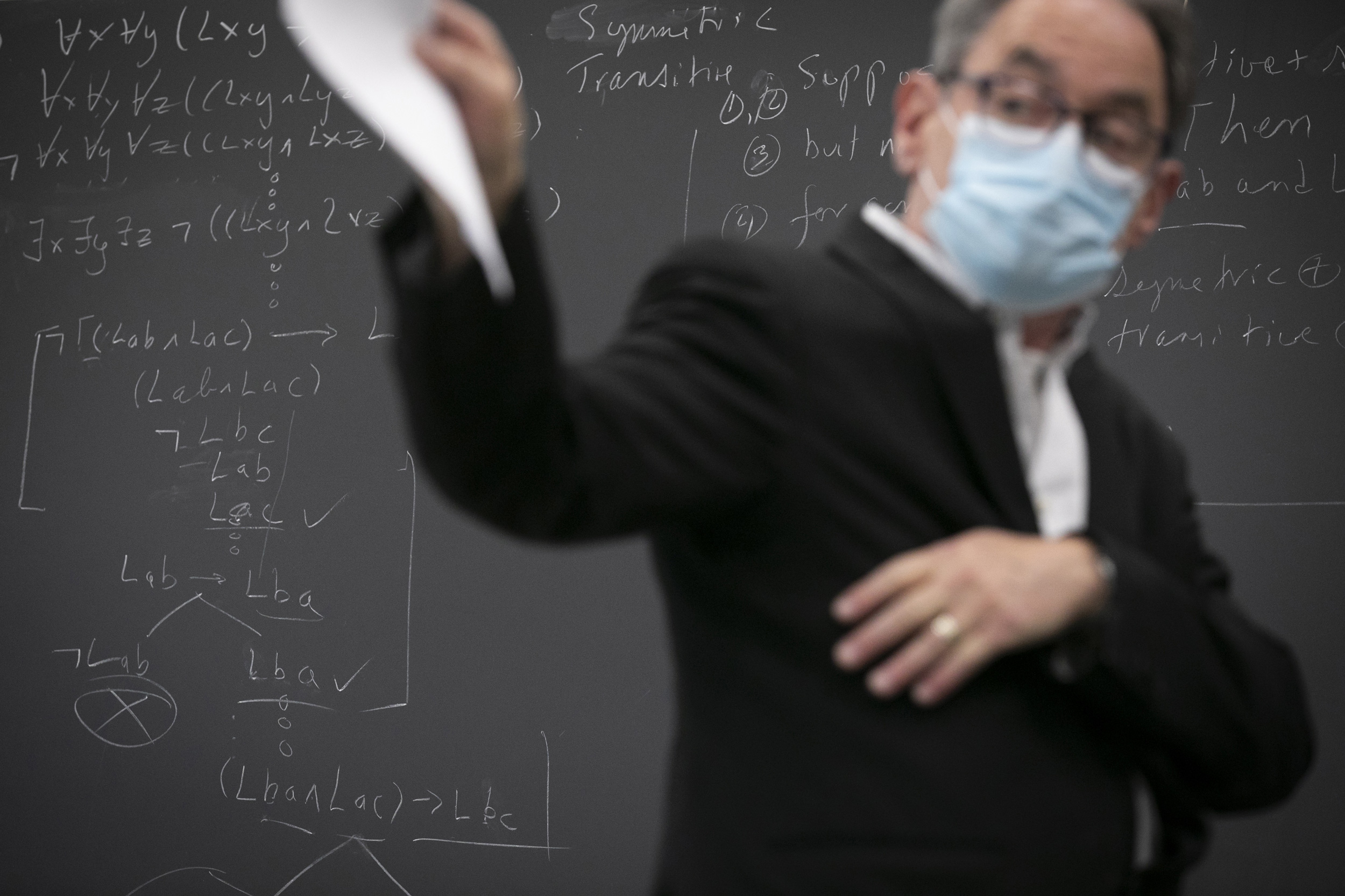

“An introductory logic class tries to do a number of things: set out a theory of what makes a piece of reasoning good (or not so good); apply what we learn from the theory to the analysis of everyday arguments and arguments in the deductive sciences; and examine how formal tools can be used in disciplines like linguistics to theorize about natural language semantics,” said Mark Richard (pictured above), a professor of philosophy who teaches “Introduction to the Power and Form of Logic.” On this board, the class determined whether the formalization of an argument in English was a valid argument.
Share this article
You might like.

First-year fencer makes history as member of all-Harvard squad in Paris
Investments and realignment of resources creates greater access for Harvard community members

‘Champion of Harvard and our mission’ will depart at end of calendar year
The way forward for Democrats — and the country
Danielle Allen is more worried about identity politics and gaps in civic education than the power of delegates
Between bright light and a good mood, plenty of sleep
Researchers outline path to lower risk of depression
Do phones belong in schools?
Banning cellphones may help protect classroom focus, but school districts need to stay mindful of students’ sense of connection, experts say.

Harvard Tours – tickets, prices, discounts, what to expect

If you couldn’t make it to Harvard University, then worry not! You can still explore the campus – just book a through Harvard Campus Tour.
A Harvard tour gives you insights into campus life and tells you why it is the best institute in the world.
The tour revolves around exploring Harvard History, Harvard Culture, and Famous Harvardians.
This article covers everything you must know before booking tickets for the Harvard Campus Tour.
Top Harvard Tour
# 70-minute group tour
Table of Contents
What to expect.
The Harvard tours introduce you to the dynamic Harvard History, Harvard Culture, and Famous Harvardians.
Harvard campus tour covers many landmarks such as Harvard Square, Harvard Yard, the John Harvard Statue (the university founder), Harvard Lampoon, and many more.
All the tour guides are Harvard students who are charismatic, engaging, and enthusiastic.
These guides make Harvard tours more like a show or a theatre filled with non-stop fun and entertainment.
With the students’ guides by your side, you get to learn interesting facts about the university, its hidden secrets, and stories of popular Harvardians like Mark Zuckerberg, Barack Obama, Conan O’Brien, and many more.
Harvard tours are designed to entertain both adults and children. AAA Magazine called them “great for families!” The tour guides cater to guests of all ages and families.
Where to book tickets
Tickets for the Harvard tour are available to be purchased at the attraction or online in advance.
Online ticket prices tend to be cheaper than tickets at the attraction.
When you buy online, you can avoid standing in long queues and wasting time.
When you book early, you also get your preferred time slot.
Because some attractions sell a limited number of tickets, they may sell out during peak days. Booking online also helps avoid last-minute disappointment and delays.
How do online tickets work
Go to the Harvard tour booking page , select your preferred date and time and the number of tickets, and buy the tickets right away.
After the purchase, you will receive the tickets via email.
You don’t need to carry printouts.
Show the smartphone tickets at the meeting point on the day of your visit and begin your adventure.
Harvard Tour Ticket prices
Adult tickets for the Harvard Tour are available for US$23 for visitors aged between 18 and 64 years.
For children between four and 17 years of age, tickets are available for US$21.
Senior Citizens aged 65 and above can get the tickets for US$22.
Infants up to three years of age do not require a ticket.
Harvard Tour tickets

Experience Harvard University like never before with a guided walking tour.
Explore the campus while learning about the oldest university in the USA and its notable landmarks.
The tour will be led by a student guide who will share interesting anecdotes about life at Harvard.
In addition, the ticket also includes an illustrated map of Harvard Square.
The tour route covers a distance of less than one mile.
