- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
By: History.com Editors
Updated: June 6, 2023 | Original: November 9, 2009

John Cabot (or Giovanni Caboto, as he was known in Italy) was an Italian explorer and navigator who was among the first to think of sailing westward to reach the riches of Asia. Though the details of his life and expeditions are subject to debate, by the late 1490s he was living in England, where he gained a commission from King Henry VII to make an expedition across the Atlantic. He set sail in May 1497 and made landfall in late June, probably in modern-day Canada. After returning to England to report his success, Cabot departed on a final expedition in 1498, but was allegedly never seen again.
Giovanni Caboto was born circa 1450 in Genoa, and moved to Venice around 1461; he became a Venetian citizen in 1476. Evidence suggests that he worked as a merchant in the spice trade of the Levant, or eastern Mediterranean, and may have traveled as far as Mecca, then an important trading center for Oriental and Western goods.
He studied navigation and map-making during this period, and read the stories of Marco Polo and his adventures in the fabulous cities of Asia. Similar to his countryman Christopher Columbus , Cabot appears to have become interested in the possibility of reaching the rich gold, silk, gem and spice markets of Asia by sailing in a westward direction.
Did you know? John Cabot's landing in 1497 is generally thought to be the first European encounter with the North American continent since Leif Eriksson and the Vikings explored the area they called Vinland in the 11th century.
For the next several decades, Cabot’s exact activities are unknown; he may have been forced to leave Venice because of outstanding debts. He then spent several years in Valencia and Seville, Spain, where he worked as a maritime engineer with varying degrees of success.
Cabot may have been in Valencia in 1493, when Columbus passed through the city on his way to report to the Spanish monarchs the results of his voyage (including his mistaken belief that he had in fact reached Asia).
By late 1495, Cabot had reached Bristol, England, a port city that had served as a starting point for several previous expeditions across the North Atlantic. From there, he worked to convince the British crown that England did not have to stand aside while Spain took the lead in exploration of the New World , and that it was possible to reach Asia on a more northerly route than the one Columbus had taken.

First and Second Voyages
In 1496, King Henry VII issued letters patent to Cabot and his son, which authorized them to make a voyage of discovery and to return with goods for sale on the English market. After a first, aborted attempt in 1496, Cabot sailed out of Bristol on the small ship Matthew in May 1497, with a crew of about 18 men.
Cabot’s most successful expedition made landfall in North America on June 24; the exact location is disputed, but may have been southern Labrador, the island of Newfoundland or Cape Breton Island. Reports about their exploration vary, but when Cabot and his men went ashore, he reportedly saw signs of habitation but few if any people. He took possession of the land for King Henry, but hoisted both the English and Venetian flags.
Grand Banks
Cabot explored the area and named various features of the region, including Cape Discovery, Island of St. John, St. George’s Cape, Trinity Islands and England’s Cape. These may correspond to modern-day places located around what became known as Cabot Strait, the 60-mile-wide channel running between southwestern Newfoundland and northern Cape Breton Island.
Like Columbus, Cabot believed that he had reached Asia’s northeast coast. He returned to Bristol in August 1497 with extremely favorable reports of the exploration. Among his discoveries was the rich fishing grounds of the Grand Banks off the coast of Canada, where his crew was allegedly able to fill baskets with cod by simply dropping the baskets into the water.
John Cabot’s Final Voyage
In London in late 1497, Cabot proposed to King Henry VII that he set out on another expedition across the north Atlantic. This time, he would continue westward from his first landfall until he reached the island of Cipangu ( Japan ). In February 1498, the king issued letters patent for the second voyage, and that May Cabot set off once again from Bristol, but this time with five ships and about 300 men.
The exact fate of the expedition has not been established, but by July one of the ships had been damaged and sought anchorage in Ireland. Reportedly the other four ships continued westward. It was believed that the ships had been caught in a severe storm, and by 1499, Cabot himself was presumed to have perished at sea.
Some evidence, however, suggests that Cabot and some members of his crew may have stayed in the New World; other documents suggest that he and his crew returned to England at some point. A Spanish map from 1500 includes the northern coast of North America with English place names and the notation “the sea discovered by the English.”
What Did John Cabot Discover?
In addition to laying the groundwork for British land claims in Canada, his expeditions proved the existence of a shorter route across the northern Atlantic Ocean, which would later facilitate the establishment of other British colonies in North America .
One of John Cabot's sons, Sebastian, was also an explorer who sailed under the flags of England and Spain.
John Cabot. Royal Museums Greenwich . Who Was John Cabot? John Cabot University . John Cabot. The Canadian Encyclopedia .

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Explorer John Cabot made a British claim to land in Canada, mistaking it for Asia, during his 1497 voyage on the ship Matthew.
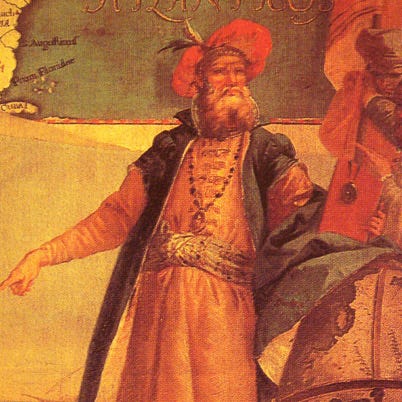

(1450-1500)
Who Was John Cabot?
John Cabot was a Venetian explorer and navigator known for his 1497 voyage to North America, where he claimed land in Canada for England. After setting sail in May 1498 for a return voyage to North America, he disappeared and Cabot's final days remain a mystery.
Cabot was born Giovanni Caboto around 1450 in Genoa, Italy. Cabot was the son of a spice merchant, Giulio Caboto. At age 11, the family moved from Genoa to Venice, where Cabot learned sailing and navigation from Italian seamen and merchants.
Cabot officially became a Venetian citizen in 1476 and began conducting trade in the eastern Mediterranean. Records indicate that he got into financial trouble and left Venice as a debtor in November 1488. During this time, Cabot became inspired by the discoveries of Bartolomeu Dias and Christopher Columbus .
Discoveries
In 1497, Cabot traveled by sea from Bristol to Canada, which he mistook for Asia. Cabot made a claim to the North American land for King Henry VII of England , setting the course for England's rise to power in the 16th and 17th centuries.
Cabot’s Route
Like Columbus, Cabot believed that sailing west from Europe was the shorter route to Asia. Hearing of opportunities in England, Cabot traveled there and met with King Henry VII, who gave him a grant to "seeke out, discover, and finde" new lands for England. In early May of 1497, Cabot left Bristol, England, on the Matthew , a fast and able ship weighing 50 tons, with a crew of 18 men. Cabot and his crew sailed west and north, under Cabot's belief that the route to Asia would be shorter from northern Europe than Columbus's voyage along the trade winds. On June 24, 1497, 50 days into the voyage, Cabot landed on the east coast of North America.
The precise location of Cabot’s landing is subject to controversy. Some historians believe that Cabot landed at Cape Breton Island or mainland Nova Scotia. Others believe he may have landed at Newfoundland, Labrador or even Maine. Though the Matthew 's logs are incomplete, it is believed that Cabot went ashore with a small party and claimed the land for the King of England.
In July 1497, the ship sailed for England and arrived in Bristol on August 6, 1497. Cabot was soon rewarded with a pension of £20 and the gratitude of King Henry VII.
Wife and Kids
In 1474, Cabot married a young woman named Mattea. The couple had three sons: Ludovico, Sancto and Sebastiano. Sebastiano would later follow in his father’s footsteps, becoming an explorer in his own right.
Death and Legacy
It is believed Cabot died sometime in 1499 or 1500, but his fate remains a mystery. In February 1498, Cabot was given permission to make a new voyage to North America; in May of that year, he departed from Bristol, England, with five ships and a crew of 300 men. The ships carried ample provisions and small samplings of cloth, lace points and other "trifles," suggesting an expectation of fostering trade with Indigenous peoples. En route, one ship became disabled and sailed to Ireland, while the other four ships continued on. From this point, there is only speculation as to the fate of the voyage and Cabot.
For many years, it was believed that the ships were lost at sea. More recently, however, documents have emerged that place Cabot in England in 1500, laying speculation that he and his crew actually survived the voyage. Historians have also found evidence to suggest that Cabot's expedition explored the eastern Canadian coast, and that a priest accompanying the expedition might have established a Christian settlement in Newfoundland.
QUICK FACTS
- Name: John Cabot
- Birth Year: 1450
- Birth City: Genoa
- Birth Country: Italy
- Gender: Male
- Best Known For: Explorer John Cabot made a British claim to land in Canada, mistaking it for Asia, during his 1497 voyage on the ship Matthew.
- Nacionalities
- Interesting Facts
- John Cabot was inspired by the discoveries of Bartolomeu Dias and Christopher Columbus.
- Cabot's youngest son also became an explorer in his own right
- Death Year: 1500
- Sayled in this tracte so farre towarde the weste, that the Ilande of Cuba bee on my lefte hande, in manere in the same degree of longitude.

