

Why does time change when traveling close to the speed of light? A physicist explains
Assistant Professor of Physics and Astronomy, Rochester Institute of Technology
Disclosure statement
Michael Lam does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Rochester Institute of Technology provides funding as a member of The Conversation US.
View all partners
- Bahasa Indonesia

Curious Kids is a series for children of all ages. If you have a question you’d like an expert to answer, send it to [email protected] .
Why does time change when traveling close to the speed of light? – Timothy, age 11, Shoreview, Minnesota
Imagine you’re in a car driving across the country watching the landscape. A tree in the distance gets closer to your car, passes right by you, then moves off again in the distance behind you.
Of course, you know that tree isn’t actually getting up and walking toward or away from you. It’s you in the car who’s moving toward the tree. The tree is moving only in comparison, or relative, to you – that’s what we physicists call relativity . If you had a friend standing by the tree, they would see you moving toward them at the same speed that you see them moving toward you.
In his 1632 book “ Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems ,” the astronomer Galileo Galilei first described the principle of relativity – the idea that the universe should behave the same way at all times, even if two people experience an event differently because one is moving in respect to the other.
If you are in a car and toss a ball up in the air, the physical laws acting on it, such as the force of gravity, should be the same as the ones acting on an observer watching from the side of the road. However, while you see the ball as moving up and back down, someone on the side of the road will see it moving toward or away from them as well as up and down.
Special relativity and the speed of light
Albert Einstein much later proposed the idea of what’s now known as special relativity to explain some confusing observations that didn’t have an intuitive explanation at the time. Einstein used the work of many physicists and astronomers in the late 1800s to put together his theory in 1905, starting with two key ingredients: the principle of relativity and the strange observation that the speed of light is the same for every observer and nothing can move faster. Everyone measuring the speed of light will get the same result, no matter where they are or how fast they are moving.
Let’s say you’re in the car driving at 60 miles per hour and your friend is standing by the tree. When they throw a ball toward you at a speed of what they perceive to be 60 miles per hour, you might logically think that you would observe your friend and the tree moving toward you at 60 miles per hour and the ball moving toward you at 120 miles per hour. While that’s really close to the correct value, it’s actually slightly wrong.
This discrepancy between what you might expect by adding the two numbers and the true answer grows as one or both of you move closer to the speed of light. If you were traveling in a rocket moving at 75% of the speed of light and your friend throws the ball at the same speed, you would not see the ball moving toward you at 150% of the speed of light. This is because nothing can move faster than light – the ball would still appear to be moving toward you at less than the speed of light. While this all may seem very strange, there is lots of experimental evidence to back up these observations.
Time dilation and the twin paradox
Speed is not the only factor that changes relative to who is making the observation. Another consequence of relativity is the concept of time dilation , whereby people measure different amounts of time passing depending on how fast they move relative to one another.
Each person experiences time normally relative to themselves. But the person moving faster experiences less time passing for them than the person moving slower. It’s only when they reconnect and compare their watches that they realize that one watch says less time has passed while the other says more.
This leads to one of the strangest results of relativity – the twin paradox , which says that if one of a pair of twins makes a trip into space on a high-speed rocket, they will return to Earth to find their twin has aged faster than they have. It’s important to note that time behaves “normally” as perceived by each twin (exactly as you are experiencing time now), even if their measurements disagree.
You might be wondering: If each twin sees themselves as stationary and the other as moving toward them, wouldn’t they each measure the other as aging faster? The answer is no, because they can’t both be older relative to the other twin.
The twin on the spaceship is not only moving at a particular speed where the frame of references stay the same but also accelerating compared with the twin on Earth. Unlike speeds that are relative to the observer, accelerations are absolute. If you step on a scale, the weight you are measuring is actually your acceleration due to gravity. This measurement stays the same regardless of the speed at which the Earth is moving through the solar system, or the solar system is moving through the galaxy or the galaxy through the universe.
Neither twin experiences any strangeness with their watches as one moves closer to the speed of light – they both experience time as normally as you or I do. It’s only when they meet up and compare their observations that they will see a difference – one that is perfectly defined by the mathematics of relativity.
Hello, curious kids! Do you have a question you’d like an expert to answer? Ask an adult to send your question to [email protected] . Please tell us your name, age and the city where you live.
And since curiosity has no age limit – adults, let us know what you’re wondering, too. We won’t be able to answer every question, but we will do our best.
- General Relativity
- Special Relativity
- Time dilation
- Speed of light
- Albert Einstein
- Curious Kids
- Theory of relativity
- Curious Kids US

Economics Editor

Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Indigenous Strategy and Services)

Director and Chief of Staff, Indigenous Portfolio

Chief People & Culture Officer
Lecturer / senior lecturer in construction and project management.
Speed of Light Calculator
Table of contents
With this speed of light calculator, we aim to help you calculate the distance light can travel in a fixed time . As the speed of light is the fastest speed in the universe, it would be fascinating to know just how far it can travel in a short amount of time.
We have written this article to help you understand what the speed of light is , how fast the speed of light is , and how to calculate the speed of light . We will also demonstrate some examples to help you understand the computation of the speed of light.
What is the speed of light? How fast is the speed of light?
The speed of light is scientifically proven to be the universe's maximum speed. This means no matter how hard you try, you can never exceed this speed in this universe. Hence, there are also some theories on getting into another universe by breaking this limit. You can understand this more using our speed calculator and distance calculator .
So, how fast is the speed of light? The speed of light is 299,792,458 m/s in a vacuum. The speed of light in mph is 670,616,629 mph . With this speed, one can go around the globe more than 400,000 times in a minute!
One thing to note is that the speed of light slows down when it goes through different mediums. Light travels faster in air than in water, for instance. This phenomenon causes the refraction of light.
Now, let's look at how to calculate the speed of light.
How to calculate the speed of light?
As the speed of light is constant, calculating the speed of light usually falls on calculating the distance that light can travel in a certain time period. Hence, let's have a look at the following example:
- Source: Light
- Speed of light: 299,792,458 m/s
- Time traveled: 100 seconds
You can perform the calculation in three steps:
Determine the speed of light.
As mentioned, the speed of light is the fastest speed in the universe, and it is always a constant in a vacuum. Hence, the speed of light is 299,792,458 m/s .
Determine the time that the light has traveled.
The next step is to know how much time the light has traveled. Unlike looking at the speed of a sports car or a train, the speed of light is extremely fast, so the time interval that we look at is usually measured in seconds instead of minutes and hours. You can use our time lapse calculator to help you with this calculation.
For this example, the time that the light has traveled is 100 seconds .
Calculate the distance that the light has traveled.
The final step is to calculate the total distance that the light has traveled within the time . You can calculate this answer using the speed of light formula:
distance = speed of light × time
Thus, the distance that the light can travel in 100 seconds is 299,792,458 m/s × 100 seconds = 29,979,245,800 m
What is the speed of light in mph when it is in a vacuum?
The speed of light in a vacuum is 670,616,629 mph . This is equivalent to 299,792,458 m/s or 1,079,252,849 km/h. This is the fastest speed in the universe.
Is the speed of light always constant?
Yes , the speed of light is always constant for a given medium. The speed of light changes when going through different mediums. For example, light travels slower in water than in air.
How can I calculate the speed of light?
You can calculate the speed of light in three steps:
Determine the distance the light has traveled.
Apply the speed of light formula :
speed of light = distance / time
How far can the speed of light travel in 1 minute?
Light can travel 17,987,547,480 m in 1 minute . This means that light can travel around the earth more than 448 times in a minute.
Speed of light
The speed of light in the medium. In a vacuum, the speed of light is 299,792,458 m/s.

- Login/Register
- Solar System
- Exotic Objects
- Upcoming Events
- Deep-Sky Objects
- Observing Basics
- Telescopes and Equipment
- Astrophotography
- Space Exploration
- Human Spaceflight
- Robotic Spaceflight
- The Magazine
What is the speed of light? Here’s the history, discovery of the cosmic speed limit

On one hand, the speed of light is just a number: 299,792,458 meters per second. And on the other, it’s one of the most important constants that appears in nature and defines the relationship of causality itself.
As far as we can measure, it is a constant. It is the same speed for every observer in the entire universe. This constancy was first established in the late 1800’s with the experiments of Albert Michelson and Edward Morley at Case Western Reserve University . They attempted to measure changes in the speed of light as the Earth orbited around the Sun. They found no such variation, and no experiment ever since then has either.
Observations of the cosmic microwave background, the light released when the universe was 380,000 years old, show that the speed of light hasn’t measurably changed in over 13.8 billion years.
In fact, we now define the speed of light to be a constant, with a precise speed of 299,792,458 meters per second. While it remains a remote possibility in deeply theoretical physics that light may not be a constant, for all known purposes it is a constant, so it’s better to just define it and move on with life.
How was the speed of light first measured?
In 1676 the Danish astronomer Ole Christensen Romer made the first quantitative measurement of how fast light travels. He carefully observed the orbit of Io, the innermost moon of Jupiter. As the Earth circles the Sun in its own orbit, sometimes it approaches Jupiter and sometimes it recedes away from it. When the Earth is approaching Jupiter, the path that light has to travel from Io is shorter than when the Earth is receding away from Jupiter. By carefully measuring the changes to Io’s orbital period, Romer calculated a speed of light of around 220,000 kilometers per second.
Observations continued to improve until by the 19 th century astronomers and physicists had developed the sophistication to get very close to the modern value. In 1865, James Clerk Maxwell made a remarkable discovery. He was investigating the properties of electricity and magnetism, which for decades had remained mysterious in unconnected laboratory experiments around the world. Maxwell found that electricity and magnetism were really two sides of the same coin, both manifestations of a single electromagnetic force.