Ticket Prices
Adult ticket (18 to 64 years): US$23 Senior ticket (65+ years): US$22 Child ticket (4 to 17 years): US$21 Infant tickets (up to 3 years): Free
Along with their Harvard Campus Tour, some tourists prefer to book a group tour of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology .
Where do Harvard tours start from?
The Harvard campus tour starts from Harvard Square.
Located at the junction of Massachusetts Avenue, Brattle Street, and John F. Kennedy Street, Harvard Square is thronged by visitors, students, and artists daily.
You’ll find your tour guides outside the Harvard Red Line Subway Station next to the Out of Town News Kiosk. Get Directions
The closest street address is 1380 Massachusetts Ave, Cambridge, MA 02138.
The 70-minute Harvard Tour is available throughout the week.
Visitors can choose between tour slots starting at 10 am and continuing every half hour till 4.30 pm.
How long does the Harvard Tour last?
The Harvard walking tour lasts for about 70 minutes.
There are umpteen stops on the 1-mile (1.6 km) long tour.
The tour guides will tell you the stories and significance of various landmarks you pass by.

Is a tour of Harvard worth it?
Established in 1636, Harvard is America’s oldest university and perhaps the most famous institution of higher education on the planet. Harvard is very much worth visiting.
This prestigious university contains tall buildings, libraries packed with books, and iconic sites that are breathtaking.
Whether you’re a student or not, the campus has much to please your mind and soul.
Since the students will walk you through the campus, you get an insider perspective about the university.
All of this makes the Harvard Tour worth your money and time.
Sites you will see on the Harvard Tour
You’ll walk through the university gates, around the yard, and past some historic buildings with Harvard Tour guides.
The major sites covered under Harvard Tours are:
Harvard Square
It is a commercial center in Cambridge with streets lined with cafes, restaurants, retail stores, cinemas, and bookstores.
Johnston Gate
This majestic gate takes you to the world of knowledge and wisdom. It is one of the many doorways to Harvard Yard.
Harvard Yard
It is the heart of Harvard University, enclosed by wrought iron fences, walls, and a thick canopy of trees. The John Harvard Statue is situated in this beautiful yard.
Science Center
It is a place for science and math buffs who experiment and do research.
Memorial Hall
The cornerstone of the building was laid in 1870 in memory of those who laid down their lives during the Civil War.
New College Theatre
It hosts several theatrical and musical performances of Harvard students every year. NCT is also open to the general public to enjoy the performances of Harvard-affiliated groups and performers.
The Harvard Lampoon
Sometimes referred to as “Lampoon Castle,” this sturdy castle consists of an office, library, dining hall, and a lounge. It is famous for publishing comic and humor magazines.
Lowell Bell Tower
This blue-capped bell tower is in proximity to Harvard Yard and Harvard Square. It houses the iconic Russian bells.
What to bring on the tour?
It is better to come prepared for the weather to avoid surprises.
When coming for the tour, you can bring along the following items-
- Comfortable shoes
- Jacket
Things to know before starting a tour
Before starting the campus tour, keep in mind the following points-
- The tour will go on despite rain or sunshine.
- Reach the tour’s starting point (Harvard Square) at least 10-15 minutes before the scheduled time.
The tour does not take you inside any of the buildings.
FAQs about the Harvard Walking Tour
Here are some questions visitors usually ask before taking the Harvard Walking Tour.
What is included in the Harvard University Tour?
The tour includes a guided walk through Harvard Yard and visits to various historic buildings on campus.
What should I wear on the Harvard University Walking Tours?
Comfortable shoes and weather-appropriate clothing are recommended.
Should I pre-book tickets for the Harvard University Tour?
Yes, it is best to buy tickets in advance to ensure availability and have a hassle-free experience.
How long are the Harvard University Walking Tours?
The tours last approximately 70 minutes.
Are the Harvard University Tours wheelchair accessible?
Yes, the tours are wheelchair accessible.
Can I bring a backpack or bag to the Harvard University Walking Tour?
Yes, you can bring a backpack or bag on the tour, but it will be subject to security screening.
Is there a gift shop at the Harvard University Information Center?
Yes, there is a gift shop at the Harvard University Information Center where you can purchase souvenirs and other items related to Harvard University.
Are pets allowed on the Harvard University Walking Tours?
No, pets are not allowed on the tour.
Are cameras allowed on the Harvard University Walking Tours?
Yes, cameras are allowed, and visitors are free to take photographs.
Are there restrooms on the Harvard Tour?
Yes, restrooms are available at the Harvard University Information Center.
Sources # College.harvard.edu # Harvard.edu # Apply.college.harvard.edu # Seas.harvard.edu The travel specialists at TheBetterVacation.com use only high-quality sources while researching & writing their articles. We make every attempt to keep our content current, reliable and trustworthy .
Popular attractions in Boston
# Boston Tea Party Ships & Museum # Boston Trolley Tours # New England Aquarium # Boston Ghost Tours # Zoo New England # Codzilla Boston # Fenway Park tours # Boston Harbor Cruises # Whale Watching in Boston # Harvard Tours # Boston Duck Tours
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Check out all the things to do in Boston
This article was researched & written by
Jamshed V Rajan
He is a two-faced traveler, who enjoys both the hustle-bustle of an urban holiday and the serenity of a break from the rest of the World. During some of his vacations, he is a resort hopper, and on others, he barely spends time in his hotel. He loves to try mouth-watering local cuisines, especially non-vegetarian dishes. Favourite Cities: Amsterdam, Las Vegas, Dublin, Prague, Vienna
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
FireStorm Internet runs this website to provide the most accurate and up-to-day information about tourist attractions.
Our Address
FireStorm Internet, 203, 30C, Bollineni Hillside, Perumbakkam Main Road, Nookampalayam, Chennai, India. Pin Code: 600126
About Us Advertise with Us The Team Contact Us Affiliate Disclaimer Content Policy Privacy Policy Terms of Service
Food Tours Ghost Tours Stadium Tours HOHO Bus Tours Best Cruises Best Zoos Travel Tips Visual Stories
© 2024 FireStorm Internet
Connect with the GSD

Fall 2024 Virtual Open Houses
Register below to join faculty, staff, and current students at our Open Houses to learn more about the GSD and your program(s) of interest.
Master in Design Engineering (MDE) Virtual Open House October 29, 2024, 11:00 a.m. – 12:30 a.m. (ET)
Master in Design Studies (MDes) Virtual Open House October 31, 2024, 1:00 p.m. – 3:00 p.m. (ET)
Doctor of Design (DDes) Virtual Open House October 31, 2024, 10:00 a.m. – 12:30 p.m. (ET)
Master in Urban Planning (MUP) Virtual Open House November 1, 2024, 9:00 a.m. – 1:00 p.m. (ET)
Master of Architecture/Landscape Architecture in Urban Design (MAUD/MLAUD) Virtual O pen House November 1, 2024, 9:00 a.m. – 1:00 p.m. (ET)
Master in Real Estate (MRE) Virtual O pen House November 1, 2024, 11:00 a.m. – 2:00 p.m. (ET)
Master in Landscape Architecture (MLA I/AP/MLA II) Virtual O pen House November 7, 2024, 9:00 a.m. – 1:00 p.m. (ET)
Master of Architecture (MArch I/MArch II) Virtual O pen House November 8, 2024, 10:00 a.m. – 1:30 p.m. (ET)
Virtual Information Session Recordings
We invite you to explore our recorded information sessions led by admissions staff. Each session includes a program overview, application tips, and an introduction to student life at the GSD. Please register here to gain access to our video library .
Virtual Program Specific Sessions
Register below for a program specific session – more sessions to be added throughout the fall semester.
