- All courses


THE IMPORTANCE OF TOURISM FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
01 sep the importance of tourism for sustainable development.
Sustainability is a concept that has been gaining social and political recognition, not least due to the coordinated launch of the Millennium Development Goals in 2000, and now with the 2030 Agenda and its 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDG). Established in 2015 and promoted by the United Nations, the SDGs are key to ensuring an environmentally, economically and socially sustainable world.
The 2030 Agenda is the reference framework for all UN agencies, programs and funds, and the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) is responsible for ensuring international tourism plays its part in its achievement.
The following guidelines have been established:
- The principle of sustainability refers not just to the environmental impact of tourism but also to its social and economic impacts.
- To protect and preserve the natural spaces and biological ecosystems of destinations.
- To respect the traditions and cultures of host countries and develop intercultural tolerance.
- To ensure economic activities that reduce poverty in the host country.
These guidelines are only the first link in a whole chain that is concerned with and advocates sustainable tourism.
These guidelines mean that as tourism restarts, the sector is ready to grow back stronger and better for people, planet and prosperity.
- Business Event Management: Navigating the World of Corporate and Social Gatherings Explore key strategies for successful corporate and social event planning and execution with our in-depth business event management course. Read more Start now Add to cart Business Event Management: Navigating the World of Corporate and Social Gatherings Explore key strategies for successful corporate and social event planning and execution with our in-depth business event management course. Read more
- Innovation and Digital Transformation in the Tourism Industry Explore digital transformation in tourism as you learn to implement effective strategies, embrace innovation, and elevate customer engagement and operational excellence. Read more Start now Add to cart Innovation and Digital Transformation in the Tourism Industry Explore digital transformation in tourism as you learn to implement effective strategies, embrace innovation, and elevate customer engagement and operational excellence. Read more
- Destination Marketing Develop robust marketing strategies for tourism destinations, focusing on market analysis, competitive positioning, and successful campaign implementation. Read more Start now Add to cart Destination Marketing Develop robust marketing strategies for tourism destinations, focusing on market analysis, competitive positioning, and successful campaign implementation. Read more
- Restaurant Operations Elevate your restaurant management skills with this online course, exploring food safety, service types, menu development, and effective inventory management. Read more Start now Add to cart Restaurant Operations Elevate your restaurant management skills with this online course, exploring food safety, service types, menu development, and effective inventory management. Read more
- Culinary Arts and Gastronomy Explore the link between tourism and gastronomy, the role of food in culture and sustainable alignment with the 2030 Agenda. Read more Start now Add to cart Culinary Arts and Gastronomy Explore the link between tourism and gastronomy, the role of food in culture and sustainable alignment with the 2030 Agenda. Read more
- Culinary Basics for Operations, Catering Management and New Techniques Master culinary basics, innovative techniques, menu development, and catering management in this comprehensive course for aspiring chefs and culinary enthusiasts. Read more Start now Add to cart Culinary Basics for Operations, Catering Management and New Techniques Master culinary basics, innovative techniques, menu development, and catering management in this comprehensive course for aspiring chefs and culinary enthusiasts. Read more
- Train the Trainer Develop professional training skills, enhance communication, and learn to design impactful training sessions in diverse professional settings. Read more Start now Add to cart Train the Trainer Develop professional training skills, enhance communication, and learn to design impactful training sessions in diverse professional settings. Read more
- Sustainable Destination Management Learn what goes into creating destinations that captivate visitors, safeguard the planet, and enrich local communities. Read more Start now Add to cart Sustainable Destination Management Learn what goes into creating destinations that captivate visitors, safeguard the planet, and enrich local communities. Read more
- Hotel Operations Get ready for your career in hospitality with this online course, focusing on operations, guest service, revenue strategies, and more. Read more Start now Add to cart Hotel Operations Get ready for your career in hospitality with this online course, focusing on operations, guest service, revenue strategies, and more. Read more
The Media’s Growing Role in Education
In today’s rapidly evolving world, both the media sector and education share a similar predicament in terms of how to adjust to new technology. As someone who has worked in the digital media space for over 13 years, I have witnessed massive changes in how people consume their daily news, I’ve seen century-old revenue models collapse, and attention spans shorten.
In this era of unprecedented change, there is reason to be both cautious and hopeful. Opportunities and threats that were previously unimaginable are now a reality. Both media and education are facing an uncertain future due to the rapid advance of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
The challenges we face require creativity and a willingness to adapt. By working together, media and education stand a better chance of weathering the storm. Trust in both sectors is at an all-time low in many countries around the world, and continuing to operate in the same way is unlikely to change this.
Instead, we must seize this opportunity by reevaluating our core functions.
Over the past years, Morocco World News, the news outlet I founded with my brother in 2011, has built several effective partnerships with local universities, focusing on youth empowerment, employability, media literacy and skills development. Such partnerships, I believe, hold the key for a sustainable future for both sectors.
By working together, the media industry and educational institutions can teach science effectively, be more inclusive, boost awareness on issues that matter, empower young people, and encourage growth.
Embracing this technological revolution will allow us to tailor content to the needs of modern students and news consumers. We can offer content in a variety of local languages and promote both critical thinking and problem-solving through increasingly interactive content.
More importantly, sectors such as media and education have the opportunity to promote life-long learning as a vital skill in our ever-changing labour market.
As the director of an English language news outlet in an Arab and French speaking country, I have witnessed how quickly a society can adapt to change and learn new skills. Morocco is now rapidly shifting, and English has become the primary language of science, entertainment and business. Young people are on board and driving the much-needed change.
In the years ahead, AI is set to disrupt both our sectors in seismic ways, prompting us to consider new ways to stay relevant to future generations who themselves face severe uncertainty about their future careers. In my experience, media platforms and educational institutes have an important role to play in the coming upheaval, and we can only do it together.
Strengthening ties between educators and the media will result in more engaging educational content. Interactivity and customization feeds the curiosity of young minds. It also encourages creativity and critical thinking. The use of advanced technology can help boost media literacy by bringing top educational content to the forefront of the news.
How many universities have amazing communicators and public speakers whose inspiring words do not reach beyond their walls? How many news stories are short in detail due to time pressure or a lack of expertise among writing staff? Bringing the two sectors together can solve both issues by connecting journalists with the voices that matter, at a time when they are truly needed.
I believe the answer to the coming wave of transformative technology lies in human connections. We need to connect the curious to those willing to share their knowledge, we need to empower people to check facts and sources, and we need to ensure this happens in an accessible and inclusive way.
Close partnerships between media organizations and educational institutes can help democratize learning and create a new positive public function for both sectors. My experience has shown me that these partnerships are easy to build and grow and hold the key to a more sustainable future for both sectors.

Adnane Bennis Co-Founder and CEO of Morocco World News
Crisis Management in Tourism
The tourism sector has faced unprecedented volatility and uncertainty over the past 5 years, both globally and locally. The pandemic and its related restrictions, the geopolitical situation and local conflicts, the acceleration of inflation and price increases, and the disruption of logistical chains led to the share of tourism in the global economy decreasing significantly. By the end of 2023 only a few destinations had managed to return to 2019 levels.
Now, however, the outlook is more encouraging. Consumer behavior in 2024, despite ongoing uncertainty, indicates a strong will to travel. Thanks to this, the sector is adapting to changing reality – new tourist routes are emerging and existing ones are being developed, new hotels, airports, restaurants, and other infrastructure are opening.
That said, the sector is still affected by seasonality, high fixed costs, a lack of qualified people and relatively low profitability. In rapidly changing and disruptive environment, with unforeseen changes, crisis management and change management become critical to ensure the industry is sustainable and safe for tourists and business.
Crisis management in the tourism sector generally involves a strategic and proactive approach taken by business to anticipate, prepare for, respond to, and recover from unexpected events that may influence the safety, travel plans, and the overall satisfaction of tourists. The primary goal is to minimize the effects of a crisis, restore confidence, and enable a relevant recovery for all parties involved.
As for any general management activities, crisis management in tourism logically includes several steps:
1)Assessing the nature of crisis
Tourism industry crises can take different forms, each demanding a specific response. Natural disasters can disrupt travel plans, infrastructure, and local communities. Human-made events, such as terrorist attacks, civil unrest, or geopolitical tensions, can impact the safety and security of tourists in affected regions. Additionally, health-related issues, exemplified by pandemics like COVID-19, present unique challenges with widespread implications for global travel.
2)Pre-Crisis Planning and Preparation
Effective crisis management starts long before a crisis itself appears. The tourism industry must engage in pre-crisis planning and preparedness to mitigate potential risks and enhance responsiveness during emergencies. This involves conducting risk assessments, identifying vulnerabilities, and establishing crisis response teams with clear roles and responsibilities. Relevant communication plans are essential to spread accurate and timely information to tourists, employees, and the public, assuring transparency and trust.
3)Crisis Response and Communication
While crisis starts, the effectiveness of the response and communication can make a significant difference in managing the situation. Tourism enterprises must activate their crisis response teams promptly and implement pre-established protocols and procedures. Swift communication with relevant authorities, local communities, and other stakeholders is essential to assess the situation accurately and make informed decisions. Transparent communication with tourists is crucial for managing expectations, providing safety guidelines, and offering alternative solutions.
4)Flexibility and Redemption Strategies
Flexibility is a crucial component of effective crisis management in tourism. Diversifying tourism offerings, both in terms of destinations and experiences, may reduce the impact of crisis that affect specific regions or sectors. Creating contingency funds and investing in comprehensive insurance can provide financial stability during challenging times. Collaborative efforts among public and private sectors can improve the managing capabilities, fostering a collective commitment to the industry’s survival and recovery.
5)Post-Crisis Assessment and Mastering
After managing a crisis, a thorough post-crisis analysis is vital to learn from the experience and improve future crisis management strategies. The tourism industry should embrace a culture of life-long learning and adaptation, updating plans based on emerging trends and challenges. Sharing lessons learned with the industry community promotes knowledge sharing and improves practices for the tourism sector.

ARTEM KLYKOV , PhD, MBA professor of tourism, Silk Road University Samarkand visiting professor, SWISSAM International University hospitality expert media contributor coach, mentor
Integrating tourism and hospitality curricula in high schools with AHLEI
The American Hotel and Lodging Educational Institute ( AHLEI ) established in 1953, is one of the foremost certifying bodies and publishers of quality resources to train, develop, and certify hospitality industry professionals globally. AHLEI is also committed to supporting the education of those just starting to pursue their careers, the next generation of hospitality and tourism leaders, innovators and champions!
AHLEI conducted extensive Gen Z research prior to creating our newest curricula. These results also influenced the new Education Toolkit , created in partnership with UN Tourism for the incorporation of tourism as a subject in high schools.
Young people who are excited about creating great experiences, meeting new people, making a positive impact on their communities and growing in their careers are increasingly drawn to the hospitality industry.
Why Introduce Tourism and Hospitality to School-Age Students?
AHLEI’s research pointed to some intriguing findings. Students are making decisions increasingly early about the career they want to pursue but many don’t consider hospitality. Why? Because of preconceived notions about the opportunities available to them. Additional findings include:
- Gen Z students are very practical. They are looking for a return on their educational investments. The more we can educate them about career growth and earning potential, the more they will start thinking seriously about tourism and hospitality as a career choice.
- Gen Z students prioritize feeling proud of what they do and where they work. They are motivated by exciting and interesting careers, Instagram-worthy experiences, and the positive impact the hospitality industry has on communities and economies.
- Gen Z is interested in inclusivity and in the freedom to be who they are. Hospitality is an amazing industry that encourages guests and employees alike to be their authentic selves.
AHLEI hears from our industry partners that while some young people may not be as skilled at test-taking or formal education, if they have great interpersonal skills, positive energy and good problem-solving instincts, there is a home for them in the hospitality industry. There are excellent opportunities for anyone with these qualities who is willing to work hard and learn.
Thus, in our new curriculum we emphasized relevance in the real world, encouraging exploration and practice through inquiry-based and problem-solving activities, and engaging students through our design choices, narrative voice, and multimedia resources. Let’s explore our newest resources.
Implementing the HTM Curriculum
The AHLEI high school curriculum, Hospitality and Tourism Management provides an engaging comprehensive exploration of different segments within the industry and the career paths in each.
This article includes:
- Implementation of the curriculum including organization, coverage and educator support
- Key themes and learning objectives of the text
- Endorsement by the U.S. hotel and lodging industry
- Testimonials from international partners
The AHLEI authoring and instructional design teams place a high priority on creating relevant, accurate, up to date and industry-driven content. Passive memorization is not the goal. Our materials are designed to help students think and do! There are elements incorporated regularly throughout learning and teacher resource materials designed to prompt student output and higher levels of learning.
Organization
Hospitality & Tourism Management is a single-volume textbook that can be aligned with any length program, though it is most often used alongside one- or two-year programs. The text is broken into modular units covering each segment of the industry. Each unit is comprised of self-contained chapters that dive deeper into skills and concepts. Optional activities, case studies and projects offer more rigor and application if desired. This modular approach along with helpful pacing guides allow educators to easily align the curriculum with the preferred order and structure of their program.
Hospitality is a huge and varied industry and the HTM curriculum includes a comprehensive overview of lodging and hotels, food and beverage operations, event management, travel and tourism. Coverage includes an overview of each segment, organizational structure and career paths, key roles and responsibilities. Opening chapters highlight the importance of the role of the industry and introduce students to core concepts and skills around providing excellent guest service. Closing chapters focus on business and leadership concepts like marketing, finance and entrepreneurship.
The coverage in HTM is based on input from dozens of industry professionals, teachers and subject matter experts for a relevant contemporary take on hospitality education with both practical and aspirational applications.
Teacher Support
The online teacher resource portal for Hospitality & Tourism Management includes a wealth of supplementary materials to help educators deliver the content to their students. The Teacher’s Companion includes notes, additional activities and discussion questions as well as organizational tools and engaging videos summarizing the main concepts in each chapter. Test Banks, Power Points, Instructor activity guide and lesson plan tools are also available to make class prep easy.
AHLEI also offers The Certified Hospitality Instructor (CHI) Program , a self-paced training course to help educators without an industry background effectively teach content in these areas. In addition to the course and exam, candidates for the CHI must also complete 120 hours of internship with a hospitality organization.
Hospitality and Tourism Specialist Credential
The HTM curriculum prepares students to earn their Hospitality Tourism Specialist credential from the American Hotel & Lodging Association, (AHLA), today the largest trade hotel association in the U.S. with 32,000 hotel members. Endorsed by some of the premier hospitality brands in the world, the HTS credential demonstrates student mastery of industry concepts. Students may earn the credential upon passing the AHLEI HTS exam and showing 100 hours of work experience in a hospitality role.
Assessment and credentialling is a large part of our program development. Credentials serve as a “passport” for students leaving the classroom, demonstrating the mastery that they achieved and using it as an entry into jobs within any segment of the industry.
Key Themes and Learning Objectives
Career readiness and technical skills.
One of the key themes throughout Hospitality and Tourism Management is that hospitality is a business, and a mastery of both technical and “soft” skills will open endless possibilities for career advancement. Operational and managerial topics as well as key math concepts are introduced in each unit. In addition, the text focuses on career readiness skills like written and verbal communication, problem-solving and teamwork, all in the context of a hospitality workplace.
Global Awareness
Hospitality is a global industry, supporting local economies and bringing together people from around the world. Global awareness and appreciation of and respect for different cultures is another core theme featured throughout. The text features international examples, discussions of cultural awareness, and coverage of cultural and operational differences in different countries.
Application
Throughout the text are scenarios, case studies, projects, activities, discussion questions and more, all designed for learners to immediately apply what they are learning, even from within the classroom. This presentation maximizes student engagement, understanding and retention of key concepts.
Endorsements and Formal Recognition
Hospitality and Tourism Management Second Edition is recognized by leaders in the U.S. hotel and lodging industry, including:
- Marriott International
- BF Saul Company Hospitality Group
- G6 Hospitality LLC
- RRI West Management
- Real Hospitality Group
- Mid-Continent Hospitality
- TradeWinds Island Resorts
These industry leaders appreciate that HTM Second Edition highlights the knowledge and skills that hospitality leaders look for in their employees today. HTM program completion, along with the HTS credential, fully prepares a learner to be a high-potential candidate for entry-level positions with the experience needed to bring value to the industry and grow in their careers.