As Maxwell explored the consequences of his new theory, he found that changing magnetic fields can lead to changing electric fields, which then lead to a new round of changing magnetic fields. The fields leapfrog over each other and can even travel through empty space. When Maxwell went to calculate the speed of these electromagnetic waves, he was surprised to see the speed of light pop out – the first theoretical calculation of this important number.
What is the most precise measurement of the speed of light?
Because it is defined to be a constant, there’s no need to measure it further. The number we’ve defined is it, with no uncertainty, no error bars. It’s done. But the speed of light is just that – a speed. The number we choose to represent it depends on the units we use: kilometers versus miles, seconds versus hours, and so on. In fact, physicists commonly just set the speed of light to be 1 to make their calculations easier. So instead of trying to measure the speed light travels, physicists turn to more precisely measuring other units, like the length of the meter or the duration of the second. In other words, the defined value of the speed of light is used to establish the length of other units like the meter.
How does light slow down?
Yes, the speed of light is always a constant. But it slows down whenever it travels through a medium like air or water. How does this work? There are a few different ways to present an answer to this question, depending on whether you prefer a particle-like picture or a wave-like picture.
In a particle-like picture, light is made of tiny little bullets called photons. All those photons always travel at the speed of light, but as light passes through a medium those photons get all tangled up, bouncing around among all the molecules of the medium. This slows down the overall propagation of light, because it takes more time for the group of photons to make it through.
In a wave-like picture, light is made of electromagnetic waves. When these waves pass through a medium, they get all the charged particles in motion, which in turn generate new electromagnetic waves of their own. These interfere with the original light, forcing it to slow down as it passes through.
Either way, light always travels at the same speed, but matter can interfere with its travel, making it slow down.
Why is the speed of light important?
The speed of light is important because it’s about way more than, well, the speed of light. In the early 1900’s Einstein realized just how special this speed is. The old physics, dominated by the work of Isaac Newton, said that the universe had a fixed reference frame from which we could measure all motion. This is why Michelson and Morley went looking for changes in the speed, because it should change depending on our point of view. But their experiments showed that the speed was always constant, so what gives?
Einstein decided to take this experiment at face value. He assumed that the speed of light is a true, fundamental constant. No matter where you are, no matter how fast you’re moving, you’ll always see the same speed.
This is wild to think about. If you’re traveling at 99% the speed of light and turn on a flashlight, the beam will race ahead of you at…exactly the speed of light, no more, no less. If you’re coming from the opposite direction, you’ll still also measure the exact same speed.
This constancy forms the basis of Einstein’s special theory of relativity, which tells us that while all motion is relative – different observers won’t always agree on the length of measurements or the duration of events – some things are truly universal, like the speed of light.
Can you go faster than light speed?
Nope. Nothing can. Any particle with zero mass must travel at light speed. But anything with mass (which is most of the universe) cannot. The problem is relativity. The faster you go, the more energy you have. But we know from Einstein’s relativity that energy and mass are the same thing. So the more energy you have, the more mass you have, which makes it harder for you to go even faster. You can get as close as you want to the speed of light, but to actually crack that barrier takes an infinite amount of energy. So don’t even try.
How is the speed at which light travels related to causality?
If you think you can find a cheat to get around the limitations of light speed, then I need to tell you about its role in special relativity. You see, it’s not just about light. It just so happens that light travels at this special speed, and it was the first thing we discovered to travel at this speed. So it could have had another name. Indeed, a better name for this speed might be “the speed of time.”
Related: Is time travel possible? An astrophysicist explains
We live in a universe of causes and effects. All effects are preceded by a cause, and all causes lead to effects. The speed of light limits how quickly causes can lead to effects. Because it’s a maximum speed limit for any motion or interaction, in a given amount of time there’s a limit to what I can influence. If I want to tap you on the shoulder and you’re right next to me, I can do it right away. But if you’re on the other side of the planet, I have to travel there first. The motion of me traveling to you is limited by the speed of light, so that sets how quickly I can tap you on the shoulder – the speed light travels dictates how quickly a single cause can create an effect.
The ability to go faster than light would allow effects to happen before their causes. In essence, time travel into the past would be possible with faster-than-light travel. Since we view time as the unbroken chain of causes and effects going from the past to the future, breaking the speed of light would break causality, which would seriously undermine our sense of the forward motion of time.
Why does light travel at this speed?
No clue. It appears to us as a fundamental constant of nature. We have no theory of physics that explains its existence or why it has the value that it does. We hope that a future understanding of nature will provide this explanation, but right now all investigations are purely theoretical. For now, we just have to take it as a given.

Earth gets a new mini moon this weekend

Short-lived organics on Ceres hint at a past ocean — and conditions ripe for life

Early galaxies may be smaller than initially thought

BlackHoleFinder invites you to discover new black holes

Nuclear bombs really could deflect asteroids, lab tests suggest

Why weren’t astronomers sure that supermassive black holes could merge?

Traces of Earth’s earliest atmosphere could be buried on the Moon
![light speed travel time Albireo (Beta [β] Cygni) is a classic example of a double star with contrasting colors.](https://www.astronomy.com/uploads/2024/08/Albireo.jpg)
What gives stars their colors?

Black hole caught blasting jets out into the cosmic void
- Newsletters
Would you really age more slowly on a spaceship at close to light speed?
- Neel V. Patel archive page

Every week, the readers of our space newsletter, The Airlock , send in their questions for space reporter Neel V. Patel to answer. This week: time dilation during space travel.
I heard that time dilation affects high-speed space travel and I am wondering the magnitude of that affect. If we were to launch a round-trip flight to a nearby exoplanet—let's say 10 or 50 light-years away––how would that affect time for humans on the spaceship versus humans on Earth? When the space travelers came back, will they be much younger or older relative to people who stayed on Earth? —Serge
Time dilation is a concept that pops up in lots of sci-fi, including Orson Scott Card’s Ender’s Game , where one character ages only eight years in space while 50 years pass on Earth. This is precisely the scenario outlined in the famous thought experiment the Twin Paradox : an astronaut with an identical twin at mission control makes a journey into space on a high-speed rocket and returns home to find that the twin has aged faster.
Time dilation goes back to Einstein’s theory of special relativity, which teaches us that motion through space actually creates alterations in the flow of time. The faster you move through the three dimensions that define physical space, the more slowly you’re moving through the fourth dimension, time––at least relative to another object. Time is measured differently for the twin who moved through space and the twin who stayed on Earth. The clock in motion will tick more slowly than the clocks we’re watching on Earth. If you’re able to travel near the speed of light, the effects are much more pronounced.
Unlike the Twin Paradox, time dilation isn’t a thought experiment or a hypothetical concept––it’s real. The 1971 Hafele-Keating experiments proved as much, when two atomic clocks were flown on planes traveling in opposite directions. The relative motion actually had a measurable impact and created a time difference between the two clocks. This has also been confirmed in other physics experiments (e.g., fast-moving muon particles take longer to decay ).
So in your question, an astronaut returning from a space journey at “relativistic speeds” (where the effects of relativity start to manifest—generally at least one-tenth the speed of light ) would, upon return, be younger than same-age friends and family who stayed on Earth. Exactly how much younger depends on exactly how fast the spacecraft had been moving and accelerating, so it’s not something we can readily answer. But if you’re trying to reach an exoplanet 10 to 50 light-years away and still make it home before you yourself die of old age, you’d have to be moving at close to light speed.
There’s another wrinkle here worth mentioning: time dilation as a result of gravitational effects. You might have seen Christopher Nolan’s movie Interstellar , where the close proximity of a black hole causes time on another planet to slow down tremendously (one hour on that planet is seven Earth years).
This form of time dilation is also real, and it’s because in Einstein’s theory of general relativity, gravity can bend spacetime, and therefore time itself. The closer the clock is to the source of gravitation, the slower time passes; the farther away the clock is from gravity, the faster time will pass. (We can save the details of that explanation for a future Airlock.)
Keep Reading
Most popular.

Why OpenAI’s new model is such a big deal
The bulk of LLM progress until now has been language-driven. This new model enters the realm of complex reasoning, with implications for physics, coding, and more.
- James O'Donnell archive page

A controversial Chinese CRISPR scientist is still hopeful about embryo gene editing. Here’s why.
He Jiankui, who went to prison for three years for making the world’s first gene-edited babies, talked to MIT Technology Review about his new research plans.
- Zeyi Yang archive page

Meet the radio-obsessed civilian shaping Ukraine’s drone defense
Since Russia’s invasion, Serhii “Flash” Beskrestnov has become an influential, if sometimes controversial, force—sharing expert advice and intel on the ever-evolving technology that’s taken over the skies. His work may determine the future of Ukraine, and wars far beyond it.
- Charlie Metcalfe archive page

Two Nobel Prize winners want to cancel their own CRISPR patents in Europe
There’s a surprise twist in the battle to control genome editing.
- Antonio Regalado archive page
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from mit technology review.
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.
Thank you for submitting your email!
It looks like something went wrong.
We’re having trouble saving your preferences. Try refreshing this page and updating them one more time. If you continue to get this message, reach out to us at [email protected] with a list of newsletters you’d like to receive.

- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- Science Experiments for Kids
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
What Is the Speed of Light?

