- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Business Essentials

Voyage Policy: What it Means, How it Works
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/wk_headshot_aug_2018_02__william_kenton-5bfc261446e0fb005118afc9.jpg)
What Is a Voyage Policy?
A voyage policy is marine insurance coverage for risks to a ship's cargo during a specific voyage. Unlike most insurance policies it is not time-based but expires when the ship arrives at its destination. It covers only the cargo, not the ship that carries it.
A voyage policy is also known as marine cargo insurance.
Key Takeaways
- A voyage policy, or marine cargo insurance, covers losses incurred to a ship's contents during a journey.
- A voyage policy is used mainly by exporters who need to ship only occasionally or only in small amounts of cargo.
- Exporters who ship routinely generally use open cover marine insurance.
Understanding a Voyage Policy
Voyage policies are commonly used by exporters who need marine shipping only occasionally or for relatively small amounts of cargo. Large exporters who ship by sea routinely tend to prefer open cover marine insurance, which covers all cargo shipped by the policyholder for a specified time period.
A voyage policy covers unforeseen risks but not preventable risks. For a voyage policy to be valid, the vessel transporting the cargo must be in good condition and capable of making the journey, and the vessel's crew must be competent.
A voyage policy is in effect only while the ship is at sea; additional insurance is needed to cover losses during loading and unloading of cargo.
Voyage policies generally cover accidental damage and collisions as well as natural disasters. Losses due to delays may be covered as well. Voyage policies may specifically exclude losses caused by willful misconduct, ordinary leakage, ordinary wear and tear, improper or inadequate packaging, and labor strikes. Acts of war and terrorist activity also are usually excluded.
The policyholder may need to purchase additional insurance to cover the cargo during the entire transport process as voyage policies typically exclude losses that occur during the loading and unloading of the cargo.
The policy is in place for the duration of the voyage, however long it takes. If there are unanticipated delays en route, the coverage remains in place. This allows for factors such as inclement weather at sea or a shortage of docking at the destination port.
Because each policy is specific to a particular cargo and voyage, all details of both are recorded in the policy contract.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/carriage-paid-cpt.asp-final-1f5aad52797e4f43b8e9e2fd06e99145.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
IRDAI License Number: IRDAI/INT/ISNP/2022/250

- Cover defense cost
- Legal advice, if required
- Covernote/Risk Held Letter/Binder Letter Issued immediately after premium payment to the insurance company
- Get comparative quotes from leading public sector and private insurance companies

Underwriter approval is needed.
Feel free to contact us if you have any questions by calling 9711 901 903 or sending an email to [email protected]

The policy covers physical loss or damage to insured goods during transit by sea, rail, road, air or post parcel.

Anyone can have this policy who have to send goods from one place to another and one should have insurable interest.

Scope: The policy covers physical loss or damage to insured goods during transit by sea, rail, road, air or post parcel
Coverage: The policy coverage is guided by standard marine clauses
- Movement of goods within India- Inland Transit Clause-A, B, C
- Export/Import- Institute Cargo clause- A, B, C
The policy commonly covers loss or damage due to Fire, lightening, breakage of bridges, collision, overturning and sinking/capsizing etc.

- Seal Intact Clause
- Repacking Clause
- Conceal Damage Clause

Sum Insured of the policy is fixed on Agreed value basis, depending on terms of sale - FOB, C& F, CIP, CIF with loading of 10-15% for incidental charges.

- Willful misconduct
- Ordinary leakage/loss in weight or volume, wear and tear
- Improper packing
- Inherent vice
- Insolvency/financial default of carriers
- War, strike, riot and civil commotion
Why Choose PolicyLo.com

Important Points to remember while Buying the Policy

Policy should be started before consignment start date
- Policy should be started before consignment start date to avoid gap in coverage.

Proforma invoice should be shared upfront
- Policy document contains the details of proforma/original invoice like Cargo/Goods description and value therefore it is required upfront.

Invoice Number and exact location of transit should be mentioned in the policy
- It need to be checked that invoice number, transit details (From & To) are clearly mentioned in the policy document.

General Claim Intimation Format
As regards the modalities of claim reporting and settlement, you have to immediately report the claim at [email protected] and mark a copy to your account manager and insurance company.
Intimation Template for the Notification of Loss
- Policy No.:
- Description of Loss:
- Nature of Damage:
- Estimate of loss:
- Date of Loss:
- Date when loss detected:
- Site of loss (Address):
- Name of contact person at site of loss:
- Phone No of Contact Person:
- Policy Copy including all endorsement:
Loss should be intimated to the insurer within 24 hours of the loss.
Immediate Action Client Should Take
Intimate the Transporter
- Make a note of the loss on the L.R./POD. Get the same signed by the driver / the deliveryman. Do not give a clean receipt under any circumstances. All the material received has to be inspected at the time of delivery. In case the entire consignment cannot be inspected at the time of delivery make the following note on the L.R./P.O.D. Received subject to verification.
- Send an intimation letter to the courier/transporter informing them of the loss, as per Annexure I within 24 hrs of the loss. Send the letter by Registered A.D. Keep a photocopy of the A.D. card and postal receipt.
- Send a recovery letter to the courier/transporter raising a claim for the loss within 24 hrs of the loss describing the nature, its quantum and the financial implication of the loss. Send the letter by Registered A.D. Keep a photocopy of the A.D. card and the postal receipt.
- Arrange to get the shortage/damage certificate from the courier/transporter.
Survey of the Loss
The surveyors deputed by the insurer will call upon the insured to inspect the loss.
- Please keep the following documents handy when the surveyor visits:
A. Copy of the intimation letter sent to the insurance company.
B. Invoice Copy
C. Packing List
E. Copy of FIR in case lodged. FIR will be lodged by the transporter / courier in case of theft of goods, damage to goods due to rioting, damage to goods due to a major road accident etc.
F. Shortage / Breakage certificate, if received from the courier / transporter.
G. Copy of the intimation letter sent to the courier / transporter as described above and a copy of the A.D. card with postal receipt, if the original A.D. has not returned back.
H. Copy of the recovery letter sent to the courier / transporter and a copy of the A.D. card with postal receipt, if the original A.D. has not returned back.
- A claim form has to be filled with the description of the loss and its quantum Estimate of loss.
- The surveyor will submit his report to the insurer.
- In case any document is taken by the surveyor in original get the same acknowledged from him.
- Send all the documents mentioned above, in original, to Epoch to file the claim on the insurer.
Indicative General Documents for Settlement of Claim
Ocean Transit
- Claim Form duly filled in & signed
- Original Policy /Certificate
- Short Landing Certificate /Landed But Missing Cargo/Damage Certificate (as applicable)
- Suppliers Invoice
- Packing List
- Quadruplicate copy of Bill of Entry
- Steamer Survey report in original. (if arranged)
- Copy of Claim Notice served on Carrier/Port authorities along with postal acknowledgment card
- Copy of correspondence with the carrier/Port authorities/Customs authorities
- Copies of Correspondence exchanged with the suppliers (reply from suppliers is a must) in connection with short packing (if applicable)
- Lost Overboard Certificate from the Port Trust countersigned by the master of the vessel or steamer agents (in respect of Loss Over Board /Sling Losses)
- Original Repair Bills with receipt/Proforma Invoice for value of item lost/damaged
- Copy of Application filed with Customs for refund of Duty (if applicable)
- Photographs if arranged
- Letter of Subrogation cum special power of Attorney
Inland Transit (Rail)
- Open delivery Certificate or copy of application for open delivery, Reply received from the Railways refusing open delivery, Copy of the letter of protest sent to Railways with the acknowledgment thereto and certified extract of the remarks made in the station delivery or complaints book
- Copy of Claim Notice served on Railway along with postal acknowledgment card
- Copy of correspondence with the Railways
- Original Railway Receipt
- Original Repair Bills with receipt/Proforma Invoice for value of items lost/damaged
Inland Transit (Road)
- Original Open delivery certificate or copy of notice given to carriers advising about survey, protest made to them (for Packages delivered apparently in damaged condition)
- Packing list
- Copy of Claim Notice served on carriers along with postal acknowledgment card
- Copy of correspondence exchanged with the carriers
- Copies of correspondence exchanged with the suppliers (reply from suppliers is a must) in connection with short packing (for short receipt claims)
- Original Non Delivery Certificate (for Non Delivery Claims)
- Original Repair Bills with receipt / program invoice for value of items lost/damaged
- Letter of Subrogation cum Special Power of Attorney
Air Transit
- Original Airway Bill
- Quadruplicate copy of bill of Entry
- Copies of correspondence exchanged with the suppliers (reply from suppliers is a must) in connection with short packing (for short receipt claims).
- Original Short Delivery Certificate (for Short Delivery Claims)
- Copy of application filed with Customs for refund of Duty
Postal Transit
- Original Post Parcel Receipt
- Copy of Claim Notice served on Postal Authorities along with postal acknowledgment card
- Copy of correspondence exchanged with the Postal authorities
- Original certificate of damage /loss issued by the postal authorities (for Shortage/Damage Claims)
Our Insurance Partners
Claim case study - 1.
A client trading in high quality paper had a consignment of raw material badly damaged by heavy rain.
It was found on discussing with the surveyors that the proper covering on the truck was not maintained. It would have adversely effected the claim.
We convinced the insurance company that this was one solitary instance and otherwise the tarpaulin covering was always adequately done. The claim was paid accordingly.
It was made very clear to the client that the right kind of transporters should be used so that such occurrences do not recur.
Claim Case Study - 2
Client deals in solar module. The module efficiency decreases if it falls due to micro cracks not apparent from external appearance.
Since testing had to be done on large number of sample modules, the cost of which was high. The cost of disposal latter was also extremely high. It was opined by the surveyor that both this costs will have to be borne by the insured.
We were able to Negotiate strongly with the surveyor that this cost testing and salvage was necessary for both the sites. It was eventually agreed that 50% of these costs will be paid to the insured.
Claim Preparation and Salvage Disposal add-on was advised to be taken in the policy.
Need Assistance