Expand Your Horizons with HTM
The second edition of HTM offers learners a global perspective of the industry, its opportunities and its impact on the world.
Two of AHLEI’s valued governmental partners, and UNWTO member states, share the positive impact the HTM program can have on a national tourism industry below.
Jamaica’s Minister of Tourism, Hon. Edmund Bartlett, CD, MP., states:
“The Hospitality and Tourism Management Program has been a game-changer for Jamaica’s tourism industry and our nation. We have witnessed remarkable transformations through this innovative program in partnership with the esteemed American Hotel and Lodging Educational Institute (AHLEI). Our students now have the opportunity to acquire certification from AHLEI and an Associate Degree in Customer Service, equipping them with the skills and expertise needed to excel in the hospitality sector. Since its introduction in select high schools in September 2018, the HTM Program has ushered in a new era of professionalism and excellence in our tourism sector. We have witnessed a significant upskilling among our youth, creating a more competent and dedicated workforce prepared to deliver exceptional service. I am incredibly proud of the hard work and dedication put forth by our students, schools, and industry partners who have embraced the HTM Program. Together, we are shaping a brighter future for Jamaica that empowers our youth and ensures our country remains a premier global destination for years to come.”
Ms. Janet Forbes-Dean, Subject Coordinator for Family and Consumer Science Education at Jack Hayward Senior High School in Grand Bahama, says:
“The high school students at the Jack Hayward Senior High School have attained numerous AHLEI International Certifications over the past thirteen (13) years. These certifications are our core examination. There is no Bahamas General Certificate of Secondary Education (B.G.C.S.E.) national examination for hospitality students. AHLEI’s program is awesome. We have former and current students who received one or more certifications in Kitchen Cook, Breakfast Attendant, Front Desk Attendant, HTMP Year 1, Restaurant Server, START, Golden Opportunities, Guest Service Gold, and Golden Opportunities Tourism. These certifications along with the high school Hospitality and Tourism Curriculum are essential for students who are desirous of continuing a career in Hospitality.”
Get Started Today with AHLEI’s Hospitality & Tourism Program
We can’t wait to help you get started. Learn more here .
For further questions, contact Ed Kastli, Channel Vice President of International Sales, at [email protected] .

Elizabeth O’Brien Senior Product Manager
Enhancing Tourism Education t hrough Volunteer Teaching Experiences
Submitted by Stephen Sayers,
English Lecturer; Faculty Advisor to the IFTM Volunteer Circle
In 2019, ‘The IFTM Volunteer Circle’ (IFTMVC) began providing support for poverty alleviation through bi-annual volunteer teaching trips for 7-10 days to raise the interest and ability of junior high-school students at the Second National High School in Cong Jiang County, Gui Zhou. Historically, local students in Cong Jiang have been unable to gain access to better universities due to poor English scores in their ‘high-school entrance’ exams.
Traveling to the location, and participating in community engagement – meaningful, interactive, and immersive – is creating an educational experience that complements theoretical lessons, is highly memorable, and most importantly capable of transforming volunteers. In the words of one volunteer:
“I often choose to be alone because I find it difficult to integrate into the community. But when I met this group of students, their enthusiasm had an infectious force, so I unconsciously fell into it. Their enthusiasm and vitality made me confident and dare to communicate with them!”
An analysis of 50 students’ reflections and those of several students shared four years after their initial trips illustrates transformation in three areas: personality traits, skills development, and perspectives.
- Personality traits
Students expressed transformation in many aspects of their ‘inner-world’. They showed an increased sense of “happiness”, “optimism”, “confidence”, “boldness”, “being outgoing”, “gratitude”, “well-being”, “fulfillment”, “enthusiasm”, “cherishing life”, and “gratefulness”. They saw that they had demonstrated “responsibility”, “adaptability”, and “initiative” and had an improved “attitude”.
“I used to be a very introverted and sensitive person, and I was afraid that people would hurt me, so I built a tall wall in my heart to protect myself from being hurt. After this trip, I find myself happier and more optimistic. The naivety and braveness of those children encourage me a lot.”
“ Through this activity, I experienced the joy of being a teacher. I gradually became less shy during the activity. I started to become bolder and took the initiative to communicate with those students who were not fond of speaking English. I successfully helped them to confidently speak English.”
“After this trip, I can better adapt to the environment, and I know how to communicate with others better, which is the biggest gain for me.”
“This event made me cherish my life now. I should no longer complain about the living environment, and no longer worry about small difficulties. Now I can do so many meaningful things, not because I am excellent, but because I am lucky enough.”
- Skills development
Another area of transformation concerned skills development, including “communication”, “public speaking”, “problem-solving”, “teaching”, “social”, “leadership” and “critical thinking”.
“I was a bit shy in the first class as it was my first time standing in front of the classroom as a “teacher”. However, I think I made some progress. Gradually I talked louder and became more comfortable in the class. I improved public speaking skills in a way.”
“This journey has changed me a lot, including my work attitude, accuracy of information, understanding of students, and teaching skills… The local teachers taught me some teaching skills and some software to assist in teaching.”
“The trip changed me in different ways… it improved my social skills. I am not an out-going person, sometimes it may be hard to talk a lot with others from the very beginning…”
“The trip changed my view of my influence to the world. I can’t change (all) the students totally, but I can influence someone and it is enough.”
“… for myself, I will not wear something like AJ shoes anymore… Maybe it doesn’t matter but it just makes me feel uncomfortable anyway…”
- Perspectives
In order to strengthen students’ attitudes of ‘mutual respect and understanding’ (GCET – Article 1), one of the guided reflection questions challenged the prevailing attitude that volunteering is the ‘haves’ providing for the ‘have nots’. Many students developed the sense of perception to see the inter-connectedness of volunteering and personal transformation.
“I used to think volunteering is… to try my best to provide help to others in need. After this trip, I think volunteering is not only unilateral help, but also an opportunity to learn.”
“I always thought that volunteering was just a donation to help children in poor areas. After this activity, and integrating into the children’s life, I realized the meaning of volunteer activities. We open the window of the world for them, and they bring us the touch and beauty of life.”
“This is my second time participating in this project, and the change from being a participant to a leader has given me a deeper understanding of the entire activity… through… planning and organizing, I realized that the success of an activity doesn’t solely depend on the richness of its content. It also requires meticulous organization and smooth coordination of various aspects. Learning from previous experiences and continuously improving the activity plan can attract capable individuals to participate and maximize the project’s impact. This is how my understanding of volunteering has changed. It has made me realize that volunteering is a collective effort…”
Four years after her first trip and now a Master’s student at University College of London, (UCL) shared her reflective thoughts. Her words testify to the power that well-designed volunteer trips have in setting a student on a path to ‘becoming’ a life-long learner and protagonist for the greater good.
“I would like to say that participating in and organizing (the) volunteer trips (has been) one of the best and most worthy things in my life so far… During my two volunteer experiences in Cong Jiang, China, I actively participated in teaching English and engaging in various extracurricular activities with the students. The first time in 2019, I observed… many locals who believed education is useless, (and that) boys are better than girls… I recognized the deep-rooted challenges in altering perspectives towards education… and (that) it is a long-term task. I also realized the impact of education on shaping beliefs, and life choices… these volunteer experiences shaped me to be a better person with more confidence and belief that I have the ability to achieve something…
Furthermore, these experiences have undoubtedly influenced my future aspirations. I would like to engage in volunteer activities continuously and am now participating in volunteer activities actively in London. They also sparked my interest in educational development and community engagement. As I envision my future, I see myself actively contributing to educational institutions or possibly even to international organizations or non-government organizations…”
Though much still needs to be learned to optimize the dual path of personal and social transformation that can be effected through these trips, it is clear they provide a path to a profound transformation in students’ and directly contribute to the IFTM vision, “As an advocate of community engagement, IFTM takes pride in producing graduates that not only excel professionally but also work for the greater good of society” (President’s Message; IFTM Website). This author believes that with ‘collective will’ and the wise allocation of resources this kind of innovative educational experience – integrating students and community engagement – can be extended to benefit all undergraduates and many more local communities.

Stephen Sayers English Lecturer Faculty Advisor to the IFTM Volunteer Circle
Startup Niches in Tourism in 2024: Opportunities and Potential for Growth
By Fabio Passos
In the ever-evolving landscape of the tourism sector,2024 promises to bring new opportunities for entrepreneurs looking to venture into the world of startups. As a professor, consultant, and mentor specializing in tourism and hospitality, with a focus on entrepreneurship, innovation, and business planning, I am always vigilant regarding emerging trends. In this article, I will highlight two startup niches that deserve special attention in 2024.
Women’s Travel Journey
The women’s travel journey is a growing niche that offers numerous possibilities for the development of tourism ventures. This segment encompasses the routing of trips exclusively for women, as well as the creation of spaces and tourist services that cater to the specific needs and preferences of this audience.
Within this niche, opportunities abound in various areas, including transportation, accommodation, guided tours, and dining. Startups can develop solutions that provide safe and inclusive experiences for solo female travelers, while also promoting connections among women who wish to explore the world together.
While there are already some initiatives focused on women’s travel journeys, including initiatives in Brazil where I have had the privilege to provide mentorship, there is still significant room for growth and innovation within this market. The emphasis on safety, community building, and personalization of travel experiences may be the key to success in this expanding niche.
Startups that venture into this market can stand out by creating exclusive travel packages for women, offering cultural, culinary, and adventure experiences tailored to female preferences. Furthermore, ensuring an environment in which travelers feel secure is crucial to attracting this audience.
Vacation Rental Property Management
The vacation rental property market has experienced exponential growth over recent years, largely driven by the success of Airbnb. However, this segment is now undergoing a phase of professionalization, presenting an opportunity for startups to excel.
Many investors and entrepreneurs operating in the vacation rental property market lack specific hospitality expertise. This can result in challenges related to customer service, governance, and property rate pricing. Startups can fill this gap by offering innovative solutions that help property owners manage their properties more efficiently and profitably.
Startups can focus on enhancing the guest experience by creating tools and services that make stays more enjoyable and hassle-free. Process automation, reservation management, and predictive maintenance are some areas where innovation can enhance the professionalization of vacation rental properties.
In summary, in 2024, the tourism sector offers exciting opportunities for entrepreneurs looking to explore specialized niches. Women’s travel journeys and vacation rental property management are just two examples of areas with significant growth potential. If you are interested in discussing these niches or other topics related to tourism and hospitality, I am available for further conversation.

Fabio Passos Fabio, with a B.A. in Tourism, a graduate degree in Marketing, and an MA in Business Administration, boasts an impressive track record of over 15 years in both the national and international realms of tourism and hospitality. His diverse experience encompasses roles in hotels, property management, aviation, travel agencies, and cruise lines. Of particular note is Fabio’s keen interest in the home rental business, where he has emerged as a recognized expert in consultancy services. As the proprietor of Studio na Carioca and Passos do Turismo, he is dedicated to offering training programs for vacation rental owners, equipping them with the essential skills needed to elevate their revenue and excel in various critical aspects of home rentals.
Embracing Sustainability: Innovative Real Estate Solutions in the Hospitality Industry
By Rani Majzoub
The urgency to respond to climate change demands that all industries rethink and transform their practices and accelerate the shift to greater sustainability. The hospitality sector, historically singled out for its climate impact, is responding to this call and reimagining its foundations to embrace sustainable practices.
Innovative real estate solutions lie at the centre of this transformation. They are not merely a response to the growing environmental crisis but rather an embodiment of a commitment to reducing the industry’s ecological footprint whilst enhancing the guest experience. This article will delve into this profound shift, exploring the innovative measures shaping the future of hospitality and tourism, where sustainability and luxury harmoniously coexist.
Eco-friendly Building Design
Sustainable architecture is taking centre stage, with a visionary approach to building renovations. The adoption of eco-friendly designs exemplifies this shift, which prioritizes energy efficiency and environmental responsibility, encompassing a strategy ranging from incorporating renewable energy sources to efficient insulation and implementation of green roofs. Beyond their aesthetic appeal, these roofs are meticulously engineered to curtail energy consumption and provide a unique selling point for eco-conscious travellers. From solar panel installation to rainwater harvesting systems, these developments are revolutionizing tourism’s relationship with the environment.
Smart Technologies
The integration of smart technologies marks an inflection point in sustainable hospitality real estate. Automation and sensor-based systems are effective tools for diminishing energy consumption, optimizing climate control, and enhancing security. Solutions such as key cards for room lighting and temperature control, alongside mobile apps for managing rooms, empower guests to participate in energy conservation. These technologies not only enhance guest experiences but also promote resource efficiency.
A notable example is the seamless integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) in hotel operations, allowing real-time adjustments of room conditions based on guest preferences and occupancy. This will elevate guest comfort to unprecedented heights and showcase the fusion of technology and sustainability as the future of hospitality real estate.
Water Conservation
Fresh water, a precious and finite resource, assumes even greater significance in regions grappling with water scarcity. In such places, the need to conserve water is imperative. Innovative real estate solutions involve water-efficient fixtures, including low-flow faucets, showerheads, and greywater recycling systems, serving the dual purpose of curtailing water consumption and mitigating the ecological repercussions of wastewater. A notable trend in the sector is the adoption of rainwater harvesting systems, which collect and store rainwater for uses such as irrigation, toilet flushing, and cooling systems. Through diminishing reliance on municipal water sources, hotels make meaningful contributions to water conservation while trimming utility bills, underscoring the intersection of ecological responsibility and cost-efficiency.
Sustainable Materials
From furniture décor to linens, the hospitality sector is witnessing a resounding shift towards sustainability. This transformative wave embraces the spirit of reuse and locality. Recycled, upcycled, and locally sourced materials are now finding their way into the heart of hospitality, reshaping the aesthetics and ethics of hospitality.
We can consider the choice of reclaimed wood or recycled plastics for crafting hotel furniture, a nod to the industry’s commitment to reducing waste and endorsing eco-friendly practices. The adoption of such materials reduces the environmental footprint and presents an opportunity for hotels to craft distinctive and alluring interior designs. Guests, too, are becoming increasingly appreciative of the narratives that accompany these furnishings, carrying with them a unique story of renewal and resourcefulness. This newfound synergy between aesthetics and environmental responsibility is reshaping the landscape of hospitality.
Community Engagement & Education
Sustainability transcends the confines of premises; forward-thinking establishments are actively engaging with the community while educating their guests on sustainable practices. This multi-faceted approach enriches the guest experience and fosters a relationship between the hotel and its community. These interactions can take shape in various ways, such as partnerships with eco-friendly artisans and sourcing food locally to reduce carbon footprint while contributing and empowering the community.
Hotels are increasingly offering eco-friendly excursions, encouraging guests to partake in nature-focused activities, enriching their experience and inspiring their sense of responsibility towards the environment.
Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources serve as a foundational element in the development of sustainable real estate. With the emergence of solar panels, wind turbines and geothermal systems, these have become intertwined into the fabric of hotel and resort facilities, marking a solid step away from the reliance on fossil fuels. By generating their own renewable energy, establishments trim operational costs and significantly reduce their carbon footprint.
Solar panel installations on rooftops or in parking areas emerge as powerful generators of clean electricity. Concurrently, some forward-thinking establishments are exploring the possibilities for wind turbines and geothermal heating and cooling systems to reduce their dependence on non-renewable energy. Such initiatives manifest as sustainable choices and sound financial strategies, illustrating the escalating potential of renewable energy.
Waste Reduction and Recycling
Innovative solutions extend to waste management, where hotels proactively reduce, recycle, and efficiently manage waste. Strategies include comprehensive recycling programs, organic waste composting, and collaboration with local initiatives for responsible waste disposal, contributing to environmental sustainability and the local community. By adopting a circular approach, hotels minimize landfill-bound waste and reduce the need for virgin resources in goods production, fostering a sustainable and economically sound future.
The shift to sustainability in the hospitality industry, driven by its environmental concerns and long-term strategic thinking, is transforming the sector. As travellers increasingly prioritize environmental issues, hotels and resorts are leading the way in sustainability, benefiting both the planet and their bottom line. Looking ahead, we anticipate a future enriched with more ground-breaking solutions to reshape the tourism sector even further, setting a sustainable precedent for the future. This journey is imperative in addressing global environmental challenges and meeting travellers’ eco-friendly expectations, promising a brighter, sustainable future for hospitality.