The speed of light is the rate at which light travels. The speed of light in a vacuum is a constant value that is denoted by the letter c and is defined as exactly 299,792,458 meters per second. Visible light , other electromagnetic radiation, gravity waves, and other massless particles travel at c. Matter , which has mass, can approach the speed of light, but never reach it.
Value for the Speed of Light in Different Units
Here are values for the speed of light in various units:
- 299,792,458 meters per second ( exact number )
- 299,792 kilometers per second (rounded)
- 3×10 8 m/s (rounded)
- 186,000 miles per second (rounded)
- 671,000,000 miles per hour (rounded)
- 1,080,000,000 kilometers per hour (rounded)
Is the Speed of Light Really Constant?
The speed of light in a vacuum is a constant. However, scientists are exploring whether the speed of light has changed over time.
Also, the rate at which light travels changes as it passes through a medium. The index of refraction describes this change. For example, the index of refraction of water is 1.333, which means light travels 1.333 times slower in water than in a vacuum. The index of refraction of a diamond is 2.417. A diamond slows the speed of light by more than half its speed in a vacuum.
How to Measure the Speed of Light
One way of measuring the speed of light uses great distances, such as distant points on the Earth or known distances between the Earth and astronomical objects. For example, you can measure the speed of light by measuring the time it takes for light to travel from a light source to a distant mirror and back again. The other way of measuring the speed of light is solving for c in equations. Now that the speed of light is defined, it is fixed rather than measured. Measuring the speed of light today indirectly measures the length of the meter, rather than c .
In 1676, Danish astronomer Ole Rømer discovered light travels at a speed by studying the movement of Jupiter’s moon Io. Prior to this, it seemed light propagated instantaneously. For example, you see a lightning strike immediately, but don’t hear thunder until after the event . So, Rømer’s finding showed light takes time to travel, but scientists did not know the speed of light or whether it was constant. In 1865, James Clerk Maxwell proposed that light was an electromagnetic wave that travelled at a speed c . Albert Einstein suggested c was a constant and that it did not change according to the frame of reference of the observer or any motion of a light source. In other words, Einstein suggested the speed of light is invariant . Since then, numerous experiments have verified the invariance of c .
Is It Possible to Go Faster Than Light?
The upper speed limit for massless particles is c . Objects that have mass cannot travel at the speed of light or exceed it. Among other reasons, traveling at c gives an object a length of zero and infinite mass. Accelerating a mass to the speed of light requires infinite energy. Furthermore, energy, signals, and individual photos cannot travel faster than c . At first glance, quantum entanglement appears to transmit information faster than c . When two particles are entangled, changing the state of one particle instantaneously determines the state of the other particle, regardless of the distance between them. But, information cannot be transmitted instantaneously (faster than c ) because it isn’t possible to control the initial quantum state of the particle when it is observed.
However, faster-than-light speeds appear in physics. For example, the phase velocity of x-rays through glass often exceeds c. However, the information isn’t conveyed by the waves faster than the speed of light. Distant galaxies appear to move away from Earth faster than the speed of light (outside a distance called the Hubble sphere), but the motion isn’t due to the galaxies traveling through space. Instead, space itself it expanding. So again, no actual movement faster than c occurs.
While it isn’t possible to go faster than the speed of light, it doesn’t necessarily mean warp drive or other faster-than-light travel is impossible. The key to going faster than the speed of light is to change space-time. Ways this might happen include tunneling using wormholes or stretching space-time into a “warp bubble” around a spacecraft. But, so far these theories don’t have practical applications.
- Brillouin, L. (1960). Wave Propagation and Group Velocity. Academic Press.
- Ellis, G.F.R.; Uzan, J.-P. (2005). “‘c’ is the speed of light, isn’t it?”. American Journal of Physics . 73 (3): 240–27. doi: 10.1119/1.1819929
- Helmcke, J.; Riehle, F. (2001). “Physics behind the definition of the meter”. In Quinn, T.J.; Leschiutta, S.; Tavella, P. (eds.). Recent advances in metrology and fundamental constants . IOS Press. p. 453. ISBN 978-1-58603-167-1.
- Newcomb, S. (1886). “The Velocity of Light”. Nature . 34 (863): 29–32. doi: 10.1038/034029c0
- Uzan, J.-P. (2003). “The fundamental constants and their variation: observational status and theoretical motivations”. Reviews of Modern Physics . 75 (2): 403. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.75.403
Related Posts

Why is the speed of light the way it is?
It's just plain weird.

Paul M. Sutter is an astrophysicist at SUNY Stony Brook and the Flatiron Institute, host of Ask a Spaceman and Space Radio , and author of " How to Die in Space ." He contributed this article to Space.com's Expert Voices: Op-Ed & Insights .
We all know and love the speed of light — 299,792,458 meters per second — but why does it have the value that it does? Why isn't it some other number? And why do we care so much about some random speed of electromagnetic waves? Why did it become such a cornerstone of physics?
Well, it's because the speed of light is just plain weird.
Related: Constant speed of light: Einstein's special relativity survives a high-energy test
Putting light to the test
The first person to realize that light does indeed have a speed at all was an astronomer by the name of Ole Romer. In the late 1600s, he was obsessed with some strange motions of the moon Io around Jupiter. Every once in a while, the great planet would block our view of its little moon, causing an eclipse, but the timing between eclipses seemed to change over the course of the year. Either something funky was happening with the orbit of Io — which seemed suspicious — or something else was afoot.
After a couple years of observations, Romer made the connection. When we see Io get eclipsed, we're in a certain position in our own orbit around the sun. But by the next time we see another eclipse, a few days later, we're in a slightly different position, maybe closer or farther away from Jupiter than the last time. If we are farther away than the last time we saw an eclipse, then that means we have to wait a little bit of extra time to see the next one because it takes that much longer for the light to reach us, and the reverse is true if we happen to be a little bit closer to Jupiter.
The only way to explain the variations in the timing of eclipses of Io is if light has a finite speed.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Making it mean something
Continued measurements over the course of the next few centuries solidified the measurement of the speed of light, but it wasn't until the mid-1800s when things really started to come together. That's when the physicist James Clerk Maxwell accidentally invented light.
Maxwell had been playing around with the then-poorly-understood phenomena of electricity and magnetism when he discovered a single unified picture that could explain all the disparate observations. Laying the groundwork for what we now understand to be the electromagnetic force , in those equations he discovered that changing electric fields can create magnetic fields, and vice versa. This allows waves of electricity to create waves of magnetism, which go on to make waves of electricity and back and forth and back and forth, leapfrogging over each other, capable of traveling through space.
And when he went to calculate the speed of these so-called electromagnetic waves, Maxwell got the same number that scientists had been measuring as the speed of light for centuries. Ergo, light is made of electromagnetic waves and it travels at that speed, because that is exactly how quickly waves of electricity and magnetism travel through space.
And this was all well and good until Einstein came along a few decades later and realized that the speed of light had nothing to do with light at all. With his special theory of relativity , Einstein realized the true connection between time and space, a unified fabric known as space-time. But as we all know, space is very different than time. A meter or a foot is very different than a second or a year. They appear to be two completely different things.
So how could they possibly be on the same footing?
There needed to be some sort of glue, some connection that allowed us to translate between movement in space and movement in time. In other words, we need to know how much one meter of space, for example, is worth in time. What's the exchange rate? Einstein found that there was a single constant, a certain speed, that could tell us how much space was equivalent to how much time, and vice versa.
Einstein's theories didn't say what that number was, but then he applied special relativity to the old equations of Maxwell and found that this conversion rate is exactly the speed of light.
Of course, this conversion rate, this fundamental constant that unifies space and time, doesn't know what an electromagnetic wave is, and it doesn't even really care. It's just some number, but it turns out that Maxwell had already calculated this number and discovered it without even knowing it. That's because all massless particles are able to travel at this speed, and since light is massless, it can travel at that speed. And so, the speed of light became an important cornerstone of modern physics.
But still, why that number, with that value, and not some other random number? Why did nature pick that one and no other? What's going on?
Related: The genius of Albert Einstein: his life, theories and impact on science