- How is premium calculated for specific transit insurance policy? Factors such as length of the journey, means of transport, nature of the product are considered before determining the premium for the transit insurance policy.
- When should one pay premium for specific transit insurance? Since, the insurance policy applies to a single trip the premium has to be paid before the transit of the goods commences. If you fail to do so, you will not get the cover against the claim.
- Is there any minimum premium for Specific Marine Policies? Minimum Premium does vary between insurer to insurer but overall policy is economical.
- Can the policy for Specific Marine be issued in less than couple of hours in order to submit it further? These days insurers are using the technology and issuing the Marine Specific Policies through portal.
- Can the tail end transit be covered? A tail end transit cover is offered by insurer but generally on ITC-B cover.
- Is intentional storage covered under any marine Policy? No, intentional storage is not covered under Marine Insurance.
- What is Specific Transit Insurance Policy? Specific transit insurance policy is part of the marine cargo policy that applies to goods or freight for a single trip or transit.
- Do marine insurance policies cover cargo carried via aerial route? Institute Cargo Clause (Air), covers cargo carried via aerial routes
- Intimation Mail to Insurance company
- Commercial Invoice Copy
- Consignment Note
- Notification to carriers in case of shortage claims
- Which Perils are covered in ITC B Policy? Fire, Lightening, breakage of bridge, collision with or by the carrying vehicle, overturning of the carrying vehicle, derailment or accidents of like nature to the carrying railway wagon/vehicle.
- Which Perils are covered in ITC C Policy? Fire & Lightening
- What is the difference between excess and franchise? A franchise is a provision in the insurance policy whereby the insurer will not pay unless damage (or loss) exceeds the franchise amount whereas, an excess (deductible) is a provision in the insurance policy whereby the insurer will pay any amounts of damage that exceed the Excess (deductible) amount.
- What is specific Transit Insurance Policy? Specific transit insurance policy is part of the marine cargo policy that applies to goods or freight for a single trip or transit.
- Who should take specific transit insurance policy? Specific transit insurance policy is specially designed for business owners and sellers who are required to send out goods seldom or rarely.
- Can the policy be taken once goods are about to reach the destination site. Marine specific policy should always be taken before dispatching the cargo.
- What cover is offered to Tail end Transits? In case of Tail end transits, insurers generally offers ITC-B Cover but if inspection can be arranged then ITC A Can be offered.

An ODC cargo is a shipment where the length, breadth or height is more than the ...
The reason this above question needs to be asked is- there is no standardized pr...

What is a voyage policy? Definition and examples

The term ‘cargo’ refers to goods or produce that are transported by sea, land, or air.
Voyage policies, which protect just the goods in transit and not the vessel, are important for businesses involved in international trade. International trade includes the exportation and importation of goods.
Investopedia has the following definition of the term :
“A voyage policy is marine insurance coverage for risks to a ship’s cargo during a specific voyage.”
Voyage policies have several inclusions. Among them are damage due to faulty packaging or crew misconduct. This type of policy does not usually cover preventable risks. The policyholder will need to buy a separate policy to cover preventable risks.
Voyage insurance not time-based
Most insurance policies are time-based, but not this type. The policy expires as soon as the vessel arrives at its destination.
Exporting companies that need marine shipping only occasionally use this type of insurance the most. It is also useful for companies exporting a relatively small amount of cargo by sea .
Major exporters that deliver their goods by sea regularly prefer open cover marine insurance. Open cover protects all the cargo that the policyholder ships for a specified period.
Regarding a voyage policy, DieselShip.com says the following :
“The policy would be issued before the inception of the voyage. At the time of taking a specific voyage insurance policy, it is essential to give the complete details of the risk along with complete information about the bill of lading, vessel name, etc.”
The voyage policy covers the cargo during the whole voyage by sea, even if there are unexpected or unforeseen delays en route.
Marine insurance – a brief history
Marine insurance dates back to Ancient Greece and Rome. It wasn’t until the fourteenth century that proper marine insurance contracts were developed. These took place in Genoa and other Italian towns. From there, they spread to northern Europe.
Lloyd’s Coffee House, which opened in Tower Street in London in 1686, was the world’s first marine insurance market. People who worked in the shipping industry wanting to insure cargoes and ships would meet at Lloyd’s Coffee House. Individuals willing to act as underwriters also met there.
According to Risk & Insurance:
“ Lloyd’s Coffee House specialized in information about shipping. At this time, there were more than 80 coffee houses within the City of London’s walls, each claimed its own specialization.”
“By the 1730’s, Lloyd’s was emerging as the spot for marine underwriting by individuals.”
Share this:
- Renewable Energy
- Artificial Intelligence
- 3D Printing
- Financial Glossary

Bringing you the Best Analytical Legal News
- Case Briefs
NCDRC | What are the obligations of the insured taking a Marine Insurance Policy? Principle of Utmost Good Faith favours whom? Commission delineates
National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC): Anup K. Thakur (Presiding Member) dismissed a consumer complaint against the insurance company in case of
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Skype (Opens in new window)

National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC): Anup K. Thakur (Presiding Member) dismissed a consumer complaint against the insurance company in case of a Marine Cargo Specific Voyage Policy, holding that it was for the insured/complainant to ensure full compliance of all the policy conditions in its own interest and that the principle of utmost good faith in the present case favoured the insurance company strongly.
Complainant, Mauria Udyog Ltd. and Jotindra Steel & Tubes Ltd. purchased marine cargo-specific voyage insurance policy from United Insurance Co. Ltd., Noida (OP-1) and facts in both the cases are identical.
Issue for Consideration:
Whether the OP had committed any deficiency in service by withdrawing the guarantee and impliedly, denying the insurance claim on the ground that the Marine Vessel (M.V )was not a classified M.V ad did not satisfy the condition mentioned in the policy viz. “Institute Classification Clause with deletion of held cover provision”.
Bench stated that both parties claimed that they had acted in good faith.
OP’s case was that it depended entirely on the information furnished by the insured to issue the policy and when it came to know that the M.V. was not a classified M.V., it immediately withdrew the guarantee it had extended to the adjusters and informed the complainant.
Complainant, on the other hand, argued that it supplied information on the M.V. when it came to it’s knowledge as it was only one of the importers of cargo, on CIF basis, it had no means of knowing the classification of the vessel any sooner. Further, it was not it’s responsibility alone to have ascertained the classification of the M.V. and the implied seaworthiness or otherwise. OP too could have and should have ascertained the M.V.’s classification status, as per it’s own internal circulars. That the OP singularly failed to do so was a deficiency in service and the complainant should not have to suffer repudiation of its genuine claim on this account.
Insurance contract is a contract of utmost good faith, as laid down by the Supreme Court.
Whether the principle of good faith was violated?
Bench on perusal of the records found that M.V. was old and that at the time of it’s engagement in the instant case, it was not classed with any approved society under the International Association of Classification Societies (IACS).
This finding of the surveyor has not been disputed. Indeed, complainant’s argument has remained confined to claiming that it was not as if the vessel was not classified at all; rather, it was listed in the International Register of Shipping. OP has, on the other hand, firmly held that the vessel was not classified as required by the policy clause “Institute Classification Clause with deletion of held cover provision” . Indisputably, therefore, it can be safely concluded that as per OP’s policy clause, the vessel was not worthy of being insured. Yet, it was.
Should the OP have insured the complainant’s cargo, without full knowledge of the vessel and its classification?
Bench held that the complainant failed to establish it’s case.
It was the complainant, the importer, who had purchased the insurance cover. It was, therefore, reasonable that it had to be vigilant about all the conditions of taking an insurance cover.
The complainant, a regular importer, ought to have known the terms and conditions accompanying a Marine Cargo Specific Voyage Policy.
Although was for the OP to do the necessary due diligence on the classification of the vessel, but, It was the complainant whose cargo was to be insured against all risks associated with the marine voyage. It was therefore for the complainant to have ensured full compliance of all the policy conditions, in it’s own interest.
Hence, merely a cover note, with details of vessel and voyage left blank, on “To Be Declared” basis, from the OP-insurance company, could not have meant that the complainant could then have assumed the contract of insurance as complete and taken no further steps other than a mere communication of details of the shipment, including the vessel’s name, to the OP.
Bench, however, added that it was unreasonable for the OP insurance company to proceed on good faith and issue the insurance policy, in the hope that all the terms and conditions would be complied with, if and when a claim were to be filed.
OP displayed the good faith in issuing the insurance policy, leaving the box in the policy schedule blank.
Utmost Good Faith
The principle of utmost good faith, in the instant case, favours the OP strongly. It was the complainant’s responsibility, first and foremost, to have kept the OP fully apprised of the classification status of the M.V. as soon as it came to know.
In view of the above discussion, the instant consumer complaint was dismissed. [Mauria Udyog Ltd. v. United India Insurance Company Ltd., 2021 SCC OnLine NCDRC 16 , decided on 28-01-2021]
Advocates for the parties:
For the Complainant: Joy Basu, Sr. Advocate with T.S. Ahuja, Advocate
For the Opposite Parties: Amit Kr. Singh, Advocate

Section 125 CrPC: Can the second wife be entitled to maintenance from her husband?