European Explorers

Was Christopher Columbus a Hero or Villain?

Christopher Columbus

10 Famous Explorers Who Connected the World

Sir Walter Raleigh

Ferdinand Magellan

Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo

Leif Eriksson

Vasco da Gama

Bartolomeu Dias

Giovanni da Verrazzano

Jacques Marquette

René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle
Search The Canadian Encyclopedia
Enter your search term
Why sign up?
Signing up enhances your TCE experience with the ability to save items to your personal reading list, and access the interactive map.
- MLA 8TH EDITION
- Hunter, Douglas . "John Cabot". The Canadian Encyclopedia , 19 May 2017, Historica Canada . www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/john-cabot. Accessed 11 September 2024.
- The Canadian Encyclopedia , 19 May 2017, Historica Canada . www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/john-cabot. Accessed 11 September 2024." href="#" class="js-copy-clipboard b b-md b-invert b-modal-copy">Copy
- APA 6TH EDITION
- Hunter, D. (2017). John Cabot. In The Canadian Encyclopedia . Retrieved from https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/john-cabot
- The Canadian Encyclopedia . Retrieved from https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/john-cabot" href="#" class="js-copy-clipboard b b-md b-invert b-modal-copy">Copy
- CHICAGO 17TH EDITION
- Hunter, Douglas . "John Cabot." The Canadian Encyclopedia . Historica Canada. Article published January 07, 2008; Last Edited May 19, 2017.
- The Canadian Encyclopedia . Historica Canada. Article published January 07, 2008; Last Edited May 19, 2017." href="#" class="js-copy-clipboard b b-md b-invert b-modal-copy">Copy
- TURABIAN 8TH EDITION
- The Canadian Encyclopedia , s.v. "John Cabot," by Douglas Hunter, Accessed September 11, 2024, https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/john-cabot
- The Canadian Encyclopedia , s.v. "John Cabot," by Douglas Hunter, Accessed September 11, 2024, https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/john-cabot" href="#" class="js-copy-clipboard b b-md b-invert b-modal-copy">Copy
Thank you for your submission
Our team will be reviewing your submission and get back to you with any further questions.
Thanks for contributing to The Canadian Encyclopedia.
Article by Douglas Hunter
Published Online January 7, 2008
Last Edited May 19, 2017