Making it meaningless
Well, the number doesn't really matter. It has units after all: meters per second. And in physics any number that has units attached to it can have any old value it wants, because it means you have to define what the units are. For example, in order to express the speed of light in meters per second, first you need to decide what the heck a meter is and what the heck a second is. And so the definition of the speed of light is tied up with the definitions of length and time.
In physics, we're more concerned with constants that have no units or dimensions — in other words, constants that appear in our physical theories that are just plain numbers. These appear much more fundamental, because they don't depend on any other definition. Another way of saying it is that, if we were to meet some alien civilization , we would have no way of understanding their measurement of the speed of light, but when it comes to dimensionless constants, we can all agree. They're just numbers.
One such number is known as the fine structure constant, which is a combination of the speed of light, Planck's constant , and something known as the permittivity of free space. Its value is approximately 0.007. 0.007 what? Just 0.007. Like I said, it's just a number.
So on one hand, the speed of light can be whatever it wants to be, because it has units and we need to define the units. But on the other hand, the speed of light can't be anything other than exactly what it is, because if you were to change the speed of light, you would change the fine structure constant. But our universe has chosen the fine structure constant to be approximately 0.007, and nothing else. That is simply the universe we live in, and we get no choice about it at all. And since this is fixed and universal, the speed of light has to be exactly what it is.
So why is the fine structure constant exactly the number that it is, and not something else? Good question. We don't know.
Learn more by listening to the episode "Why is the speed of light the way it is?" on the Ask A Spaceman podcast, available on iTunes and on the Web at http://www.askaspaceman.com. Thanks to Robert H, Michael E., @DesRon94, Evan W., Harry A., @twdixon, Hein P., Colin E., and Lothian53 for the questions that led to this piece! Ask your own question on Twitter using #AskASpaceman or by following Paul @PaulMattSutter and facebook.com/PaulMattSutter.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
Paul M. Sutter is an astrophysicist at SUNY Stony Brook and the Flatiron Institute in New York City. Paul received his PhD in Physics from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign in 2011, and spent three years at the Paris Institute of Astrophysics, followed by a research fellowship in Trieste, Italy, His research focuses on many diverse topics, from the emptiest regions of the universe to the earliest moments of the Big Bang to the hunt for the first stars. As an "Agent to the Stars," Paul has passionately engaged the public in science outreach for several years. He is the host of the popular "Ask a Spaceman!" podcast, author of "Your Place in the Universe" and "How to Die in Space" and he frequently appears on TV — including on The Weather Channel, for which he serves as Official Space Specialist.
Hubble Space Telescope spies a spiral galaxy in a cosmic 'clock'
The W boson caused a particle mystery — but scientists have cracked the case
SpaceX, NASA 'go' for 1st astronaut launch to ISS from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station pad
- voidpotentialenergy This is just my opinion but i think L speed is it's speed because the particle part of it is the fastest it can interact with the quanta distance in quantum fluctuation. Light is particle and wave so the wave happens in the void between quanta. Gravity probably travels in that void and why gravity seems instant. Reply
- rod The space.com article wraps up the discussion with, "So on one hand, the speed of light can be whatever it wants to be, because it has units and we need to define the units. But on the other hand, the speed of light can't be anything other than exactly what it is, because if you were to change the speed of light, you would change the fine structure constant. But our universe has chosen the fine structure constant to be approximately 0.007, and nothing else. That is simply the universe we live in, and we get no choice about it at all. And since this is fixed and universal, the speed of light has to be exactly what it is. So why is the fine structure constant exactly the number that it is, and not something else? Good question. We don't know." It seems that the *universe* made this decision, *But our universe has chosen the fine structure constant to be...* I did not know that the universe was capable of making decisions concerning constants used in physics. E=mc^2 is a serious constant. Look at nuclear weapons development, explosive yields, and stellar evolution burn rates for p-p chain and CNO fusion rates. The report indicates why alpha (fine structure constant) is what it is and c is what it is, *We don't know*. Reply
Admin said: We all know and love the speed of light, but why does it have the value that it does? Why isn't it some other number? And why did it become such a cornerstone of physics? Why is the speed of light the way it is? : Read more
rod said: The space.com article wraps up the discussion with, "So on one hand, the speed of light can be whatever it wants to be, because it has units and we need to define the units. But on the other hand, the speed of light can't be anything other than exactly what it is, because if you were to change the speed of light, you would change the fine structure constant. But our universe has chosen the fine structure constant to be approximately 0.007, and nothing else. That is simply the universe we live in, and we get no choice about it at all. And since this is fixed and universal, the speed of light has to be exactly what it is. So why is the fine structure constant exactly the number that it is, and not something else? Good question. We don't know." It seems that the *universe* made this decision, *But our universe has chosen the fine structure constant to be...* I did not know that the universe was capable of making decisions concerning constants used in physics. E=mc^2 is a serious constant. Look at nuclear weapons development, explosive yields, and stellar evolution burn rates for p-p chain and CNO fusion rates. The report indicates why alpha (fine structure constant) is what it is and c is what it is, *We don't know*.
- rod FYI. When someone says *the universe has chosen*, I am reminded of these five lessons from a 1982 Fed. court trial. The essential characteristics of science are: It is guided by natural law; It has to be explanatory by reference to natural law; It is testable against the empirical world; Its conclusions are tentative, i.e., are not necessarily the final word; and It is falsifiable. Five important points about science. Reply
- Gary If the universe is expanding , how can the speed of light be constant ( miles per second , if each mile is getting longer ) ? Can light's velocity be constant while the universe expands ? So, with the expansion of the universe , doesn't the speed of light need to increase in order to stay at a constant velocity in miles per second ? Or, do the miles in the universe remain the same length as the universe 'adds' miles to its diameter ? Are the miles lengthening or are they simply being added / compounded ? Reply
- Gary Lets say we're in outer space and we shoot a laser through a block of glass. What causes the speed of the laser light to return to the speed it held prior to entering the block of glass ? Is there some medium in the vacuum of space that governs the speed of light ? Do the atoms in the glass push it back up to its original speed. If so, why don't those same atoms constantly push the light while it travels through the block of glass ? Reply
Gary said: Lets say we're in outer space and we shoot a laser through a block of glass. What causes the speed of the laser light to return to the speed it held prior to entering the block of glass ? Is there some medium in the vacuum of space that governs the speed of light ? Do the atoms in the glass push it back up to its original speed. If so, why don't those same atoms constantly push the light while it travels through the block of glass ?
Gary said: If the universe is expanding , how can the speed of light be constant ( miles per second , if each mile is getting longer ) ? Can light's velocity be constant while the universe expands ? So, with the expansion of the universe , doesn't the speed of light need to increase in order to stay at a constant velocity in miles per second ? Or, do the miles in the universe remain the same length as the universe 'adds' miles to its diameter ? Are the miles lengthening or are they simply being added / compounded ?
- View All 31 Comments
Most Popular
- 2 Watch spectacular Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS rise during the early hours of Sept. 28 with this free livestream
- 3 Lego Ideas submissions Lunar Landscape, Space Projection Telescope and Voyager 1's Pale Blue Dot need to be made into real sets
- 4 Chinese rocket launches 8 satellites to orbit from ship at sea (video, photos)
- 5 China's CAS Space launches 5 satellites with its 4th rocket (video)
What is the speed of light?
Light is faster than anything else in the known universe, though its speed can change depending on what it's passing through.

The universe has a speed limit, and it's the speed of light. Nothing can travel faster than light — not even our best spacecraft — according to the laws of physics.
So, what is the speed of light?
Light moves at an incredible 186,000 miles per second (300,000 kilometers per second), equivalent to almost 700 million mph (more than 1 billion km/h). That's fast enough to circumnavigate the globe 7.5 times in one second, while a typical passenger jet would take more than two days to go around once (and that doesn't include stops for fuel or layovers!).
Light moves so fast that, for much of human history, we thought it traveled instantaneously. As early as the late 1600s, though, scientist Ole Roemer was able to measure the speed of light (usually referred to as c ) by using observations of Jupiter's moons, according to Britannica .
Around the turn of the 19th century, physicist James Clerk Maxwell created his theories of electromagnetism . Light is itself made up of electric and magnetic fields, so electromagnetism could describe the behavior and motion of light — including its theoretical speed. That value was 299,788 kilometers per second, with a margin of error of plus or minus 30. In the 1970s, physicists used lasers to measure the speed of light with much greater precision, leaving an error of only 0.001. Nowadays, the speed of light is used to define units of length, so its value is fixed; humans have essentially agreed the speed of light is 299,792.458 kilometers per second, exactly.
Light doesn't always have to go so fast, though. Depending on what it's traveling through — air, water, diamonds, etc. — it can slow down. The official speed of light is measured as if it's traveling in a vacuum, a space with no air or anything to get in the way. You can most clearly see differences in the speed of light in something like a prism, where certain energies of light bend more than others, creating a rainbow.
— How many moons does Earth have ?
— What would happen if the moon were twice as close to Earth?
— If you're on the moon, does the Earth appear to go through phases?
Interestingly, the speed of light is no match for the vast distances of space, which is itself a vacuum. It takes 8 minutes for light from the sun to reach Earth, and a couple years for light from the other closest stars (like Proxima Centauri) to get to our planet. This is why astronomers use the unit light-years — the distance light can travel in one year — to measure vast distances in space.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Because of this universal speed limit, telescopes are essentially time machines . When astronomers look at a star 500 light-years away, they're looking at light from 500 years ago. Light from around 13 billion light-years away (equivalently, 13 billion years ago) shows up as the cosmic microwave background, remnant radiation from the Big Bang in the universe's infancy. The speed of light isn't just a quirk of physics; it has enabled modern astronomy as we know it, and it shapes the way we see the world — literally.
Briley Lewis (she/her) is a freelance science writer and Ph.D. Candidate/NSF Fellow at the University of California, Los Angeles studying Astronomy & Astrophysics. Follow her on Twitter @briles_34 or visit her website www.briley-lewis.com .
The James Webb telescope has brought cosmology to a tipping point. Will it soon reveal new physics?
One of the universe's biggest paradoxes could be even weirder than we thought, James Webb telescope study reveals
'We have changed the view of our galaxy forever': Astronomers capture most detailed ever infrared map of the Milky Way
Most Popular
- 2 Watch extremely rare footage of a bigfin squid 'walking' on long, spindly arms deep in the South Pacific
- 3 'The secret to living to 110 was, don't register your death': Ig Nobel winner Saul Justin Newman on the flawed data on extreme aging
- 4 New self-swab HPV test is an alternative to Pap smears. Here's how it works.
- 5 Nuking an asteroid could save Earth from destruction, researchers show in 1st-of-its-kind X-ray experiment
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Manage Your Subscription
- Give a Gift Subscription
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
- Space Travel + Astronomy
Here's What Actually Happens When You Travel at the Speed of Light, According to NASA
NASA created a fun video to answer all of our burning questions about near-light-speed travel.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Stacey-Leasca-2000-631fabdcfe624115bea0ce8e25fdec96.jpg)
Ever wish you could travel at the speed of light to your favorite destinations ? Once you see the reality of that speed, you may rethink everything.
"There are some important things you should probably know about approaching the speed of light," NASA's video, Guide to Near-light-speed Travel , explains. "First, a lot of weird things can happen, like time and space getting all bent out of shape."
According to the video, if you're traveling at nearly the speed of light, the clock inside your rocket would show it takes less time to travel to your destination than it would on Earth. But, since the clocks at home would be moving at a standard rate you'd return home to everyone else being quite a bit older.
"Also, because you're going so fast, what would otherwise be just a few hydrogen atoms that you'd run into quickly becomes a lot of dangerous particles. So you should probably have shields that keep them from frying your ship and also you."
Finally, the video tackles the fact that even if you were moving at the speed of light, the "universe is also a very big place, so you might be in for some surprises." For example, your rocket's clock will say it takes about nine months to get from Earth to the edge of the solar system. An Earth clock would say it took about a year and a half. Fortunately, NASA astronauts have a slew of tips for avoiding jet lag along the way.
"If you want to get to farther out vacation spots," the video explains, "you'll probably need more than a few extra snacks. A trip to the Andromeda Galaxy, our nearest large neighbor galaxy, can take over one million years. And a trip to the farthest known galaxy where it currently sits might take over 15 billion years, which is more vacation time than I think I'll ever have."
The video doesn't explain how your rocket will travel at the speed of light. Our technology just isn't there yet, but maybe the aliens will share that tech with us soon. Until then, you can track the first crew launch of Artemis II , a rocket that will fly around the moon in 2024 before making its first lunar landing in 2025.
Related Articles

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.