Delhi HC granted bail to a man accused of raping woman he met on dating app on pretext of marriage

Do convicts have a fundamental right to procreate? Watch to know what Delhi High Court recently held

Book release of 8th edition of “Criminology, Penology and Victimology” revised by Sanjay Vashishtha
One comment.
This is very useful post. It will help ship owners. Thanks.
Join the discussion
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Table of Content
- What is Marine Insurance
Marine Insurance Act 1963
- How Marine Insurance works
Types of Marine Insurance
- Which clauses cover Marine Insurance
Difference between Fire Insurance & Marine Insurance
Explore Drip Capital’s Innovative Trade Financing Solutions
13 July 2021
Marine Insurance | Meaning, Types, Benefits & Coverage
What is marine insurance.
Marine insurance refers to a contract of indemnity. It is an assurance that the goods dispatched from the country of origin to the land of destination are insured. Marine insurance covers the loss/damage of ships, cargo, terminals, and includes any other means of transport by which goods are transferred, acquired, or held between the points of origin and the final destination.
The term originated when parties began to ship goods via sea. Despite what the name implies, marine insurance applies to all modes of transportation of goods. For instance, when goods are shipped by air, the insurance is known as the contract of marine cargo insurance.
Importance of Marine Insurance
Marine insurance is required in many import-export trade proceedings. Admitting the terms, both parties are liable for the payment of goods under insurance. However, the subject matter of marine insurance goes beyond contractual obligations, and there are several valid arguments necessary for buying it before dispatching the export cargo.
Goods in transit need to be insured by one of the three parties:-
- The Forwarding Agent
- The Exporter
- The Importer
Also, it can be taken by anyone involved in the transit of goods.
Also Read: Role of a Freight Forwarder | Functions, Duties & more
Where to get Marine Insurance?
The process to purchase marine insurance in India is easy. The country’s geographical position allows many banks and financial institutions to provide marine insurance.
The Marine Insurance Act, in India, came into existence in 1963. As per section three of the act, any time the term ‘marine insurance’ is used, expressed or even extended for the insuring of goods against loss or damage, the insurer will be at risk to bear the charges. The insurer will consider all the certainty of goods in case of misfortune sustained during marine ventures.
Principles of Marine Insurance
Principle of Good faith - Parties demand absolute trust on the part of both; the insurer and the guaranteed.
Principle of Proximate Cause - The proximate cause is not adjacent in time; also, it is inefficient. Nevertheless, it is the definitive and adequate cause of loss.
Principle of Insurable Interest - Any object presented as a marine risk and the assured covering the insurance of goods - both should have legal relevance. Also, a series is devoted called 'Incoterms' to respectfully assign the insurance of goods to each party.
Principle of Indemnity - The insurance extended to the parties will only be applicable up to the loss. The parties can't buy insurance to gain profits. If they do, they won't get more than the actual loss.
Principle of Contribution - Sometimes, the risk coverage for goods has more than one insurer. In such cases, the amount has to be fairly distributed amongst the insurers.
Features of Marine Insurance

How Marine Insurance works?
Marine insurance best transfers the liability of the goods from the parties and intermediaries involved to the insurance company. The legal liability of the intermediaries handling the goods is limited to begin with. The exporter, instead of bearing the sole responsibility of the goods, can buy an insurance policy and get maritime insurance coverage for the exported goods against any possible loss or damage.
The carrier of the goods, be it the airline or the shipping company, may bear the cost of damages and losses to the goods while on board. However, the compensation agreed upon is mostly on a ‘per package’ or ‘per consignment’ basis. The coverage so provided may not be sufficient to cover the cost of the goods shipped. Therefore, exporters prefer to ship their products after getting it insured the same with an insurance company.
The Scope of Marine insurance is necessary to meet the contractual obligations of exports. To align with agreements such as cost insurance and freight (CIF) or carriage and insurance paid (CIP) , the exporter needs to take marine insurance to protect the buyer’s or their bank’s interest and honor the contractual obligation. Similarly, in the case of Delivered Duty Unpaid (DDU) and Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) terms, the seller may not be obligated to insure the goods, although in practice they generally do.
To get marine insurance and avoid insurance claims, ensure the following:
Packing of goods should be done keeping in mind their safety during loading and unloading
Packing should be good enough to withstand natural hazards to the best extent possible
Keep in mind the possibility of clumsy handling or theft when packing goods.
How to calculate Marine Insurance Premium?
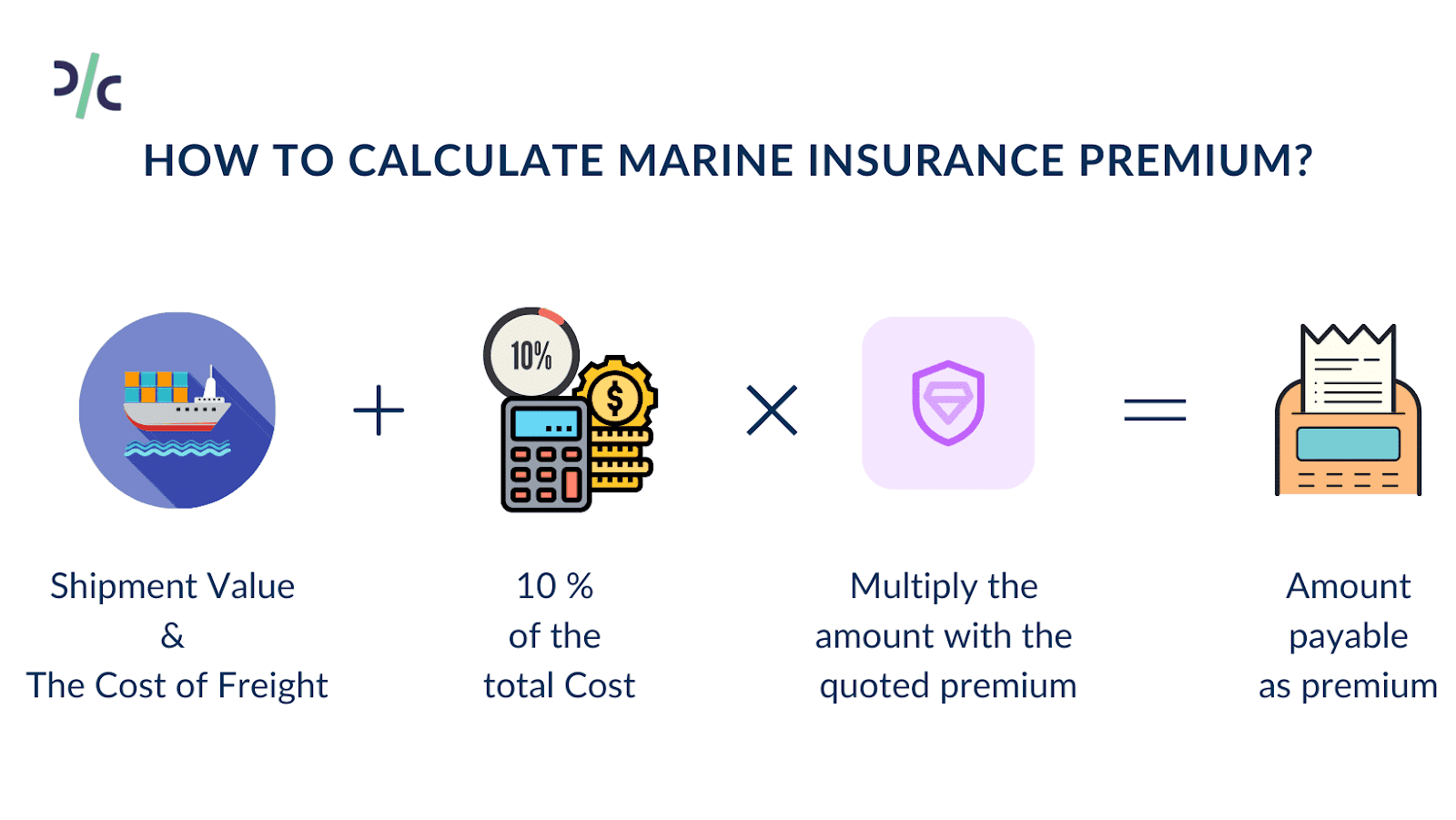
Freight Insurance
Liability insurance, hull insurance, marine cargo insurance.
In freight insurance, for example, if the goods are damaged in transit, the operator would lose freight receivables & so the insurance will be provided on compensation for loss of freight.
Marine Liability insurance is where compensation is bought to provide any liability occurring on account of a ship crashing or colliding.
Hull Insurance covers the hull & torso of the transportation vehicle. It covers the transportation against damages and accidents.
Marine cargo policy refers to the insurance of goods dispatched from the country of origin to the country of destination.