Master in Design Engineering (MDE) Virtual Information Session September 16, 2024, 10:00 a.m. – 11:00 a.m. (ET)
Recruitment Fairs/School Visits
The GSD will be participating in various recruitment fairs and school visits throughout fall 2024. Additional events will be added as they are confirmed. We hope to meet you soon!
Chicago Architecture + Design College Day (in-person) September 21, 2024, 10:00 a.m. – 1:00 p.m. (CT) Register for Chicago Architecture + Design
Idealist Graduate School Fair in NYC (in-person) October 9, 2024, 5:00 p.m. – 8:00 p.m. (ET) Register for Idealist NYC
2024 Philadelphia Architecture and Design College Fair (in-person) October 20, 2024, 10:00 a.m. – 2:00 p.m. (ET) Register for Philadelphia Architecture and Design Fair
NOMA Annual Conference: The Exchange (in-person) October 23 – 27, 2024, Maryland Admissions will be available on October 26, from 9 a.m. to 4 p.m. (ET) Learn more about NOMA Conference here
If you’re in the Cambridge area….
During the fall semester, we invite you to explore the GSD campus on a tour led by one of our current students. Register for a tour here .
Peer Reviewed
GPT-fabricated scientific papers on Google Scholar: Key features, spread, and implications for preempting evidence manipulation
Article metrics.
CrossRef Citations
Altmetric Score
PDF Downloads
Academic journals, archives, and repositories are seeing an increasing number of questionable research papers clearly produced using generative AI. They are often created with widely available, general-purpose AI applications, most likely ChatGPT, and mimic scientific writing. Google Scholar easily locates and lists these questionable papers alongside reputable, quality-controlled research. Our analysis of a selection of questionable GPT-fabricated scientific papers found in Google Scholar shows that many are about applied, often controversial topics susceptible to disinformation: the environment, health, and computing. The resulting enhanced potential for malicious manipulation of society’s evidence base, particularly in politically divisive domains, is a growing concern.
Swedish School of Library and Information Science, University of Borås, Sweden
Department of Arts and Cultural Sciences, Lund University, Sweden
Division of Environmental Communication, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Sweden

Research Questions
- Where are questionable publications produced with generative pre-trained transformers (GPTs) that can be found via Google Scholar published or deposited?
- What are the main characteristics of these publications in relation to predominant subject categories?
- How are these publications spread in the research infrastructure for scholarly communication?
- How is the role of the scholarly communication infrastructure challenged in maintaining public trust in science and evidence through inappropriate use of generative AI?
research note Summary
- A sample of scientific papers with signs of GPT-use found on Google Scholar was retrieved, downloaded, and analyzed using a combination of qualitative coding and descriptive statistics. All papers contained at least one of two common phrases returned by conversational agents that use large language models (LLM) like OpenAI’s ChatGPT. Google Search was then used to determine the extent to which copies of questionable, GPT-fabricated papers were available in various repositories, archives, citation databases, and social media platforms.
- Roughly two-thirds of the retrieved papers were found to have been produced, at least in part, through undisclosed, potentially deceptive use of GPT. The majority (57%) of these questionable papers dealt with policy-relevant subjects (i.e., environment, health, computing), susceptible to influence operations. Most were available in several copies on different domains (e.g., social media, archives, and repositories).
- Two main risks arise from the increasingly common use of GPT to (mass-)produce fake, scientific publications. First, the abundance of fabricated “studies” seeping into all areas of the research infrastructure threatens to overwhelm the scholarly communication system and jeopardize the integrity of the scientific record. A second risk lies in the increased possibility that convincingly scientific-looking content was in fact deceitfully created with AI tools and is also optimized to be retrieved by publicly available academic search engines, particularly Google Scholar. However small, this possibility and awareness of it risks undermining the basis for trust in scientific knowledge and poses serious societal risks.
Implications
The use of ChatGPT to generate text for academic papers has raised concerns about research integrity. Discussion of this phenomenon is ongoing in editorials, commentaries, opinion pieces, and on social media (Bom, 2023; Stokel-Walker, 2024; Thorp, 2023). There are now several lists of papers suspected of GPT misuse, and new papers are constantly being added. 1 See for example Academ-AI, https://www.academ-ai.info/ , and Retraction Watch, https://retractionwatch.com/papers-and-peer-reviews-with-evidence-of-chatgpt-writing/ . While many legitimate uses of GPT for research and academic writing exist (Huang & Tan, 2023; Kitamura, 2023; Lund et al., 2023), its undeclared use—beyond proofreading—has potentially far-reaching implications for both science and society, but especially for their relationship. It, therefore, seems important to extend the discussion to one of the most accessible and well-known intermediaries between science, but also certain types of misinformation, and the public, namely Google Scholar, also in response to the legitimate concerns that the discussion of generative AI and misinformation needs to be more nuanced and empirically substantiated (Simon et al., 2023).
Google Scholar, https://scholar.google.com , is an easy-to-use academic search engine. It is available for free, and its index is extensive (Gusenbauer & Haddaway, 2020). It is also often touted as a credible source for academic literature and even recommended in library guides, by media and information literacy initiatives, and fact checkers (Tripodi et al., 2023). However, Google Scholar lacks the transparency and adherence to standards that usually characterize citation databases. Instead, Google Scholar uses automated crawlers, like Google’s web search engine (Martín-Martín et al., 2021), and the inclusion criteria are based on primarily technical standards, allowing any individual author—with or without scientific affiliation—to upload papers to be indexed (Google Scholar Help, n.d.). It has been shown that Google Scholar is susceptible to manipulation through citation exploits (Antkare, 2020) and by providing access to fake scientific papers (Dadkhah et al., 2017). A large part of Google Scholar’s index consists of publications from established scientific journals or other forms of quality-controlled, scholarly literature. However, the index also contains a large amount of gray literature, including student papers, working papers, reports, preprint servers, and academic networking sites, as well as material from so-called “questionable” academic journals, including paper mills. The search interface does not offer the possibility to filter the results meaningfully by material type, publication status, or form of quality control, such as limiting the search to peer-reviewed material.
To understand the occurrence of ChatGPT (co-)authored work in Google Scholar’s index, we scraped it for publications, including one of two common ChatGPT responses (see Appendix A) that we encountered on social media and in media reports (DeGeurin, 2024). The results of our descriptive statistical analyses showed that around 62% did not declare the use of GPTs. Most of these GPT-fabricated papers were found in non-indexed journals and working papers, but some cases included research published in mainstream scientific journals and conference proceedings. 2 Indexed journals mean scholarly journals indexed by abstract and citation databases such as Scopus and Web of Science, where the indexation implies journals with high scientific quality. Non-indexed journals are journals that fall outside of this indexation. More than half (57%) of these GPT-fabricated papers concerned policy-relevant subject areas susceptible to influence operations. To avoid increasing the visibility of these publications, we abstained from referencing them in this research note. However, we have made the data available in the Harvard Dataverse repository.
The publications were related to three issue areas—health (14.5%), environment (19.5%) and computing (23%)—with key terms such “healthcare,” “COVID-19,” or “infection”for health-related papers, and “analysis,” “sustainable,” and “global” for environment-related papers. In several cases, the papers had titles that strung together general keywords and buzzwords, thus alluding to very broad and current research. These terms included “biology,” “telehealth,” “climate policy,” “diversity,” and “disrupting,” to name just a few. While the study’s scope and design did not include a detailed analysis of which parts of the articles included fabricated text, our dataset did contain the surrounding sentences for each occurrence of the suspicious phrases that formed the basis for our search and subsequent selection. Based on that, we can say that the phrases occurred in most sections typically found in scientific publications, including the literature review, methods, conceptual and theoretical frameworks, background, motivation or societal relevance, and even discussion. This was confirmed during the joint coding, where we read and discussed all articles. It became clear that not just the text related to the telltale phrases was created by GPT, but that almost all articles in our sample of questionable articles likely contained traces of GPT-fabricated text everywhere.