With gratitude to Anan Zeitoun, Director of Real Estate Advisory, and Haya Serhan, Consultant in Real Estate Advisory for their contributions.

Rani Majzoub Head of Real Estate Advisory at KPMG Saudi, Head of Advisory at KPMG Lebanon.
New perspectives for tourism education
By Christine Böckelmann
On a global scale, tourism has a high economic significance: it accounts for 10% of all jobs and for many people’s income. At the same time, the tourism sector faces a major challenge: more and more people want to travel and explore foreign countries and cultures and they want to do so in a more sustainable way. Hand-in-hand with this, society is also demanding that the sector rethink its approach to sustainability. This is not only about the environment. It’s also about economic sustainability in the sense of the impact on local economic development, from which the tourism regions and countries benefit as a whole. It also relates to social sustainability in the sense of decent working conditions that provide employees in tourism businesses with a secure income.
For this holistic transformation, the tourism sector needs professionals with comprehensive skills not only in hospitality management, but also in economics, regional development, digitalisation and human resources development. It needs professionals who can keep an eye not just on one single company, but on an entire economic system, and who know how to use digitalisation for innovative business developments. This is especially challenging as the tourism sector is not a magnet for the top talent it so needs. On the one hand, a study from Poland has shown that more than half of those who have qualifications related to tourism (54.7%) are not currently working in jobs related to their studies. A large part of the investment in tourism education is therefore lost. On the other hand, due mainly to working conditions, many professionals stay in the sector only for a few years; when the opportunity arises, they migrate to other industries. This again turns skills development in the tourism sector into a challenge.
One effective way to attract and then retain top talent is to offer a high-level university degree with a top reputation. This requires a study programme that attracts young people thanks to its quality. It must also feature content that is relevant to Gen Z values, and offer a wide range of career options. Such a programme must provide comprehensive skills in sustainability (ecological, economic, social), high-level skills in digitalisation (tourism tech, digital dynamics and innovation), and high-level communication and social skills.
With the Bachelor of Science in International Sustainable Tourism , the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) and the Lucerne University of Applied Sciences and Arts (HSLU) have jointly created such a study programme, the first of its kind. In addition to providing a holistic tourism education, the course also addresses current issues presented by companies, which students then work on together. This ensures that the programme is always aligned with the requirements of practice. Internships and opening doors to the UNWTO and HSLU networks enable students to gain closer ties to the sector. This lays the foundations for students to remain in tourism after graduation.
However, education alone cannot provide the required transformation. In addition to the new focus on holistic tourism development in education, it is also important that companies make an effort to offer young people jobs where a good work-life balance is possible, giving them “work tasks with purpose” as well as excellent career opportunities. Otherwise, despite all our best efforts, they will migrate again to other industries.

Christine Böckelmann
Guaranteeing inclusion and diversity in travel advancements of the tourism sector
By Muzzammil Ahussain, CEO-Almosafer
In the dynamic realm of tourism, inclusion and diversity have emerged as the bedrock principles, shaping the sector’s present and future. This is clearly reflected in our work at Almosafer, as well as in the Saudi Vision 2030.
Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 is more than just an ambitious plan; it’s a robust testament to the nation’s drive for progress. With the target of creating one million jobs in the tourism sector by 2030, the roadmap is clear and based on a firm belief in the boundless potential of our youth. By nurturing their dreams and aspirations, we’re not just planting seeds for opportunities; we’re creating the blueprint for an inclusive and diverse tomorrow.
Educating the Next Generation through Almosafer Academy
The Almosafer Academy has been designed to offer Saudi nationals a well-balanced mix of theoretical education and real-world experiences. Through various sessions, workshops, and immersive trips, we are crafting a future where our travel experts not only understand the industry’s mechanics but also appreciate its diverse nuances.
Our enduring partnership with Princess Nourah University further underlines our commitment. By offering a seamless blend of academic instruction with practical insights, we’re sculpting a generation of tourism students who are not just educated but also enlightened. They will have the skills and experience tourism employers need and the soft skills tourists look for when traveling.
Almosafer’s Collaboration with the Human Resource Development Fund
Our recent partnership with the Human Resource Development Fund is another step forward in our journey to support and cultivate Saudi talent. This synergy not only underscores our commitment to nurturing talent but also reiterates the importance of private and public sector partnerships in achieving national goals.
Empowering Female Leaders: Pioneering a Change in the Middle East
Beyond the world of academia, our partnership with the UNWTO Women in Tech Startup Competition is empowering women techpreneurs across the region, above all by fostering an environment where women can innovate, lead, and redefine the tech landscape. Alongside this, the Unlock Her Future Prize by the Bicester Collection, which Almosafer is supporting and celebrating women entrepreneurs who drive change and make a positive impact on their communities.
Tourism and Its Societal Impacts
By guaranteeing inclusion and diversity in our operations, we’re not just facilitating travel; we’re fostering connections, understanding, and global unity. Moreover, the role of technology in achieving this cannot be understated. As digital advancements reshape how we travel, it’s vital that these technological strides resonate with our core values of inclusion and diversity. Almosafer invests heavily in ensuring that our digital platforms are intuitive, user-friendly, and accessible to all, regardless of background or ability.
In conclusion, the essence of travel is to experience the unknown, to immerse oneself in diverse cultures, traditions, and histories. At Almosafer, our vision is to ensure that every traveler feels represented, valued, and understood. As we stand on the cusp of a new dawn in tourism, let us remember our shared responsibilities. The true essence of tourism lies in an ecosystem where each individual, regardless of their background, finds a voice, and every journey becomes a testament to Saudi Arabia’s grander vision for the future.

Muzzammil Ahussain
Chief Executive Officer – Almosafer
El Impacto del Turismo y la Importancia de su Talento Humano
Cuando los cambios tocan a nuestra puerta, no queda más que buscar herramientas o mecanismos para abordarlos con el fin de mejorar la manera en que hemos venido haciendo las cosas. Esta fue la invitación que tan abruptamente le hizo la pandemia al mundo entero.
En Chile, de acuerdo a datos del Instituto Nacional de Estadísticas (INE), la mayor pérdida de empleos en turismo se reflejó en el trimestre mayo-junio-julio de 2020, pasando de tener 651.797 puestos de trabajo en ese mismo trimestre de 2019 a 369.520.
Estos datos equivalen a una pérdida del 43,3% de los puestos de trabajo, lo que de manera inmediata, mostró los efectos de la pandemia en el país, pero que una vez terminadas las restricciones sanitarias comenzaron a revertirse. Según los últimos reportes del trimestre móvil abril-mayo-junio 2023 se han recuperado un 94,1% de los empleos, faltando sólo 37.690 para alcanzar las cifras prepandemia.
Lo interesante de este proceso de reactivación del empleo, es que ha venido de la mano de un cambio de visión y de una oportunidad para repensar el talento humano que conforma el turismo, la hotelería y la gastronomía. Es así como desde la Subsecretaría de Turismo de Chile hemos transitado hacia la perspectiva del “nuevo capital humano” (Brown), paradigma con el que esperamos ampliar dicho concepto, desde una visión únicamente económica que contempla un conjunto de conocimientos, habilidades y aprendizajes que cuentan los colaboradores de una organización (Adam Smith) hacia un concepto de talento humano que englobe el proceso de desarrollo personal como un proceso integral.
Y considerando que el turismo es un sector económico por naturaleza, con un fuerte enfoque en lo humano y cercano, es que ha emergido con mayor fuerza la necesidad de potenciar las llamadas “habilidades para la vida” o “habilidades socioemocionales”, en quienes dan vida al sector: sus trabajadoras y trabajadores. La proactividad, la comunicación efectiva, el trabajo en equipo son elementos, que no siendo conocimientos técnicos, permiten un desarrollo efectivo de las funciones asociadas a la entrega de servicios turísticos y con ello, otorgan garantía de calidad a las experiencias vividas por los visitantes. Por lo tanto, su incorporación en el quehacer de cada una de las personas que forman parte de la cadena de valor del sector es uno de los principales desafíos.
Las oportunidades y desafíos son múltiples, el impacto del desarrollo turístico en el mundo depende de muchos factores, pero el factor humano jamás dejará de ser su eje central. Si lo humano no es abordado de manera eficiente y eficaz, el aporte social, cultural y económico que trae consigo el desarrollo de esta industria no verá la luz y, es precisamente en esta línea, que Chile ha trabajado en la definición de un Plan Estratégico de Capital Humano de Turismo 2023-2026 para abordar las diversas dimensiones que tiene una temática tan relevante como esta.
De este modo el Plan Estratégico de Capital Humano de Turismo 2023-2026 busca recoger todos aquellos aprendizajes y desafíos post pandemia para poner el foco en tres principales elementos a abordar durante los próximos cuatro años: Empleo, Estándares para el Ecosistema Turístico y Formación y Desarrollo de talento.
Cada uno de los ejes estratégicos definidos, dan cuenta de elementos fundamentales para avanzar hacia la profesionalización del sector, así el eje EMPLEO buscará fomentar mejores condiciones laborales y políticas de contratación. El eje ESTÁNDARES PARA LA INDUSTRIA TURÍSTICA impulsará la asociatividad con foco en la competitividad del sector, para ofrecer una mejor calidad en la entrega de servicios turísticos. Y el eje FORMACIÓN Y DESARROLLO DE TALENTO trabajara para fortalecer las cualificaciones y habilidades a nivel técnico, de idiomas y socioemocionales de quienes forman parte de la industria.
Sin duda este instrumento encarna, como se menciona al comienzo de este artículo, una herramienta para abordar las necesidades y cambios de capital humano en el sector turismo y si bien, el contenido del documento resulta fundamental para la implementación de la política pública, lo es mucho más el modelo de trabajo publico privado a partir del cual fue construido: la gobernanza que representa la Mesa Nacional de Capital Humano de Turismo . Es esta gobernanza la que impulsará cada una de las iniciativas identificadas como necesarias para mejorar las brechas de capital humano del sector y no solo por estar contenidas en un documento público, sino más bien por el sentido de pertenencia que le otorga haber sido parte fundamental de la construcción del instrumento.
Muchos han sido los aprendizajes que hemos acuñado los últimos años, y las medidas que hemos implementado están surtiendo efectos positivos, así lo demuestran los datos de empleo, pero sin duda, el mayor de los aprendizajes es más bien, seguir trabajando sin perder el foco en lo importante, las personas.

Marcella Mansilla
Encargada de Capital Humano y Género
Ministerio de Economía, Fomento y Turismo Subsecretaría de Turismo, Gobierno de Chile
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 31 March 2023
The benefits of tourism for rural community development
- Yung-Lun Liu 1 ,
- Jui-Te Chiang 2 &
- Pen-Fa Ko 2
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 10 , Article number: 137 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
22k Accesses
16 Citations
5 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Business and management
- Development studies
While the main benefits of rural tourism have been studied extensively, most of these studies have focused on the development of sustainable rural tourism. The role of tourism contributions to rural community development remains unexplored. Little is known about what tourism contribution dimensions are available for policy-makers and how these dimensions affect rural tourism contributions. Without a clear picture and indication of what benefits rural tourism can provide for rural communities, policy-makers might not invest limited resources in such projects. The objectives of this study are threefold. First, we outline a rural tourism contribution model that policy-makers can use to support tourism-based rural community development. Second, we address several methodological limitations that undermine current sustainability model development and recommend feasible methodological solutions. Third, we propose a six-step theoretical procedure as a guideline for constructing a valid contribution model. We find four primary attributes of rural tourism contributions to rural community development; economic, sociocultural, environmental, and leisure and educational, and 32 subattributes. Ultimately, we confirm that economic benefits are the most significant contribution. Our findings have several practical and methodological implications and could be used as policy-making guidelines for rural community development.
Similar content being viewed by others

Creativity development of tourism villages in Bandung Regency, Indonesia: co-creating sustainability and urban resilience
Eco-tourism, climate change, and environmental policies: empirical evidence from developing economies

When urban poverty becomes a tourist attraction: a systematic review of slum tourism research
Introduction.
In many countries, rural areas are less developed than urban areas. They are often perceived as having many problems, such as low productivity, low education, and low income. Other issues include population shifts from rural to urban areas, low economic growth, declining employment opportunities, the loss of farms, impacts on historical and cultural heritage, sharp demographic changes, and low quality of life. These issues indicate that maintaining agricultural activities without change might create deeper social problems in rural regions. Li et al. ( 2019 ) analyzed why some rural areas decline while others do not. They emphasized that it is necessary to improve rural communities’ resilience by developing new tourism activities in response to potential urban demands. In addition, to overcome the inevitability of rural decline, Markey et al. ( 2008 ) pointed out that reversing rural recession requires investment orientation and policy support reform, for example, regarding tourism. Therefore, adopting rural tourism as an alternative development approach has become a preferred strategy in efforts to balance economic, social, cultural, and environmental regeneration.
Why should rural regions devote themselves to tourism-based development? What benefits can rural tourism bring to a rural community, particularly during and after the COVID pandemic? Without a clear picture and answers to these questions, policy-makers might not invest limited resources in such projects. Understanding the contributions of rural tourism to rural community development is critical for helping government and community planners realize whether rural tourism development is beneficial. Policy-makers are aware that reducing rural vulnerability and enhancing rural resilience is a necessary but challenging task; therefore, it is important to consider the equilibrium between rural development and potential negative impacts. For example, economic growth may improve the quality of life and enhance the well-being index. However, it may worsen income inequality, increase the demand for green landscapes, and intensify environmental pollution, and these changes may impede natural preservation in rural regions and make local residents’ lives more stressful. This might lead policy-makers to question whether they should support tourism-based rural development. Thus, the provision of specific information on the contributions of rural tourism is crucial for policy-makers.
Recently, most research has focused on rural sustainable tourism development (Asmelash and Kumar, 2019 ; Polukhina et al., 2021 ), and few studies have considered the contributions of rural tourism. Sustainability refers to the ability of a destination to maintain production over time in the face of long-term constraints and pressures (Altieri et al., 2018 ). In this study, we focus on rural tourism contributions, meaning what rural tourism contributes or does to help produce something or make it better or more successful. More specifically, we focus on rural tourism’s contributions, not its sustainability, as these goals and directions differ. Today, rural tourism has responded to the new demand trends of short-term tourists, directly providing visitors with unique services and opportunities to contact other business channels. The impact on the countryside is multifaceted, but many potential factors have not been explored (Arroyo et al., 2013 ; Tew and Barbieri, 2012 ). For example, the demand for remote nature-based destinations has increased due to the fear of COVID-19 infection, the perceived risk of crowding, and a desire for low tourist density. Juschten and Hössinger ( 2020 ) showed that the impact of COVID-19 led to a surge in demand for natural parks, forests, and rural areas. Vaishar and Šťastná ( 2022 ) demonstrated that the countryside is gaining more domestic tourists due to natural, gastronomic, and local attractions. Thus, they contended that the COVID-19 pandemic created rural tourism opportunities.
Following this change in tourism demand, rural regions are no longer associated merely with agricultural commodity production. Instead, they are seen as fruitful locations for stimulating new socioeconomic activities and mitigating public mental health issues (Kabadayi et al., 2020 ). Despite such new opportunities in rural areas, there is still a lack of research that provides policy-makers with information about tourism development in rural communities (Petrovi’c et al., 2018 ; Vaishar and Šťastná, 2022 ). Although there are many novel benefits that tourism can bring to rural communities, these have not been considered in the rural community development literature. For example, Ram et al. ( 2022 ) showed that the presence of people with mental health issues, such as nonclinical depression, is negatively correlated with domestic tourism, such as rural tourism. Yang et al. ( 2021 ) found that the contribution of rural tourism to employment is significant; they indicated that the proportion of nonagricultural jobs had increased by 99.57%, and tourism in rural communities had become the leading industry at their research site in China, with a value ten times higher than that of agricultural output. Therefore, rural tourism is vital in counteracting public mental health issues and can potentially advance regional resilience, identity, and well-being (López-Sanz et al., 2021 ).