Early Years in Venice
John Cabot had a complex and shadowy early life. He was probably born before 1450 in Italy and was awarded Venetian citizenship in 1476, which meant he had been living there for at least fifteen years. People often signed their names in different ways at this time, and Cabot was no exception. In one 1476 document he identified himself as Zuan Chabotto, which gives a clue to his origins. It combined Zuan, the Venetian form for Giovanni, with a family name that suggested an origin somewhere on the Italian peninsula, since a Venetian would have spelled it Caboto. He had a Venetian wife, Mattea, and three sons, one of whom, Sebastian, rose to the rank of pilot-major of Spain for the Indies trade. Cabot was a merchant; Venetian records identify him as a hide trader, and in 1483 he sold a female slave in Crete. He was also a property developer in Venice and nearby Chioggia.
Cabot in Spain
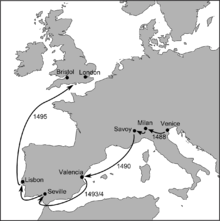
In 1488, Cabot fled Venice with his family because he owed prominent people money. Where the Cabot family initially went is unknown, but by 1490 John Cabot was in Valencia, Spain, which like Venice was a city of canals. In 1492, he partnered with a Basque merchant named Gaspar Rull in a proposal to build an artificial harbour for Valencia on its Mediterranean coast. In April 1492, the project captured the enthusiasm of Fernando (Ferdinand), king of Aragon and husband of Isabel, queen of Castille, who together ruled what is now a unified Spain. The royal couple had just agreed to send Christopher Columbus on his now-famous voyage to the Americas. In the autumn of 1492, Fernando encouraged the governor-general of Valencia to find a way to finance Cabot’s harbour scheme. However, in March 1493, the council of Valencia decided it could not fund Cabot’s plan. Despite Fernando’s attempt to move the project forward that April, the scheme collapsed.
Cabot disappeared from the historical record until June 1494, when he resurfaced in another marine engineering plan dear to the Spanish monarchs. He was hired to build a fixed bridge link in Seville to its maritime centre, the island of Triana in the Guadalquivir River, which otherwise was serviced by a troublesome floating one. Though Columbus had reached the Americas, he believed he had found land on the eastern edge of Asia, and Seville had been chosen as the headquarters of what Spain imagined was a lucrative transatlantic trade route. Cabot’s assignment thus was an important one, but something went wrong. In December 1494, a group of leading citizens of Seville gathered, unhappy with Cabot’s lack of progress, given the funds he had been provided. At least one of them thought he should be banished from the city. By then, Cabot probably had left town.
Cabot in England
Following the demise of Cabot’s Seville bridge project, the marine engineer again disappeared from the historical record. In March 1496 he resurfaced, this time as the commander of a proposed westward voyage under the flag of the King of England, Henry VII. Although there is no documentary proof, during Cabot’s absence from the historical record, between April 1493 and June 1494, he could have sailed with Columbus’s second voyage to the Caribbean. Most of the names of the over 1,000 people who accompanied Columbus weren’t recorded; however, Cabot could have been among the marine engineers on the voyage’s 17 ships who were expected to construct a harbour facility in what is now Haiti. Had Cabot been present on this journey, Henry VII would have had some basis to believe the would-be Venetian explorer could make a similar voyage to the far side of the Atlantic. It would help explain why Henry VII hired Cabot, a foreigner with a problematic résumé and no known nautical expertise, to make such a journey.
On 5 March 1496, Henry awarded Cabot and his three sons a generous letters patent, a document granting them the right to explore and exploit areas unknown to Christian monarchs. The Cabots were authorized to sail to “all parts of the eastern, western and northern sea, under our banners, flags and ensigns,” with as many as five ships, manned and equipped at their own expense. The Cabots were to “find, discover and investigate whatsoever islands, countries, regions or provinces of heathens and infidels, in whatsoever part of the world placed, which before this time were unknown to all Christians.” The Cabots would serve as Henry’s “vassals, and governors lieutenants and deputies” in whatever lands met the criteria of the patent, and they were given the right to “conquer, occupy and possess whatsoever towns, castles, cities and islands by them discovered.” With the letters patent, the Cabots could secure financial backing. Two payments were made in April and May 1496 to John Cabot by the House of Bardi (a family of Florentine merchants) to fund his search for “the new land,” suggesting his investors thought he was looking for more than a northern trade route to Asia.
First Voyage (1496)
Cabot’s first voyage departed Bristol, England, in 1496. Sailing westward in the north Atlantic was no easy task. The prevailing weather patterns track from west to east, and ships of Cabot’s time could scarcely sail toward the wind. No first-hand accounts of Cabot’s first attempt to sail west survive. Historians only know that it was a failure, with Cabot apparently rebuffed by stormy weather.
Second Voyage (1497)
Cabot mounted a second attempt from Bristol in May 1497, using a ship called the Matthew . It may have been a happy coincidence that its name was the English version of Cabot’s wife’s name, Mattea. There are no records of the ship’s individual crewmembers, and all the accounts of the voyage are second-hand — a remarkable lack of documentation for a voyage that would be the foundation of England’s claim to North America.
Historians have long debated exactly where Cabot explored. The most authoritative report of his journey was a letter by a London merchant named Hugh Say. Written in the winter of 1497-98, but only discovered in Spanish archives in the mid-1950s, Say’s letter (written in Spanish) was addressed to a “great admiral” in Spain who may have been Columbus.
The rough latitudes Say provided suggest Cabot made landfall around southern Labrador and northernmost Newfoundland , then worked his way southeast along the coast until he reached the Avalon Peninsula , at which point he began the journey home. Cabot led a fearful crew, with reports suggesting they never ventured more than a crossbow’s shot into the land. They saw two running figures in the woods that might have been human or animal and brought back an unstrung bow “painted with brazil,” suggesting it was decorated with red ochre by the Beothuk of Newfoundland or the Innu of Labrador. He also brought back a snare for capturing game and a needle for making nets. Cabot thought (wrongly) there might be tilled lands, written in Say’s letter as tierras labradas , which may have been the source of the name for Labrador. Say also said it was certain the land Cabot coasted was Brasil, a fabled island thought to exist somewhere west of Ireland.
Others who heard about Cabot’s voyage suggested he saw two islands, a misconception possibly resulting from the deep indentations of Newfoundland’s Conception and Trinity Bays, and arrived at the coast of East Asia. Some believed he had reached another fabled island, the Isle of Seven Cities, thought to exist in the Atlantic.
There were also reports Cabot had found an enormous new fishery. In December 1497, the Milanese ambassador to England reported hearing Cabot assert the sea was “swarming with fish, which can be taken not only with the net, but in baskets let down with a stone.” The fish of course were cod , and their abundance on the Grand Banks later laid the foundation for Newfoundland’s fishing industry.
Third Voyage (1498)
Henry VII rewarded Cabot with a royal pension on December 1497 and a renewed letters patent in February 1498 that gave him additional rights to help mount the next voyage. The additional rights included the ability to charter up to six ships as large as 200 tons. The voyage was again supposed to be mounted at Cabot’s expense, although the king personally invested in one participating ship. Despite reports from the 1497 voyage of masses of fish, no preparations were made to harvest them.
A flotilla of probably five ships sailed in early May. What became of it remains a mystery. Historians long presumed, based on a flawed account by the chronicler Polydore Vergil, that all the ships were lost, but at least one must have returned. A map made by Spanish cartographer Juan de la Cosa in 1500 — one of the earliest European maps to incorporate the Americas — included details of the coastline with English place names, flags and the notation “the sea discovered by the English.” The map suggests Cabot’s voyage ventured perhaps as far south as modern New England and Long Island.
Cabot’s royal pension did continue to be paid until 1499, but if he was lost on the 1498 voyage, it may only have been collected in his absence by one of his sons, or his widow, Mattea.
Despite being so poorly documented, Cabot’s 1497 voyage became the basis of English claims to North America. At the time, the westward voyages of exploration out of Bristol between 1496 and about 1506, as well as one by Sebastian Cabot around 1508, were probably considered failures. Their purpose was to secure trade opportunities with Asia, not new fishing grounds, which not even Cabot was interested in, despite praising the teeming schools. Instead of trade with Asia, Cabot and his Bristol successors found an enormous land mass blocking the way and no obvious source of wealth.
- Newfoundland and Labrador
Further Reading
Douglas Hunter, The Race to the New World: Christopher Columbus, John Cabot and a Lost History of Discovery (2012).
External Links
Heritage Newfoundland and Labrador A biography of John Cabot from this site sponsored by Memorial University.
Dictionary of Canadian Biography An account of John Cabot’s life from the Dictionary of Canadian Biography.
Recommended
Giovanni da verrazzano, jacques cartier, sir humphrey gilbert: elizabethan explorer.
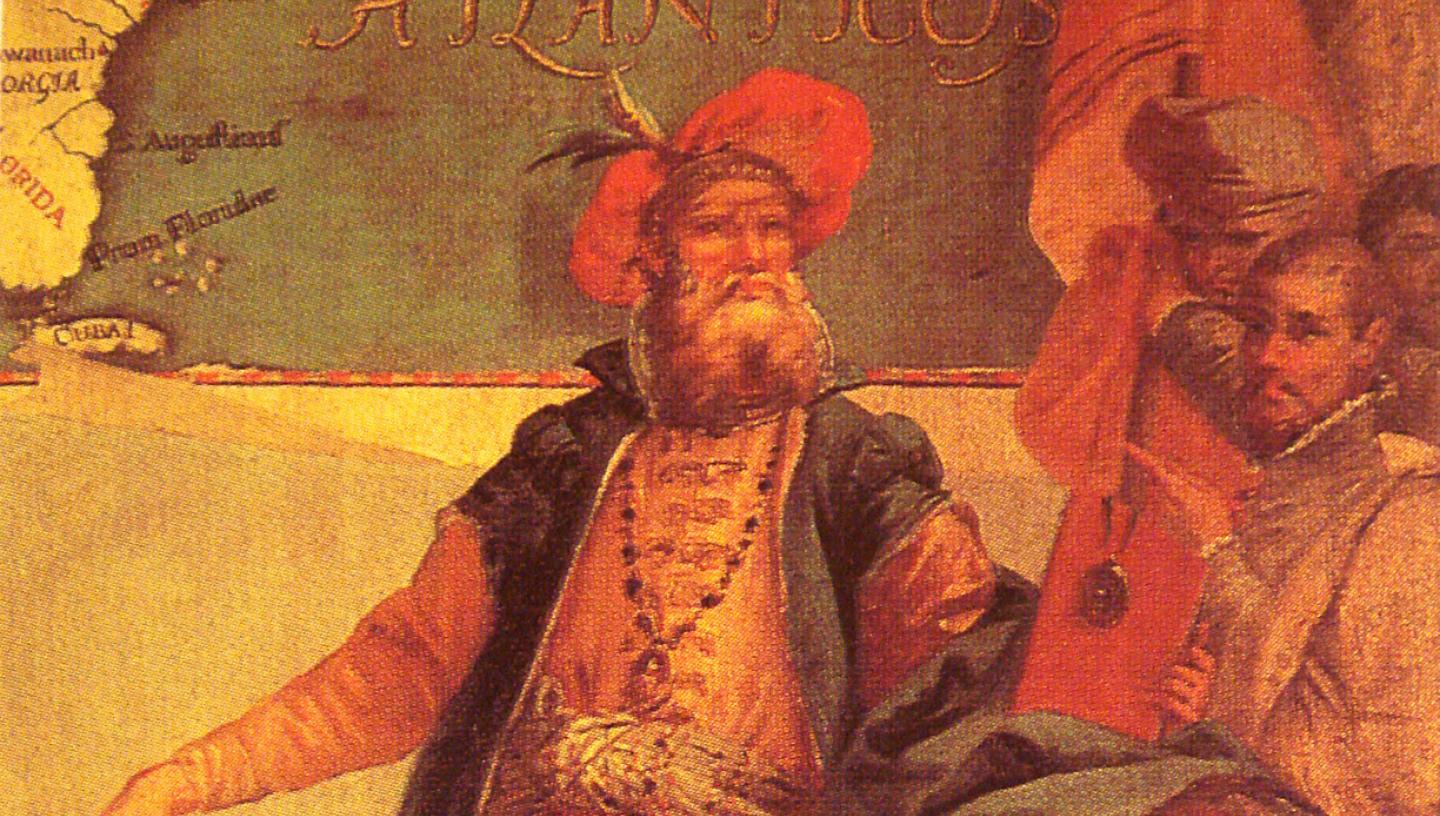