NASA Invites Public to Join as Virtual Guests for SpaceX Crew-9 Launch
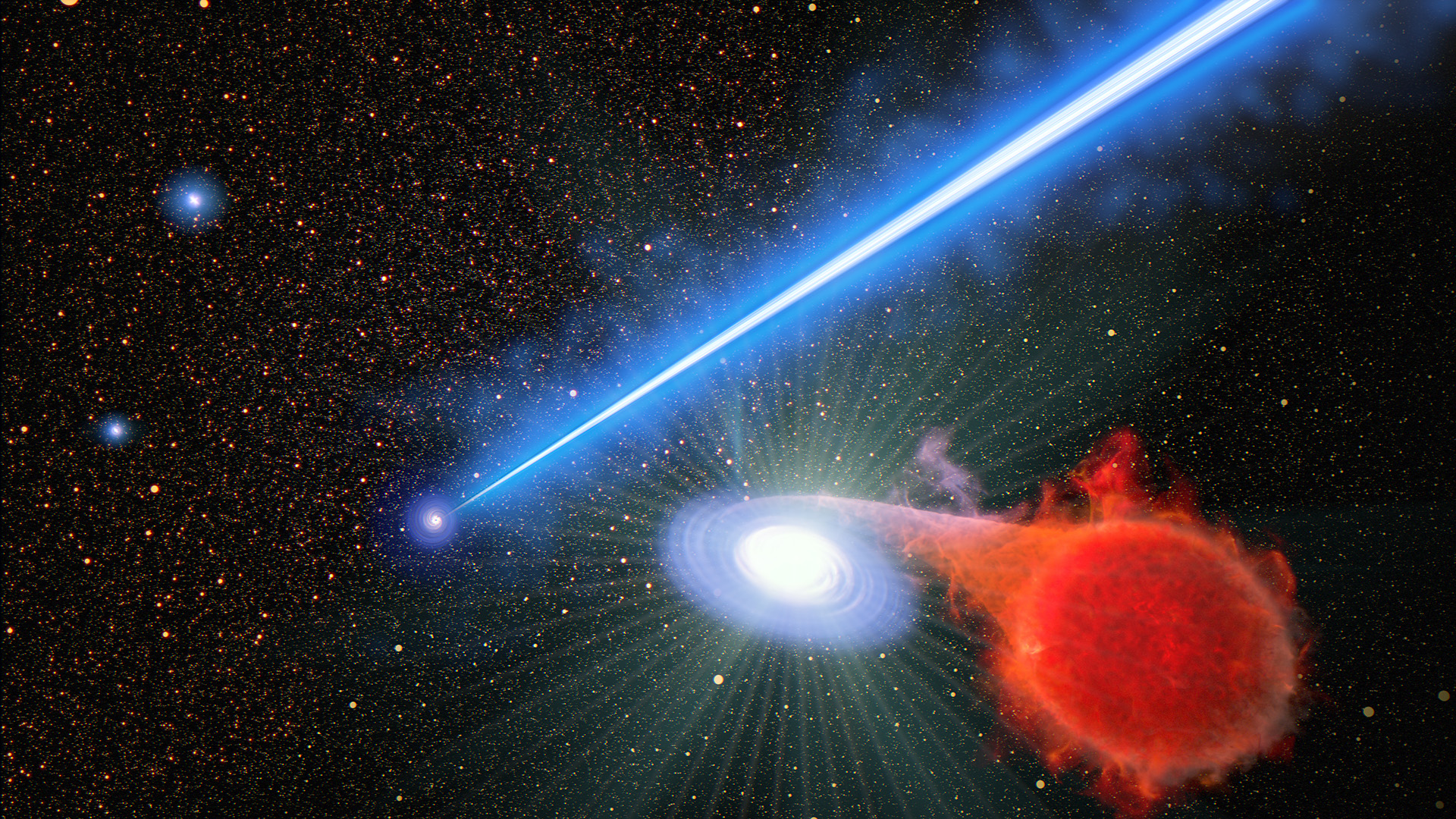
NASA’s Hubble Finds that a Black Hole Beam Promotes Stellar Eruptions

What’s Up: September 2024 Skywatching Tips from NASA
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
NASA en Español
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Guest Program
- Image of the Day
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

Hubble Captures Stellar Nurseries in a Majestic Spiral
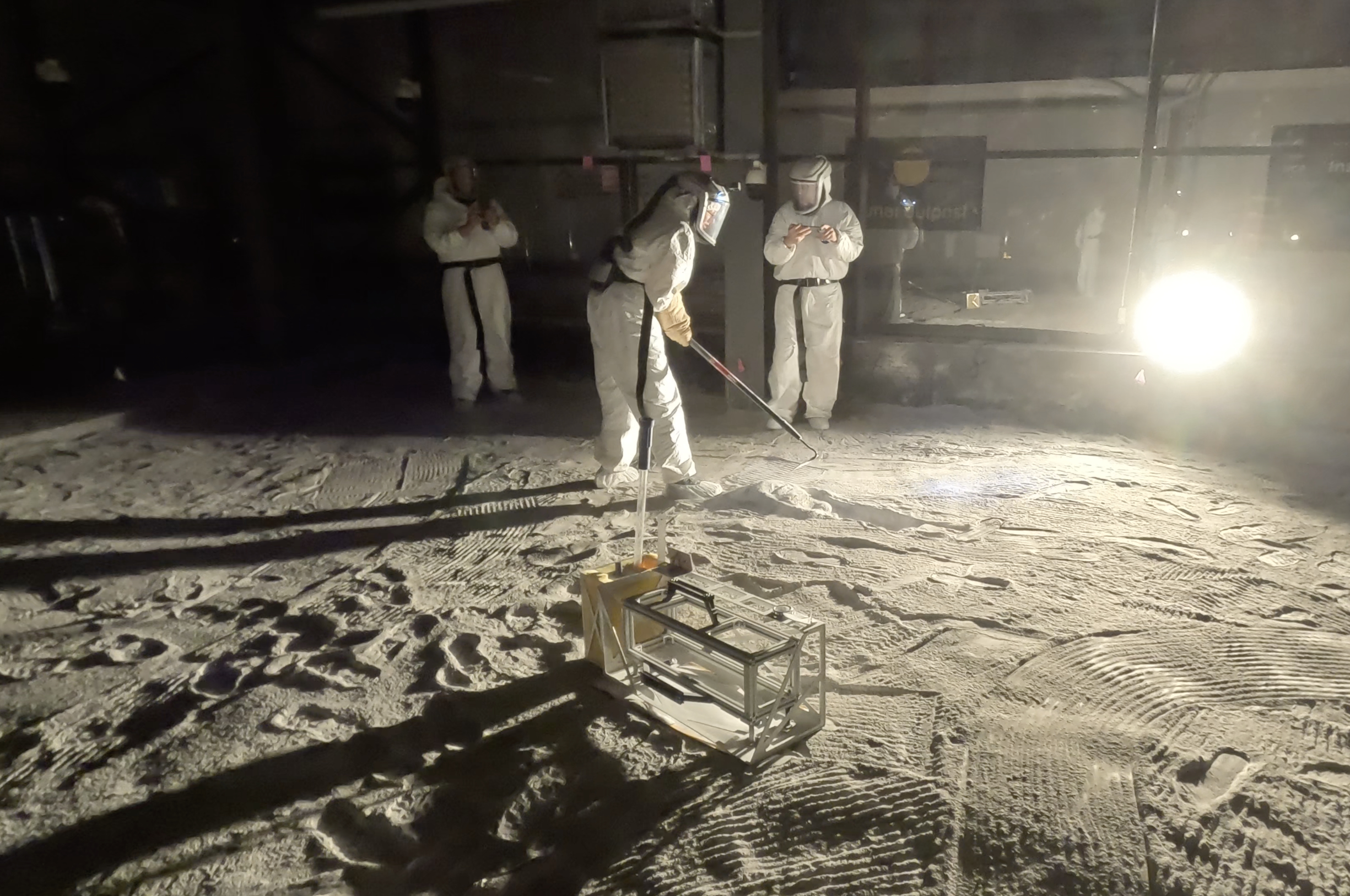

NASA’s Artemis Science Instrument Gets Tested in Moon-Like Sandbox

NASA’s BioSentinel Studies Solar Radiation as Earth Watches Aurora
Educational activities in space.

NASA Astronaut Tracy C. Dyson’s Scientific Mission aboard Space Station

Amendment 55: F.20 MOSAICS Seed Funding Winter 2025 review Cut-Off Date Extended.

NASA’s Eyes for Museums

NASA Analysis Shows Irreversible Sea Level Rise for Pacific Islands

How NASA Uses and Improves Solar Power

Backyard Worlds: Cool Neighbors

Amendment 56: A.24 Weather and Atmospheric Dynamics NURTURE Campaign Schedule Change
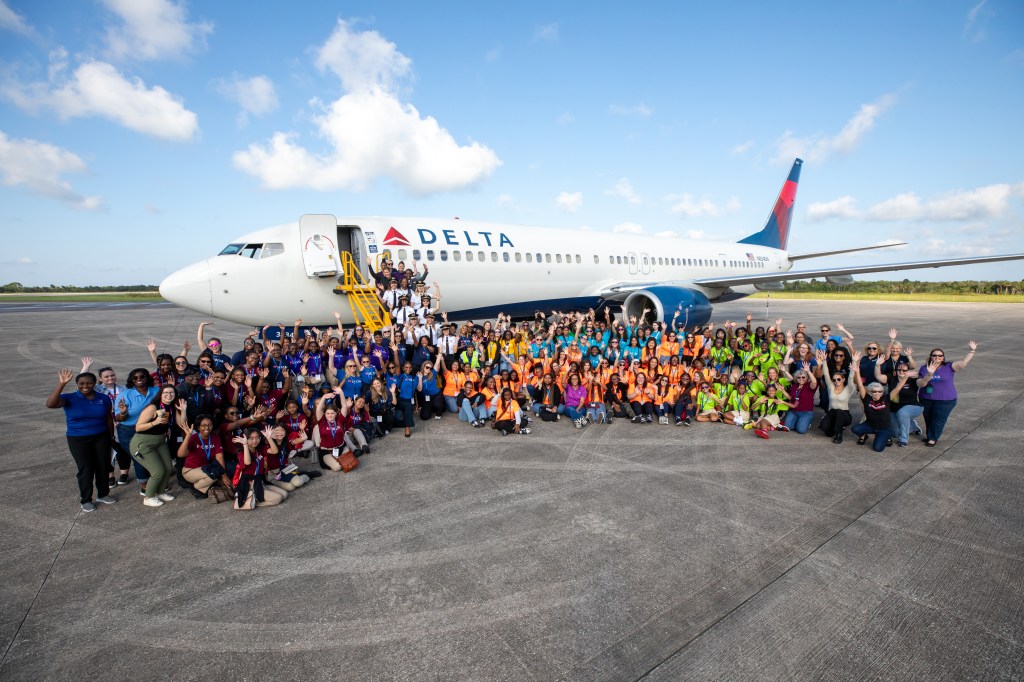

Girls in STEM Inspired to Fly High at NASA Kennedy

ARMD Solicitations

Students Soar at NASA Glenn’s Aviation Day

The Science of the Perfect Cup for Coffee

NASA’s Record-Breaking Laser Demo Completes Mission

Amendment 52: B.9 Low-Cost Access to Space 2028 Peruvian campaign Update

NASA Moon to Mars Architecture Art Challenge

Bring NASA Into Your Classroom This Fall Through Virtual Experiences

How Do I Navigate NASA Learning Resources and Opportunities?