Since the government plays a critical role in rural tourism development, providing valuable insights, perspectives, and recommendations to policy-makers to foster sustainable policies and practices in rural destinations is essential (Liu et al., 2020 ). Despite the variables developed over time to address particular aspects of rural tourism development, there is still a lack of specific variables and an overall measurement framework for understanding the contributions of rural tourism. Therefore, more evidence is needed to understand how rural tourism influences rural communities from various structural perspectives and to prompt policy-makers to accept rural tourism as an effective development policy or strategy for rural community development. In this paper, we aim to fill this gap.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: the section “Literature review” presents the literature review. Our methodology is described in the section “Methodology”, and our results are presented in the section “Results”. Our discussion in the section “Discussion/implications” places our findings in perspective by describing their theoretical and practical implications, and we provide concluding remarks in the section “Conclusion”.
Literature review
The role of rural tourism.
The UNWTO ( 2021 ) defined rural tourism as a type of tourism in which a visitor’s experience is related to a wide range of products generally linked to nature-based activity, agriculture, rural lifestyle/culture, angling, and sightseeing. Rural tourism has been used as a valid developmental strategy in rural areas in many developed and developing countries. This developmental strategy aims to enable a rural community to grow while preserving its traditional culture (Kaptan et al., 2020 ). In rural areas, ongoing encounters and interactions between humans and nature occur, as well as mutual transformations. These phenomena take place across a wide range of practices that are spatially and temporally bound, including agriculture, forestry, fishing, hunting, farm tourism, cultural heritage preservation, and country life (Hegarty and Przezbórska, 2005 ). To date, rural tourism in many places has become an important new element of the regional rural economy; it is increasing in importance as both a strategic sector and a way to boost the development of rural regions (Polukhina et al., 2021 ). Urban visitors’ demand for short-term leisure activities has increased because of the COVID-19 pandemic (Slater, 2020 ). Furthermore, as tourists shifted their preferences from exotic to local rural tourism amid COVID-19, Marques et al. ( 2022 ) suggested that this trend is a new opportunity that should be seized, as rural development no longer relies on agriculture alone. Instead, other practices, such as rural tourism, have become opportunities for rural areas. Ironically, urbanization has both caused severe problems in rural areas and stimulated rural tourism development as an alternative means of economic revitalization (Lewis and Delisle, 2004 ). Rural tourism provides many unique events and activities that people who live in urban areas are interested in, such as agricultural festivals, crafts, historical buildings, natural preservation, nostalgia, cuisine, and opportunities for family togetherness and relaxation (Christou, 2020 ; Getz, 2008 ). As rural tourism provides visitors from urban areas with various kinds of psychological, educational, social, esthetic, and physical satisfaction, it has brought unprecedented numbers of tourists to rural communities, stimulated economic growth, improved the viability of these communities, and enhanced their living standards (Nicholson and Pearce, 2001 ). For example, rural tourism practitioners have obtained significant economic effects, including more income, more direct sales, better profit margins, and more opportunities to sell agricultural products or craft items (Everett and Slocum, 2013 ). Local residents can participate in the development of rural tourism, and it does not necessarily depend on external resources. Hence, it provides entrepreneurial opportunities (Lee et al., 2006 ). From an environmental perspective, rural tourism is rooted in a contemporary theoretical shift from cherishing local agricultural resources to restoring the balance between people and ecosystems. Thus, rural land is preserved, natural landscapes are maintained, and green consumerism drives farmers to focus on organic products, green chemistry, and value-added products, such as land ethics (Higham and Ritchie, 2001 ). Therefore, the potential contributions of rural tourism are significant and profound (Marques, 2006 ; Phillip et al., 2010 ). Understanding its contributions to rural community development could encourage greater policy-maker investment and resident support (Yang et al., 2010 ).
Contributions of rural tourism to rural community development
Maintaining active local communities while preventing the depopulation and degradation of rural areas requires a holistic approach and processes that support sustainability. What can rural tourism contribute to rural development? In the literature, rural tourism has been shown to bring benefits such as stimulating economic growth (Oh, 2005 ), strengthening rural and regional economies (Lankford, 1994 ), alleviating poverty (Zhao et al., 2007 ), and improving living standards in local communities (Uysal et al., 2016 ). In addition to these economic contributions, what other elements have not been identified and discussed (Su et al., 2020 )? To answer these questions, additional evidence is a prerequisite. Thus, this study examines the following four aspects. (1) The economic perspective: The clustering of activities offered by rural tourism stimulates cooperation and partnerships between local communities and serves as a vehicle for creating various economic benefits. For example, rural tourism improves employment opportunities and stability, local residents’ income, investment, entrepreneurial opportunities, agricultural production value-added, capital formation, economic resilience, business viability, and local tax revenue (Atun et al., 2019 ; Cheng and Zhang, 2020 ; Choi and Sirakaya, 2006 ; Chong and Balasingam, 2019 ; Cunha et al., 2020 ). (2) The sociocultural perspective: Rural tourism no longer refers solely to the benefits of agricultural production; through economic improvement, it represents a greater diversity of activities. It is important to take advantage of the novel social and cultural alternatives offered by rural tourism, which contribute to the countryside. For example, rural tourism can be a vehicle for introducing farmers to potential new markets through more interactions with consumers and other value chain members. Under such circumstances, the sociocultural benefits of rural tourism are multifaceted. These include improved rural area depopulation prevention (López-Sanz et al., 2021 ), cultural and heritage preservation, and enhanced social stability compared to farms that do not engage in the tourism business (Ma et al., 2021 ; Yang et al., 2021 ). Additional benefits are improved quality of life; revitalization of local crafts, customs, and cultures; restoration of historical buildings and community identities; and increased opportunities for social contact and exchange, which enhance community visibility, pride, and cultural integrity (Kelliher et al., 2018 ; López-Sanz et al., 2021 ; Ryu et al., 2020 ; Silva and Leal, 2015 ). (3) The environmental perspective: Many farms in rural areas have been rendered noncompetitive due to a shortage of labor, poor managerial skills, and a lack of financial support (Coria and Calfucura, 2012 ). Although there can be immense pressure to maintain a farm in a family and to continue using land for agriculture, these problems could cause families to sell or abandon their farms or lands (Tew and Barbieri, 2012 ). In addition, unless new income pours into rural areas, farm owners cannot preserve their land and its natural aspects; thus, they tend to allow their land to become derelict or sell it. In the improved economic conditions after farms diversify into rural tourism, rural communities have more money to provide environmental care for their natural scenic areas, pastoral resources, forests, wetlands, biodiversity, pesticide mitigation, and unique landscapes (Theodori, 2001 ; Vail and Hultkrantz, 2000 ). Ultimately, the entire image of a rural community is affected; the community is imbued with vitality, and farms that participate in rural tourism instill more togetherness among families and rural communities. In this study, the environmental benefits induced by rural tourism led to improved natural environmental conservation, biodiversity, environmental awareness, infrastructure, green chemistry, unspoiled land, and family land (Di and Laura, 2021 ; Lane, 1994 ; Ryu et al., 2020 ; Yang et al., 2021 ). (4) The leisure and educational perspective: Rural tourism is a diverse strategy associated with an ongoing flow of development models that commercialize a wide range of farming practices for residents and visitors. Rural territories often present a rich set of unique resources that, if well managed, allow multiple appealing, authentic, and memorable tourist experiences. Tourists frequently comment that the rural tourism experience positively contrasts with the stress and other negatively perceived conditions of daily urban life. This is reflected in opposing, compelling images of home and a visited rural destination (Kastenholz et al., 2012 ). In other words, tourists’ positive experiences result from the attractions and activities of rural tourism destinations that may be deemed sensorially, symbolically, or socially opposed to urban life (Kastenholz et al. 2018 ). These experiences are associated with the “search for authenticity” in the context of the tension between the nostalgic images of an idealized past and the demands of stressful modern times. Although visitors search for the psychological fulfillment of hedonic, self-actualization, challenge, accomplishment, exploration, and discovery goals, some authors have uncovered the effects of rural tourism in a different context. For example, Otto and Ritchie ( 1996 ) revealed that the quality of a rural tourism service provides a tourist experience in four dimensions—hedonic, peace of mind, involvement, and recognition. Quadri-Felitti and Fiore ( 2013 ) identified the relevant impact of education, particularly esthetics, versus memory on satisfaction in wine tourism. At present, an increasing number of people and families are seeking esthetic places for relaxation and family reunions, particularly amid COVID-19. Rural tourism possesses such functions; it remains a novel phenomenon for visitors who live in urban areas and provides leisure and educational benefits when visitors to a rural site contemplate the landscape or participate in an agricultural process for leisure purposes (WTO, 2020 ). Tourists can obtain leisure and educational benefits, including ecological knowledge, information about green consumerism, leisure and recreational opportunities, health and food security, reduced mental health issues, and nostalgia nurturing (Alford and Jones, 2020 ; Ambelu et al., 2018 ; Christou, 2020 ; Lane, 1994 ; Li et al., 2021 ). These four perspectives possess a potential synergy, and their effects could strengthen the relationship between rural families and rural areas and stimulate new regional resilience. Therefore, rural tourism should be understood as an enabler of rural community development that will eventually attract policy-makers and stakeholders to invest more money in developing or advancing it.
Methodology
The literature on rural tourism provides no generally accepted method for measuring its contributions or sustainability intensity. Although many statistical methods are available, several limitations remain, particularly in terms of the item generation stage and common method bias (CMB). For example, Marzo-Navar et al. ( 2015 ) used the mean and SD values to obtain their items. However, the use of the mean has been criticized because it is susceptible to extreme values or outliers. In addition, they did not examine omitted variables and CMB. Asmelash and Kumar ( 2019 ) used the Delphi method with a mean value for deleting items. Although they asked experts to suggest the inclusion of any missed variables, they did not discuss these results. Moreover, they did not assess CMB. Islam et al. ( 2021 ) used a sixteen-step process to formulate sustainability indicators but did not consider omitted variables, a source of endogeneity bias. They also did not designate a priority for each indicator. Although a methodologically sound systematic review is commonly used, little attention has been given to reporting interexpert reliability when multiple experts are used to making decisions at various points in the screening and data extraction stages (Belur et al., 2021 ). Due to the limitations of the current methods for assessing sustainable tourism development, we aim to provide new methodological insights. Specifically, we suggest a six-stage procedure, as shown in Fig. 1 .
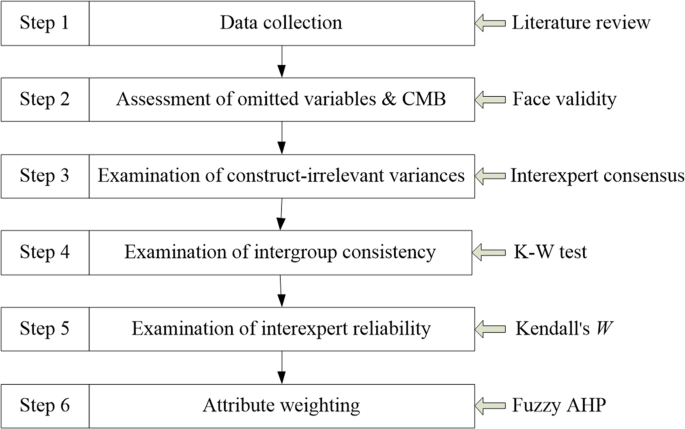
Steps required in developing the model for analysis after obtaining the data.
Many sources of data collection can be used, including literature reviews, inferences about the theoretical definition of the construct, previous theoretical and empirical research on the focal construct, advice from experts in the field, interviews, and focus groups. In this study, the first step was to retrieve data from a critical literature review. The second step was the assessment of omitted variables to produce items that fully captured all essential aspects of the focal construct domain. In this case, researchers must not omit a necessary measure or fail to include all of the critical dimensions of the construct. In addition, the stimuli of CMB, for example, double-barreled items, items containing ambiguous or unfamiliar terms, and items with a complicated syntax, should be simplified and made specific and concise. That is, researchers should delete items contaminated by CMB. The third step was the examination of construct-irrelevant variance to retain the variances relevant to the construct of interest and minimize the extent to which the items tapped concepts outside the focal construct domain. Variances irrelevant to the targeted construct should be deleted. The fourth step was to examine intergroup consistency to ensure that there was no outlier impact underlying the ratings. The fifth step was to examine interexpert reliability to ensure rating conformity. Finally, we prioritized the importance of each variable with the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process (AHP), which is a multicriteria decision-making approach. All methods used in this study are expert-based approaches.
Selection of experts
Because this study explores the contributions of rural tourism to rural community development, it involves phenomena in the postdevelopment stage; therefore, a few characteristics are essential for determining the choice of experts. The elements used to identify the experts in this study were (1) the number of experts, (2) expertise, (3) knowledge, (4) diversity, (5) years working in this field, and 5) commitment to participation. Regarding the number of experts, Murphy-Black et al. ( 1998 ) suggested that the more participants there are, the better, as a higher number reduces the effects of expert attrition and rater bias. Taylor-Powell ( 2002 ) pointed out that the number of participants in an expert-based study depends not only on the purpose of the research but also on the diversity of the target population. Okoli and Pawlowski ( 2004 ) recommended a target number of 10–18 experts for such a purpose. Therefore, we recruited a group of 18 experts based on their stated interest in the topic and asked them to comment on our rationale concerning the rating priorities among the items. We asked them to express a degree of agreement or disagreement with each item we provided. We adopted a heterogeneous and anonymous arrangement to ensure that rater bias did not affect this study. The 18 experts had different backgrounds, which might have made it easier for them to reach a consensus objectively. We divided the eighteen experts into three subgroups: (1) at least six top managers from rural tourism businesses, all of whom had been in the rural tourism business for over 10 years; (2) at least six academics who taught subjects related to tourism at three different universities in Taiwan; and (3) at least six government officials involved in rural development issues in Taiwan.
Generating items to represent the construct
Step 1: data collection.
Data collection provides evidence for investigation and reflects the construct of interest. While there is a need to know what rural tourism contributes, previous studies have provided no evidence for policy-makers to establish a rural community strategy; thus, it is essential to use a second source to achieve this aim. We used a literature review for specific topics; the data we used were based on the findings being presented in papers on rural tourism indexed in the SSCI (Social Sciences Citation Index) and SCIE (Science Citation Index Expanded). In this study, we intended to explore the role of rural tourism and its contributions to rural development. Therefore, we explored the secondary literature on the state of the questions of rural development, sustainable development, sustainability indicators, regional resilience, farm tourism, rural tourism, COVID-19, tourist preferences, and ecotourism using terms such as land ethics, ecology, biodiversity, green consumerism, environmentalism, green chemistry, community identity, community integration, community visibility, and development goals in an ad hoc review of previous studies via Google Scholar. Based on the outcomes of this first data collection step, we generated thirty-three subattributes and classified them into four domains.
Step 2: Examine the face validity of omitted variables and CMB
Face validity is defined as assessing whether a measurement scale or questionnaire includes all the necessary items (Dempsey and Dempsey, 1992 ). Based on the first step, we generated data subattributes from our literature review. However, there might have been other valuable attributes or subattributes that were not considered or excluded. Therefore, our purposes for examining face validity were twofold. First, we assessed the omitted variables, defined as the occurrence of crucial aspects or facets that were omitted (Messick, 1995 ). These comprise a threat to construct validity that, if ignored by researchers, might result in unreliable findings. In other words, face validity is used to distinguish whether the researchers have adequately captured the full dimensions of the construct of interest. If not, the evaluation instrument or model is deficient. However, the authors found that most rural tourism studies have not assessed the issue of omitted variables (An and Alarcon, 2020 ; Lin, 2022 ). Second, we mitigated the CMB effect. In a self-report survey, it is necessary to provide a questionnaire without CMB to the targeted respondents, as CMB affects respondent comprehension. Therefore, we assessed item characteristic effects, item context effects, and question response process effects. These three effects are related to the respondents’ understanding, retrieval, mood, affectivity, motivation, judgment, response selection, and response reporting (Podsakoff et al., 2003 ). Specifically, items containing flaws from these three groups in a questionnaire can seriously influence an empirical investigation and potentially result in misleading conclusions. We assessed face validity by asking all the experts to scrutinize the content items that we collected from the literature review and the questionnaire that we drafted. The experts could then add any attribute or subattribute they thought was essential that had been omitted. They could also revise the questionnaire if CMB were embedded. We added the new attributes or subattributes identified by the experts to those collected from the literature review.