Find out how Cabot helped kick-start England's transatlantic voyages of discovery
Italian explorer, John Cabot, is famed for discovering Newfoundland and was instrumental in the development of the transatlantic trade between England and the Americas.
Although not born in England, John Cabot led English ships on voyages of discovery in Tudor times. John Cabot (about 1450–98) was an experienced Italian seafarer who came to live in England during the reign of Henry VII. In 1497 he sailed west from Bristol hoping to find a shorter route to Asia, a land believed to be rich in gold, spices and other luxuries. After a month, he discovered a 'new found land', today known as Newfoundland in Canada. Cabot is credited for claiming North America for England and kick-starting a century of English transatlantic exploration.
Why did Cabot come to England?
Born in Genoa around 1450, Cabot's Italian name was Giovanni Caboto. He had read of fabulous Chinese cities in the writings of Marco Polo and wanted to see them for himself. He hoped to reach them by sailing west, across the Atlantic.
Like Christopher Columbus, Cabot found it very difficult to convince backers to pay for the ships he needed to test out his ideas about the world. After failing to persuade the royal courts of Europe, he arrived with his family in 1484, to try to persuade merchants in London and Bristol to pay for his planned voyage. Before he set off, Cabot heard that Columbus had sailed west across the Atlantic and reached land. At the time, everyone believed that this land was the Indies, or Spice Islands.

Why did King Henry VII agree to help to pay for Cabot's expedition?
If Cabot’s predictions about the new route were right, he wouldn’t be the only one to profit. King Henry VII would also take his share. Everybody believed that Cathay and Cipangu (China and Japan) were rich in gold, gems, spices and silks. If Asia had been where Cabot thought it was, it would have made England the greatest trading centre in the world for goods from the east.
What did Cabot find on his voyage?
John Cabot's ship, the Matthew , sailed from Bristol with a crew of 18 in 1497. After a month at sea, he landed and took the area in the name of King Henry VII. Cabot had reached one of the northern capes of Newfoundland. His sailors were able to catch huge numbers of cod simply by dipping baskets into the water. Cabot was rewarded with the sum of £10 by the king, for discovering a new island off the coast of China! The king would’ve been far more generous if Cabot had brought home spices.
What happened to Cabot?
In 1498, Cabot was given permission by Henry VII to take ships on a new expedition to continue west from Newfoundland. The aim was to discover Japan. Cabot set out from Bristol with 300 men in May 1498. The five ships carried supplies for a year's travelling. There is no further record of Cabot and his crews, though there is now some evidence he may have returned and died in England. His son, Sebastian (1474–1577), followed in his footsteps, exploring various parts of the world for England and Spain.
View a replica of John Cabot's ship, which is open to the public in Bristol
Gifts inspired by seafaring in the Tudor and Stuart eras
Learn more about the emergence of a maritime nation

- Art History
- U.S. History
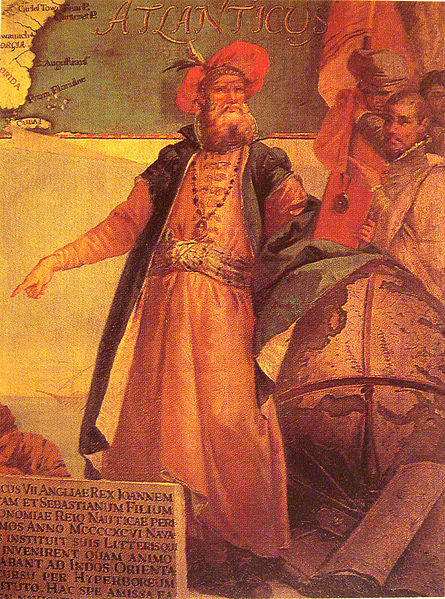

Italian or French or English?
Cabot’s biological name and birthplace has been the subject of debates throughout history. In Italy, he was famously known as Giovanni Caboto . However, evidence from the early 15th century point to Cabot’s background as being non-Italian. In France, he was known as Jean Cabot , while in Spain, he is named Juan Caboto . Also according to the 1484 Venetian Testamentary documentation, Cabot registered himself under the name “Zuan Chaboto” in Venice. In England, he used the name “John Cabot” which was supported by the Venetian residents in London. In October 2010, an anonymous Italian banker from London discovered a document pertaining to Cabot’s original name, which was reportedly identified as “Giovanni Chabotte.”
Naturalized Citizenship
Based on ancient Venetian records, Cabot became an active member of a religious confraternity administered by the St. John the Evangelist Brotherhood in 1470. Seven years later, Cabot acquired his first-ever Venetian citizenship which allowed him to play a crucial role in the Mediterranean maritime trading years. In 1483, Cabot documented the detailed events covered throughout the trade, one of which included the selling of “Crete” slaves in the Sultan Territories of Egypt . In 1497, he visited the Milanese ambassador to London who was then based in the Mecca region in the Arab states. Due to his key roles in pioneering the Venetian years of exploration, he was given the name “Zuan Cabotto.”
In 1484, Cabot married a Venetian named Mattea . The couple eventually had three sons – Sebastian, Ludovico and Sancto. According to Venetian sources, Cabot settled in Spain to pursue his civil engineering profession months after he built a house for his family. After dealing with financial issues during the late 1480s, Cabot migrated from Venice to work as a full-time insolvent debtor in Valencia in November 1488. During his stay in Valencia, some creditors attempted to arrest him in accordance with the “Lettre De Raccomandiazone a Giustizia” (A Letter of Recommendation to Justice). However, the attempt failed to push through after Cabot’s proposals under his “John Cabot Montecalunya” document were rejected by authorities in Valencia. In 1494, Cabot moved to Seville where he worked on the proposal of the Guadalquivir River Bridge construction. The Seville city council initially rejected Cabot’s proposal in December 1494. Cabot continued migrating from one place to another until he finally reached the English territory in 1495.
Explorers Abound

Cabot’s first voyage began in 1497. Bristol-based merchant John Day , who happened to be one of Cabot’s backers, wrote a letter to Columbus. The letter stated the significance of the 1497 voyage, which eventually provoked Columbus’ decision to take a crucial role in it. In March 1496, Cabot finally received his patent from Columbus. The second part of voyage meanwhile started during the annual feast of St. John the Baptist in June 1497. During Cabot’s second voyage, he found a ship from a certain American island. The ship, which was initially found by the Bristow merchants, was recovered by Cabot’s navigation team in August 1497.
In the middle of 1497, the Newfoundland Post Office in America commemorated the 400th day of Cabot’s North American voyage. The office issued a commemorative stamp in honor of Cabot. According to the Bristol Chronicler publication, the first voyage letter submitted to Columbus was actually issued by an anonymous Venetian merchant in Bristol. Cabot became aware of the publicized issue, yet he neither confirmed nor denied it. The dispatch for the second letter was reportedly issued by the Duke of Milan who admittedly mentioned the short details of Cabot’s succeeding voyages.
Northwest Passage
After Cabot’s two voyages, he immediately approached Henry VII . In August 10, 1497, the king rewarded Cabot 10 pounds – which were then the equivalent of his salary during the first two years of working as a craftsman in London. In August 23 of the same year, Venetian explorer Soncino praised Cabot for being a great admiral in the Atlantic and North American voyage. Perkin Warbeck , who secured Henry VII’s throne during the 1497 Second Cornish Uprising, awarded him 20 pounds worth of pension grants in December 1497. In February 1498, Warbeck gave Cabot his full royal patent acquisition for his succeeding expeditions. The Great Chronicle, a London newspaper, reported that Cabot departed along with five ships from Bristol during the first week of May 1498. The departure was approved by Henry VII. According to the Spanish envoy based in London, one of the ships was devastated by a powerful storm. Cabot and his league of navigation backers unexpectedly landed in Ireland after the destruction. In 1499, Cabot fulfilled his final voyage – the North West Passage expedition.
Cabot’s exact cause of death remains a mystery in the chronicles of history. However, his legacy continues to be very well-respected all around the world. In 1972, the John Cabot University was established in Rome, Italy. A decade later, the exalted John Cabot bronze statue designed by Stephen Joyce was created. The latter is currently displayed at the Bristol Harbour area. The Cabot Circus shopping center opened at Bristol in 1998.
Newest Additions
- Malala Yousafzai
- Greta Thunberg
- Frederick Douglass
- Wangari Maathai
Copyright © 2020 · Totallyhistory.com · All Rights Reserved. | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Contact Us
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar

- Native Americans
- Age of Exploration
- Revolutionary War
- Mexican-American War
- War of 1812
- World War 1
- World War 2
- Family Trees
- Explorers and Pirates
John Cabot Facts, Voyage, and Accomplishments
Published: Jul 25, 2016 · Modified: Nov 11, 2023 by Russell Yost · This post may contain affiliate links ·
John Cabot was a Genoese navigator and explorer whose 1497 discovery of parts of North America under the commission of Henry VII of England is commonly held to have been the first European exploration of the mainland of North America since the Norse Vikings' visits to Vinland in the eleventh century.

It would also be one of the last times, until Queen Elizabeth, that England would set foot in the New World.
John Cabot Facts: Early Life
John cabot facts: england and expeditions, john cabot facts: historical thoughts, online resources.
He may have been born slightly earlier than 1450, which is the approximate date most commonly given for his birth.
In 1471, Caboto was accepted into the religious confraternity of St John the Evangelist. Since this was one of the city's prestigious confraternities, his acceptance suggests that he was already a respected member of the community.
Following his gaining full Venetian citizenship in 1476, Caboto would have been eligible to engage in maritime trade, including the trade to the eastern Mediterranean that was the source of much of Venice's wealth.
A 1483 document refers to his selling a slave in Crete whom he had acquired while in the territories of the Sultan of Egypt, which then comprised most of what is now Palestine, Syria, and Lebanon.
Cabot is mentioned in many Venetian records of the 1480s. These indicate that by 1484, he was married to Mattea and already had at least two sons.
Cabot's sons are Ludovico, Sebastian, and Sancto. The Venetian sources contain references to Cabot's being involved in house building in the city. He may have relied on this experience when seeking work later in Spain as a civil engineer.
Cabot appears to have gotten into financial trouble in the late 1480s and left Venice as an insolvent debtor by 5 November 1488.
He moved to Valencia, Spain, where his creditors attempted to have him arrested. While in Valencia, John Cabot proposed plans for improvements to the harbor. These proposals were rejected.
Early in 1494, he moved on to Seville, where he proposed, was contracted to build, and, for five months, worked on the construction of a stone bridge over the Guadalquivir River. This project was abandoned following a decision of the City Council on 24 December 1494.
After this, Cabot appears to have sought support from the Iberian crowns of Seville and Lisbon for an Atlantic expedition before moving to London to seek funding and political support. He likely reached England in mid-1495.
Like other Italian explorers, including Christopher Columbus , Cabot led an expedition on commission to another European nation, in his case, England.
Cabot planned to depart to the west from a northerly latitude where the longitudes are much closer together and where, as a result, the voyage would be much shorter. He still had an expectation of finding an alternative route to China.
On 5 March 1496, Henry VII gave Cabot and his three sons letters patent with the following charge for exploration:
...free authority, faculty, and power to sail to all parts, regions, and coasts of the eastern, western, and northern sea, under our banners, flags, and ensigns, with five ships or vessels of whatsoever burden and quality they may be, and with so many and with such mariners and men as they may wish to take with them in the said ships, at their own proper costs and charges, to find, discover and investigate whatsoever islands, countries, regions or provinces of heathens and infidels, in whatsoever part of the world placed, which before this time were unknown to all Christians.
Those who received such patents had the right to assign them to third parties for execution. His sons are believed to have still been under the age of 18
Cabot went to Bristol to arrange preparations for his voyage. Bristol was the second-largest seaport in England. From 1480 onward, it supplied several expeditions to look for Hy-Brazil. According to Celtic legend, this island lay somewhere in the Atlantic Ocean. There was a widespread belief among merchants in the port that Bristol men had discovered the island at an earlier date but then lost track of it.
Cabot's first voyage was little recorded. Winter 1497/98 letter from John Day (a Bristol merchant) to an addressee believed to be Christopher Columbus refers briefly to it but writes mostly about the second 1497 voyage. He notes, "Since your Lordship wants information relating to the first voyage, here is what happened: he went with one ship, his crew confused him, he was short of supplies and ran into bad weather, and he decided to turn back." Since Cabot received his royal patent in March 1496, it is believed that he made his first voyage that summer.
What is known as the "John Day letter" provides considerable information about Cabot's second voyage. It was written during the winter of 1497/8 by Bristol merchant John Day to a man who is likely Christopher Columbus . Day is believed to have been familiar with the key figures of the expedition and thus able to report on it.
If the lands Cabot had discovered lay west of the meridian laid down in the Treaty of Tordesillas, or if he intended to sail further west, Columbus would likely have believed that these voyages challenged his monopoly rights for westward exploration.
Leaving Bristol, the expedition sailed past Ireland and across the Atlantic, making landfall somewhere on the coast of North America on 24 June 1497. The exact location of the landfall has long been disputed, with different communities vying for the honor.
Cabot is reported to have landed only once during the expedition and did not advance "beyond the shooting distance of a crossbow." Pasqualigo and Day both state that the expedition made no contact with any native people; the crew found the remains of a fire, a human trail, nets, and a wooden tool.
The crew appeared to have remained on land just long enough to take on fresh water; they also raised the Venetian and Papal banners, claiming the land for the King of England and recognizing the religious authority of the Roman Catholic Church. After this landing, Cabot spent some weeks "discovering the coast," with most "discovered after turning back."
On return to Bristol, Cabot rode to London to report to the King.
On 10 August 1497, he was given a reward of £10 – equivalent to about two years' pay for an ordinary laborer or craftsman. The explorer was feted; Soncino wrote on 23 August that Cabot "is called the Great Admiral and vast honor is paid to him and he goes dressed in silk and these English run after him like mad."
Such adulation was short-lived, for over the next few months, the King's attention was occupied by the Second Cornish Uprising of 1497, led by Perkin Warbeck.
Once Henry's throne was secure, he gave more thought to Cabot. On 26 September, just a few days after the collapse of the revolt, the King made an award of £2 to Cabot. In December 1497, the explorer was awarded a pension of £20 per year, and in February 1498, he was given a patent to help him prepare a second expedition.
In March and April, the King also advanced a number of loans to Lancelot Thirkill of London, Thomas Bradley, and John Cair, who were to accompany Cabot's new expedition.
Cabot departed with a fleet of five ships from Bristol at the beginning of May 1498, one of which had been prepared by the King. Some of the ships were said to be carrying merchandise, including cloth, caps, lace points, and other "trifles."
This suggests that Cabot intended to engage in trade on this expedition. The Spanish envoy in London reported in July that one of the ships had been caught in a storm and been forced to land in Ireland but that Cabot and the other four ships had continued on.
For centuries, no other records were found (or at least published) that relate to this expedition; it was long believed that Cabot and his fleet were lost at sea. But at least one of the men scheduled to accompany the expedition, Lancelot Thirkill of London, is recorded as living in London in 1501.
The historian Alwyn Ruddock worked on Cabot and his era for 35 years. She had suggested that Cabot and his expedition successfully returned to England in the spring of 1500. She claimed their return followed an epic two-year exploration of the east coast of North America, south into the Chesapeake Bay area and perhaps as far as the Spanish territories in the Caribbean. Ruddock suggested Fr. Giovanni Antonio de Carbonariis and the other friars who accompanied the 1498 expedition had stayed in Newfoundland and founded a mission.
If Carbonariis founded a settlement in North America, it would have been the first Christian settlement on the continent and may have included a church, the only medieval church to have been built there.
The Cabot Project at the University of Bristol was organized in 2009 to search for the evidence on which Ruddock's claims rest, as well as to undertake related studies of Cabot and his expeditions.
The lead researchers on the project, Evan Jones and Margaret Condon, claim to have found further evidence to support aspects of Ruddock's case, particularly in relation to the successful return of the 1498 expedition to Bristol.
They have located documents that appear to place John Cabot in London by May 1500 but have yet to publish their documentation.
- John Cabot's Wikipedia Page
- Cabot Project
- Find a Grave: John Cabot Memorial
- John Cabot Study Guide
- The History Junkie's Guide to Famous Explorers
- The History Junkie's Guide to Colonial America
Search Omniatlas
Navigate between maps, north america 1497: john cabot’s expeditions.
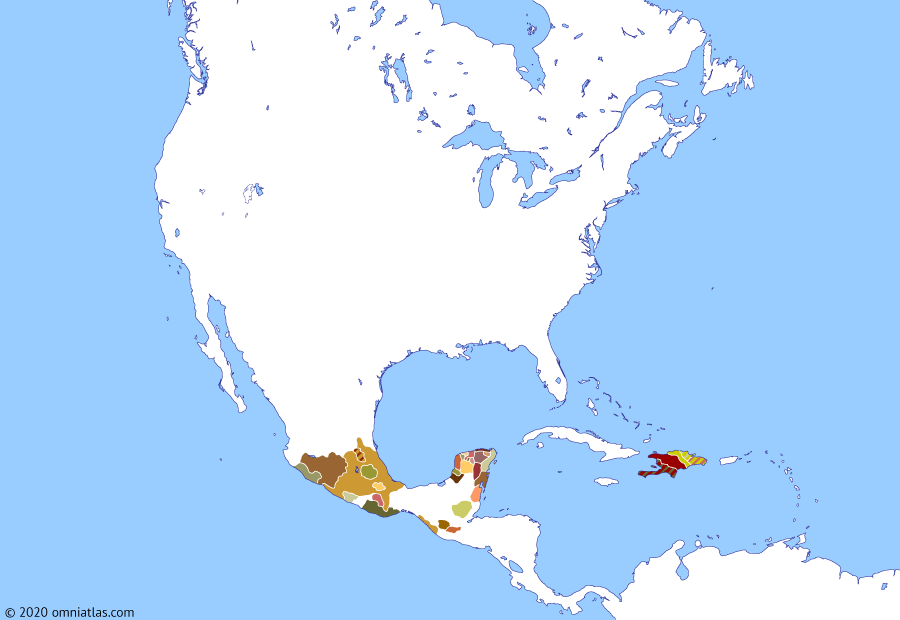
?? 1497–Aug 1499 Roldán in revolt against Columbus
May–Aug 1497 John Cabot explores coast of Newfoundland
24 June 1497
Age of columbus, north america, john cabot’s expeditions.
Columbus’ discoveries created excitement in Europe and in 1496 Henry VII of England agreed to sponsor another Italian navigator, John Cabot , in his own explorations. Cabot arrived off the coast of Newfoundland in 1497, possibly—his voyages are poorly documented—returning to explore the coast of North America the following year, but, like Columbus, was disappointed to find no wealthy Asian kingdoms. Meanwhile, Columbus faced renewed problems in Hispaniola when Roldán led a revolt of Spanish settlers and Taíno against his authority (1497–99) .
Main Events
1497–31 aug 1499 roldán’s rebellion ▲.
In 1496 Christopher Columbus left Hispaniola for Spain, leaving his brother Bartholomew in charge of the colony. Dissatisfied with the governance of the Columbus brothers, Francisco Roldán, the mayor of La Isabela, seized this opportunity to lead many of the Spanish settlers and soldiers in revolt in 1497. Basing himself in the semi-independent Taíno chiefdom of Jaragua, Roldán’s actions also encouraged the short-lived revolt of the chiefdoms of Maguá and Higüey the following year. In 1498 Columbus returned, finally bringing an end to the revolt by buying Roldán off with concessions. in wikipedia
? May–6 Aug 1497 John Cabot’s second voyage ▲
In March 1496 the Venetian navigator Giovanni Caboto—John Cabot in English—was granted letters patent by Henry VII of England to explore the seas. After an unsuccessful first voyage, Cabot departed Bristol aboard the Matthew in May 1497, sighting part of North America—most likely Cape Breton Island or one of Newfoundland’s capes—on 24 June. Landing just once to take possession of the land for the king, Cabot proceeded northwards along the coast before returning to arrive back in England in August. in wikipedia
Current Topic: John Cabot
- By Time Period
- By Location
- Mission Statement
- Books and Documents
- Ask a NL Question
- How to Cite NL Heritage Website
- ____________
- Archival Mysteries
- Alien Enemies, 1914-1918
- Icefields Disaster
- Colony of Avalon
- Let's Teach About Women
- Silk Robes and Sou'westers
- First World War
- Première Guerre mondiale
- DNE Word Form Database
- Dialect Atlas of NL
- Partners List from Old Site
- Introduction
- Bibliography
- Works Cited
- Abbreviations
- First Edition Corrections
- Second Edition Preface
- Bibliography (supplement)
- Works Cited (supplement)
- Abbreviations (supplement)
- Documentary Video Series (English)
- Une série de documentaires (en français)
- Arts Videos
- Archival Videos
- Table of Contents
- En français
- Exploration and Settlement
- Government and Politics
- Indigenous Peoples
- Natural Environment
- Society and Culture
- Archives and Special Collections
- Ferryland and the Colony of Avalon
- Government House
- Mount Pearl Junior High School
- Registered Heritage Structures
- Stephenville Integrated High School Project
- Women's History Group Walking Tour