Evidence hacking and backfiring effects
Generative pre-trained transformers (GPTs) can be used to produce texts that mimic scientific writing. These texts, when made available online—as we demonstrate—leak into the databases of academic search engines and other parts of the research infrastructure for scholarly communication. This development exacerbates problems that were already present with less sophisticated text generators (Antkare, 2020; Cabanac & Labbé, 2021). Yet, the public release of ChatGPT in 2022, together with the way Google Scholar works, has increased the likelihood of lay people (e.g., media, politicians, patients, students) coming across questionable (or even entirely GPT-fabricated) papers and other problematic research findings. Previous research has emphasized that the ability to determine the value and status of scientific publications for lay people is at stake when misleading articles are passed off as reputable (Haider & Åström, 2017) and that systematic literature reviews risk being compromised (Dadkhah et al., 2017). It has also been highlighted that Google Scholar, in particular, can be and has been exploited for manipulating the evidence base for politically charged issues and to fuel conspiracy narratives (Tripodi et al., 2023). Both concerns are likely to be magnified in the future, increasing the risk of what we suggest calling evidence hacking —the strategic and coordinated malicious manipulation of society’s evidence base.
The authority of quality-controlled research as evidence to support legislation, policy, politics, and other forms of decision-making is undermined by the presence of undeclared GPT-fabricated content in publications professing to be scientific. Due to the large number of archives, repositories, mirror sites, and shadow libraries to which they spread, there is a clear risk that GPT-fabricated, questionable papers will reach audiences even after a possible retraction. There are considerable technical difficulties involved in identifying and tracing computer-fabricated papers (Cabanac & Labbé, 2021; Dadkhah et al., 2023; Jones, 2024), not to mention preventing and curbing their spread and uptake.
However, as the rise of the so-called anti-vaxx movement during the COVID-19 pandemic and the ongoing obstruction and denial of climate change show, retracting erroneous publications often fuels conspiracies and increases the following of these movements rather than stopping them. To illustrate this mechanism, climate deniers frequently question established scientific consensus by pointing to other, supposedly scientific, studies that support their claims. Usually, these are poorly executed, not peer-reviewed, based on obsolete data, or even fraudulent (Dunlap & Brulle, 2020). A similar strategy is successful in the alternative epistemic world of the global anti-vaccination movement (Carrion, 2018) and the persistence of flawed and questionable publications in the scientific record already poses significant problems for health research, policy, and lawmakers, and thus for society as a whole (Littell et al., 2024). Considering that a person’s support for “doing your own research” is associated with increased mistrust in scientific institutions (Chinn & Hasell, 2023), it will be of utmost importance to anticipate and consider such backfiring effects already when designing a technical solution, when suggesting industry or legal regulation, and in the planning of educational measures.
Recommendations
Solutions should be based on simultaneous considerations of technical, educational, and regulatory approaches, as well as incentives, including social ones, across the entire research infrastructure. Paying attention to how these approaches and incentives relate to each other can help identify points and mechanisms for disruption. Recognizing fraudulent academic papers must happen alongside understanding how they reach their audiences and what reasons there might be for some of these papers successfully “sticking around.” A possible way to mitigate some of the risks associated with GPT-fabricated scholarly texts finding their way into academic search engine results would be to provide filtering options for facets such as indexed journals, gray literature, peer-review, and similar on the interface of publicly available academic search engines. Furthermore, evaluation tools for indexed journals 3 Such as LiU Journal CheckUp, https://ep.liu.se/JournalCheckup/default.aspx?lang=eng . could be integrated into the graphical user interfaces and the crawlers of these academic search engines. To enable accountability, it is important that the index (database) of such a search engine is populated according to criteria that are transparent, open to scrutiny, and appropriate to the workings of science and other forms of academic research. Moreover, considering that Google Scholar has no real competitor, there is a strong case for establishing a freely accessible, non-specialized academic search engine that is not run for commercial reasons but for reasons of public interest. Such measures, together with educational initiatives aimed particularly at policymakers, science communicators, journalists, and other media workers, will be crucial to reducing the possibilities for and effects of malicious manipulation or evidence hacking. It is important not to present this as a technical problem that exists only because of AI text generators but to relate it to the wider concerns in which it is embedded. These range from a largely dysfunctional scholarly publishing system (Haider & Åström, 2017) and academia’s “publish or perish” paradigm to Google’s near-monopoly and ideological battles over the control of information and ultimately knowledge. Any intervention is likely to have systemic effects; these effects need to be considered and assessed in advance and, ideally, followed up on.
Our study focused on a selection of papers that were easily recognizable as fraudulent. We used this relatively small sample as a magnifying glass to examine, delineate, and understand a problem that goes beyond the scope of the sample itself, which however points towards larger concerns that require further investigation. The work of ongoing whistleblowing initiatives 4 Such as Academ-AI, https://www.academ-ai.info/ , and Retraction Watch, https://retractionwatch.com/papers-and-peer-reviews-with-evidence-of-chatgpt-writing/ . , recent media reports of journal closures (Subbaraman, 2024), or GPT-related changes in word use and writing style (Cabanac et al., 2021; Stokel-Walker, 2024) suggest that we only see the tip of the iceberg. There are already more sophisticated cases (Dadkhah et al., 2023) as well as cases involving fabricated images (Gu et al., 2022). Our analysis shows that questionable and potentially manipulative GPT-fabricated papers permeate the research infrastructure and are likely to become a widespread phenomenon. Our findings underline that the risk of fake scientific papers being used to maliciously manipulate evidence (see Dadkhah et al., 2017) must be taken seriously. Manipulation may involve undeclared automatic summaries of texts, inclusion in literature reviews, explicit scientific claims, or the concealment of errors in studies so that they are difficult to detect in peer review. However, the mere possibility of these things happening is a significant risk in its own right that can be strategically exploited and will have ramifications for trust in and perception of science. Society’s methods of evaluating sources and the foundations of media and information literacy are under threat and public trust in science is at risk of further erosion, with far-reaching consequences for society in dealing with information disorders. To address this multifaceted problem, we first need to understand why it exists and proliferates.
Finding 1: 139 GPT-fabricated, questionable papers were found and listed as regular results on the Google Scholar results page. Non-indexed journals dominate.
Most questionable papers we found were in non-indexed journals or were working papers, but we did also find some in established journals, publications, conferences, and repositories. We found a total of 139 papers with a suspected deceptive use of ChatGPT or similar LLM applications (see Table 1). Out of these, 19 were in indexed journals, 89 were in non-indexed journals, 19 were student papers found in university databases, and 12 were working papers (mostly in preprint databases). Table 1 divides these papers into categories. Health and environment papers made up around 34% (47) of the sample. Of these, 66% were present in non-indexed journals.
Finding 2: GPT-fabricated, questionable papers are disseminated online, permeating the research infrastructure for scholarly communication, often in multiple copies. Applied topics with practical implications dominate.
The 20 papers concerning health-related issues are distributed across 20 unique domains, accounting for 46 URLs. The 27 papers dealing with environmental issues can be found across 26 unique domains, accounting for 56 URLs. Most of the identified papers exist in multiple copies and have already spread to several archives, repositories, and social media. It would be difficult, or impossible, to remove them from the scientific record.