Step 3: Examine interexpert consensus for construct-irrelevant variances
After examining face validity, we needed to rule out items irrelevant to the construct of interest; otherwise, the findings would be invalid. We examined the interexpert consensus to achieve this aim. The purpose was to estimate the experts’ ratings of each item. In other words, interexpert consensus assesses the extent to which experts make the same ratings (Kozlowski and Hattrup, 1992 ; Northcote et al., 2008 ). In prior studies, descriptive statistics have often been used to capture the variability among individual characteristics, responses, or contributions to the subject group (Landeta, 2006 ; Roberson et al., 2007 ). Many expert-based studies have applied descriptive statistics to determine consensus and quantify its degree (Paraskevas and Saunders, 2012 ; Stewart et al., 2016 ). Two main groups of descriptive statistics, central tendencies (mode, mean, and median) and level of dispersion (standard deviation, interquartile, and coefficient of variation), are commonly used when determining consensus (Mukherjee et al., 2015 ). Choosing the cutoff point of interexpert consensus was critical because we used it as a yardstick for item retention and its value can also be altered by a number on the Likert scale (Förster and von der Gracht, 2014 ). In the case of a 5-point Likert scale, the coefficient of variation (CV) is used to measure interexpert consensus. Hence, CV ≤ 0.3 indicated high consensus (Zinn et al., 2001 ). In addition, based on the feedback obtained from the expert panel, we used standard deviation (SD) as another measurement to assess the variation in our population. Henning and Jordaan ( 2016 ) indicate that SD ≤ 1 represents a high level of consensus, meaning that it can act as a guideline for cutoff points. In addition, following Vergani et al. ( 2022 ), we used the percentage agreement (% AGR) to examine interexpert consensus. If the responses reached ≧ 70% 4 and 5 in the case of a 5-point Likert scale, it indicated that the item had interexpert consensus; thus, we could retain it. Moreover, to avoid the impact of outliers, we used the median instead of the mean as another measurement. Items had a high consensus if their median value was ≥4.00 (Rice, 2009 ). Considering these points, we adopted % AGR, median, SD, and CV to examine interexpert consensus.
Step 4: Examine intergroup consistency
In this expert-based study, the sample size was small. Any rater bias could have caused inconsistency among the subgroups of experts; therefore, we needed to examine the effect of rater bias on intergroup consistency. When the intergroup ratings showed substantially different distributions, the aggregated data were groundless. Dajani et al. ( 1979 ) remarked that interexpert consensus is meaningless if the consistency of responses in a study is not reached, as it means that any rater bias could distort the median, SD, or CV. Most studies have used one-way ANOVA to determine whether there is a significant difference between the expected and observed frequency in three or more categories. However, this method is based on large sample size and normal distribution. In the case of expert-based studies, the expert sample size is small, and the assessment distribution tends to be skewed. Thus, we used the nonparametric test instead of one-way ANOVA for consistency measurement (Potvin and Roff, 1993 ). We used the Kruskal‒Wallis test (K–W) to test the intergroup consistency among the three subgroups of experts. The purpose of the K–W test is to determine whether there are significant differences among three or more subgroups regarding the ratings of the domains (Huck, 2004 ). The judgment criteria in the K-W test depended on the level of significance, and we set the significance level at p < 0.05 (Love and Irani, 2004 ), with no significant differences among groups set at p > 0.05 (Loftus et al., 2000 ; Rice, 2009 ). We used SPSS to conduct the K–W test to assess intergroup consistency in this study.
Step 5: Examine interexpert reliability
Interexpert reliability, on the one hand, is usually defined as the proportion of systematic variance to the total variance in ratings (James et al., 1984 ). On the other hand, interexpert reliability estimation is not concerned with the exact or absolute value of ratings. Rather, it measures the relative ordering or ranking of rated objects. Thus, interexpert reliability estimation concerns the consistency of ratings (Tinsley and Weiss, 1975 ). If an expert-based study did not achieve interexpert reliability, we could not trust its analysis (Singletary, 1994 ). Thus, we examined interexpert reliability in this expert-based study. Many methods are available in the literature for measuring interexpert reliability, but there seems to be little consensus on a standard method. We used Kendall’s W to assess the reliability among the experts for each sample group (Goetz et al., 1994 ) because it was available for any sample size or ordinal number. If W was 1, all the experts were unanimous, and each had assigned the same order to the list of objects or concerns. As Spector et al. ( 2002 ) and Schilling ( 2002 ) suggested, reliabilities well above the recommended value of .70 indicate sufficient internal reliability. In this study, there was a strong consensus when W > 0.7. W > 0.5 represented a moderate consensus; and W < 0.3 indicated weak interexpert agreement (Schmidt et al., 2001 ). To measure Kendall’s W , we used SPSS 23 to assess interexpert reliability.
Step 6: Examine the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process
After examining face validity, interexpert consensus, intergroup consistency, and interexpert reliability, we found that the aggregated items were relevant, authentic, and reliable in relation to the construct of interest. To provide policy-makers with a clear direction regarding which contributions are more or less important, we scored each attribute and subattribute using a multicriteria decision-making technique. Fuzzy AHP is a well-known decision-making tool for modeling unstructured problems. It enables decision-makers to model a complex issue in a hierarchical structure that indicates the relationships between the goal, criteria, and subcriteria on the basis of scores (Park and Yoon, 2011 ). The fuzzy AHP method tolerates vagueness and ambiguity (Mikhailov and Tsvetinov, 2004 ). In other words, fuzzy AHP can capture a human’s appraisal of ambiguity when considering complex, multicriteria decision-making problems (Erensal et al., 2006 ). In this study, we used Power Choice 2.5 software to run fuzzy AHP, determine weights, and develop the impact structure of rural tourism on sustainable rural development.
Face validity
To determine whether we had omitted variables, we asked all 18 experts to scrutinize our list of four attributes and 33 subattributes for omitted variables and determine whether the questionnaire contained any underlying CMB. We explained the meaning of omitted variables, the stimuli of CMB, and the two purposes of examining face validity to all the experts. In their feedback, the eighteen experts added one item as an omitted variable: business viability. The experts suggested no revisions to the questionnaire we had drafted. These results indicated that one omitted variable was revealed and that our prepared questionnaire was clear, straightforward, and understandable. The initially pooled 34 subattributes represented the construct of interest, and all questionnaires used for measurement were defendable in terms of CMB. The biasing effects of method variance did not exist, indicating that the threat of CMB was minor.
Interexpert consensus
In this step, we rejected any items irrelevant to the construct of interest. Consensus measurement played an essential role in aggregating the experts’ judgments. This study measured the AGR, median, SD, and CV. Two items, strategic alliance (AGR = 50%) and carbon neutrality (AGR = 56%) were rated < 70%, and we rejected them accordingly. These results are shown in Table 1 . The AGR, median, SD, and CV values were all greater than the cutoff points, thus indicating that the majority of experts in this study consistently recognized high values and reached a consensus for the rest of the 32 subattributes. Consequently, the four attributes and 32 subattributes remained and were initially identified as determinants for further analysis.
Intergroup consistency and interexpert reliability
In this study, with scores based on a 5-point Likert scale, we conducted the K–W test to assess intergroup differences for each subattribute. Based on the outcomes, the K–W test yielded significant results for all 32 subattributes; all three groups of experts reached consistency at p > 0.05. This result indicated that no outlier or extreme value underlay the ratings, and therefore, intergroup consistency was reached. Finally, we measured interexpert reliability with Kendall’s W . The economic perspective was W = 0.73, the sociocultural perspective was W = 0.71, the environmental perspective was W = 0.71, and the leisure and educational perspective was W = 0.72. These four groups of W were all ≧ 0.7, indicating high reliability for the ranking order and convergence judged by all subgroup experts. These results are shown in Table 2 .
The hierarchical framework
The results of this study indicate that rural tourism contributions to rural community development comprise four attributes and thirty-two subattributes. The economic perspective encompasses nine subattributes and is weighted at w = 0.387. In addition, rural tourism has long been considered a possible means of sociocultural development and regeneration of rural areas, particularly those affected by the decline in traditional rural
activities, agricultural festivals, and historical buildings. According to the desired benefits, the sociocultural perspective encompasses nine subattributes and is weighted at w = 0.183. Moreover, as rural tourism can develop on farms and locally, its contribution to maintaining and enhancing environmental regeneration and protection is significant. Therefore, an environmental perspective can determine rural tourism’s impact on pursuing environmental objectives. Our results indicate that the environmental perspective encompasses seven subattributes and that its weight is w = 0.237. Furthermore, the leisure and educational perspective indicates the attractiveness of rural tourism from visitors’ viewpoint and their perception of a destination’s value and contributions. These results show that this perspective encompasses seven subattributes and is weighted at w = 0.193. This specific contribution model demonstrates a 3-level hierarchical structure, as shown in Fig. 2 . The scores for each criterion could indicate each attribute’s importance and explain the priority order of the groups. Briefly, the critical sequence of each measure in the model at Level 2 is as follows: economic perspective > environmental perspective > leisure and educational perspective > sociocultural perspective. Since scoring and ranking were provided by 18 experts from three different backgrounds and calculated using fuzzy AHP, our rural tourism contribution model is established. It can provide policy-makers with information on the long-term benefits and advantages following the completion of excellent community development in rural areas.
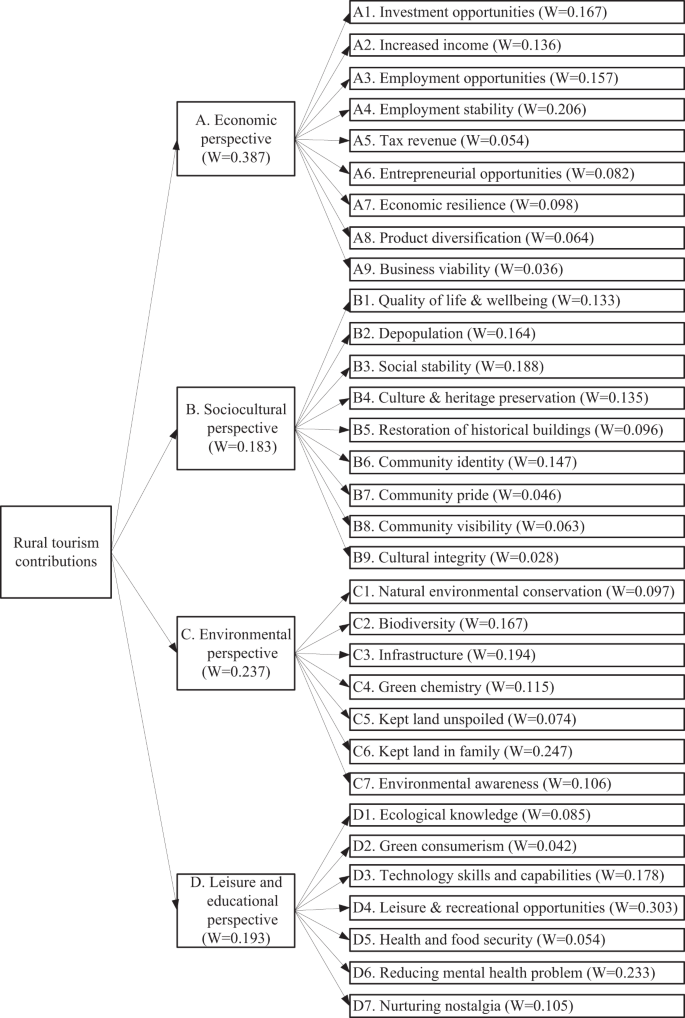
The priority index of each attribute and sub-attribute.
Discussion/Implications
In the era of sustainable rural development, it is vital to consider the role of rural tourism and how research in this area shapes access to knowledge on rural community development. This study provides four findings based on the increasing tendency of policy-makers to use such information to shape their policy-making priorities. It first shows that the demand for rural tourism has soared, particularly during COVID-19. Second, it lists four significant perspectives regarding the specific contributions of rural tourism to rural community development and delineates how these four perspectives affect rural tourism development. Our findings are consistent with those of prior studies. For example, geography has been particularly important in the rural or peripheral tourism literature (Carson, 2018 ). In terms of the local geographical context, two contributions could be made by rural tourism. The first stems from the environmental perspective. When a rural community develops rural tourism, environmental protection awareness is increased, and the responsible utilization of natural resources is promoted. This finding aligns with Lee and Jan ( 2019 ). The second stems from the leisure and educational perspective. The geographical context of a rural community, which provides tourists with geographical uniqueness, advances naturally calming, sensory-rich, and emotion-generating experiences for tourists. These results suggest that rural tourism will likely positively impact tourists’ experience. This finding is consistent with Kastenhoz et al. ( 2020 ). Third, although expert-based approaches have considerable benefits in developing and testing underlying phenomena, evidence derived from interexpert consensus, intergroup consistency, and interexpert reliability has been sparse. This study provides such evidence. Fourth, this research shows that rural tourism makes four main contributions, economic, sociocultural, environmental, leisure, and educational, to rural community development. Our results show four key indicators at Level 2. The economic perspective is strongly regarded as the most important indicator, followed by the environmental perspective, leisure and educational perspective, and sociocultural perspective, which is weighted as the least important. The secondary determinants of contributions have 32 subindicators at Level 3: each was identified and assigned a different weight. These results imply that the attributes or subattributes with high weights have more essential roles in understanding the contributions of rural tourism to rural community development. Policy-makers can use these 32 subindicators to formulate rural tourism development policies or strategies.
This study offers the following five practical implications for policymakers and rural communities:
First, we argue that developing rural tourism within a rural community is an excellent strategy for revitalization and countering the effects of urbanization, depopulation, deforestation, and unemployment.
Second, our analytical results indicate that rural tourism’s postdevelopment contribution is significant from the economic, sociocultural, environmental, leisure, and educational perspectives, which is consistent with Lee and Jan ( 2019 ).
Third, there is an excellent opportunity to build or invest more in rural tourism during COVID-19, not only because of the functions of rural tourism but also because of its timing. Many prior studies have echoed this recommendation. For example, Yang et al. ( 2021 ) defined rural tourism as the leading industry in rural areas, offering an output value ten times higher than that of agriculture in China. In addition, rural tourism has become more attractive to urban tourists amid COVID-19. Vaishar and Šťastná ( 2022 ) suggested that the COVID-19 pandemic created a strong demand for rural tourism, which can mitigate threats to public mental health, such as anxiety, depression, loneliness, isolation, and insomnia. Marques et al. ( 2022 ) showed that tourists’ preference for tourism in rural areas increased substantially during COVID-19.
Fourth, the contributions of this study to policy development are substantial. The more focused rural tourism in rural areas is, the more effective revitalization becomes. This finding highlights the importance of such features in developing rural tourism to enhance rural community development from multiple perspectives. This finding echoes Zawadka et al. ( 2022 ); i.e., policy-makers should develop rural tourism to provide tourists with a safe and relaxed environment and should not ignore the value of this model for rural tourism.
Fifth, our developed model could drive emerging policy issues from a supporting perspective and provide policy-makers with a more comprehensive overview of the development of the rural tourism sector, thus enabling them to create better policies and programs as needed. For example, amid COVID-19, rural tourism created a safe environment for tourists, mainly by reducing their fears of contamination (Dennis et al., 2021 ). This novel contribution that rural tourism destinations can provide to residents and visitors from other places should be considered and built into any rural community development policy.
This study also has the following four methodological implications for researchers:
First, it addresses methodological limitations that still impede tourism sustainability model development. Specifically, we suggest a six-stage procedure as the guideline; it is imperative that rural tourism researchers or model developers follow this procedure. If they do not, their findings tend to be flawed.
Second, to ensure that collected data are without extraneous interference or differences via subgroups of experts, the assessment of intergroup consistency with the K–W test instead of one-way ANOVA is proposed, especially in small samples and distribution-free studies.
Third, providing interexpert reliability evidence within expert-based research is critical; we used Kendall’s W to assess the reliability among experts for each sample group because it applies to any sample size and ordinal number.
Finally, we recommend using fuzzy AHP to establish a model with appropriate indicators for decision-making or selection. This study offers novel methodological insights by estimating a theoretically grounded and empirically validated rural tourism contribution model.