Types of Marine Insurance policies
- Floating Policy
- Voyage Policy
- Time Policy
- Mixed Policy
- Named Policy
- Port Risk Policy
- Fleet Policy
- Single Vessel Policy
- Blanket Policy
Floating policy
Floating in Marine Insurance policy, large exporters may opt for an open policy, also known as a blanket policy, instead of taking insurance separately for each shipment. An open policy is a one-time insurance that provides insurance cover against all shipments made during the agreed period, often a year. The exporter may need to declare periodically (say, once a month) the detail of all shipments made during the period, type of goods, modes of transport, destinations, etc.
Voyage policy
A specific policy can be taken for a single lot or consignment only. The exporter needs to purchase insurance cover every time a shipment is sent overseas. The drawback is that extra effort and time is involved each time an exporter sends a consignment. With open policies, on the other hand, shipments are insured automatically.
Time policy
Time policy in marine insurance is generally issued for a year’s period. One can issue for more than a year or they may extend to complete a specific voyage. But it is normally for a fixed period. Also under marine insurance in India, time policy can be issued only once a year.
Mixed policy
Mixed policy is a mixture of two policies i.e Voyage policy and Time policy.
Named policy
Named policy is one of the most popular policies in marine insurance policy. The name of the ship is mentioned in the insurance document, stating the policy issued is in the name of the ship.
Port Risk policy
It is a policy taken to ensure the safety of the ship when it is stationed in a port.
Fleet policy
Several ships belonging to the company/owner are covered under one policy. Where it has the advantage of covering even the old ships. Also the policy is a time based policy.
Single Vessel policy
In single vessel policy only one vessel is covered under marine insurance policy.
Blanket policy
In this policy, the owner has to pay the maximum protection amount at the time of buying the policy.
Which clauses cover Marine Insurance?
The Maritime insurance coverage provided by marine insurance can be understood by going through the risks handled by the insurance policies loaded with various marine insurance clauses:
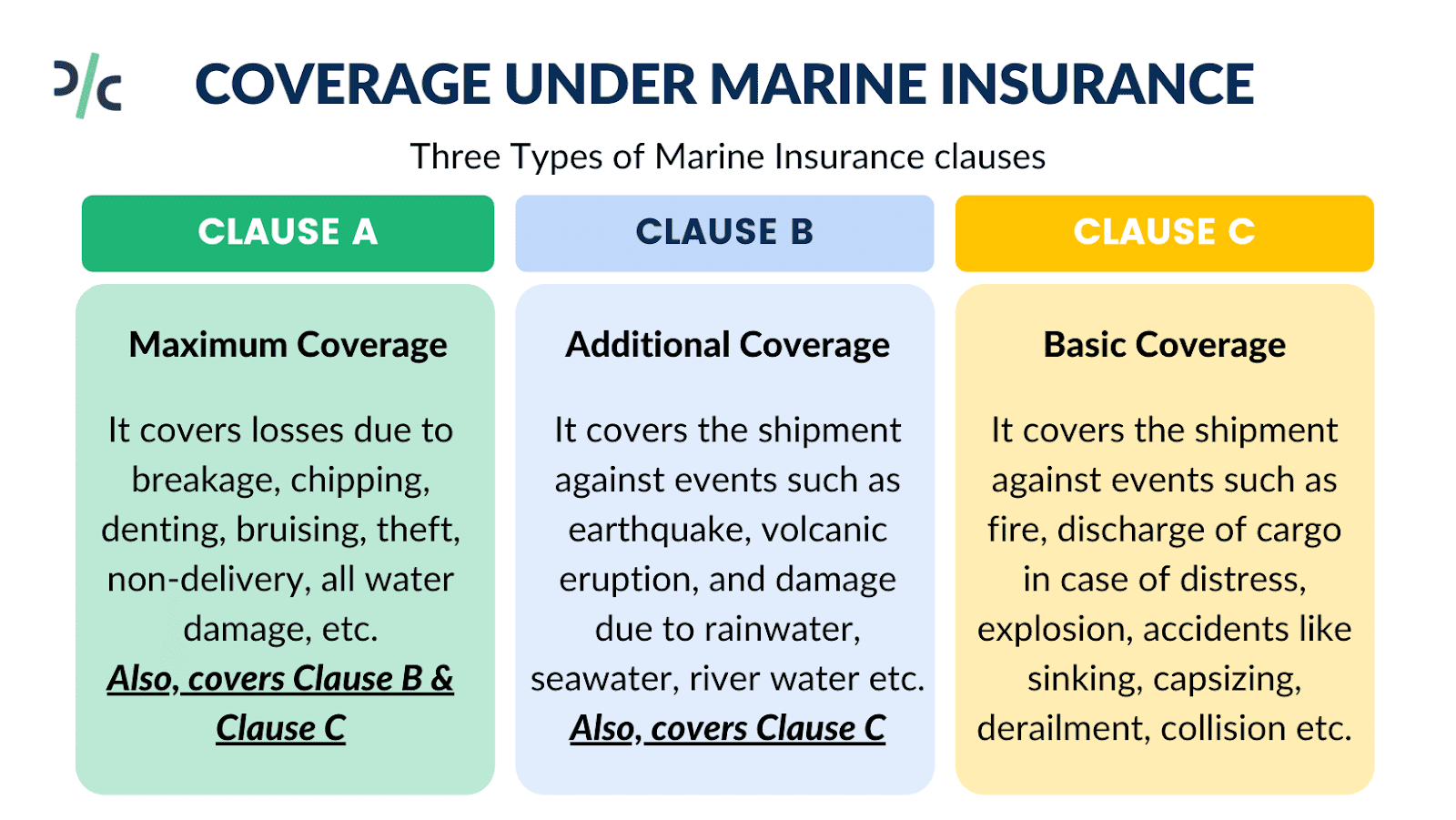
Institute Cargo Clause C provides basic coverage and includes a restricted list of risk covers. It covers the shipment against events such as fire, discharge of cargo in case of distress, explosion, accidents like sinking, capsizing, derailment, collision, etc.
Institute Cargo clause B offers an additional layer of protection. Not only does it include all the risk covers provided under Clause C, but it also covers the shipment against events such as earthquake, volcanic eruption, and damage due to rainwater, seawater, river water, etc., and loss to package overboard or during loading and unloading.
Institute Cargo Clause A provides maximum coverage as it covers all risk of loss or damage to the goods. Apart from the risks covered under Clauses B and C, it also covers losses due to breakage, chipping, denting, bruising, theft, non-delivery, all water damage, etc.
Risks such as wars, strikes, riots, and civil commotions are not covered under the institute cargo clauses. However, the insurer may provide this cover on payment of additional marine insurance premium.
So in terms & conditions of marine insurance coverage, these three types of marine insurance clauses: Institute Cargo Clauses A, B, and C. Clause A provides maximum coverage, Clause C provides basic risk coverage.
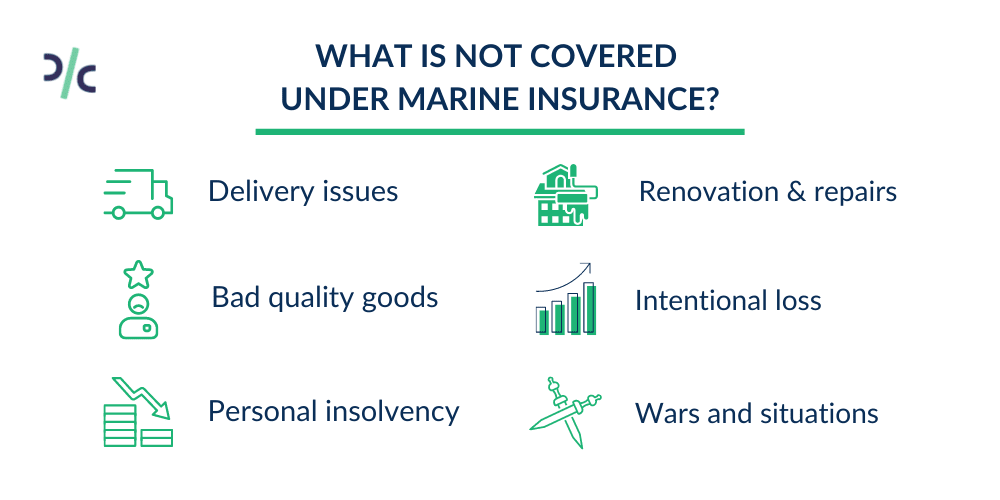
What is not covered under Marine Insurance?
Fire insurance is an insurance that covers the risk of fire. The subject matter is any physical asset or property. The moral responsibility is an important condition here. There is no expected profit margin in terms of fire insurance. The insurable interest must be present before taking the policy and also at the time of loss.
Whereas, the Functions of Marine insurance is one that encompasses risks associated with the sea. The subject matter is the ship, freight or cargo. It does not consist of any clause related to the moral responsibility of the cargo owner or the ship. 10 to 15% profit margin is expected in terms of marine insurance. Also in marine insurance the insurable interest must be only at the time of loss.
- How International Ocean Freight Shipping Works?
- Shipper's Letter of Instruction | Meaning, Format & more
- FCL and LCL | Meaning & Difference
- Procedure & Charges for LCL Shipments
- Demurrage - Meaning & Charges in Shipping
- How CBM is calculated in Shipping?
- 24 Types of Containers used in International Shipping