As apparent from Table 2, GPT-fabricated, questionable papers are seeping into most parts of the online research infrastructure for scholarly communication. Platforms on which identified papers have appeared include ResearchGate, ORCiD, Journal of Population Therapeutics and Clinical Pharmacology (JPTCP), Easychair, Frontiers, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineer (IEEE), and X/Twitter. Thus, even if they are retracted from their original source, it will prove very difficult to track, remove, or even just mark them up on other platforms. Moreover, unless regulated, Google Scholar will enable their continued and most likely unlabeled discoverability.
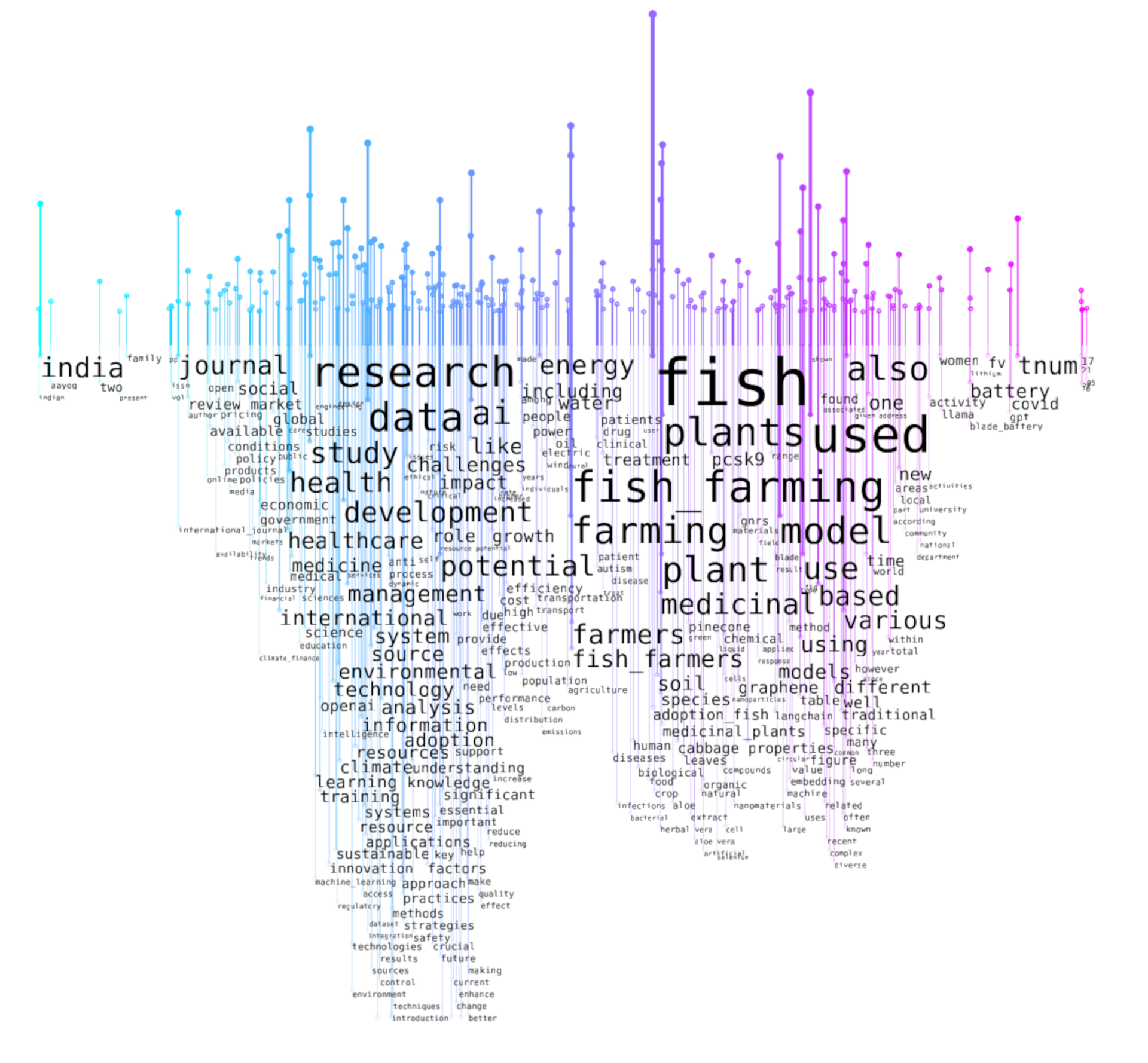
A word rain visualization (Centre for Digital Humanities Uppsala, 2023), which combines word prominences through TF-IDF 5 Term frequency–inverse document frequency , a method for measuring the significance of a word in a document compared to its frequency across all documents in a collection. scores with semantic similarity of the full texts of our sample of GPT-generated articles that fall into the “Environment” and “Health” categories, reflects the two categories in question. However, as can be seen in Figure 1, it also reveals overlap and sub-areas. The y-axis shows word prominences through word positions and font sizes, while the x-axis indicates semantic similarity. In addition to a certain amount of overlap, this reveals sub-areas, which are best described as two distinct events within the word rain. The event on the left bundles terms related to the development and management of health and healthcare with “challenges,” “impact,” and “potential of artificial intelligence”emerging as semantically related terms. Terms related to research infrastructures, environmental, epistemic, and technological concepts are arranged further down in the same event (e.g., “system,” “climate,” “understanding,” “knowledge,” “learning,” “education,” “sustainable”). A second distinct event further to the right bundles terms associated with fish farming and aquatic medicinal plants, highlighting the presence of an aquaculture cluster. Here, the prominence of groups of terms such as “used,” “model,” “-based,” and “traditional” suggests the presence of applied research on these topics. The two events making up the word rain visualization, are linked by a less dominant but overlapping cluster of terms related to “energy” and “water.”