John Cabot's Voyage of 1497
There is very little precise contemporary information about the 1497 voyage. If Cabot kept a log, or made maps of his journey, they have disappeared. What we have as evidence is scanty: a few maps from the first part of the 16th century which appear to contain information obtained from Cabot, and some letters from non-participants reporting second-hand on what had occurred. As a result, there are many conflicting theories and opinions about what actually happened.

Cabot's ship was named the Matthew , almost certainly after his wife Mattea. It was a navicula , meaning a relatively small vessel, of 50 toneles - able to carry 50 tons of wine or other cargo. It was decked, with a high sterncastle and three masts. The two forward masts carried square mainsails to propel the vessel forward. The rear mast was rigged with a lateen sail running in the same direction as the keel, which helped the vessel sail into the wind.

There were about 20 people on board. Cabot, a Genoese barber(surgeon), a Burgundian, two Bristol merchants, and Bristol sailors. Whether any of Cabot's sons were members of the crew cannot be verified.
The Matthew left Bristol sometime in May, 1497. Some scholars think it was early in the month, others towards the end. It is generally agreed that he would have sailed down the Bristol Channel, across to Ireland, and then north along the west coast of Ireland before turning out to sea.
But how far north did he go? Again, it is impossible to be certain. All one can say is that Cabot's point of departure was somewhere between 51 and 54 degrees north latitude, with most modern scholars favouring a northerly location.
The next point of debate is how far Cabot might have drifted to the south during his crossing. Some scholars have argued that ocean currents and magnetic variations affecting his compass could have pulled Cabot far off course. Others think that Cabot could have held approximately to his latitude. In any event, some 35 days after leaving Bristol he sighted land, probably on 24 June. Where was the landfall?
Cabot was back in Bristol on 6 August, after a 15 day return crossing. This means that he explored the region for about a month. Where did he go?
Version française
Related Subjects
Share and print this article:.