Getting SSPICY: NASA Funds Orbital Debris Inspection Mission

NASA Relaunches Art Program with Space-Themed Murals

La NASA invita a los medios al lanzamiento de Europa Clipper

El X-59 de la NASA avanza en las pruebas de preparación para volar

La NASA invita a creadores de las redes sociales al lanzamiento de la misión Europa Clipper
How to travel at (nearly) the speed of light.

One hundred years ago, on May 29, 1919, measurements of a solar eclipse offered proof for Einstein’s theory of general relativity. Even before that, Einstein had developed the theory of special relativity, which revolutionized the way we understand light. To this day, it provides guidance on understanding how particles move through space — a key area of research to keep spacecraft and astronauts safe from radiation.
The theory of special relativity showed that particles of light, photons, travel through a vacuum at a constant pace of 670,616,629 miles per hour — a speed that’s immensely difficult to achieve and impossible to surpass in that environment. Yet all across space, from black holes to our near-Earth environment, particles are, in fact, being accelerated to incredible speeds, some even reaching 99.9% the speed of light.
Scientists suspect magnetic reconnection is one way that particles are accelerated to nearly light speed. This illustration depicts the magnetic fields around Earth, which snap and realign, causing charged particles to be flung away at high speeds. Find out all three ways that this acceleration happens .
Image Credit: NASA
Learn About the True Speed of Light and How It's Used
Roberto Moiola/Sysaworld/Getty Images
- An Introduction to Astronomy
- Important Astronomers
- Solar System
- Stars, Planets, and Galaxies
- Space Exploration
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Physics and Astronomy, Purdue University
- B.S., Physics, Purdue University
Light moves through the universe at the fastest speed astronomers can measure. In fact, the speed of light is a cosmic speed limit, and nothing is known to move faster. How fast does light move? This limit can be measured and it also helps define our understanding of the universe's size and age.
What Is Light: Wave or Particle?
Light travels fast, at a velocity of 299, 792, 458 meters per second. How can it do this? To understand that, it's helpful to know what light actually is and that's largely a 20th-century discovery.
The nature of light was a great mystery for centuries. Scientists had trouble grasping the concept of its wave and particle nature. If it was a wave what did it propagate through? Why did it appear to travel at the same speed in all directions? And, what can the speed of light tell us about the cosmos? It wasn't until Albert Einstein described this theory of special relativity in 1905 it all came into focus. Einstein argued that space and time were relative and that the speed of light was the constant that connected the two.
What Is the Speed of Light?
It is often stated that the speed of light is constant and that nothing can travel faster than the speed of light. This isn't entirely accurate. The value of 299,792,458 meters per second (186,282 miles per second) is the speed of light in a vacuum. However, light actually slows down as it passes through different media. For instance, when it moves through glass, it slows down to about two-thirds of its speed in a vacuum. Even in air, which is nearly a vacuum, light slows down slightly. As it moves through space, it encounters clouds of gas and dust, as well as gravitational fields, and those can change the speed a tiny bit. The clouds of gas and dust also absorb some of the light as it passes through.
This phenomenon has to do with the nature of light, which is an electromagnetic wave. As it propagates through a material its electric and magnetic fields "disturb" the charged particles that it comes in contact with. These disturbances then cause the particles to radiate light at the same frequency, but with a phase shift. The sum of all these waves produced by the "disturbances" will lead to an electromagnetic wave with the same frequency as the original light, but with a shorter wavelength and, hence a slower speed.
Interesting, as fast as light moves, its path can be bent as it passes by regions in space with intense gravitational fields. This is fairly easily seen in galaxy clusters, which contain a lot of matter (including dark matter), which warps the path of light from more distant objects, such as quasars.
Lightspeed and Gravitational Waves
Current theories of physics predict that gravitational waves also travel at the speed of light, but this is still being confirmed as scientists study the phenomenon of gravitational waves from colliding black holes and neutron stars. Otherwise, there are no other objects that travel that fast. Theoretically, they can get close to the speed of light, but not faster.
One exception to this may be space-time itself. It appears that distant galaxies are moving away from us faster than the speed of light. This is a "problem" that scientists are still trying to understand. However, one interesting consequence of this is that a travel system based on the idea of a warp drive . In such a technology, a spacecraft is at rest relative to space and it's actually space that moves, like a surfer riding a wave on the ocean. Theoretically, this might allow for superluminal travel. Of course, there are other practical and technological limitations that stand in the way, but it's an interesting science-fiction idea that is getting some scientific interest.
Travel Times for Light
One of the questions that astronomers get from members of the public is: "how long would it take light to go from object X to Object Y?" Light gives them a very accurate way to measure the size of the universe by defining distances. Here are a few of the common ones distance measurements:
- The Earth to the Moon : 1.255 seconds
- The Sun to Earth : 8.3 minutes
- Our Sun to the next closest star : 4.24 years
- Across our Milky Way galaxy : 100,000 years
- To the closest spiral galaxy (Andromeda) : 2.5 million years
- Limit of the observable universe to Earth : 13.8 billion years
Interestingly, there are objects that are beyond our ability to see simply because the universe IS expanding, and some are "over the horizon" beyond which we cannot see. They will never come into our view, no matter how fast their light travels. This is one of the fascinating effects of living in an expanding universe.
Edited by Carolyn Collins Petersen
- Learn about the Doppler Effect
- Alpha Centauri: Gateway to the Stars
- Radiation in Space Gives Clues about the Universe
- Time Travel: Dream or Possible Reality?
- What is Matter?
- What is Blueshift?
- The Composition of the Universe
- Cold Dark Matter
- How Redshift Shows the Universe is Expanding
- How Meteors Form and What They Are
- What are Rotation and Revolution?
- Explore Johannes Kepler's Laws of Motion
- What Is Luminosity?
- Deciphering Star Charts for Skygazing
- Astronomy 101 - Learning About Stars
- Can Humans Hear Sound in Space?