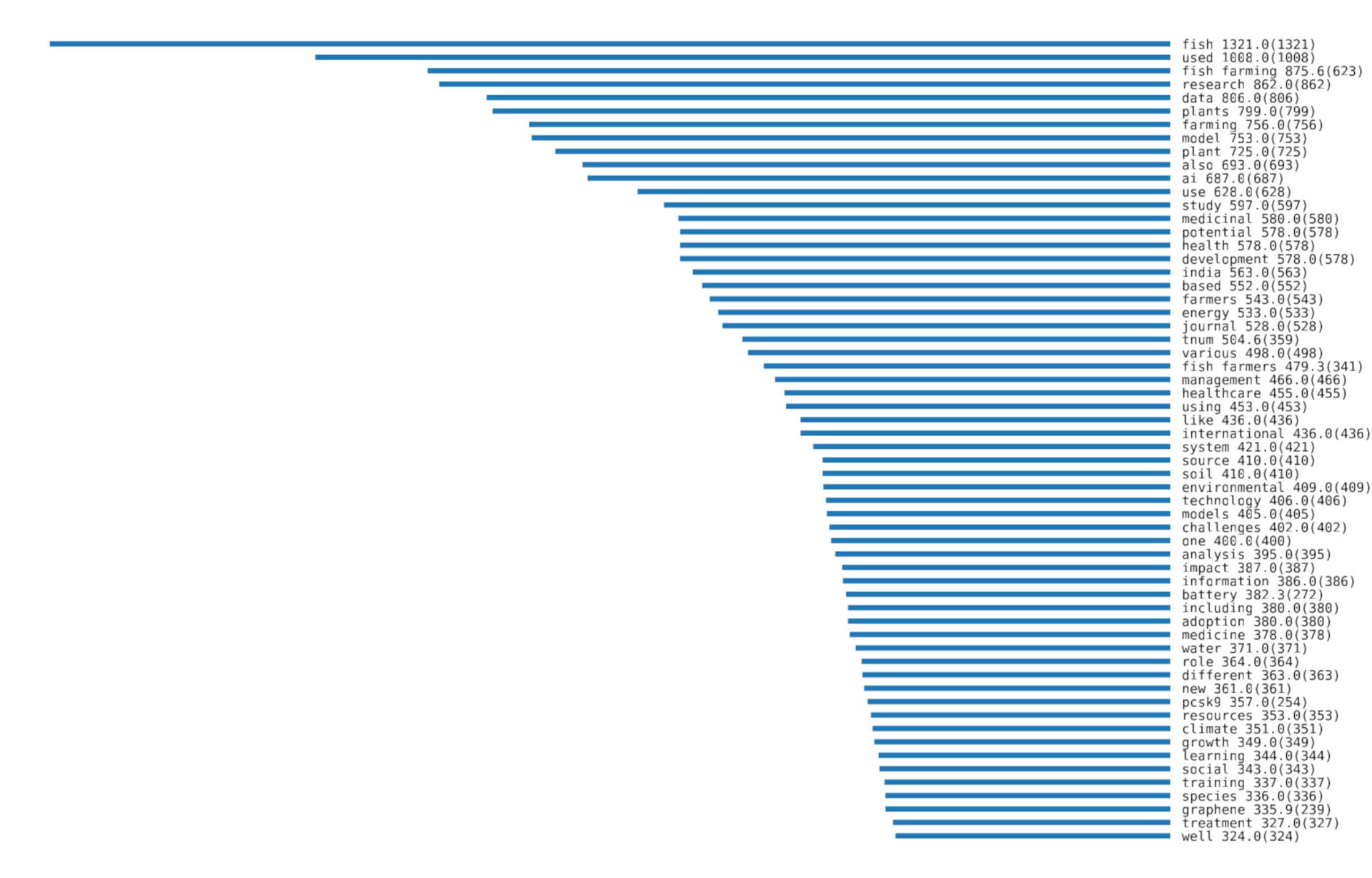
The bar chart of the terms in the paper subset (see Figure 2) complements the word rain visualization by depicting the most prominent terms in the full texts along the y-axis. Here, word prominences across health and environment papers are arranged descendingly, where values outside parentheses are TF-IDF values (relative frequencies) and values inside parentheses are raw term frequencies (absolute frequencies).
Finding 3: Google Scholar presents results from quality-controlled and non-controlled citation databases on the same interface, providing unfiltered access to GPT-fabricated questionable papers.
Google Scholar’s central position in the publicly accessible scholarly communication infrastructure, as well as its lack of standards, transparency, and accountability in terms of inclusion criteria, has potentially serious implications for public trust in science. This is likely to exacerbate the already-known potential to exploit Google Scholar for evidence hacking (Tripodi et al., 2023) and will have implications for any attempts to retract or remove fraudulent papers from their original publication venues. Any solution must consider the entirety of the research infrastructure for scholarly communication and the interplay of different actors, interests, and incentives.
We searched and scraped Google Scholar using the Python library Scholarly (Cholewiak et al., 2023) for papers that included specific phrases known to be common responses from ChatGPT and similar applications with the same underlying model (GPT3.5 or GPT4): “as of my last knowledge update” and/or “I don’t have access to real-time data” (see Appendix A). This facilitated the identification of papers that likely used generative AI to produce text, resulting in 227 retrieved papers. The papers’ bibliographic information was automatically added to a spreadsheet and downloaded into Zotero. 6 An open-source reference manager, https://zotero.org .
We employed multiple coding (Barbour, 2001) to classify the papers based on their content. First, we jointly assessed whether the paper was suspected of fraudulent use of ChatGPT (or similar) based on how the text was integrated into the papers and whether the paper was presented as original research output or the AI tool’s role was acknowledged. Second, in analyzing the content of the papers, we continued the multiple coding by classifying the fraudulent papers into four categories identified during an initial round of analysis—health, environment, computing, and others—and then determining which subjects were most affected by this issue (see Table 1). Out of the 227 retrieved papers, 88 papers were written with legitimate and/or declared use of GPTs (i.e., false positives, which were excluded from further analysis), and 139 papers were written with undeclared and/or fraudulent use (i.e., true positives, which were included in further analysis). The multiple coding was conducted jointly by all authors of the present article, who collaboratively coded and cross-checked each other’s interpretation of the data simultaneously in a shared spreadsheet file. This was done to single out coding discrepancies and settle coding disagreements, which in turn ensured methodological thoroughness and analytical consensus (see Barbour, 2001). Redoing the category coding later based on our established coding schedule, we achieved an intercoder reliability (Cohen’s kappa) of 0.806 after eradicating obvious differences.
The ranking algorithm of Google Scholar prioritizes highly cited and older publications (Martín-Martín et al., 2016). Therefore, the position of the articles on the search engine results pages was not particularly informative, considering the relatively small number of results in combination with the recency of the publications. Only the query “as of my last knowledge update” had more than two search engine result pages. On those, questionable articles with undeclared use of GPTs were evenly distributed across all result pages (min: 4, max: 9, mode: 8), with the proportion of undeclared use being slightly higher on average on later search result pages.
To understand how the papers making fraudulent use of generative AI were disseminated online, we programmatically searched for the paper titles (with exact string matching) in Google Search from our local IP address (see Appendix B) using the googlesearch – python library(Vikramaditya, 2020). We manually verified each search result to filter out false positives—results that were not related to the paper—and then compiled the most prominent URLs by field. This enabled the identification of other platforms through which the papers had been spread. We did not, however, investigate whether copies had spread into SciHub or other shadow libraries, or if they were referenced in Wikipedia.
We used descriptive statistics to count the prevalence of the number of GPT-fabricated papers across topics and venues and top domains by subject. The pandas software library for the Python programming language (The pandas development team, 2024) was used for this part of the analysis. Based on the multiple coding, paper occurrences were counted in relation to their categories, divided into indexed journals, non-indexed journals, student papers, and working papers. The schemes, subdomains, and subdirectories of the URL strings were filtered out while top-level domains and second-level domains were kept, which led to normalizing domain names. This, in turn, allowed the counting of domain frequencies in the environment and health categories. To distinguish word prominences and meanings in the environment and health-related GPT-fabricated questionable papers, a semantically-aware word cloud visualization was produced through the use of a word rain (Centre for Digital Humanities Uppsala, 2023) for full-text versions of the papers. Font size and y-axis positions indicate word prominences through TF-IDF scores for the environment and health papers (also visualized in a separate bar chart with raw term frequencies in parentheses), and words are positioned along the x-axis to reflect semantic similarity (Skeppstedt et al., 2024), with an English Word2vec skip gram model space (Fares et al., 2017). An English stop word list was used, along with a manually produced list including terms such as “https,” “volume,” or “years.”