Contact | © Copyright 1997 – 2024 Newfoundland and Labrador Heritage Web Site, unless otherwise stated.
- Movie Review: Coraline 15th Anniversary
- History Short: Epically Bungled Bank Robberies
- History Short: The Most Watched TV Events in History!
- Animated Map of the 2022 Russian Invasion of Ukraine (through August 31st, 2024)
- September 9, 2024: Your Chance to Preview The Killer’s Game
- A Timeline of European History Since 1648
- A Timeline of European History to 1648
- In Space, the Audience Can Hear You Scream! (Movie Review)

John Cabot, The Columbus of England
A Brief History
On March 5, 1496, in the wake of the tremendous news about the voyage of Christopher Columbus to the New World, King Henry VII of England granted “letters patent” to John Cabot, an Italian sailor and adventurer, along with his sons, to explore the world on behalf of the English Crown. As Columbus was an Italian (Genoese) working for the King and Queen of Spain, so too was Cabot, an Italian originally from The Kingdom of Naples , employed by a foreign power. Cabot became (probably) the first European since perhaps the Vikings in the 11 th Century to visit North America, giving England their entry into the settlement of North America by a European country.
Digging Deeper
Born Giovanni Caboto (in Italian), we remember this exploring legend by his Anglicized name, John Cabot. While on business in Venice, Italy, Cabot is known to have used the Venetian form of his name, Zuan Chabotto. As if not confusing enough, Cabot’s Italian banker in London referred to him as Giovanni Chabbote. His exact birthplace on or about 1450 is unknown, possibly in the Province of Genoa , or maybe in the Province of Latina (more likely). One of Cabot’s sons later claimed John Cabot had originally hailed from Genoa, and other contemporaneous sources also refer to him as “Genoese like Columbus.” Still not sure? Cabot was made a citizen of Venice in 1476, a status that required at least 15 years residence at that time, implying that Cabot had lived in Venice at least from 1461 to 1476.

Probably from a family of at least some social standing, Cabot is believed to have entered the maritime trading business soon after being granted Venetian citizenship in 1476. Records indicate he was already married with 2 sons by 1484 (he had a total of 3 sons, Ludovico, Sebastian, and Sancto), and might have been involved in the construction business in Venice. Financial problems led to Cabot seeking work in Spain, moving to Valencia (the author has been there, and the city is beautiful!) ahead of his creditors in 1488. The next few years found Cabot unsuccessfully attempting various construction projects, and by 1494 he was seeking sponsorship to mount an expedition to the New World. Failing to find funding in Seville and Lisbon, Cabot traveled to London, England in 1495 in search of a sponsor. Cabot was given an audience with King Henry VII, arranged by a fellow Italian, a Papal Tax Collector.
Permission was received from King Henry VII, with the following stipulations:
“…free authority, faculty and power to sail to all parts, regions and coasts of the eastern, western and northern sea, under our banners, flags and ensigns, with five ships or vessels of whatsoever burden and quality they may be, and with so many and with such mariners and men as they may wish to take with them in the said ships, at their own proper costs and charges, to find, discover and investigate whatsoever islands, countries, regions or provinces of heathens and infidels, in whatsoever part of the world placed, which before this time were unknown to all Christians.”
Cabot secured financing, probably from the Italian expatriate banking community in London and Bristol. Cabot’s first voyage, 1496, has no substantial documentation, and is believed to have been aborted early with a turn around back to England before getting very far. His second voyage, of 1497, probably made landfall on the Canadian East coast, possibly in what is now Newfoundland, Nova Scotia, Labrador, or even Maine. A record of this voyage is documented by a letter sent to Christopher Columbus from England by a third party. Despite the lack of firm information about Cabot’s first landfall, authorities in Canada and the UK have designated Cape Bonavista in Newfoundland as the “official” site of Cabot’s landing. Cabot reportedly did not venture far inland, nor meet with any natives, although he did report finding evidence of human activity. He spent the rest of that first voyage to reach North America “discovering” the coastline. Of course, the crew did take the time to replenish fresh water stocks and plant Venetian and Papal flags, as well as claiming the land for England. (England was still Catholic at this time.)
Upon his return to England, Cabot regaled the King with his report, and was awarded a monetary prize of £10! Paltry pay for being the first person to reach North America from Europe (since the Vikings) and the first representative of England in the New World. A while later the King lavished another £2 on our intrepid explorer, and in December of 1497 awarded Cabot with a pension of £20 per year, this being a pretty decent amount of money in those days. (Annual income for a tradesman would be around £5 per year.)

In 1498, Cabot set sail with new letters of patent and a fleet of 5 ships, this time packed with trade items for trading with Native Americans. One of the ships only made it as far as Ireland and Cabot forged ahead with the other 4 ships. What happened next is unknown to history, with the possibility that Cabot and his ships were lost at sea, either on the way to North America or on the return. A tantalizing bit of information is that a sailor known to have been on the expedition is recorded as having been in London in 1501, and some recent historical investigation has concluded that Cabot and/or at least some of his men did make it back to England in 1500, but the evidence seems inconclusive to others.
The reports from the first successful voyage of John Cabot on behalf of England inspired other English expeditions to North America and ultimately resulted in the colonization of Canada and what is now the United States by British settlements, resulting in the 2 great countries that occupy the Northern portion of North America today. For this achievement, we thank John Cabot, whatever his real name and fate were!

Question for students (and subscribers): What do you think happened to Cabot and his last expedition? Did you know of Cabot’s role in exploring North America? Please let us know in the comments section below this article.
If you liked this article and would like to receive notification of new articles, please feel welcome to subscribe to History and Headlines by liking us on Facebook and becoming one of our patrons !
Your readership is much appreciated!
Historical Evidence
For more information, please see…
Burgan, Michael. The Story of North America’s First Explorers . Capstone Press, 2016.
Garfield, Henry. The Lost Voyage of John Cabot . Atheneum Books, 2010.
Pope, Peter. The Many Landfalls of John Cabot . University of Toronto Press, 1997.
Seelye, James, and Shawn Shelby, Editors. Shaping North America [3 volumes]: From Exploration to the American Revolution . ABC-CLIO, 2018.
The featured image in this article, a Newfoundland Postage stamp, 1897 issue, obtained from eBay ( eBay item I320594637410 ), is in the public domain .
This is because it is one of the following :
- It is a photograph taken prior to 1 June 1957; or
- It was published prior to 1969; or
- It is an artistic work other than a photograph or engraving (e.g. a painting) which was created prior to 1969.
HMSO has declared that the expiry of Crown Copyrights applies worldwide (ref: HMSO Email Reply ) More information .
See also Copyright and Crown copyright artistic works .
You can also watch a video version of this article on YouTube.

Major Daniel Zar is a retired veteran of the United States Marine Corps. He served during the Cold War and has traveled to many countries around the world. Prior to his military service, he graduated from Cleveland State University, having majored in sociology. Following his military service, he worked as a police officer eventually earning the rank of captain prior to his retirement.
Related Posts
History short: tires are high technology, history short: tourism gone bad, history short: the most people to survive a shipwreck.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.

John Cabot’s Voyage of 1497
Founding of newfoundland and cape breton.
There is very little precise contemporary information about the 1497 voyage. If Cabot kept a log, or made maps of his journey, they have disappeared. What we have as evidence is scanty: a few maps from the first part of the 16th century which appear to contain information obtained from Cabot, and some letters from non-participants reporting second-hand on what had occurred. As a result, there are many conflicting theories and opinions about what actually happened.

Cabot’s ship was named the Matthew , almost certainly after his wife Mattea. It was a navicula , meaning a relatively small vessel, of 50 toneles – able to carry 50 tons of wine or other cargo. It was decked, with a high sterncastle and three masts. The two forward masts carried square mainsails to propel the vessel forward. The rear mast was rigged with a lateen sail running in the same direction as the keel, which helped the vessel sail into the wind.