Scientists Believe Light Speed Travel Is Possible. Here’s How.
A functioning warp drive would allow humans to reach the far ends of the cosmos in the blink of an eye.
I n late 2020, physicist Harold “Sonny” White, PhD, research director of the nonprofit Limitless Space Institute , noticed something peculiar—and familiar—in a circular pattern of data plots generated by a recent experiment.
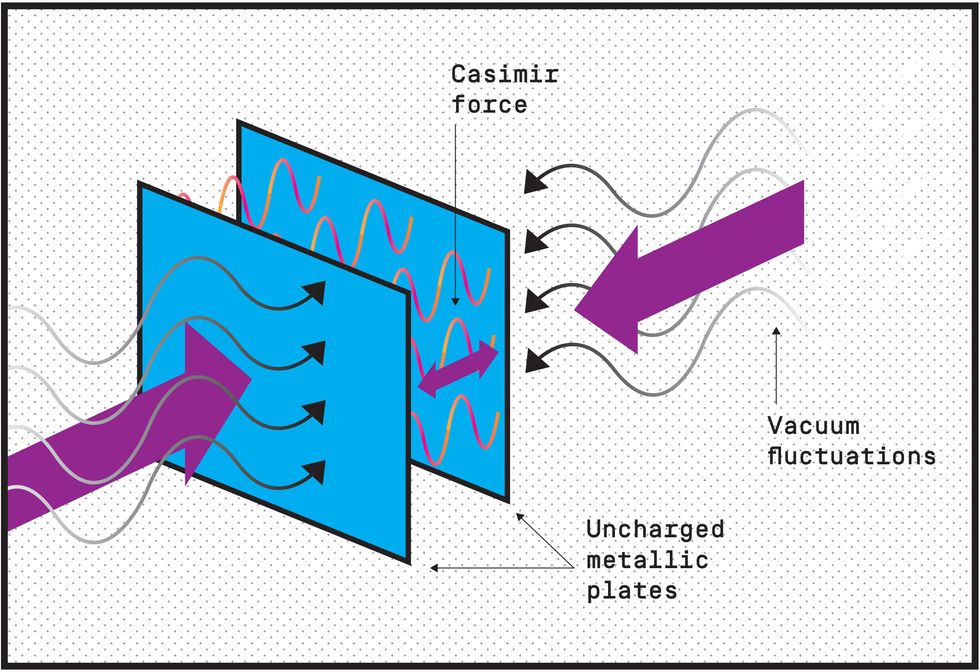
White and his team in LSI’s Houston laboratory were conducting research for the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, or DARPA, and had set up these particular experiments to study the energy densities within Casimir cavities, the mysterious spaces between microscopic metal plates in a vacuum. The data plot indicated areas of diminished energy between the plates, which caused them to push toward each other as if trying to fill the void. This is known as negative vacuum energy density, a phenomenon in quantum mechanics called, appropriately enough, the Casimir effect . It’s something that’s helping scientists understand the soupy physics of microscale structures, which some researchers hope can be applied to energy applications that are more practical, such as circuits and electromechanical systems.
But White noticed that the pattern of negative vacuum energy between the plates and around tiny cylindrical columns that they’d inserted in the space looked familiar. It precisely echoed the energy pattern generated by a type of exotic matter that some physicists believe could unlock high-speed interstellar travel. “We then looked, mathematically, at what happens if we placed a one-micron sphere inside of a four-micron cylinder under the same conditions, and found that this kind of structure could generate a little nanoscale warp bubble encapsulating that central region,” White explains.
That’s right—a warp bubble. The essential component of a heretofore fictional warp drive that has for decades been the obsession of physicists, engineers, and sci-fi fans. Warp drive, of course, is the stuff of Star Trek legend, a device enclosed within a spacecraft that gives the mortals aboard the ability to rip around the cosmos at superhuman speed. To the lay sci-fi fan, it’s a “black box”—a convenient, completely made-up workaround to avoid the harsh realities of interstellar travel. However, after decades of speculation, research, and experimentation, scientists believe a warp drive could actually work.
To emphasize: White didn’t actually make a warp bubble. But the data from his study led to an aha moment: For the first time, a buildable warp bubble showed promise of success.
Warp technology’s core science is surprisingly sound. Though the specific mechanics of an actual device haven’t been fully unpacked, the math points toward feasibility. In short, a real-life warp drive would use massive amounts of energy, which can come in the form of mass, to create enough gravitational pull to distort spacetime in a controlled fashion, allowing a ship to speed along inside a self-generated bubble that itself is able to travel at essentially any speed. Warp drives popped up in fiction intermittently for several decades before Star Trek creator Gene Roddenberry plugged one into the USS Enterprise in 1966. But Miguel Alcubierre, PhD, a Mexican theoretical physicist and professed Star Trek enthusiast, gave the idea real-world legs when he released a paper in 1994 speculating that such a drive was mathematically possible. It was the first serious treatment of a warp drive’s feasibility, and it made headlines around the world. His breakthrough inspired more scientists to nudge the theoretical aspects of warp drive toward concrete, practical applications.
“I proposed a ‘geometry’ for space that would allow faster-than-light travel as seen from far away, essentially expanding space behind the object we want to move and contracting it in front,” Alcubierre says. “This forms a ‘bubble’ of distorted space, inside of which an object—a spaceship, say—could reside.”
Physicists tend to speak in relative terms. By injecting the sly qualifier “as seen from far away,” Alcubierre might sound like he’s describing the galactic equivalent of an optical illusion —an effect perhaps similar to driving past a truck going the opposite direction on the highway when you’re both going 60 miles an hour. Sure feels like a buck-twenty, doesn’t it? But the A-to-B speed is real; the warp effect simply shortens the literal distance between two points. You’re not, strictly speaking, moving faster than light. Inside the bubble, all appears relatively normal, and light moves faster than you are, as it should. Outside the bubble, however, you’re haulin’ the mail.
THOUGH THE SPECIFIC MECHANICS OF AN ACTUAL DEVICE HAVEN’T BEEN UNPACKED, THE MATH POINTS TOWARD FEASIBILITY.
Alcubierre’s proposal had solved one of the initial hurdles to achieving warp speeds: The very idea clashes with Einstein’s long-accepted theory of general relativity, which states that nothing can travel faster than the speed of light, but it doesn’t preclude space itself from traveling faster than that. In fact, scientists speculate that the same principles explain the rapid expansion of the universe after the Big Bang .
While concluding that warp speed was indeed possible, Alcubierre also found that it would require an enormous amount of energy to sustain the warp bubble. He theorized that negative energy—the stuff hinted at by White’s experimentation with Casimir cavities—could be a solution. The only problem is that no one has yet proved that negative energy is real. It’s the unobtanium of our spacefaring imaginations, something researchers only believe to exist. In theory, however, this unknown matter may be sufficiently powerful that future warp drive designers could channel it to contract spacetime around it. In conceptual drawings of warp-capable spacecraft , enormous material rings containing this energy source surround a central fuselage. When activated, it warps spacetime around the entire ship. The more intense the warping, the faster the warp travel is achieved.
Of course, it’s not that simple. Physicist José Natário, PhD, a professor at the Instituto Superior Técnico in Lisbon, wrote his own influential paper about the mathematical feasibility of warp drives in 2001. However, he is concerned about practical conundrums, like the amount of energy required. “You need to be able to curve spacetime quite a lot in order to do this,” he says. “We’re talking about something that would be much, much more powerful than the sun.”
Alcubierre is similarly skeptical that his theoretical ideas might ever be used to develop a working warp drive. “In order to have a bubble about 100 meters wide traveling at precisely the speed of light, you would need about 100 times the mass of the planet Jupiter converted into negative energy, which of course sounds absurd,” he says. By that standard, he concludes, a warp drive is very unlikely.
Physicists love a challenge, though. In the 29 years since Alcubierre published his paper, other scientists have wrestled with the implications of the work, providing alternative approaches to generating the energy using more accessible power sources, finding oblique entry points to the problem, and batting ideas back and forth in response to one another’s papers. They use analogies involving trampolines , tablecloths, bowling balls, balloons, conveyor belts, and music to explain the physics.
They even have their own vocabulary. It’s not faster-than-light travel; it’s superluminal travel, thank you. Then there’s nonphysical and physical—a.k.a. the critical distinction between theoretical speculation and something that can actually be engineered. (Pro tip: We’re aiming for physical here, folks.) They do mention Star Trek a lot, but never Star Wars . Even the scruffiest-looking nerf herder knows that the ships in Star Wars use hyperdrive, which consumes fuel, rather than warp drives, which don’t use propulsive technology but instead rely on, well, warping. They’re also vague about details like what passengers would experience, what gravity is like on board since you’re carrying around boatloads of energy, and what would happen if someone, say, jumped out of the ship while warping. (A speculative guess: Nothing good.)
Such research isn’t typically funded by academic institutions or the DARPAs and NASAs of the world, so much of this work occurs in the scientists’ spare time. One such scientist and Star Trek enthusiast is physicist Erik Lentz, PhD. Now a researcher at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory in Richland, Washington, Lentz was doing postdoctoral work at Göttingen University in Germany when, amid the early, isolated days of the pandemic, he mulled the idea of faster-than-light travel. He published a paper in 2021 arguing that warp drives could be generated using positive energy sources instead of the negative energy that Alcubierre’s warp drive seemed to require.
“There are a number of barriers to entry to actually being able to build a warp drive,” Lentz says. “The negative energy was the most obvious, so I tried to break that barrier down.”
He explored a new class of solutions in Einstein’s general relativity while focusing on something called the weak-energy condition, which, he explains, tracks the positivity of energy in spacetime. He hit upon a “soliton solution”—a wave that maintains its shape and moves at a constant velocity—that could both satisfy the energy-level challenge and travel faster than light. Such a warp bubble could travel along using known energy sources, though harnessing those at the levels needed are still far beyond our capabilities. The next step, he notes, may be bringing the energy requirements for a warp drive to within the range of a nuclear fusion reactor.
A fusion-powered device could theoretically travel to and from Proxima Centauri , Earth’s nearest star, in years instead of decades or millennia, and then go faster and faster as power sources improve. Current conventional rocket technology, on the other hand, would take 50,000 years just for a one-way trip—assuming, of course, there was an unlimited fuel supply for those engines.
“IF YOU COLLIDE WITH SOMETHING ON YOUR PATH, IT WOULD ALMOST CERTAINLY BE CATASTROPHIC.”
Like Alcubierre’s original thesis, Lentz’s paper had a seismic impact on the warp drive community, prompting yet another group of scientists to dig into the challenge. Physicist Alexey Bobrick and technology entrepreneur Gianni Martire have been particularly prolific. In 2021, they released a paper theorizing that a class of subliminal warp drives, traveling at just a fraction of light speed, could be developed from current scientific understanding. While that paper essentially argued that it’s perfectly acceptable to walk before you can run, they followed it up with another theory earlier this year that describes how a simulated black hole , created using sound waves and glycerin and tested with a laser beam, could be used to evaluate the levels of gravitational force needed to warp spacetime. The duo coded that breakthrough into a public app that they hope will help more quickly push theoretical ideas to practical ones. Though the team is waiting for the technology to clear a peer review stage before releasing details, the app is essentially a simulator that allows scientists to enter their warp-speed equations to validate whether they’re practical.
“When somebody publishes a warp metric for the first time, people say, ‘Okay, is your metric physical?’” Martire says. The answer to that question—whether the metric has practical potential or is strictly theoretical—is hard to establish given the challenges of testing these hypotheses. That determination could take six to eight months. “Now we can tell you within seconds, and it shows you visually how off you are or how close you are,” he says.
While useful, the app will speed up the preliminary math only for future researchers. Galaxy-sized challenges remain before we ever experience turbocharged interstellar travel. Alcubierre worries in particular about what may happen near the walls of the warp bubble. The distortion of space is so violent there, he notes, that it would destroy anything that gets close. “If you collide with something on your path, it would almost certainly be catastrophic,” he says.
Natário mulls even more practical issues, like steering and stopping. “It’s a bubble of space, that you’re pushing through space,” he says. “So, you’d have to tell space ... to curve in front of your spaceship.” But therein lies the problem: You can’t signal to the space in front of you to behave the way you want it to.
His opinion? Superluminal travel is impossible. “You need these huge deformations that we have no idea how to accomplish,” Natário says. “So yes, there has been a lot of effort toward this and studying these weird solutions, but this is all still completely theoretical, abstract, and very, very, very, very far from getting anywhere near a practical warp drive.” That’s “very” to the power of four, mind you—each crushing blow pushing us exponentially, excruciatingly further and further away from our yearned-for superluminal lives.
Ultimately, the pursuit of viable high-speed interstellar transportation also points to a more pressing terrestrial challenge: how the scientific community tackles ultra-long-term challenges in the first place. Most of the research so far has come from self-starters without direct funding, or by serendipitous discoveries made while exploring often unrelated research, such as Dr. White’s work on Casimir cavities.
Many scientists argue that we’re in a multi-decade period of stagnation in physics research, and warp drive—despite its epic time horizons before initial research leads to galaxy-spanning adventures—is somewhat emblematic of that stagnation. Sabine Hossenfelder, a research fellow at the Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies and creator of the YouTube channel Science Without the Gobbledygook , noted in a 2020 blog post that physics research has drifted away from frequent, persistent physical experimentation to exorbitant infusions of cash into relatively few devices. She writes that with fewer experiments, serendipitous discoveries become increasingly unlikely. Without those discoveries, the technological progress needed to keep experiments economically viable never materializes.
When asked whether this applied equally to warp drive, Hossenfelder sees a faint but plausible connection. “Warp drives are an idea that is not going to lead to applications in the next 1,000 years or so,” she says. “So they don’t play a big role in that one way to another. But when it comes to the funding, you see some overlap in the problems.”
So, despite all the advances, the horizon for a warp drive remains achingly remote. That hasn’t fazed the scientists involved, though. A few years ago, while teaching in France, White visited the Strasbourg Cathedral with his wife. While admiring its 466-foot-tall spire, he was struck by the fact that construction began in 1015 but didn’t wrap up until 1439—a span of 424 years. Those who built the basement had no chance of ever seeing the finished product, but they knew they had to do their part to aid future generations. “I don’t have a crystal ball,” White says. “I don’t know what the future holds. But I know what I need to be doing right now.”
Eric Adams is a writer and photographer who focuses on technology, transportation, science, travel, and other subjects for a wide range of outlets, including Wired, The Drive, Gear Patrol, Men's Health, Popular Science, Forbes, and others.
Pop Mech Pro

Where You Can Look at Every Single UFO Report Ever

This Study Backs a Quantum Theory of Consciousness

Aliens May Be Hiding Underground, Scientists Say

The Brain Could Be 100 Million Times More Powerful

Following Pager Explosions, Is Your Device Safe?