- Artificial Intelligence
- / Search engines
Cite this Essay
Haider, J., Söderström, K. R., Ekström, B., & Rödl, M. (2024). GPT-fabricated scientific papers on Google Scholar: Key features, spread, and implications for preempting evidence manipulation. Harvard Kennedy School (HKS) Misinformation Review . https://doi.org/10.37016/mr-2020-156
- / Appendix B
Bibliography
Antkare, I. (2020). Ike Antkare, his publications, and those of his disciples. In M. Biagioli & A. Lippman (Eds.), Gaming the metrics (pp. 177–200). The MIT Press. https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/11087.003.0018
Barbour, R. S. (2001). Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: A case of the tail wagging the dog? BMJ , 322 (7294), 1115–1117. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.322.7294.1115
Bom, H.-S. H. (2023). Exploring the opportunities and challenges of ChatGPT in academic writing: A roundtable discussion. Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging , 57 (4), 165–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-023-00809-2
Cabanac, G., & Labbé, C. (2021). Prevalence of nonsensical algorithmically generated papers in the scientific literature. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology , 72 (12), 1461–1476. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.24495
Cabanac, G., Labbé, C., & Magazinov, A. (2021). Tortured phrases: A dubious writing style emerging in science. Evidence of critical issues affecting established journals . arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2107.06751
Carrion, M. L. (2018). “You need to do your research”: Vaccines, contestable science, and maternal epistemology. Public Understanding of Science , 27 (3), 310–324. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963662517728024
Centre for Digital Humanities Uppsala (2023). CDHUppsala/word-rain [Computer software]. https://github.com/CDHUppsala/word-rain
Chinn, S., & Hasell, A. (2023). Support for “doing your own research” is associated with COVID-19 misperceptions and scientific mistrust. Harvard Kennedy School (HSK) Misinformation Review, 4 (3). https://doi.org/10.37016/mr-2020-117
Cholewiak, S. A., Ipeirotis, P., Silva, V., & Kannawadi, A. (2023). SCHOLARLY: Simple access to Google Scholar authors and citation using Python (1.5.0) [Computer software]. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5764801
Dadkhah, M., Lagzian, M., & Borchardt, G. (2017). Questionable papers in citation databases as an issue for literature review. Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling , 11 (2), 181–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-016-0370-6
Dadkhah, M., Oermann, M. H., Hegedüs, M., Raman, R., & Dávid, L. D. (2023). Detection of fake papers in the era of artificial intelligence. Diagnosis , 10 (4), 390–397. https://doi.org/10.1515/dx-2023-0090
DeGeurin, M. (2024, March 19). AI-generated nonsense is leaking into scientific journals. Popular Science. https://www.popsci.com/technology/ai-generated-text-scientific-journals/
Dunlap, R. E., & Brulle, R. J. (2020). Sources and amplifiers of climate change denial. In D.C. Holmes & L. M. Richardson (Eds.), Research handbook on communicating climate change (pp. 49–61). Edward Elgar Publishing. https://doi.org/10.4337/9781789900408.00013
Fares, M., Kutuzov, A., Oepen, S., & Velldal, E. (2017). Word vectors, reuse, and replicability: Towards a community repository of large-text resources. In J. Tiedemann & N. Tahmasebi (Eds.), Proceedings of the 21st Nordic Conference on Computational Linguistics (pp. 271–276). Association for Computational Linguistics. https://aclanthology.org/W17-0237
Google Scholar Help. (n.d.). Inclusion guidelines for webmasters . https://scholar.google.com/intl/en/scholar/inclusion.html
Gu, J., Wang, X., Li, C., Zhao, J., Fu, W., Liang, G., & Qiu, J. (2022). AI-enabled image fraud in scientific publications. Patterns , 3 (7), 100511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patter.2022.100511
Gusenbauer, M., & Haddaway, N. R. (2020). Which academic search systems are suitable for systematic reviews or meta-analyses? Evaluating retrieval qualities of Google Scholar, PubMed, and 26 other resources. Research Synthesis Methods , 11 (2), 181–217. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1378
Haider, J., & Åström, F. (2017). Dimensions of trust in scholarly communication: Problematizing peer review in the aftermath of John Bohannon’s “Sting” in science. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology , 68 (2), 450–467. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.23669
Huang, J., & Tan, M. (2023). The role of ChatGPT in scientific communication: Writing better scientific review articles. American Journal of Cancer Research , 13 (4), 1148–1154. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10164801/
Jones, N. (2024). How journals are fighting back against a wave of questionable images. Nature , 626 (8000), 697–698. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-00372-6
Kitamura, F. C. (2023). ChatGPT is shaping the future of medical writing but still requires human judgment. Radiology , 307 (2), e230171. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.230171
Littell, J. H., Abel, K. M., Biggs, M. A., Blum, R. W., Foster, D. G., Haddad, L. B., Major, B., Munk-Olsen, T., Polis, C. B., Robinson, G. E., Rocca, C. H., Russo, N. F., Steinberg, J. R., Stewart, D. E., Stotland, N. L., Upadhyay, U. D., & Ditzhuijzen, J. van. (2024). Correcting the scientific record on abortion and mental health outcomes. BMJ , 384 , e076518. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj-2023-076518
Lund, B. D., Wang, T., Mannuru, N. R., Nie, B., Shimray, S., & Wang, Z. (2023). ChatGPT and a new academic reality: Artificial Intelligence-written research papers and the ethics of the large language models in scholarly publishing. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 74 (5), 570–581. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.24750
Martín-Martín, A., Orduna-Malea, E., Ayllón, J. M., & Delgado López-Cózar, E. (2016). Back to the past: On the shoulders of an academic search engine giant. Scientometrics , 107 , 1477–1487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-016-1917-2
Martín-Martín, A., Thelwall, M., Orduna-Malea, E., & Delgado López-Cózar, E. (2021). Google Scholar, Microsoft Academic, Scopus, Dimensions, Web of Science, and OpenCitations’ COCI: A multidisciplinary comparison of coverage via citations. Scientometrics , 126 (1), 871–906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03690-4
Simon, F. M., Altay, S., & Mercier, H. (2023). Misinformation reloaded? Fears about the impact of generative AI on misinformation are overblown. Harvard Kennedy School (HKS) Misinformation Review, 4 (5). https://doi.org/10.37016/mr-2020-127
Skeppstedt, M., Ahltorp, M., Kucher, K., & Lindström, M. (2024). From word clouds to Word Rain: Revisiting the classic word cloud to visualize climate change texts. Information Visualization , 23 (3), 217–238. https://doi.org/10.1177/14738716241236188
Swedish Research Council. (2017). Good research practice. Vetenskapsrådet.
Stokel-Walker, C. (2024, May 1.). AI Chatbots Have Thoroughly Infiltrated Scientific Publishing . Scientific American. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/chatbots-have-thoroughly-infiltrated-scientific-publishing/
Subbaraman, N. (2024, May 14). Flood of fake science forces multiple journal closures: Wiley to shutter 19 more journals, some tainted by fraud. The Wall Street Journal . https://www.wsj.com/science/academic-studies-research-paper-mills-journals-publishing-f5a3d4bc
The pandas development team. (2024). pandas-dev/pandas: Pandas (v2.2.2) [Computer software]. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10957263
Thorp, H. H. (2023). ChatGPT is fun, but not an author. Science , 379 (6630), 313–313. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adg7879
Tripodi, F. B., Garcia, L. C., & Marwick, A. E. (2023). ‘Do your own research’: Affordance activation and disinformation spread. Information, Communication & Society , 27 (6), 1212–1228. https://doi.org/10.1080/1369118X.2023.2245869
Vikramaditya, N. (2020). Nv7-GitHub/googlesearch [Computer software]. https://github.com/Nv7-GitHub/googlesearch
This research has been supported by Mistra, the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Environmental Research, through the research program Mistra Environmental Communication (Haider, Ekström, Rödl) and the Marcus and Amalia Wallenberg Foundation [2020.0004] (Söderström).