There are two limitations to this study. First, we examine all subattributes by interexpert consensus to delete construct-irrelevant variances that might receive criticism for their lack of statistical rigor. Future studies can use other rigorous methods, such as AD M( j ) or rWG ( j ) , interexpert agreement indices to assess and eliminate construct-irrelevant variances. Second, we recommend maximizing rural tourism contributions to rural community development by using the general population as a sample to identify any differences. More specifically, we recommend using Cronbach’s alpha, confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), and structural equation modeling (SEM) to test the overall reliability and validity of the data and results. It is also necessary to provide results for goodness-of-fit measures—e.g., the goodness-of-fit index (GFI), adjusted goodness-of-fit index (AGFI), comparative fit index (CFI), normed fit index (NFI), Tucker–Lewis Index (TLI), standardized root mean square residual (SRMR), or root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA).
Numerous empirical studies have illustrated how rural tourism can positively and negatively affect the contexts in rural areas where it is present. This study reveals the positive contributions of rural tourism to rural community development. The findings show that using rural tourism as a revitalization strategy is beneficial to nonurban communities in terms of their economic, sociocultural, environmental, and leisure and educational development. The contribution from the economic perspective is particularly important. These findings suggest that national, regional, and local governments or community developers should make tourism a strategic pillar in their policies for rural development and implement tourism-related development projects to gain 32 benefits, as indicated in Fig. 2 . More importantly, rural tourism was advocated and proved effective for tourists and residents to reduce anxiety, depression, or insomnia during the COVID-19 pandemic. With this emerging contribution, rural tourism is becoming more critical to tourists from urban areas and residents involved in rural community development. With this model, policy-makers should not hesitate to develop or invest more in rural communities to create additional tourism-based activities and facilities. As they could simultaneously advance rural community development and public mental health, policy-makers should include these activities among their regional resilience considerations and treat them as enablers of sustainable rural development. We conclude that amid COVID-19, developing rural tourism is an excellent strategy for promoting rural community development and an excellent alternative that could counteract the negative impacts of urbanization and provide stakeholders with more positive interests. The proposed rural tourism contribution model also suggests an unfolding research plan.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Alford P, Jones R (2020) The lone digital tourism entrepreneur: Knowledge acquisition and collaborative transfer. Tour Manag 81:104–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2020.104139
Article Google Scholar
Altieri MA, Farrell JG, Hecht SB, Liebman M, Magdoff F et al (2018) The agroecosystem: determinants, resources, processes, and sustainability. Agroecology 41–68. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780429495465-3
Ambelu G, Lovelock B, Tucker H (2018) Empty bowls: conceptualising the role of tourism in contributing to sustainable rural food security. J Sustain Tour 26(10):1749–1765. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2018.1511719
An W, Alarcon S (2020) How can rural tourism be sustainable? A systematic review. Sustainability 12(18):7758. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187758
Arroyo C, Barbieri C, Rich SR (2013) Defining agritourism: a comparative study of stakeholders’ perceptions in Missouri and North Carolina. Tour Manag 37:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2012.12.007
Asmelash AG, Kumar S (2019) Assessing progress of tourism sustainability: Developing and validating sustainability indicators. Tour Manag 71:67–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2018.09.020
Atun RA, Nafa H, Türker ÖO (2019) Envisaging sustainable rural development through ‘context-dependent tourism’: case of Northern Cyprus. Environ Dev Sustain 21:1715–1744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-018-0100-8
Belur J, Tompson L, Thornton A, Simon M (2021) Interrater reliability in systematic review methodology: exploring variation in coder decision-making. Sociol Methods Res 50(2):837–865. https://doi.org/10.1177/0049124118799372
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Carson DA (2018) Challenges and opportunities for rural tourism geographies: a view from the ‘boring’ peripheries. Tour Geogr 20(4):737–741. https://doi.org/10.1080/4616688.2018.1477173
Cheng L, Zhang J (2020) Is tourism development a catalyst of economic recovery following natural disaster? An analysis of economic resilience and spatial variability. Curr Issues Tour 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2019.1711029
Choi H-SC, Sirakaya E (2006) Sustainability indicators for managing community tourism. Tour Manag 27(6):1274–1289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2005.05.018
Chong KY, Balasingam AS (2019) Tourism sustainability: economic benefits and strategies for preservation and conservation of heritage sites in Southeast Asia. Tour Rev 74(2):268–279. https://doi.org/10.1108/TR-11-2017-0182
Christou PA (2020) Tourism experiences as the remedy to nostalgia: conceptualizing the nostalgia and tourism nexus. Curr Issues Tour 23(5):612–625. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2018.1548582
Coria J, Calfucura E (2012) Ecotourism and the development of indigenous communities: the good, the bad and the ugly. Ecol Econ 73(15):47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2011.10.024
Cunha C, Kastenholz E, Carneiro MJ (2020) Entrepreneurs in rural tourism: do lifestyle motivations contribute to management practices that enhance sustainable entrepreneurial ecosystems? J Hosp Tour Manag 44:215–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2020.06.007
Dajani JS, Sincoff MZ, Talley WK (1979) Stability and agreement criteria for the termination of Delphi studies. Technol Forecast Soc Change 13(1):83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1625(79)90007-6
Dempsey PA, Dempsey AD (1992) Nursing research with basic statistical applications, 3rd edn. Jones and Bartlett, Boston
Google Scholar
Dennis D, Radnitz C, Wheaton MG (2021) A perfect storm? Health anxiety, contamination fears, and COVID-19: lessons learned from past pandemics and current challenges. Int J Cogn Ther 14:497–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41811-021-00109-7
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Di TF, Laura M (2021) How green possibilities can help in a future sustainable conservation of cultural heritage in Europe. Sustainability 13(7):3609. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073609
Erensal YC, ncan TÖ, Demircan ML (2006) Determining key capabilities in technology management using fuzzy analytic hierarchy process: a case study of Turkey. Inf Sci 176(18):2755–2770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2005.11.004
Everett S, Slocum SL (2013) Food and tourism: an effective partnership? A UK-based review. J Sustain Tour 21(6):789–809. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2012.741601
Förster B, von der Gracht H (2014) Assessing Delphi panel composition for strategic foresight—a comparison of panels based on company-Internal and external participants. Technol Forecast Soc Change 84:215–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/.techfore.2013.07.012
Getz D (2008) Event tourism: definition, evolution and research. Tour Manag 29(3):403–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2007.07.017
Goetz CG, Stebbins GT, Shale HM, Lang AE, Chernik DA, Chmura TA, Ahlskog JE, Dorflinger EE (1994) Utility of an objective dyskinesia rating scale for Parkinson’s disease: inter- and intrarater reliability assessment. Mov Disord 9(4):390–394. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.870090403
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Hegarty C, Przezborska L (2005) Rural and agri-tourism as a tool for reorganizing rural areas in old and new member states—a comparison study of Ireland and Poland. Int J Tour Res 7(2):63–77. https://doi.org/10.1002/jtr.513
Henning JIF, Jordaan H (2016) Determinants of financial sustainability for farm credit applications—a Delphi study. Sustainability 8(1):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8010077
Higham JES, Ritchie B (2001) The evolution of festivals and other events in rural Southern New Zealand. Event Manag 7(1):39–49. https://doi.org/10.3727/152599501108751461
Huck SW (2004) Reading statistics and research, 4th edn. Allyn and Bacon, Boston
Islam MS, Lovelock B, Coetzee WJL (2021) Liberating sustainability indicators: developing and implementing a community-operated tourism sustainability indicator system in Boga Lake, Bangladesh. J Sustain Tour. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.1928147
James LR, Demaree RG, Wolf G (1984) Estimating within-group interrater reliability with and without response bias. J Appl Psychol 69(1):322–327. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.69.1.85
Juschten M, Hössinger R (2020) Out of the city - But how and where? A mode-destination choice model for urban–rural tourism trips in Austria. Curr Issues Tour 24(10):1465–1481. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2020.1783645
Kabadayi S, O’Connor G, Tuzovic S (2020) Viewpoint: the impact of coronavirus on service ecosystems as service mega-disruptions. J Serv Mark 34(6):809–817. reurl.cc/oen0lM
Kaptan AÇ, Cengı̇z TT, Özkök F, Tatlı H (2020) Land use suitability analysis of rural tourism activities: Yenice, Turkey. Tour Manag 76:103949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2019.07.003
Kastenholz E, Carneiro MJ, Marques CP, Lima J (2012) Understanding and managing the rural tourism experience—the case of a historical village in Portugal. Tour Manag Perspect 4:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2012.08.009
Kastenholz E, Carneiro M, Marques CP, Loureiro SMC (2018) The dimensions of rural tourism experience: impacts on arousal, memory and satisfaction. J Travel Tour Mark 35(2):189–201. https://doi.org/10.1080/10548408.2017.1350617
Kastenhoz E, Marques CP, Carneiro MJ (2020) Place attachment through sensory-rich, emotion-generating place experiences in rural tourism. J Destin Mark Manage 17:100455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdmm.2020.100455
Kelliher F, Rein L, Johnson TG, Joppe M (2018) The role of trust in building rural tourism micro firm network engagement: a multi-case study. Tour Manag 68:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2018.02.014
Kozlowski SW, Hattrup K (1992) A disagreement about within-group agreement: disentangling issues of consistency versus consensus. J Appl Psychol 77(2):161–167. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.77.2.161
Landeta J (2006) Current validity of the Delphi method in social sciences. Technol Forecast Soc Change 73(5):467–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2005.09.002
Lankford SV (1994) Attitudes and perceptions toward tourism and rural regional development. J Travel Res 32(3):35–43. https://doi.org/10.1177/004728759403200306
Lane B (1994) What is rural tourism? J Sustain Tour 2(1&2):7–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669589409510680
Lee TH, Jan FH (2019) Can community-based tourism contribute to sustainable development? Evidence from residents perceptions of the sustainability. Tour Manag 70:368–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2018.09.003
Lee J, Árnason A, Nightingale A, Shucksmith M (2006) Networking: Social capital and identities in European rural development. Sociol Rural 45(4):269–283. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9523.2005.00305.x
Lewis JB, Delisle L (2004) Tourism as economic self-development in rural Nebraska: a case study. Tour Anal 9(3):153–166. https://doi.org/10.3727/108354204278122
Li Y, Westlund H, Liu Y (2019) Why some rural areas decline while some others not: an overview of rural evolution in the world. J Rural Stud 68:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2019.03.003
Li Z, Zhang X, Yang K, Singer R, Cui R (2021) Urban and rural tourism under COVID-19 in China: research on the recovery measures and tourism development. Tour Rev 76(4):718–736. https://doi.org/10.1108/TR-06-2020-0357
Lin CL (2022) Evaluating the urban sustainable development strategies and common suited paths considering various stakeholders. Environ Dev Sustain 1–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-02021-8
Liu CY, Doub XT, Lia JF, Caib LA (2020) Analyzing government role in rural tourism development: an empirical investigation from China. J Rural Stud 79:177–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2020.08.046
Loftus IM, Naylor AR, Goodall SM, Crowther LJ, Bell PRF, Thompson MM (2000) Increased matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity in unstable carotid plaques: a potential role in acute plaque disruption. Stroke 31(1):40–47. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.31.1.40
López-Sanz JM, Penelas-Leguía A, Gutiérrez-Rodríguez P, Cuesta-Valiño P (2021) Sustainable development and rural tourism in depopulated areas. Land 10(9):985. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10090985
Love PED, Irani Z (2004) An exploratory study of information technology evaluation and benefits management practices of SMEs in the construction industry. Inf Manag 42(1):227–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2003.12.011
Ma X, Wang R, Dai M, Ou Y (2021) The influence of culture on the sustainable livelihoods of households in rural tourism destinations. J Sustain Tour 29:1235–1252. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2020.1826497
Markey S, Halseth G, Manson D (2008) Challenging the inevitability of rural decline: advancing the policy of place in northern British Columbia. J Rural Stud 24:409–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2008.03.012
Marques H (2006) Searching for complementarities between agriculture and tourism—the demarcated wine-producing regions of Northern Portugal. Tour Econ 12(1):147–155. https://doi.org/10.5367/000000006776387141
Marques CP, Guedes A, Bento R (2022) Rural tourism recovery between two COVID-19 waves: the case of Portugal. Curr Issues Tour 25(6):857–863. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2021.1910216
Marzo-Navar M, Pedraja-Iglesia M, Vinzon L (2015) Sustainability indicators of rural tourism from the perspective of the residents. Tour Geogr 17(4):586–602. https://doi.org/10.1080/14616688.2015.1062909
Messick S (1995) Validity of psychological assessment: Validation of inferences from persons’ responses and performances as scientific inquiry into score meaning. Am Psychol 50(9):741–749. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.50.9.741
Mikhailov L, Tsvetinov P (2004) Evaluation of services using a fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. Appl Soft Comput 5(1):23–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2004.04.001
Mukherjee N, Huge J, Sutherland WJ, McNeill J, Van Opstal M, Dahdouh-Guebas F, Koedam N (2015) The Delphi technique in ecology and biological conservation: applications and guidelines. Methods. Ecol Evol 6(9):1097–1109. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12387
Murphy-Black T, Lamping D, McKee M, Sanderson C, Askham J, Marteau T (1998) CEM and their use in clinical guideline development—factors which influence the process and outcome of CDMs. Health Technol Assess 2(3):1–88
Nicholson RE, Pearce DG (2001) Why do people attend events: a comparative analysis of visitor motivations at four south island events. J Travel Res 39:449–460. https://doi.org/10.1177/004728750103900412
Northcote J, Lee D, Chok S, Wegner A (2008) An email-based Delphi approach to tourism program evaluation: involving stakeholders in research design. Curr Issues Tour 11(3):269–279. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500802140315
Oh CO (2005) The contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy. Tour Manag 26(1):39–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2003.09.014
Okoli C, Pawlowski SD (2004) The Delphi method as a research tool: an example, design considerations and applications. Inf Manag 42(1):15–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2003.11.002
Otto JE, Ritchie JRB (1996) The service experience in tourism. Tour Manag 17(3):165–174
Paraskevas A, Saunders MNK (2012) Beyond consensus: an alternative use of Delphi enquiry in hospitality research. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 24(6):907–924. https://doi.org/10.1108/09596111211247236
Park DB, Yoon YS (2011) Developing sustainable rural tourism evaluation indicators. Int J Tour Res 13(5):401–415. https://doi.org/10.1002/jtr.804
Petrovi´c MD, Vujko A, Gaji´c T, Vukovi´c DB, Radovanovi´c M, Jovanovi´c JM, Vukovi´c N (2018) Tourism as an approach to sustainable rural development in post-socialist countries: a comparative study of Serbia and Slovenia. Sustainability 10(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010054
Phillip S, Hunter C, Blackstock K (2010) A typology for defining agritourism. Tour Manag 31(6):754–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2009.08.001
Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie SB, Lee JY et al. (2003) Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J Appl Psychol 88:879–903. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Polukhina A, Sheresheva M, Efremova M, Suranova O, Agalakova O, Antonov-Ovseenko A (2021) The concept of sustainable rural tourism development in the face of COVID-19 crisis: evidence from Russia. J Risk Financ Manag 14:38. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm14010038
Potvin C, Roff DA (1993) Distribution-free and robust statistical methods: viable alternatives to parametric statistics. Ecology 74(6):1617–1628. https://doi.org/10.2307/1939920
Quadri-Felitti DL, Fiore AM (2013) Destination loyalty: effects of wine tourists’ experiences, memories, and satisfaction on intentions. Tour Hosp Res 13(1):47–62. https://doi.org/10.1177/1467358413510017
Ram Y, Collins-Kreiner N, Gozansky E, Moscona G, Okon-Singer H (2022) Is there a COVID-19 vaccination effect? A three-wave cross-sectional study. Curr Issues Tour 25(3):379–386. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2021.1960285
Rice K (2009) Priorities in K-12 distance education: a Delphi study examining multiple perspectives on policy, practice, and research. Educ Technol Soc 12(3):163–177
Roberson QM, Sturman MC, Simons TL (2007) Does the measure of dispersion matter in multilevel research? Organ Res Methods 10(4):564–588. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428106294746
Ryu K, Roy PA, Kim H, Ryu H (2020) The resident participation in endogenous rural tourism projects: a case study of Kumbalangi in Kerala, India. J Travel Tour Mark 37(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/10548408.2019.1687389
Schilling MA (2002) Technology success and failure in winner-take-all markets: the impact of learning orientation, timing, and network externalities. Acad Manag J 45(2):387–398. https://doi.org/10.5465/3069353
Schmidt R, Lyytinen K, Keil M, Cule P (2001) Identifying software project risks: an international Delphi study. J Manag Inf Syst 17(4):5–36. https://reurl.cc/RrE1qG
Silva L, Leal J (2015) Rural tourism and national identity building in contemporary Europe: evidence from Portugal. J Rural Stud 38:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2015.02.005
Singletary M (1994) Mass communication research: contemporary methods and applications. Longman, New York