There were about 20 people on board. Cabot, a Genoese barber(surgeon), a Burgundian, two Bristol merchants, and Bristol sailors. Whether any of Cabot’s sons were members of the crew cannot be verified.
The Matthew left Bristol sometime in May, 1497. Some scholars think it was early in the month, others towards the end. It is generally agreed that he would have sailed down the Bristol Channel, across to Ireland, and then north along the west coast of Ireland before turning out to sea.
But how far north did he go? Again, it is impossible to be certain. All one can say is that Cabot’s point of departure was somewhere between 51 and 54 degrees north latitude, with most modern scholars favouring a northerly location.
The next point of debate is how far Cabot might have drifted to the south during his crossing. Some scholars have argued that ocean currents and magnetic variations affecting his compass could have pulled Cabot far off course. Others think that Cabot could have held approximately to his latitude. In any event, some 35 days after leaving Bristol he sighted land, probably on 24 June. Where was the landfall?
Cabot was back in Bristol on 6 August, after a 15 day return crossing. This means that he explored the region for about a month.
Newfoundland Joining Canada
Newfoundland resisted joining Canada and was an independent dominion in the early 20th century. Fishing was always the dominant industry, but the economy collapsed in the Great Depression of the 1930s and the people voluntarily relinquished their independence to become a British colony again. Prosperity and self-confidence returned during the Second World War, and after intense debate the people voted to join Canada in 1949.
The “golden era” came in the early 20th century however the sudden collapse of the cod fishing industry was a terrific blow in the 1990s. The historic cultural and political tensions between British Protestants and Irish Catholics faded, and a new spirit of a unified Newfoundland identity has recently emerged through songs and popular culture.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This is a demo store for testing purposes — no orders shall be fulfilled. Dismiss

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
John Cabot (or Giovanni Caboto, as he was known in Italy) was an Italian explorer and navigator who was among the first to think of sailing westward to reach the riches of Asia. Though the details ...
John Cabot (Italian: Giovanni Caboto [dʒoˈvanni kaˈbɔːto]; c. 1450 - c. 1499) [2] was an Italian [2] [3] navigator and explorer.His 1497 voyage to the coast of North America under the commission of Henry VII, King of England is the earliest known European exploration of coastal North America since the Norse visits to Vinland in the eleventh century. To mark the celebration of the 500th ...
John Cabot, navigator and explorer who by his voyages in 1497 and 1498 helped lay the groundwork for the later British claim to Canada. His voyages were commissioned by England's King Henry VII, and the effect of Cabot's efforts was to reveal the viability of a short route across the North Atlantic. ... In 1496 Cabot made a voyage from ...
John Cabot was a Venetian explorer and navigator known for his 1497 voyage to North America, where he claimed land in Canada for England. ... On June 24, 1497, 50 days into the voyage, Cabot ...
John Cabot (aka Giovanni Caboto, c. 1450 - c. 1498 CE) was an Italian explorer who famously visited the eastern coast of Canada in 1497 CE and 1498 CE in his ship the Mathew (also spelt Matthew).Sponsored by Henry VII of England (r. 1485-1509 CE) to search for a sea route to Asia, Cabot's expeditions 'discovered' what the Italian called 'Newe Founde Launde'.
John Cabot (a.k.a. Giovanni Caboto), merchant, explorer (born before 1450 in Italy, died at an unknown place and date). In 1496, King Henry VII of England granted Cabot the right to sail in search of a westward trade route to Asia and lands unclaimed by Christian monarchs. Cabot mounted three voyages, the second of which, in 1497, was the most ...
John Cabot, for example, was an Italian explorer known for his 1497 voyage to North America, where, though mistaking the land for Asia, he reached Newfoundland. Cabot is thought to have died only a few years later, possibly on a similar voyage.
John Cabot (about 1450-98) was an experienced Italian seafarer who came to live in England during the reign of Henry VII. In 1497 he sailed west from Bristol hoping to find a shorter route to Asia, a land believed to be rich in gold, spices and other luxuries. After a month, he discovered a 'new found land', today known as Newfoundland in Canada.
Overview. In 1497 John Cabot (1450?-1499?), an Italian explorer sailing for England, reached land somewhere in the northern part of North America. Although unsuccessful in his attempt to reach Asia, his landfall gave England a territorial claim in the New World that would be the basis for her eventual colonization of parts of that continent.
Whatever Cabot did was in the name of the English Crown. Cabot made his first try in 1496. It was a failure. All we know about the voyage is contained in a 1497 letter from John Day, an English merchant in the Spanish trade, to Christopher Columbus.
HISTORY OF NORTH AMERICA sails with John Cabot and shares in his exploits as he explores the northeastern coast of the continent under the flag of England. E...
Cabot's first voyage began in 1497. Bristol-based merchant John Day, who happened to be one of Cabot's backers, wrote a letter to Columbus. The letter stated the significance of the 1497 voyage, which eventually provoked Columbus' decision to take a crucial role in it. In March 1496, Cabot finally received his patent from Columbus.
The captain of the Matthew was an Italian explorer named Giovanni Caboto who is better known as John Cabot. [1] After a voyage which had got no further than Iceland, Cabot left again with only one vessel, the Matthew, a small ship (50 tons), but fast and able.The crew consisted of only 18 men. The Matthew departed 2 May 1497. [2] He sailed to Dursey Head (latitude 51°36N), Ireland, from where ...
Cabot's first voyage was little recorded. Winter 1497/98 letter from John Day (a Bristol merchant) to an addressee believed to be Christopher Columbus refers briefly to it but writes mostly about the second 1497 voyage. He notes, "Since your Lordship wants information relating to the first voyage, here is what happened: he went with one ship ...
Having secured permission from King Henry VII in March 1496, Cabot made an unsuccessful voyage later that year. Cabot Expedition, 1497. In 1497 he tried a second time, leaving Bristol in May and returning in August.
In March 1496 the Venetian navigator Giovanni Caboto—John Cabot in English—was granted letters patent by Henry VII of England to explore the seas. After an unsuccessful first voyage, Cabot departed Bristol aboard the Matthew in May 1497, sighting part of North America—most likely Cape Breton Island or one of Newfoundland's capes—on 24 ...
IIn 1497, John Cabot (Giovanni Cabotto) set off on a voyage to Asia.On his way he, like Christopher Columbus, ran into an island off the coast of North America. As a result, Cabot became the second European to discover North America, thus laying an English claim which would be followed up only after an interval of over one hundred years.
On St. John's Day -- June 24, 1497 Cabot set into a bay and named the area 'Terra Nova' or "New Found Land." ... Cabot did set out on a follow-up voyage, leaving England with five ships in 1498 ...
Over the years, the exact location of John Cabot's 1497 landfall has been a great subject of debate for scholars and historians. "Discovery of North America, by John and Sebastian Cabot" drawn by A.S. Warren for Ballou's Pictorial Drawing-Room Companion, April 7, 1855. From Charles de Volpi, Newfoundland: A pictorial Record (Sherbrooke, Quebec ...
A while later the King lavished another £2 on our intrepid explorer, and in December of 1497 awarded Cabot with a pension of £20 per year, this being a pretty decent amount of money in those days. (Annual income for a tradesman would be around £5 per year.) Route of 1497 voyage posited by Jones and Condon. Map by Evan T Jones.
Over the years, the exact location of John Cabot's 1497 landfall has been a great subject of debate for scholars and historians. "Discovery of North America, by John and Sebastian Cabot" drawn by A.S. Warren for Ballou's Pictorial Drawing-Room Companion, April 7, 1855. From Charles de Volpi, Newfoundland: A pictorial Record (Sherbrooke ...
mention John Cabot by name, there is no doubt that it refers to Cabot's 1497 voyage. Prior to the finding of this letter, documentary evidence relating to the 1497 voyage consisted of the four following letters: Lorenzo Pasqualigo to his brothers in Venice (August 23, 1497), Raimondo di Sancino to the Duke of Milan (August 24, and December 18 ...