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
The research described in this article was carried out under Swedish legislation. According to the relevant EU and Swedish legislation (2003:460) on the ethical review of research involving humans (“Ethical Review Act”), the research reported on here is not subject to authorization by the Swedish Ethical Review Authority (“etikprövningsmyndigheten”) (SRC, 2017).
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original author and source are properly credited.
Data Availability
All data needed to replicate this study are available at the Harvard Dataverse: https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/WUVD8X
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments on the article manuscript as well as the editorial group of Harvard Kennedy School (HKS) Misinformation Review for their thoughtful feedback and input.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Harvard and the Legacy of Slavery Walking Tour Experience explores Harvard University's entanglements with the institution of slavery through a 10-stop tour around Harvard's campus. Learn more about the tour. Harvard College In-Person Campus Visit. Options: in-person, student-led. Harvard College Virtual Tour. Options: virtual.
Harvard University Visitor Center. Harvard University established the Visitor Center in 1962 as the front door to the University, where students greet visitors from all over the world, answer questions about campus, and provide official tours of Harvard. Email [email protected].
If the on-campus sessions are full, here are a few options for you: Sign up for an online session here - this is a 1 hour live session with an admissions officer. Click here to do a self-paced virtual tour of Harvard's campus. If you are in the area, you may stop by our office at 5 James Street from 9am-5pm Monday to Friday (11am-5pm on ...
Special Group Visits/Tours: We are able to host groups from college access programs and select high schools on a limited basis. To submit a request, please complete the Group Visit Request Form below. For all other group tour requests, contact the Harvard University Visitor Center, which offers historical campus tours led by current students ...
Explore Harvard from Home. Use our Virtual Tour to discover spaces that aren't even available on an in-person campus tour, such as classrooms, laboratories, residence halls, and more. Even better, it's available 24 hours a day, seven days a week, and never reaches capacity. Open the accessible version of Harvard College's virtual experience.
The tour showcases Harvard's campus and provides a history of the University, general information, and insight into the student's individual experience. Virtual Harvard Women's History Tour On this virtual student-led tour, you will encounter stories and sights that illustrate women's challenges and triumphs over the past three centuries, as ...
Harvard's campus is defined by its brick buildings, but hidden among and on top of those buildings are beautiful, peaceful, sometimes bountiful gardens. There are the Center for Astrophysics and Divinity School gardens in Cambridge, the Countway Library and Yawkey Center gardens in Boston, and the Business School bee gardens in Allston.
Location. 5 James Street. Cambridge, MA 02138. United States. Learn from current students, stroll through Harvard Yard, and discover historic Cambridge, Massachusetts. We offer daily information sessions and campus tours, Monday through Friday, starting at 9:30 am. Registration is required, so remember to sign up before you arrive.
March 11, 2022. By Amy Kamosa. The Harvard Visitor's Center has launched a new Visit Harvard mobile app that will provide free, self-guided, self-paced themed walking tours of the University. The first tour released on the app is a historic walking tour of the Cambridge Campus. It incorporates 14 locations throughout campus that highlight some ...
Campus map. Use our official map to navigate Harvard's campus and find auditoriums, churches, libraries, museums, and other important buildings. Find addresses, directions, and parking information for your next visit to Harvard's museums, theaters, hospitals, and athletic facilities.
The Hahvahd Tour is the most popular walking tour of Harvard University. Guided by current Harvard undergrads, the tour is a 75-minute historic tour of Harvard Yard and the surrounding neighborhood of Harvard Square. The Tour receives consistent praise from guests and major media outlets. Trip Advisor rates the tour one of the top attractions ...
Tour Harvard safely with Harvard students. Book your spot today and make memories that will last a lifetime. The Hahvahd Tour is the most popular walking tour of Harvard University. Guided by current Harvard undergrads and Harvard Square locals, the tour is a 75-minute historic tour of Harvard Yard
Harvard Yard & John Harvard statue. The green space between undergraduate dormitories is called Harvard Yard, which is enclosed by iron fences, walls and gates. Harvard Yard is the most iconic place at Harvard University, and is a must on any Harvard campus tour. It is one of the oldest areas that became a part of Harvard University in the late ...
A tour is a great way to get to know the campus! Harvard Information Center, located in the Smith Campus Center, offers free student-led walking tours through Harvard Yard. Tours are one hour and provide a general overview of the main Cambridge camps and University history. The Information Center also has maps for self-guided walking tours. For details and schedule, as well as links to tour ...
Home to the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), the 544,000-sf building designed by Behnisch Architekten is a living laboratory for interdisciplinary research, learning, and innovation. The Science and Engineering Complex is big, but it was expressly designed to foster a sense of community—one that feels fluid, open, and accessible.
Explore Harvard and MIT's history, campus secrets, and prestige with expert guides. Experience the famous traditions! The most popular walking tour of Harvard University is The Hahvahd Tour. Guided by current Harvard undergrads and Harvard Square locals, the tour is scripted and theatrical. Guests e
Harvard Yard, in Cambridge, Massachusetts, is a grassy area enclosed by fences with twenty-seven gates. It is the oldest part of the Harvard University campus, its historic center, and its modern crossroads. Harvard Yard contains most of the freshman dormitories; Harvard's most important libraries; Memorial Church; several classroom and departmental buildings; and the offices of the Dean of ...
Guided Tours. Private, guided tours of the newly renovated Countway Library are now available! Tours take place on the first Thursday of each month at 3:00pm and begin inside the 695 Huntington Avenue entrance near the turnstiles. Please register for a tour by completing the Countway Library Guided Tours form.
For anyone thinking of attending Harvard, or for those who simply want a glimpse of college life at the famous university, this tour is a must. Get an exclusive account from current Harvard students, who provide key insights into the life and times at Cambridge with a theatrical, humorous flair. Check out the old buildings at Harvard Yard and Harvard Square and learn about the school's ...
Visiting Undergraduate Students are not eligible for Harvard financial aid, and you must secure your own funding. In order to satisfy U.S. Immigration requirements, international students must demonstrate that they can afford all expenses, including tuition, fees, living expenses, and travel. While you are responsible for securing your own off ...
Tour groups can include up to 35 people. The tour company may offer up to one tour per day in Harvard Yard, as space is available. The tour company may offer tours in Harvard Yard between 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. daily. The tour company must remain in good standing in order to annually renew the Harvard Yard Use Agreement.
Visiting lecturer in English Alan Niles focuses on highlighting the work of women in "English Literature: The First 1000 Years." "To read past literature historically means recognizing the ways women have always participated in the world of letters, alongside and in dialogue with men," he said. "And the difficulties of writing as a woman are themselves something we should study, and ...
Harvard Tour Ticket prices. Adult tickets for the Harvard Tour are available for US$23 for visitors aged between 18 and 64 years. For children between four and 17 years of age, tickets are available for US$21. Senior Citizens aged 65 and above can get the tickets for US$22. Infants up to three years of age do not require a ticket.
Monday-Friday 10:00AM-5:00PM. Address Office of Admissions 48 Quincy Street Gund Hall - 422 Cambridge, MA 02138
Academic journals, archives, and repositories are seeing an increasing number of questionable research papers clearly produced using generative AI. They are often created with widely available, general-purpose AI applications, most likely ChatGPT, and mimic scientific writing. Google Scholar easily locates and lists these questionable papers alongside reputable, quality-controlled research.
Plan Your Visit. College News. Harvard College. University Hall. Cambridge, MA 02138. Harvard College Admissions Office and Griffin Financial Aid Office. 86 Brattle Street. Cambridge, MA 02138. Plan your visit to Harvard for the ARTS FIRST festival with information on COVID-19 health policies, parking, box offices, food, and more.