Slater SJ (2020) Recommendations for keeping parks and green space accessible for mental and physical health during COVID-19 and other pandemics. Prev Chronic Dis https://doi.org/10.5888/pcd17.200204
Spector PE, Cooper CL, Sanchez JI, O’Driscoll M, Sparks K, Bernin P et al. (2002) Locus of control and well-being at work: How generalizable are western findings? Acad Manag J 45(2):453–470. https://doi.org/10.5465/3069359
Stewart BT, Gyedu A, Quansah R, Addo WL, Afoko A, Agbenorku P et al. (2016) District-level hospital trauma care audit filters: Delphi technique for defining context-appropriate indicators for quality improvement initiative evaluation in developing countries. Injury 47(1):211–219. https://reurl.cc/WrMLOk
Su MM, Dong Y, Geoffrey W, Sun Y (2020) A value-based analysis of the tourism use of agricultural heritage systems: Duotian Agrosystem, Jiangsu Province, China. J Sustain Tour 28(12):2136–2155. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2020.1795184
Taylor-Powell E (2002) Quick tips collecting group data: Delphi technique. University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI
Tew C, Barbieri C (2012) The perceived benefits of agritourism: the provider’s perspective. Tour Manag 33(1):215–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2011.02.005
Theodori GL (2001) Examining the effects of community satisfaction and attachment on individual well-being. Rural Sociol 66(4):618–828. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1549-0831.2001.tb00087.x
Tinsley HEA, Weiss DJ (1975) Interrater reliability and agreement of subjective judgments. J Couns Psychol 22(4):358–376. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0076640
UNWTO (2021) Rural tourism. https://www.unwto.org/rural-tourism . Accessed 3 Nov 2021
Uysal M, Sirgy MJ, Woo E, Kim H (2016) Quality of Life (QOL) and well-being research in tourism. Tour Manag 53:244–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2015.07.013
Vail D, Hultkrantz L (2000) Property rights and sustainable nature tourism: adaptation and mal-adaptation in Dalarna (Sweden) and Maine (USA). Ecol Econ 35(2):223–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8009(00)00190-7
Vaishar A, Šťastná M (2022) Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on rural tourism in Czechia preliminary considerations. Curr Issues Tour 25(2):187–191. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2020.1839027
Vergani L, Cuniberti M, Zanovello M et al. (2022) Return to play in long-standing adductor-related groin pain: a Delphi study among experts. Sports Med—Open 8:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40798-021-00400-z
World Tourism Organization (2020) UNWTO recommendations on tourism and rural development—a guide to making tourism an effective tool for rural development. UNWTO, Madrid
Book Google Scholar
Yang Z, Cai J, Sliuzas R (2010) Agro-tourism enterprises as a form of multi-functional urban agriculture for peri-urban development in China. Habitat Int 34(4):374–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2009.11.002
Yang J, Yang RX, Chen MH, Su CH, Zhi Y, Xi JC (2021) Effects of rural revitalization on rural tourism. J Hosp Tour Manag 47:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2021.02.008
Zawadka J, Jęczmyk A, Wojcieszak-Zbierska MM, Niedbała G, Uglis J, Pietrzak-Zawadka J (2022) Socio-economic factors influencing agritourism farm stays and their safety during the COVID-19 pandemic: evidence from Poland. Sustainability 14:3526. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14063526
Article CAS Google Scholar
Zhao W, Brent Ritchie JR (2007) Tourism and poverty alleviation: an integrative research framework. Curr Issues Tour 10(2&3):119–143. https://doi.org/10.2167/cit296.0
Zinn J, Zalokowski A, Hunter L (2001) Identifying indicators of laboratory management performance: a multiple constituency approach. Health Care Manag Rev 26(1):40–53. https://www.jstor.org/stable/44951308
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Chienkuo Technology University, Changhua, Taiwan
Yung-Lun Liu
Dayeh University, Changhua, Taiwan
Jui-Te Chiang & Pen-Fa Ko
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
We declare all authors involved in the work. The division of labor is stated as follows; Conceptualization: J-TC; Supervision: J-TC; Methodology: Y-LL; Investigation: Y-LL; Data collection, analysis, and curation: J-TC, Y-LL, P-FK; Original draft preparation: J-TC, Y-LL; Review: P-FK; Interpretation and editing: P-FK; Validation: J-TC, Y-LL, P-FK.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jui-Te Chiang .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Obtaining ethical approval from the Ethics Committee of the authors’ institution for such tourism management in Taiwan is unnecessary. This study was granted an exemption from requiring ethical approval.
Informed consent
To obtain the necessary permissions, prior to the questionnaire survey, we contacted all 18 content experts by telephone and explained the purpose of this study. This research was limited to an anonymous survey with no additional personal information recorded or analyzed beyond that shown to the survey experts. Subsequently, we sent the questionnaire with detailed information to those who confirmed that they wanted to cooperate. We have included all three authors’ contact information and the letter of withdrawal of cooperation for all eighteen experts.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Liu, YL., Chiang, JT. & Ko, PF. The benefits of tourism for rural community development. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 10 , 137 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01610-4
Download citation
Received : 03 July 2022
Accepted : 06 March 2023
Published : 31 March 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01610-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Agriculture and the Environment
- Case Studies
- Chemistry and Toxicology
- Environment and Human Health
- Environmental Biology
- Environmental Economics
- Environmental Engineering
- Environmental Ethics and Philosophy
- Environmental History
- Environmental Issues and Problems
- Environmental Processes and Systems
- Environmental Sociology and Psychology
- Environments
- Framing Concepts in Environmental Science
- Management and Planning
- Policy, Governance, and Law
- Quantitative Analysis and Tools
- Sustainability and Solutions
- Share Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
The role of tourism in sustainable development.
- Robert B. Richardson Robert B. Richardson Community Sustainability, Michigan State University
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780199389414.013.387
- Published online: 25 March 2021
Sustainable development is the foundational principle for enhancing human and economic development while maintaining the functional integrity of ecological and social systems that support regional economies. Tourism has played a critical role in sustainable development in many countries and regions around the world. In developing countries, tourism development has been used as an important strategy for increasing economic growth, alleviating poverty, creating jobs, and improving food security. Many developing countries are in regions that are characterized by high levels of biological diversity, natural resources, and cultural heritage sites that attract international tourists whose local purchases generate income and support employment and economic development. Tourism has been associated with the principles of sustainable development because of its potential to support environmental protection and livelihoods. However, the relationship between tourism and the environment is multifaceted, as some types of tourism have been associated with negative environmental impacts, many of which are borne by host communities.
The concept of sustainable tourism development emerged in contrast to mass tourism, which involves the participation of large numbers of people, often in structured or packaged tours. Mass tourism has been associated with economic leakage and dependence, along with negative environmental and social impacts. Sustainable tourism development has been promoted in various ways as a framing concept in contrast to these economic, environmental, and social impacts. Some literature has acknowledged a vagueness of the concept of sustainable tourism, which has been used to advocate for fundamentally different strategies for tourism development that may exacerbate existing conflicts between conservation and development paradigms. Tourism has played an important role in sustainable development in some countries through the development of alternative tourism models, including ecotourism, community-based tourism, pro-poor tourism, slow tourism, green tourism, and heritage tourism, among others that aim to enhance livelihoods, increase local economic growth, and provide for environmental protection. Although these models have been given significant attention among researchers, the extent of their implementation in tourism planning initiatives has been limited, superficial, or incomplete in many contexts.
The sustainability of tourism as a global system is disputed among scholars. Tourism is dependent on travel, and nearly all forms of transportation require the use of non-renewable resources such as fossil fuels for energy. The burning of fossil fuels for transportation generates emissions of greenhouse gases that contribute to global climate change, which is fundamentally unsustainable. Tourism is also vulnerable to both localized and global shocks. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to localized shocks include the impacts of natural disasters, disease outbreaks, and civil unrest. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to global shocks include the impacts of climate change, economic crisis, global public health pandemics, oil price shocks, and acts of terrorism. It is clear that tourism has contributed significantly to economic development globally, but its role in sustainable development is uncertain, debatable, and potentially contradictory.
- conservation
- economic development
- environmental impacts
- sustainable development
- sustainable tourism
- tourism development
Introduction
Sustainable development is the guiding principle for advancing human and economic development while maintaining the integrity of ecosystems and social systems on which the economy depends. It is also the foundation of the leading global framework for international cooperation—the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) (United Nations, 2015 ). The concept of sustainable development is often associated with the publication of Our Common Future (World Commission on Environment and Development [WCED], 1987 , p. 29), which defined it as “paths of human progress that meet the needs and aspirations of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.” Concerns about the environmental implications of economic development in lower income countries had been central to debates about development studies since the 1970s (Adams, 2009 ). The principles of sustainable development have come to dominate the development discourse, and the concept has become the primary development paradigm since the 1990s.
Tourism has played an increasingly important role in sustainable development since the 1990s, both globally and in particular countries and regions. For decades, tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, non-extractive option for economic development, particularly for developing countries (Gössling, 2000 ). Many developing countries have managed to increase their participation in the global economy through development of international tourism. Tourism development is increasingly viewed as an important tool in increasing economic growth, alleviating poverty, and improving food security. Tourism enables communities that are poor in material wealth, but rich in history and cultural heritage, to leverage their unique assets for economic development (Honey & Gilpin, 2009 ). More importantly, tourism offers an alternative to large-scale development projects, such as construction of dams, and to extractive industries such as mining and forestry, all of which contribute to emissions of pollutants and threaten biodiversity and the cultural values of Indigenous Peoples.
Environmental quality in destination areas is inextricably linked with tourism, as visiting natural areas and sightseeing are often the primary purpose of many leisure travels. Some forms of tourism, such as ecotourism, can contribute to the conservation of biodiversity and the protection of ecosystem functions in destination areas (Fennell, 2020 ; Gössling, 1999 ). Butler ( 1991 ) suggests that there is a kind of mutual dependence between tourism and the environment that should generate mutual benefits. Many developing countries are in regions that are characterized by high levels of species diversity, natural resources, and protected areas. Such ideas imply that tourism may be well aligned with the tenets of sustainable development.
However, the relationship between tourism and the environment is complex, as some forms of tourism have been associated with negative environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions, freshwater use, land use, and food consumption (Butler, 1991 ; Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ; Hunter & Green, 1995 ; Vitousek et al., 1997 ). Assessments of the sustainability of tourism have highlighted several themes, including (a) parks, biodiversity, and conservation; (b) pollution and climate change; (c) prosperity, economic growth, and poverty alleviation; (d) peace, security, and safety; and (e) population stabilization and reduction (Buckley, 2012 ). From a global perspective, tourism contributes to (a) changes in land cover and land use; (b) energy use, (c) biotic exchange and extinction of wild species; (d) exchange and dispersion of diseases; and (e) changes in the perception and understanding of the environment (Gössling, 2002 ).
Research on tourism and the environment spans a wide range of social and natural science disciplines, and key contributions have been disseminated across many interdisciplinary fields, including biodiversity conservation, climate science, economics, and environmental science, among others (Buckley, 2011 ; Butler, 1991 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Given the global significance of the tourism sector and its environmental impacts, the role of tourism in sustainable development is an important topic of research in environmental science generally and in environmental economics and management specifically. Reviews of tourism research have highlighted future research priorities for sustainable development, including the role of tourism in the designation and expansion of protected areas; improvement in environmental accounting techniques that quantify environmental impacts; and the effects of individual perceptions of responsibility in addressing climate change (Buckley, 2012 ).
Tourism is one of the world’s largest industries, and it has linkages with many of the prime sectors of the global economy (Fennell, 2020 ). As a global economic sector, tourism represents one of the largest generators of wealth, and it is an important agent of economic growth and development (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ). Tourism is a critical industry in many local and national economies, and it represents a large and growing share of world trade (Hunter, 1995 ). Global tourism has had an average annual increase of 6.6% over the past half century, with international tourist arrivals rising sharply from 25.2 million in 1950 to more than 950 million in 2010 . In 2019 , the number of international tourists reached 1.5 billion, up 4% from 2018 (Fennell, 2020 ; United Nations World Tourism Organization [UNWTO], 2020 ). European countries are host to more than half of international tourists, but since 1990 , growth in international arrivals has risen faster than the global average, in both the Middle East and the Asia and Pacific region (UNWTO, 2020 ).
The growth in global tourism has been accompanied by an expansion of travel markets and a diversification of tourism destinations. In 1950 , the top five travel destinations were all countries in Europe and the Americas, and these destinations held 71% of the global travel market (Fennell, 2020 ). By 2002 , these countries represented only 35%, which underscores the emergence of newly accessible travel destinations in Africa, Asia, the Middle East, and the Pacific Rim, including numerous developing countries. Over the past 70 years, global tourism has grown significantly as an economic sector, and it has contributed to the economic development of dozens of nations.
Given the growth of international tourism and its emergence as one of the world’s largest export sectors, the question of its impact on economic growth for the host countries has been a topic of great interest in the tourism literature. Two hypotheses have emerged regarding the role of tourism in the economic growth process (Apergis & Payne, 2012 ). First, tourism-led growth hypothesis relies on the assumption that tourism is an engine of growth that generates spillovers and positive externalities through economic linkages that will impact the overall economy. Second, the economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis emphasizes policies oriented toward well-defined and enforceable property rights, stable political institutions, and adequate investment in both physical and human capital to facilitate the development of the tourism sector. Studies have concluded with support for both the tourism-led growth hypothesis (e.g., Durbarry, 2004 ; Katircioglu, 2010 ) and the economic-led growth hypothesis (e.g., Katircioglu, 2009 ; Oh, 2005 ), whereas other studies have found support for a bidirectional causality for tourism and economic growth (e.g., Apergis & Payne, 2012 ; Lee & Chang, 2008 ).
The growth of tourism has been marked by an increase in the competition for tourist expenditures, making it difficult for destinations to maintain their share of the international tourism market (Butler, 1991 ). Tourism development is cyclical and subject to short-term cycles and overconsumption of resources. Butler ( 1980 ) developed a tourist-area cycle of evolution that depicts the number of tourists rising sharply over time through periods of exploration, involvement, and development, before eventual consolidation and stagnation. When tourism growth exceeds the carrying capacity of the area, resource degradation can lead to the decline of tourism unless specific steps are taken to promote rejuvenation (Butler, 1980 , 1991 ).
The potential of tourism development as a tool to contribute to environmental conservation, economic growth, and poverty reduction is derived from several unique characteristics of the tourism system (UNWTO, 2002 ). First, tourism represents an opportunity for economic diversification, particularly in marginal areas with few other export options. Tourists are attracted to remote areas with high values of cultural, wildlife, and landscape assets. The cultural and natural heritage of developing countries is frequently based on such assets, and tourism represents an opportunity for income generation through the preservation of heritage values. Tourism is the only export sector where the consumer travels to the exporting country, which provides opportunities for lower-income households to become exporters through the sale of goods and services to foreign tourists. Tourism is also labor intensive; it provides small-scale employment opportunities, which also helps to promote gender equity. Finally, there are numerous indirect benefits of tourism for people living in poverty, including increased market access for remote areas through the development of roads, infrastructure, and communication networks. Nevertheless, travel is highly income elastic and carbon intensive, which has significant implications for the sustainability of the tourism sector (Lenzen et al., 2018 ).