Avani Ghangurde
Senior associate, public relations at drip capital.
We use cookies to give you the best possible experience on our website. By continuing to browse this site, you give consent for cookies to be used in accordance with and for the purposes set out in our Privacy Policy and acknowledge that your have read, understood and consented to all terms and conditions therein.
Connect with us!
- Cargo Insurance Coverage
Types of Marine Cargo Insurance: Policies for Peace of Mind
The different types of marine cargo insurance available to shippers today offer incredible protection against several potential hazards while loading, unloading, and transporting goods bound for international transport on the high seas.
The Federal Maritime Commission ( FMC) regulates the shipment of cargo via ocean transportation services. While the FMC mandates financial responsibility to NVOCCs and forwarders, the shipper must independently provide coverage to protect their shipment. Various types of marine cargo insurance shippers can choose from marine specific transit or marine open policies.
Perhaps one of the most critical safeguards against loss at sea, marine cargo insurance is the ultimate safeguard against goods damaged in transit, theft, and total loss. The article below will help you better understand the best shield for your business.
What is Marine Cargo Insurance?
What is marine cargo insurance? How does it differ from marine insurance coverage? It is essential to know the difference between the two types of insurance and why marine cargo insurance is important to you, the shipper.
Marine cargo insurance is a form of coverage that protects cargo transported on a ship and anything owned aboard a ship during the trip. It is like car insurance but for your cargo and belongings aboard a vessel as it journeys from port to port.
Like car insurance, marine insurance has varying degrees of cost associated with it, and it is recommended by the Federal Maritime Commission (FMC) . Here are a few examples of factors that can influence the cost of covering goods in transit.
- The value of the cargo
- The product category
- Type of packaging used
- Origin and destination distances
Marine cargo insurance should not be viewed as an option but a mandatory measure; why is this? The reasoning is that accidents can and do happen; these accidents can occur at the port during loading or unloading or while traversing the seas aboard a ship.
It is essential to understand that marine cargo insurance coverage is more expansive than just pertaining to sea travel . Any inland transference at or near the port is also covered during shipping, often during storage, loading, and unloading procedures.
It is also essential to understand that besides any damages and accidents that are incurred as a part of the voyage or during the loading and unloading process. The financial cost associated with delays is also covered as part of a marine cargo insurance policy.
Consult our article on the benefits of marine cargo insurance for generalized information about this policy.
The Two Main Types of Marine Cargo Insurance
Within marine cargo insurance, two main types of coverage exist. These coverage options are in place to offer alternatives to the policyholder that are more timeline-specific than feature-specific.
Marine cargo insurance coverage is specific in that it revolves around your cargo, it is handling, and the vessel that carries your goods. Your committed interest in the cargo being shipped is protected, removing the risk of the financial loss of your investment.
Here are the two main types of marine cargo insurance:
- Marine Open Policy: Non-small to medium enterprises (SMEs), especially those who deal internationally with larger, more consistent trade volumes, will acquire a marine open policy. This policy type offers year-round insurance coverage based on the shipment and not the goods being shipped.
- Marine Specific Transit: This policy type is perfect for SMEs as it revolves around individual shipments, covering the shipment from its port of origin to its port of destination. These policies are generally acquired before goods are handled at the port of origin and last until they have reached their destination.
When selecting a coverage type, it is essential to consider several vital points surrounding your shipment. The frequency you ship, the volume of your shipments, the value, and the distance being traveled are all relative concerns when selecting a type of marine cargo insurance.
However, as you can see above, comparing both marine open policy and marine specific transit is more about volume and rate than anything. That is why SMEs generally get specific and general goods coverage annually.
The Institute of Cargo Clauses (ICC) illustrates what kind of coverage within a category of insurance coverage can be applied to international shipments or what kind of extensions can be used.
Here are the three main categories of ICC marine cargo clauses:
- Clause A – All Risk coverage is the absolute best coverage available, offering the most protection.
- Clause B – Basic coverage that is more limited and is also restricted to named or specified perils.
- Clause C – General Average coverage which is limited to fire and explosion, capsizing, sinking, and failed cargo delivery.
Both varying requirements and modes of transportation can also play a role in selecting the appropriate coverage required for a particular shipment. Clauses A through C will cover any vessels traveling by sea.
Other modes of transportation, such as coastal or inland waterways, are also covered by clauses A through C. There are additional extensions that create an added premium to the policy.
Either way, selecting marine cargo insurance coverage for your shipment is the intelligent play. An unexpected loss of freight without coverage can prove troublesome for any business, no matter how small.
Look into our article on CIF insurance to find out how it can help you with your ocean shipments.

What Does Marine Cargo Insurance Cover?
Essentially, marine cargo insurance covers your goods from damages, time delays, and total loss. These three factors can have an unbelievable impact on those who ignore the possibility of loss or damages resulting from a storm at sea, fire, or unsecured containers that result in damages.
As noted earlier, the coverage provided protects you, the shipper, from a loss on goods damaged or destroyed as a result of the following:
- Weather: The weather at sea can play a critical role in how overseas damages can and do occur. High winds and severe storms from hurricanes, typhoons, and tropical storms often are the root cause of damage while at sea.
- Piracy: The theft of goods is always a concern, especially in certain parts of the world where piracy runs rampant. While piracy typically occurs in regions like the coast of Africa, the Indian Ocean, Southeast Asia, and the Caribbean, it can still happen anywhere.
- Accidents: Unfortunate events happen all the time; no matter how careful one can be, they still happen. The handling of goods occurs during the loading, storage, and unloading process. Insurance coverage is an effective failsafe to provide financial compensation.
Here are some examples of what is and is not covered by marine cargo insurance as it relates to your cargo aboard a vessel in transit or at a port awaiting storage or shipboard loading:
Things generally covered:
- Natural weather occurrences or disasters
- Acts of piracy or theft
- Sinking while at sea
- Collisions that cause damage to cargo
- Handling during loading or unloading
- Additional fees that result from delays
Things not covered:
- Chemical reactions that result in damage
- Wear and Tear
- Firearms and munitions
- Leaking due to poor packaging
- War, strikes, riots, or civil commotions
- Fraud or damaging cargo on purpose
Marine cargo insurance, more than anything, will help stabilize international relationships. The ability to protect the interest of a foreign business partner goes an incredibly long way in solidifying reliable relationships now and in the future.
This insurance is not reserved for mega corporations or large-scale shipments but is ideal for SMEs. Marine cargo insurance is critically important to an SME in any business model as it assures the goods are protected regardless of importing or exporting.
Our article on marine cargo insurance costs will show you how much you’ll spend on this important form of protection.


Marine Cargo Insurance Claims: What You Need to Know
If you need to file a claim due to damages or any other type of loss, there is a process and a collection of information that is required. Typically in the event of loss and when a claim is filed, the shipper must also fill out a claim form.
In order to process an insurance claim effectively, a three-step process is required. Completing the claims process step by step is the most efficient way to facilitate a claim and get a settlement as fast as possible.
Step One: Notification
- Claims notification Form: A detailed summary of the claim with an estimate of the lost value; this must include all relative contact information.
- Reserve your rights: This is a notification to the responsible party that you have suffered a loss during shipping and that you are filing a claim.
- Expediency: Do not wait to turn in a claim; you should submit a notification when a claim is needed.
Step Two: Information Gathering
- Volume: The volume of a claim is considered substantial when the value exceeds $5,000 and is determined ultimately determined by the insurance provider. For smaller claims, the process is simplified.
- Specifics: Completed documentation is required to substantiate the claim. A claims adjuster will advise what documentation is needed to facilitate your claim.
- Surveyor: In the case of large volume claims, a surveyor will contact you directly, collecting all documentation for the adjuster after a detailed inspection.
- Adjuster: The adjuster goes over the report submitted by the surveyor to both process the claim and define the settlement.
Step Three: The Determination Stage
- Verification for policy/claim coverage is completed. This ensures that the claim is covered appropriately by the policy.
- A determination of the amount covered by the policy and supporting documentation is assessed.
- A payout by the adjuster is given once a final determination is made.
To reduce the amount of time needed for a filed claim to be processed, always include the following information in your completed claim forms. This information helps to answer any questions the adjuster may have regarding your claim.
- Completed claim form
- Copy of the Bill of Lading
- Copy of the insurance policy
- Copy of temperature documentation
- Copy of storage documentation
- Packing list and commercial invoice
- Any contract documentation or receipts
- Police report documents
- Estimated quote for repair or replacement
Once all three steps are complete, the documentation has been passed along to the surveyor and adjuster. The policy determines the recoverable amount and the information provided regarding additional expenses otherwise unknown.
The three steps in filing and processing a claim can be a lengthy process. Again, it is imperative to note that a claim needs to be submitted as fast as possible to speed things along and help validate your filing quickly and accurately.