America’s New Plan for Its Secret Stealth Fighter

Our Consciousness May Come From a Higher Dimension

Could This Metal Shard Be Alien Technology?

Wormholes May Be a Portal for Interstellar Travel

What We Know About India’s Secret New Submarine

Debunking the 9/11 Myths: The Airplanes

We Debunked the 9/11 Myths About United Flight 93

Is Time Travel Possible?
We all travel in time! We travel one year in time between birthdays, for example. And we are all traveling in time at approximately the same speed: 1 second per second.
We typically experience time at one second per second. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA's space telescopes also give us a way to look back in time. Telescopes help us see stars and galaxies that are very far away . It takes a long time for the light from faraway galaxies to reach us. So, when we look into the sky with a telescope, we are seeing what those stars and galaxies looked like a very long time ago.
However, when we think of the phrase "time travel," we are usually thinking of traveling faster than 1 second per second. That kind of time travel sounds like something you'd only see in movies or science fiction books. Could it be real? Science says yes!

This image from the Hubble Space Telescope shows galaxies that are very far away as they existed a very long time ago. Credit: NASA, ESA and R. Thompson (Univ. Arizona)
How do we know that time travel is possible?
More than 100 years ago, a famous scientist named Albert Einstein came up with an idea about how time works. He called it relativity. This theory says that time and space are linked together. Einstein also said our universe has a speed limit: nothing can travel faster than the speed of light (186,000 miles per second).
Einstein's theory of relativity says that space and time are linked together. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
What does this mean for time travel? Well, according to this theory, the faster you travel, the slower you experience time. Scientists have done some experiments to show that this is true.
For example, there was an experiment that used two clocks set to the exact same time. One clock stayed on Earth, while the other flew in an airplane (going in the same direction Earth rotates).
After the airplane flew around the world, scientists compared the two clocks. The clock on the fast-moving airplane was slightly behind the clock on the ground. So, the clock on the airplane was traveling slightly slower in time than 1 second per second.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Can we use time travel in everyday life?
We can't use a time machine to travel hundreds of years into the past or future. That kind of time travel only happens in books and movies. But the math of time travel does affect the things we use every day.
For example, we use GPS satellites to help us figure out how to get to new places. (Check out our video about how GPS satellites work .) NASA scientists also use a high-accuracy version of GPS to keep track of where satellites are in space. But did you know that GPS relies on time-travel calculations to help you get around town?
GPS satellites orbit around Earth very quickly at about 8,700 miles (14,000 kilometers) per hour. This slows down GPS satellite clocks by a small fraction of a second (similar to the airplane example above).
GPS satellites orbit around Earth at about 8,700 miles (14,000 kilometers) per hour. Credit: GPS.gov
However, the satellites are also orbiting Earth about 12,550 miles (20,200 km) above the surface. This actually speeds up GPS satellite clocks by a slighter larger fraction of a second.
Here's how: Einstein's theory also says that gravity curves space and time, causing the passage of time to slow down. High up where the satellites orbit, Earth's gravity is much weaker. This causes the clocks on GPS satellites to run faster than clocks on the ground.
The combined result is that the clocks on GPS satellites experience time at a rate slightly faster than 1 second per second. Luckily, scientists can use math to correct these differences in time.
If scientists didn't correct the GPS clocks, there would be big problems. GPS satellites wouldn't be able to correctly calculate their position or yours. The errors would add up to a few miles each day, which is a big deal. GPS maps might think your home is nowhere near where it actually is!
In Summary:
Yes, time travel is indeed a real thing. But it's not quite what you've probably seen in the movies. Under certain conditions, it is possible to experience time passing at a different rate than 1 second per second. And there are important reasons why we need to understand this real-world form of time travel.
If you liked this, you may like:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
If you were traveling in a rocket moving at 75% of the speed of light and your friend throws the ball at the same speed, you would not see the ball moving toward you at 150% of the speed of light.
The final step is to calculate the total distance that the light has traveled within the time. You can calculate this answer using the speed of light formula: distance = speed of light × time. Thus, the distance that the light can travel in 100 seconds is 299,792,458 m/s × 100 seconds = 29,979,245,800 m. FAQs.
The theory of special relativity showed that particles of light, photons, travel through a vacuum at a constant pace of 670,616,629 miles per hour — a speed that's immensely difficult to achieve and impossible to surpass in that environment. ... wave-particle interactions in these bubbles can launch high-energy cosmic rays at 99.6% the ...
On one hand, the speed of light is just a number: 299,792,458 meters per second. And on the other, it's one of the most important constants that appears in nature and defines the relationship of ...
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted c, is a universal physical constant that is exactly equal to 299,792,458 metres per second (approximately 300,000 kilometres per second; 186,000 miles per second; 671 million miles per hour). [Note 3] According to the special theory of relativity, c is the upper limit for the speed at which conventional matter or energy (and thus any signal ...
Gianni Woods/NASA. The idea of travelling at the speed of light is an attractive one for sci-fi writers. The speed of light is an incredible 299,792,458 meters per second. At that speed, you could circle Earth more than seven times in one second, and humans would finally be able to explore outside our solar system.In 1947 humans first surpassed the (much slower) speed of sound, paving the way ...
The speed of light traveling through a vacuum is exactly 299,792,458 meters (983,571,056 feet) per second. ... Rømer attributed this effect due the time it takes for light to travel over the ...
This week: time dilation during space travel. I heard that time dilation affects high-speed space travel and I am wondering the magnitude of that affect. If we were to launch a round-trip flight…
The speed of light is the rate at which light travels. The speed of light in a vacuum is a constant value that is denoted by the letter c and is defined as exactly 299,792,458 meters per second. Visible light, other electromagnetic radiation, gravity waves, and other massless particles travel at c. Matter, which has mass, can approach the speed ...
Putting light to the test. The first person to realize that light does indeed have a speed at all was an astronomer by the name of Ole Romer. In the late 1600s, he was obsessed with some strange ...
So, what is the speed of light? Light moves at an incredible 186,000 miles per second (300,000 kilometers per second), equivalent to almost 700 million mph (more than 1 billion km/h). That's fast ...
At 99.99% Speed Of Light. Now, suppose you could travel at 99.99% of the speed of light. This time, let's be more ambitious and travel from our solar system to Alpha Centauri, roughly 4.35 light years away from Earth.
Today the speed of light, or c as it's commonly known, is considered the cornerstone of special relativity - unlike space and time, the speed of light is constant, independent of the observer. What's more, this constant underpins much of what we understand about the Universe. It matches the speed of a gravitational wave, and yes, it's the ...
Galileo Galilei (1564 - 1642) Galileo's Principle of Relativity. Before we look at why time appears to slow down as you travel at speeds approaching the speed of light, we need to go back a few hundred years to look at the work of Galileo Galilei (1564 - 1642). Galileo was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer whose incredible body of ...
According to the video, if you're traveling at nearly the speed of light, the clock inside your rocket would show it takes less time to travel to your destination than it would on Earth. But ...
The theory of special relativity showed that particles of light, photons, travel through a vacuum at a constant pace of 670,616,629 miles per hour — a speed that's immensely difficult to achieve and impossible to surpass in that environment. Yet all across space, from black holes to our near-Earth environment, particles are, in fact, being ...
The value of 299,792,458 meters per second (186,282 miles per second) is the speed of light in a vacuum. However, light actually slows down as it passes through different media. For instance, when it moves through glass, it slows down to about two-thirds of its speed in a vacuum. Even in air, which is nearly a vacuum, light slows down slightly.
1 To travel backward in time, the spacecraft's velocity must exceed: where u is the velocity of the planet relative to Earth, and c is the speed of light. Seth Lloyd, professor of quantum ...
It's an impressive feat of theoretical gymnastics, although the amount of energy needed means this warp drive is only a hypothetical possibility for now. "The energy required for this drive traveling at light speed encompassing a spacecraft of 100 meters in radius is on the order of hundreds of times of the mass of the planet Jupiter," Lentz said.
"In order to have a bubble about 100 meters wide traveling at precisely the speed of light, you would need about 100 times the mass of the planet Jupiter converted into negative energy, which of ...
More than 100 years ago, a famous scientist named Albert Einstein came up with an idea about how time works. He called it relativity. This theory says that time and space are linked together. Einstein also said our universe has a speed limit: nothing can travel faster than the speed of light (186,000 miles per second).
Main article: Superluminal motion. In the context of this article, "faster-than-light" means the transmission of information or matter faster than c, a constant equal to the speed of light in vacuum, which is 299,792,458 m/s (by definition of the metre) [ 3 ] or about 186,282.397 miles per second. This is not quite the same as traveling faster ...
Relativity means it is possible to travel into the future. We don't even need a time machine, exactly. We need to either travel at speeds close to the speed of light, or spend time in an intense ...