Marine Cargo Insurance Costs: What Influences Cost?
When shipping goods worldwide, there are inherent risks associated with maritime cargo. Planning out the costs associated with coverage so that you, as a shipper, are prepared for the unexpected is crucial.
It is important to note that in almost all cases, the cost of coverage is roughly around half a percent in terms of the value of the entire shipment. However, the percentage of the entire value can go as high as two percent in some cases.
Many factors can and will influence the cost of a marine cargo insurance policy. Here are some examples of what will influence the cost of marine cargo insurance.
- Total Value: A percentage of the shipment’s total value in terms of all goods in a single shipment.
- Travel Route: The shipment’s total travel distance is calculated between the origin, destination, and region traveled and is also factored into the equation.
- Commodity classification: Depending on the commodity, additional costs can be added to the shipment. Examples like petroleum and other hazardous chemicals bring an added cost.
- Shipping Container: Shipping container sizes vary between 20 and 40 feet. Also, there are open variants of shipping containers, which play a role in determining the cost.
- Claims History: The cost can multiply if a shipper has a relevant history for processing multiple claims or otherwise there is a questionable history.
Along with the influence of cost, there is the potential possibility of risk associated with shipping goods across the ocean to consider. While ship losses don’t directly affect insurance costs, they do affect the reasoning for obtaining insurance in the first place.
A lot can happen once an ocean vessel leaves the port of origin and heads to its destination. The table below outlines ship losses in 2020, showing that a loss at sea, however minimal by comparison to the number of completed shipments, is a real threat.
Ship Losses in 2020
Compared to the total number of successful shipments, this statistic may seem like a drop in the bucket. Although only 49 ship losses occurred in 2020, the total cost associated with these losses was monumental in scope and can happen anytime or anywhere.
All of the above factors play a role in determining the actual cost for coverage of a shipment. Speaking with an experienced and knowledgeable consultant will determine the specifics of covering your marine cargo during an overseas shipment.
Pros and Cons of Each Type of Marine Cargo Insurance
A similarity can be drawn between covering your cargo and buying an extended warranty on goods purchased at a store or online. The same basic concept of protecting yourself against a potential inevitability is the same.
With that said, covering your cargo with protection is critically vital so that the risk of financial loss is minimized or eliminated. There are, however, both pros and cons surrounding marine open policy and marine specific transit insurance, and they are as follows.
Marine Open Policy
- Has the flexibility to cover multiple shipments during a 12-month period.
- Multiple contracts are not required, all declarations are honored by the provider.
- The insurance coverage is a stamped, enforceable contract.
- Liability of the provider can be limited if a clause of per location or per bottom is enacted.
- The insurance provider is only required to offer partial recovery under these clauses.
- Is not a cost-effective option for shippers who do not move consistent loads.
Marine Specific Transit
- Covers all types of shipping transports over a single shipment.
- Issuing a single voyage policy is easier than a continuous one.
- All types of cargo can be covered, and the maximum value is also covered.
- Does not favor a shipper who has continuous shipments due to both cost and time.
- Not a cost-effective option if you ship consistently or have multiple shipments in a particular time frame.
- Issues related to the shipment can affect liability and what is recoverable.
It is also essential to note that marine specific transit insurance covers all three types of transit clauses. Under ICC Transit Clauses A, B, and C, the premium required is generally not a costly expense.
The positives of these two types of marine cargo insurance definitely outweigh the negatives. Insurance coverage has a profound impact on a business’s financial stability. It is essential to weigh out the pros and cons of each in order to determine what is best for your shipments.
Safe and Smooth Sailing With Freight Insurance Coverage
Freight Insurance Coverage is committed to providing world-class marine cargo insurance anytime and anywhere you need the best coverage for your shipment. Get started by filling out one of our quotes , and the insurance cost is factored into the total cost of your shipment.
Figuring out the cost of insurance and any specifics can be a real hassle. Our team at Freight Insurance Coverage is standing by to help get your shipment underway with the peace of mind that your shipment is protected. You can fill out your quote here or call us at (866) 975-0749 so that we can answer any questions you might have regarding your shipment and the coverage you need.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Freight Insurance Coverage 315 NE 14th Street #4122 Ocala, FL 34470
What is Specific Voyage Insurance Policy?
- May 17, 2024
- securenow_insuropedia
Marine Insurance
(Excluding Taxes)
*Terms & conditions apply
Get quote if you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy
Insuropedia
- Buying Process
As the name itself says, a specific voyage insurance policy covers a specific single transit only. It offers coverage to goods, freights, and other interests against various losses or damages, like fire, collision, earthquake, lightning, etc.; if destroyed by rail or air while transporting goods. It will not pay anything if losses or damages happen due to war, terrorist activity, nuclear fusion, etc. Further, if goods are damaged during loading/unloading or while in storage, they won’t be covered under a specific voyage insurance policy, unless stated specifically.
The specific voyage insurance cover comes to an end as soon as the cargo arrives at the destination. The policy would be issued before the inception of the voyage. At the time of taking a specific voyage insurance policy, it is essential to give the complete details of the risk along with complete information about the bill of lading, vessel name, etc.
Specific voyage insurance policies suit those businesses that do not often need marine insurance policies in the course of their business. In those businesses where the frequency of voyages is high, a specific voyage policy may not be apt. As it becomes challenging to get a separate marine insurance policy each time you decide to transfer your goods.
A specific voyage policy covers the transportation of goods through inland transport, import, and export. It is feasible to extend the specific voyage insurance policy and gets an extra cover against perils like a strike, riot, civil commotion, etc.
When choosing the sum insured for a specific voyage insurance policy, you can consider the type of the contract. The total quantity of your goods would be defined in your insurance contract. To calculate the sum insured, make sure to consider the contract value and add 10%-15% to it to find out the incidental cost.
Since its inception, K.S Fashion has carved a niche for itself in the fashion industry. Till the time, the company was directly dealing with customers, however, a few years ago, the company ventured into export as well. Last year, the company bagged a huge contract for exporting fashion apparel to a buyer situated in Dubai.
Considering the risks that could arise during transit, the company decided to purchase a specific voyage insurance policy. As it was only one export, the company purchased a specific voyage insurance policy only. The policy was meant to cover only a single contract and would come to an end once the goods were delivered to the buyer in Dubai.
When the ship started its journey, it was a clear sky, however, after a few hours, it started raining heavily. Though they packed the goods in a proper manner; resulted in damage due to water. When the consignment reached the destination, the buyer refused to take the delivery of 20 boxes out of 90 boxes.
Additional Read: How does Warranty Work in Marine Insurance?
As K.S Fashion had a specific voyage insurance policy, it approached the insurer for the claim settlement. Here, the insurer appointed a surveyor to inspect the situation and found that losses happened due to rain which was an insured peril.
The insurer found the claim legitimate and agreed to cover it. In this case, the insurance company only covered one voyage which was from India to Dubai. As the losses happened during that voyage, the insurer agreed to cover them. The specific voyage insurance policy comes to an end, soon after the delivery of goods.
In case, losses occurred when K.S Fashion was exporting goods to another country; then it may not be covered under specific voyage insurance, even if the second export took place immediately after the first export.
Simple reason— K.S Fashion bought a specific voyage insurance policy valid only for one. The policy ended as soon as that voyage was over.
About The Author
MBA Insurance and Risk
With extensive experience in the insurance industry, Simran is a seasoned writer specializing in articles on marine insurance for SecureNow. Drawing from 5 years of expertise in the field, she possesses a comprehensive understanding of the complexities and nuances of marine insurance policies. Her articles offer valuable insights into various aspects of marine insurance, including cargo protection, hull insurance, and liability coverage for marine-related risks. Renowned for their insightful analysis and informative content, Simran is committed to providing readers with actionable information that helps them navigate the intricacies of marine insurance with confidence.
Related Posts

Best Marine Insurance Policy. Starting from Rs 350 only.
*All savings provided by insurers as per IRDAI approved insurance plan. Standard T&C apply.
Last Updated on May 17, 2024 by Chetan Sharma
- My Dashboard

Currently the video chat timings are 9:30am to 6:30pm from Monday to Saturday.

Please Share Your Details
Your quote details.
- Proposer Name
- Type Of Goods
- Basic Cover Type
- Cargo Sum Insured
Marine Cargo Insurance Policy
Plan details.

Marine Cargo Business is not constrained by borders, and goods are shipped around the world. The transit from its “Origin” to “Destination”, is exposed to various risks. The domestic movement or importing and exporting of goods can expose you (Seller/Consignor) or (Buyer/Consignee) to massive financial losses in case shipments gets damage in transit or lost. It is crucial to protect these goods from the various possible mishaps, enabling you to run you trade/business smoothly.
Special feature tailor-made for you:

Different types of shipments covered in cargo insurance:-
Types of marine cargo insurance policies are:.
Specific Policy: Covers the single specific shipment only during the policy period.
Open Policy: The agreement between a proposer and an insurer to insure all goods in transit falling within that agreement for a period of time or even indefinitely until the agreement is cancelled by either party. Full premium is collected in advance and adjusted on annual declared value of annual shipments.
Open Cover: is an agreement between the Proposer and the Insurer, the Proposer agrees to buy cargo insurance for all their cargoes whenever they have an obligation to insure and the insurer agrees to provide cargo protection for the Proposer. Premium is charged as declarations of shipments are made.
What peril does the policy cover?
Based on the type of cover selected, it covers “All Risk” to “Fire only” risk or named perils:-
- Quick Facts
What is Marine Cargo Insurance / Transit Insurance?
Transit insurance covers goods and/or merchandise while in ordinary course of transit from one location to another location.
Who can buy Marine Cargo Insurance?
The Marine Cargo Insurance policy can be taken by Sellers, Buyers, Import/Export merchants, Contractors, Banks or anyone engaged in the import and export of goods or transportation of it within the country or who has a insurable interest in it.
What are the types of shipments?
The types of shipments includes the following:
- Domestic Shipment : means transportation of cargo between two places or states within the country
- Import : means bringing into India any goods by Land, Sea or Air and where the payment is made in foreign currency only
- Export : means taking out of India any goods by Land, Sea or Air and where the amount is received in foreign currency only
- Deemed Export : refer to those transactions in which goods supplied do not leave country, and payment for such supplies is received either in Indian rupees or in free foreign exchange
- Third Country Shipment : means transportation of cargo between two countries without passing through India and the amount is received in foreign currency only
What are the type of Marine Cargo Insurance cover available?
Following types of cover are available:
- Inland Transit Clause – A
- Inland Transit Clause – B
What does Perils of the Sea mean?
"Perils of the seas" means fortuitous accidents or casualties of the seas but does not include ordinary action of the wind and waves.
What are INCOTERMS?
Incoterms are a collective of international commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. These terms are widely used in international commercial transactions, to distinguish the rights, risks and obligations of both parties (Seller/Consignor and Buyer/Consignee) concerning the transportation of goods.
There are a number of Incoterms which apply to all types of transportation and some terms are specified for one type of transportation.
Rules for Any Mode (or modes) of Transport
- CIP - Carriage and Insurance Paid
- CPT - Carriage Paid To
- DAP - Delivered At Place
- DAT - Delivered At Terminal
- DDP - Delivered Duty Paid
- EXW - Ex Works
- FCA - Free Carrier
Rules for Sea and Inland Waterway Transport Only
- CFR - Cost and Freight
- CIF - Cost, Insurance and Freight
- FAS - Free Alongside Ship
- FOB - Free On Board
Note: New Incoterms 2020 has been published recently.
What information the Insurer need to provide quotation?
- Name and address of the Proposer and his business
- Description of goods, number and nature of packages
- Value of Goods
- Voyage details (From/To)
- Mode of Conveyance (Rail/Road/Air)
- Basis of Valuation
- Packing of the cargo
- Type of Cover eg ITC A, B.
What is Sum Insured?
Sum insured is the total value of the goods including freight, taxes and any other port handling charges. This is the maximum amount which is payable in the event of a total loss of the insured cargo. The sum insured will comprise of the following:-
Cost of the goods & Freight
What are the documents required to lodge a claim?
Following documents are required to lodge the claim:
- Policy And/Or Certificate of Insurance
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing list
Additional documents depending on the nature of the claim
What are the types of cargo?
The types of cargo are :
General Cargo : Eg., Furniture, Spare Parts, Leather goods, footwear, etc
Machineries : Eg., Standard size in Containers. Oversize in Bulk or Open Top containers.
Liquid Bulk Cargo : Eg., Crude Oil, Edible Oil, etc
Dry Bulk Cargo : Eg., Coal, grain, ore and other similar products in loose form
What are the general exclusions in Marine Cargo Insurance?
Here's a list of exclusions:
- Loss damage or expense attributable to wilful misconduct of the Assured
- Ordinary leakage, ordinary loss in weight or volume, or ordinary wear and tear of the subject matter insured
- Loss damage or expense caused by insufficiency or unsuitability of packing or preparation of the subject-matter insured
- Loss damage or expense proximately caused by delay, even though the delay be caused by a risk insured against
- Loss damage or expense caused by inherent vice or nature of the subject-matter insured
- Loss damage or expense directly or indirectly caused by or arising from the use any weapon or device employing atomic or nuclear fission and/or fusion or other like reaction or radioactive force or matter
Note - Can be bought back, however, war coverage on land is an excluded peril.
What is the difference between inland/domestic transit and ocean cargo coverage?
The Inland transit/domestic transits covers shipments via land conveyances and/or air within the country.
Ocean Cargo provides coverage for international ocean and/or air shipments on a warehouse to warehouse basis (including the land connecting conveyance transits).
- Pay Premium
- Become Our Partner

- Assistant VoiceBot
- Project Management – Dry Docking and Repairs
- Ship Services
- Marine CAD Services
- Marine IT Services
- Academic services
- MEO Class 1
- MEO Class 2
- MEO Class 4
- ASM / Masters
- Class IV Level
- Academic Papers
- Year/Month Sets
- Shirts & Trousers
- Deck Officers
- Engineer Officers
- Coveralls / Boiler Suits
- Marine Uniform Shirts & Trousers
- Epaulettes for Marine Deck Officers
- Epaulettes for Marine Engineer Officers
- Marine Belts | Peak cap | Accessories
- Marine Accessories
- Marine Engineering – General
- Marine Engineering – Motor
- Marine Electro Technology
- Ship Safety & Naval Architecture
- MMD Procedures
- Merchant Navy Courses
Marine insurance – Voyage Policy
- 13 Apr 2018
- As the name implies, a specific voyage insurance policy covers a specific single transit only. It offers coverage to goods, freights and other interests against various losses or damages, like fire, collision, earthquake, lightning, etc.; Specific voyage insurance policy will not pay anything if losses or damages happen due to war, terrorist activity, nuclear fusion, etc. Further, if goods are damaged during loading/unloading or while in storage, it won’t be covered under a specific voyage insurance policy, unless stated specifically.
- The specific voyage insurance cover comes to an end as soon as the cargo arrives at the destination. The policy would be issued before the inception of the voyage. At the time of taking a specific voyage insurance policy, it is essential to give the complete details of the risk along with complete information about the bill of lading, vessel name, etc.
- Specific voyage insurance policies suit to those businesses who do not often need marine insurance policies in the course of their business. In those businesses where the frequency of voyages is high, specific voyage policy may not be apt as it becomes challenging to get a separate marine insurance policy each time you decide to transfer your goods.
- A specific voyage policy covers transportation of goods through inland transport, import and export. It is feasible to extend the specific voyage insurance policy and gets extra cover against perils like a strike, riot, civil commotion, etc.
- While choosing the sum insured for specific voyage insurance policy, you can consider the type of the contract. The total quantity of your goods would be defined in your insurance contract. To calculate the sum insured, make sure to consider the contract value and add 10%-15% to it to find out the incidental cost.
Voyage insurance policy in simple terms
– Under this policy the subject matter is insured against the risk of a particular voyage. The risk commences from the departure of ship from its port of loading and terminates as the ship reaches its arrival port. This policy is for the cargo alone hence the policy is taken by the cargo owner.
– The policy covers the subject matter during voyage only.
– Therefore it may be constrained when the ship breaks down during voyage or deviates route resulting in elongation of time. In such cases suitable clauses might have to be provided to extend the coverage.
– This policy is suitable for the ships regularly operating in a particular route or voyage & for liner shipping. This policy is used mostly in case of cargo insurance. The Policy expires on completion of voyage.
– policy doesn’t cover the port stay, loading and discharging.
Voyage insurance policy – Real case
- A fashion company ‘X’ ventured into export recently. The company bagged a huge contract of exporting fashion apparels to a buyer situated in Dubai.
- Considering the risks that could arise during transit, the company decided to purchase a specific voyage insurance policy. As it was only one export, the company purchased specific voyage insurance policy only. The policy meant to cover only a single contract and would come to an end once the goods delivered to the buyer in Dubai.
- When the ship started its journey, it was a clear sky, however, after a few hours, it started raining heavily. Though goods were packed in a proper manner; it got damaged due to water. When the consignment reached the destination, the buyer refused to take the delivery of 20 boxes out of 90 boxes.
- As company ‘X’ had a specific voyage insurance policy, it approached the insurer for the claim settlement. Here, the insurer appointed a surveyor to inspect the situation and found that losses happened due to rain which was an insured peril.
- The insurer found the claim as legitimate and agreed to cover it. In this case, the insurance company only covered one voyage which was from India to Dubai. As the losses happened during that voyage, the insurer agreed to cover it. As soon as goods were delivered, the specific voyage insurance policy came to an end.
Related Posts

Marine Insurance
Continue reading
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Follow us on Social Media
Username or email address *
Password *
Note: Entering wrong username in the login form will ban your IP address immediately. Entering wrong password multiple times will also ban your IP address temporarily.
Lost your password? Remember me
No account yet?
Voyage Policy

A voyage policy is marine insurance coverage for risks to a ship’s cargo during a specific voyage. It is one of the types of marine policies, which is taken to cover the risks of a particular voyage between two ports. Unlike most insurance policies it is not time-based but expires when the ship arrives at its destination. It covers only the cargo, not the ship that carries it. A voyage policy suits those businessmen or traders who rarely require marine insurance policies, or who export a relatively small amount of cargo by sea.
“Voyage policies generally cover against accidental damage and collisions as well as natural disasters. Losses due to delays may be covered as well.”
A voyage policy covers only unforeseeable and unpreventable risks. These policies are commonly used by exporters who need marine shipping only occasionally or for relatively small amounts of cargo. At the beginning of the voyage, the ship must be seaworthy for that transit for the policy to uphold. Its contract lays down the precise minute when the cover comes into effect and when it terminates. While a voyage policy insures the cargo in transit from one place to another, a time policy insures it for a definite period.

Any insurance policy is designed to indemnify the insured against risks of damage to property, the environment, or human life in the event of a natural calamity, accident, theft, etc. Voyage policies generally cover against accidental damage and collisions as well as natural disasters. Losses due to delays may be covered as well. It is considered seaworthy when it is fit to encounter the ordinary perils of the seas in the transit. Voyage policies may specifically exclude losses caused by willful misconduct, ordinary leakage, ordinary wear and tear, improper or inadequate packaging, and labor strikes. In addition, the ship’s crew must be reasonably competent. Acts of war and terrorist activity also are usually excluded. It is feasible to extend it to include extra cover against perils like a strike, riot, civil commotion, etc.
The policy covers damage caused by, for example, earthquake, lightning, fire, and collision. The policy covers the cargo during the whole voyage by sea, even if there are delays en route. It won’t cover losses or damage that occured as the result of a terrorist attack, war, or nuclear fusion. So, voyage policy is also known as marine cargo insurance.
Statistical Finance

Advantages of Term Loans

Analysis the Importance of Mutual Fund Analysis

Building Society in Finance Institution

Biography of Fats Domino

Annual Report 2016-2017 of Tata Investment Corporation Limited

Deep Ecology

Stockholm, Sweden

Agricultural Economics
![marine cargo specific voyage policy Report on One Bank LTD [Part-4]](https://assignmentpoint.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/one-bank1-110x55.jpg)
Report on One Bank LTD [Part-4]
Latest post.

Annite – Properties and Occurrences

Antipinite – Properties and Occurrences
A Novel Deposition Process Sheds information on Perovskite Hydrides

Animal Brains inspired AI Game changers for Autonomous Robotics

Aleutite – Properties and Occurrences

Dual Electrification
The Federal Register
The daily journal of the united states government, request access.
Due to aggressive automated scraping of FederalRegister.gov and eCFR.gov, programmatic access to these sites is limited to access to our extensive developer APIs.
If you are human user receiving this message, we can add your IP address to a set of IPs that can access FederalRegister.gov & eCFR.gov; complete the CAPTCHA (bot test) below and click "Request Access". This process will be necessary for each IP address you wish to access the site from, requests are valid for approximately one quarter (three months) after which the process may need to be repeated.
An official website of the United States government.
If you want to request a wider IP range, first request access for your current IP, and then use the "Site Feedback" button found in the lower left-hand side to make the request.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Voyage Policy: A financial protection plan that provides coverage for goods in transit by sea. In order for a voyage policy to be valid, the vessel transporting the cargo must be in good condition ...
Specific Voyage. Marine Insurance Policy. Downloads. Underwriting checklist for Marine and Marine DSU project (50.18 KB) Format to obtain information on Critical Equipments for DSU Risks (20.99 KB) Marine Cargo claim form (52.22 KB) Marine Cargo DSU Questionaire (39.42 KB) Do's & Don'ts for Marine Cargo claims (30.21 KB) Buy Online.
A voyage policy, also known as marine cargo insurance, provides coverage for the cargo of a ship during a specific journey. Unlike typical insurance policies, it is not time-based and expires upon the ship's arrival at its destination.
Information required for a Specific Marine Policy. Jun 24, 2021. 619 Views. The reason this above question needs to be asked is- there is no standardized pr... Read More. A marine-specific insurance policy provides coverage for the loss or damage caused to the goods during transit from one place to another through the water.
Here are some of the highlights of marine specific policy: The buyer gets coverage for specific voyage under a specific policy as and when required. In order to evaluate the risk, the buyer must provide details of commodity, conveyance mode, packaging, voyage details as well as the value of the commodity. The premium of the marine specific ...
Summary. According to the Indian Marine Insurance Act 1963, voyage policy is a type of marine insurance policy that provides coverage for losses due to unforeseen risks to cargo during a specific voyage. The policy contract contains complete details of the risk, along with information about the bill of lading, name of the vessel, etc. A voyage ...
A voyage policy is an insurance policy, specifically a marine insurance policy, that provides coverage due to unforeseen risks to cargo that is being transported by ship. The policy covers damage caused by, for example, earthquake, lightning, fire, and collision. It won't cover losses or damage that occured as the result of a terrorist attack ...
Specific Voyage or Time Policy. These policies are issued to firms that require coverage for a specific voyage. It is suitable for those firms who seldom require marine cargo policies in the course of their trade. ... Claims under a duty policy are only payable if the claim is otherwise admissible in the marine cargo policy covering the goods ...
The complainant, a regular importer, ought to have known the terms and conditions accompanying a Marine Cargo Specific Voyage Policy. Although was for the OP to do the necessary due diligence on the classification of the vessel, but, It was the complainant whose cargo was to be insured against all risks associated with the marine voyage.
Marine cargo policy provides insurance to such businesses which are involved in shipping of goods across the national boundaries on a regular basis. ... Specific voyage policy. This policy also provides coverage for only those specific voyages for which the policyholder asks. It is a customized policy as per the occasional need of the client ...
As a general principle, there are six types of insurance coverage: voyage policy, time policy, valued policy, unvalued policy, floating policy, open cover. These kinds of policies are incorporated into the Institute Cargo Clauses, that are common standards for marine cargo insurance (for a detailed analysis of each Institute Cargo Clause (A ...
Marine Cargo Insurance. Marine cargo policy refers to the insurance of goods dispatched from the country of origin to the country of destination. ... One can issue for more than a year or they may extend to complete a specific voyage. But it is normally for a fixed period. Also under marine insurance in India, time policy can be issued only ...
As the name suggests, a Specific Voyage Policy covers a specific single transit only. The policy would be issued before the inception of the voyage and the Assured has provide complete details of the risk along with complete information about the bill of lading, vessel name, Type of Cargo, Packing Details, Voyage Details etc.
Within marine cargo insurance, two main types of coverage exist. These coverage options are in place to offer alternatives to the policyholder that are more timeline-specific than feature-specific. Marine cargo insurance coverage is specific in that it revolves around your cargo, it is handling, and the vessel that carries your goods.
www.hdfcergo.com. UIN: Marine Cargo Open Policy - IRDAN125P0004V01200304. IRDAI Reg No. 146. MARINE CARGO INSURANCE . At HDFC ERGO, we understand that your business requires your undivided attention. With this in mind, our experts ... Specific voyage Policy: This is issued for covering Specific Shipments. Cover under this policy commences with ...
A specific voyage policy covers transportation of goods through inland transport, import, and export. It is feasible to extend the specific voyage insurance policy and gets an extra cover against perils like a strike, riot, civil commotion, etc. When choosing the sum insured for a specific voyage insurance policy, you can consider the type of ...
Marine Cargo Insurance provides coverage against any damage caused to cargo vessels which are in transit by road, rail, inland waterways from one point to another. The policy covers damage incurred to the cargo while it is grounded or in transit due to other factors like weather conditions, strikes, war, collision, sinking, navigation errors etc.
Types of marine cargo insurance policies are: . Specific Policy: Covers the single specific shipment only during the policy period. Open Policy: The agreement between a proposer and an insurer to insure all goods in transit falling within that agreement for a period of time or even indefinitely until the agreement is cancelled by either party.
The specific voyage insurance cover comes to an end as soon as the cargo arrives at the destination. The policy would be issued before the inception of the voyage. At the time of taking a specific voyage insurance policy, it is essential to give the complete details of the risk along with complete information about the bill of lading, vessel ...
This document is a marine cargo specific voyage policy issued by The New India Assurance Co. Ltd. to M/S Hallworthy Shipping Limited SA. The policy provides coverage for the shipment of 1 reel of drill line from Veshvi Uran to ONGC Nhava Supply Base / Rig Vivekanand 1 via vessel. The policy is subject to various clauses and conditions including Institute Cargo Clauses and exclusions for ...
Voyage From : To : Subject matter insured Marks & Nos. Nature of packing: Terms of cover: Basis of Valuation: Place & period of transshipment and Storage: ... Marine Cargo Specific Transit Policy UIN- IRDAN134CP0006V01200809 Page 5 of 7 Nr. Panbazar over bridge, S.S. Road, Mizoram, Guwahati - 781001(ASSAM). Arunachal Pradesh,
A voyage policy is marine insurance coverage for risks to a ship's cargo during a specific voyage. It is one of the types of marine policies, which is taken to cover the risks of a particular voyage between two ports. Unlike most insurance policies it is not time-based but expires when the ship arrives at its destination.
Digit Marine Cargo Policy ... a Specific Voyage Policy covers a specific single transit only. The policy would be issued before the inception of the voyage and the Assured has provide complete details of the risk along with complete information about the bill of lading, vessel name, Type of Cargo, Packing Details, ...
Part 64—Marine Portable Tanks and Cargo Handling Systems; E. Additional Changes From the NPRM; V. Incorporation by Reference; ... and that while the Coast Guard has attempted to address this via policy letter, ... though its applicability to passenger vessels on international voyages is mentioned in § 56.50-50(c)(2). The CFR codifies ...
There is a consensus on the need to reduce the emissions of carbon compounds. The increase in global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the maritime industry poses a serious challenge to environmental sustainability, climate change, and the operating costs of ships. This article shows how hybrid versus diesel propulsion technology for ships can help reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and ...