Concerns about environmental issues appeared in tourism research just as global awareness of the environmental impacts of human activities was expanding. The United Nations Conference on the Human Environment was held in Stockholm in 1972 , the same year as the publication of The Limits to Growth (Meadows et al., 1972 ), which highlighted the concerns about the implications of exponential economic and population growth in a world of finite resources. This was the same year that the famous Blue Marble photograph of Earth was taken by the crew of the Apollo 17 spacecraft (Höhler, 2015 , p. 10), and the image captured the planet cloaked in the darkness of space and became a symbol of Earth’s fragility and vulnerability. As noted by Buckley ( 2012 ), tourism researchers turned their attention to social and environmental issues around the same time (Cohen, 1978 ; Farrell & McLellan, 1987 ; Turner & Ash, 1975 ; Young, 1973 ).
The notion of sustainable development is often associated with the publication of Our Common Future , the report of the World Commission on Environment and Development, also known as the Brundtland Commission (WCED, 1987 ). The report characterized sustainable development in terms of meeting “the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” (WCED, 1987 , p. 43). Four basic principles are fundamental to the concept of sustainability: (a) the idea of holistic planning and strategy making; (b) the importance of preserving essential ecological processes; (c) the need to protect both human heritage and biodiversity; and (d) the need to develop in such a way that productivity can be sustained over the long term for future generations (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ). In addition to achieving balance between economic growth and the conservation of natural resources, there should be a balance of fairness and opportunity between the nations of the world.
Although the modern concept of sustainable development emerged with the publication of Our Common Future , sustainable development has its roots in ideas about sustainable forest management that were developed in Europe during the 17th and 18th centuries (Blewitt, 2015 ; Grober, 2007 ). Sustainable forest management is concerned with the stewardship and use of forests in a way that maintains their biodiversity, productivity, and regeneration capacity as well as their potential to fulfill society’s demands for forest products and benefits. Building on these ideas, Daly ( 1990 ) offered two operational principles of sustainable development. First, sustainable development implies that harvest rates should be no greater than rates of regeneration; this concept is known as maximum sustainable yield. Second, waste emission rates should not exceed the natural assimilative capacities of the ecosystems into which the wastes are emitted. Regenerative and assimilative capacities are characterized as natural capital, and a failure to maintain these capacities is not sustainable.
Shortly after the emergence of the concept of sustainable development in academic and policy discourse, tourism researchers began referring to the notion of sustainable tourism (May, 1991 ; Nash & Butler, 1990 ), which soon became the dominant paradigm of tourism development. The concept of sustainable tourism, as with the role of tourism in sustainable development, has been interpreted in different ways, and there is a lack of consensus concerning its meaning, objectives, and indicators (Sharpley, 2000 ). Growing interest in the subject inspired the creation of a new academic journal, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , which was launched in 1993 and has become a leading tourism journal. It is described as “an international journal that publishes research on tourism and sustainable development, including economic, social, cultural and political aspects.”
The notion of sustainable tourism development emerged in contrast to mass tourism, which is characterized by the participation of large numbers of people, often provided as structured or packaged tours. Mass tourism has risen sharply in the last half century. International arrivals alone have increased by an average annual rate of more than 25% since 1950 , and many of those trips involved mass tourism activities (Fennell, 2020 ; UNWTO, 2020 ). Some examples of mass tourism include beach resorts, cruise ship tourism, gaming casinos, golf resorts, group tours, ski resorts, theme parks, and wildlife safari tourism, among others. Little data exist regarding the volume of domestic mass tourism, but nevertheless mass tourism activities dominate the global tourism sector. Mass tourism has been shown to generate benefits to host countries, such as income and employment generation, although it has also been associated with economic leakage (where revenue generated by tourism is lost to other countries’ economies) and economic dependency (where developing countries are dependent on wealthier countries for tourists, imports, and foreign investment) (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Khan, 1997 ; Peeters, 2012 ). Mass tourism has been associated with numerous negative environmental impacts and social impacts (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Fennell, 2020 ; Ghimire, 2013 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Liu, 2003 ; Peeters, 2012 ; Wheeller, 2007 ). Sustainable tourism development has been promoted in various ways as a framing concept in contrast to many of these economic, environmental, and social impacts.
Much of the early research on sustainable tourism focused on defining the concept, which has been the subject of vigorous debate (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Inskeep, 1991 ; Liu, 2003 ; Sharpley, 2000 ). Early definitions of sustainable tourism development seemed to fall in one of two categories (Sharpley, 2000 ). First, the “tourism-centric” paradigm of sustainable tourism development focuses on sustaining tourism as an economic activity (Hunter, 1995 ). Second, alternative paradigms have situated sustainable tourism in the context of wider sustainable development policies (Butler, 1991 ). One of the most comprehensive definitions of sustainable tourism echoes some of the language of the Brundtland Commission’s definition of sustainable development (WCED, 1987 ), emphasizing opportunities for the future while also integrating social and environmental concerns:
Sustainable tourism can be thought of as meeting the needs of present tourists and host regions while protecting and enhancing opportunity for the future. Sustainable tourism development is envisaged as leading to management of all resources in such a way that we can fulfill economic, social and aesthetic needs while maintaining cultural integrity, essential ecological processes, biological diversity and life support systems. (Inskeep, 1991 , p. 461)
Hunter argued that over the short and long terms, sustainable tourism development should
“meet the needs and wants of the local host community in terms of improved living standards and quality of life;
satisfy the demands of tourists and the tourism industry, and continue to attract them in order to meet the first aim; and
safeguard the environmental resource base for tourism, encompassing natural, built and cultural components, in order to achieve both of the preceding aims.” (Hunter, 1995 , p. 156)
Numerous other definitions have been documented, and the term itself has been subject to widespread critique (Buckley, 2012 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ). Nevertheless, there have been numerous calls to move beyond debate about a definition and to consider how it may best be implemented in practice (Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Liu, 2003 ). Cater ( 1993 ) identified three key criteria for sustainable tourism: (a) meeting the needs of the host population in terms of improved living standards both in the short and long terms; (b) satisfying the demands of a growing number of tourists; and (c) safeguarding the natural environment in order to achieve both of the preceding aims.
Some literature has acknowledged a vagueness of the concept of sustainable tourism, which has been used to advocate for fundamentally different strategies for tourism development that may exacerbate existing conflicts between conservation and development paradigms (Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ; McKercher, 1993b ). Similar criticisms have been leveled at the concept of sustainable development, which has been described as an oxymoron with a wide range of meanings (Adams, 2009 ; Daly, 1990 ) and “defined in such a way as to be either morally repugnant or logically redundant” (Beckerman, 1994 , p. 192). Sharpley ( 2000 ) suggests that in the tourism literature, there has been “a consistent and fundamental failure to build a theoretical link between sustainable tourism and its parental paradigm,” sustainable development (p. 2). Hunter ( 1995 ) suggests that practical measures designed to operationalize sustainable tourism fail to address many of the critical issues that are central to the concept of sustainable development generally and may even actually counteract the fundamental requirements of sustainable development. He suggests that mainstream sustainable tourism development is concerned with protecting the immediate resource base that will sustain tourism development while ignoring concerns for the status of the wider tourism resource base, such as potential problems associated with air pollution, congestion, introduction of invasive species, and declining oil reserves. The dominant paradigm of sustainable tourism development has been described as introverted, tourism-centric, and in competition with other sectors for scarce resources (McKercher, 1993a ). Hunter ( 1995 , p. 156) proposes an alternative, “extraparochial” paradigm where sustainable tourism development is reconceptualized in terms of its contribution to overall sustainable development. Such a paradigm would reconsider the scope, scale, and sectoral context of tourism-related resource utilization issues.
“Sustainability,” “sustainable tourism,” and “sustainable development” are all well-established terms that have often been used loosely and interchangeably in the tourism literature (Liu, 2003 ). Nevertheless, the subject of sustainable tourism has been given considerable attention and has been the focus of numerous academic compilations and textbooks (Coccossis & Nijkamp, 1995 ; Hall & Lew, 1998 ; Stabler, 1997 ; Swarbrooke, 1999 ), and it calls for new approaches to sustainable tourism development (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Sharpley, 2000 ). The notion of sustainable tourism has been reconceptualized in the literature by several authors who provided alternative frameworks for tourism development (Buckley, 2012 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ; McKercher, 1993b ; Sharpley, 2000 ).
Early research in sustainable tourism focused on the local environmental impacts of tourism, including energy use, water use, food consumption, and change in land use (Buckley, 2012 ; Butler, 1991 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Hunter & Green, 1995 ). Subsequent research has emphasized the global environmental impacts of tourism, such as greenhouse gas emissions and biodiversity losses (Gössling, 2002 ; Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ; Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Additional research has emphasized the impacts of environmental change on tourism itself, including the impacts of climate change on tourist behavior (Gössling et al., 2012 ; Richardson & Loomis, 2004 ; Scott et al., 2012 ; Viner, 2006 ). Countries that are dependent on tourism for economic growth may be particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change (Richardson & Witkoswki, 2010 ).
The early focus on environmental issues in sustainable tourism has been broadened to include economic, social, and cultural issues as well as questions of power and equity in society (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Sharpley, 2014 ), and some of these frameworks have integrated notions of social equity, prosperity, and cultural heritage values. Sustainable tourism is dependent on critical long-term considerations of the impacts; notions of equity; an appreciation of the importance of linkages (i.e., economic, social, and environmental); and the facilitation of cooperation and collaboration between different stakeholders (Elliott & Neirotti, 2008 ).
McKercher ( 1993b ) notes that tourism resources are typically part of the public domain or are intrinsically linked to the social fabric of the host community. As a result, many commonplace tourist activities such as sightseeing may be perceived as invasive by members of the host community. Many social impacts of tourism can be linked to the overuse of the resource base, increases in traffic congestion, rising land prices, urban sprawl, and changes in the social structure of host communities. Given the importance of tourist–resident interaction, sustainable tourism development depends in part on the support of the host community (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ).
Tourism planning involves the dual objectives of optimizing the well-being of local residents in host communities and minimizing the costs of tourism development (Sharpley, 2014 ). Tourism researchers have paid significant attention to examining the social impacts of tourism in general and to understanding host communities’ perceptions of tourism in particular. Studies of the social impacts of tourism development have examined the perceptions of local residents and the effects of tourism on social cohesion, traditional lifestyles, and the erosion of cultural heritage, particularly among Indigenous Peoples (Butler & Hinch, 2007 ; Deery et al., 2012 ; Mathieson & Wall, 1982 ; Sharpley, 2014 ; Whitford & Ruhanen, 2016 ).
Alternative Tourism and Sustainable Development
A wide body of published research is related to the role of tourism in sustainable development, and much of the literature involves case studies of particular types of tourism. Many such studies contrast types of alternative tourism with those of mass tourism, which has received sustained criticism for decades and is widely considered to be unsustainable (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Fennell, 2020 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Liu, 2003 ; Peeters, 2012 ; Zapata et al., 2011 ). Still, some tourism researchers have taken issue with the conclusion that mass tourism is inherently unsustainable (Sharpley, 2000 ; Weaver, 2007 ), and some have argued for developing pathways to “sustainable mass tourism” as “the desired and impending outcome for most destinations” (Weaver, 2012 , p. 1030). In integrating an ethical component to mass tourism development, Weaver ( 2014 , p. 131) suggests that the desirable outcome is “enlightened mass tourism.” Such suggestions have been contested in the literature and criticized for dubious assumptions about emergent norms of sustainability and support for growth, which are widely seen as contradictory (Peeters, 2012 ; Wheeller, 2007 ).
Models of responsible or alternative tourism development include ecotourism, community-based tourism, pro-poor tourism, slow tourism, green tourism, and heritage tourism, among others. Most models of alternative tourism development emphasize themes that aim to counteract the perceived negative impacts of conventional or mass tourism. As such, the objectives of these models of tourism development tend to focus on minimizing environmental impacts, supporting biodiversity conservation, empowering local communities, alleviating poverty, and engendering pleasant relationships between tourists and residents.
Approaches to alternative tourism development tend to overlap with themes of responsible tourism, and the two terms are frequently used interchangeably. Responsible tourism has been characterized in terms of numerous elements, including
ensuring that communities are involved in and benefit from tourism;
respecting local, natural, and cultural environments;
involving the local community in planning and decision-making;
using local resources sustainably;
behaving in ways that are sensitive to the host culture;
maintaining and encouraging natural, economic, and cultural diversity; and
assessing environmental, social, and economic impacts as a prerequisite to tourism development (Spenceley, 2012 ).
Hetzer ( 1965 ) identified four fundamental principles or perquisites for a more responsible form of tourism: (a) minimum environmental impact; (b) minimum impact on and maximum respect for host cultures; (c) maximum economic benefits to the host country; and (d) maximum leisure satisfaction to participating tourists.
The history of ecotourism is closely connected with the emergence of sustainable development, as it was born out of a concern for the conservation of biodiversity. Ecotourism is a form of tourism that aims to minimize local environmental impacts while bringing benefits to protected areas and the people living around those lands (Honey, 2008 ). Ecotourism represents a small segment of nature-based tourism, which is understood as tourism based on the natural attractions of an area, such as scenic areas and wildlife (Gössling, 1999 ). The ecotourism movement gained momentum in the 1990s, primarily in developing countries in Latin America and sub-Saharan Africa, and nearly all countries are now engaged in some form of ecotourism. In some communities, ecotourism is the primary economic activity and source of income and economic development.
The term “ecotourism” was coined by Hector Ceballos-Lascuráin and defined by him as “tourism that consists in travelling to relatively undisturbed or uncontaminated natural areas with the specific object of studying, admiring, and enjoying the scenery and its wild plants and animals” (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1987 , p. 13). In discussing ecotourism resources, he also made reference to “any existing cultural manifestations (both past and present) found in these areas” (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1987 , p. 14). The basic precepts of ecotourism had been discussed long before the actual use of the term. Twenty years earlier, Hetzer ( 1965 ) referred to a form of tourism “based principally upon natural and archaeological resources such as caves, fossil sites (and) archaeological sites.” Thus, both natural resources and cultural resources were integrated into ecotourism frameworks from the earliest manifestations.
Costa Rica is well known for having successfully integrated ecotourism in its overall strategy for sustainable development, and numerous case studies of ecotourism in Costa Rica appear in the literature (Chase et al., 1998 ; Fennell & Eagles, 1990 ; Gray & Campbell, 2007 ; Hearne & Salinas, 2002 ). Ecotourism in Costa Rica has been seen as having supported the economic development of the country while promoting biodiversity conservation in its extensive network of protected areas. Chase et al. ( 1998 ) estimated the demand for ecotourism in a study of differential pricing of entrance fees at national parks in Costa Rica. The authors estimated elasticities associated with the own-price, cross-price, and income variables and found that the elasticities of demand were significantly different between three different national park sites. The results reveal the heterogeneity characterizing tourist behavior and park attractions and amenities. Hearne and Salinas ( 2002 ) used choice experiments to examine the preferences of domestic and foreign tourists in Costa Rica in an ecotourism site. Both sets of tourists demonstrated a preference for improved infrastructure, more information, and lower entrance fees. Foreign tourists demonstrated relatively stronger preferences for the inclusion of restrictions in the access to some trails.
Ecotourism has also been studied extensively in Kenya (Southgate, 2006 ), Malaysia (Lian Chan & Baum, 2007 ), Nepal (Baral et al., 2008 ), Peru (Stronza, 2007 ), and Taiwan (Lai & Nepal, 2006 ), among many other countries. Numerous case studies have demonstrated the potential for ecotourism to contribute to sustainable development by providing support for biodiversity conservation, local livelihoods, and regional development.
Community-Based Tourism
Community-based tourism (CBT) is a model of tourism development that emphasizes the development of local communities and allows for local residents to have substantial control over its development and management, and a major proportion of the benefits remain within the community. CBT emerged during the 1970s as a response to the negative impacts of the international mass tourism development model (Cater, 1993 ; Hall & Lew, 2009 ; Turner & Ash, 1975 ; Zapata et al., 2011 ).
Community-based tourism has been examined for its potential to contribute to poverty reduction. In a study of the viability of the CBT model to support socioeconomic development and poverty alleviation in Nicaragua, tourism was perceived by participants in the study to have an impact on employment creation in their communities (Zapata et al., 2011 ). Tourism was seen to have had positive impacts on strengthening local knowledge and skills, particularly on the integration of women to new roles in the labor market. One of the main perceived gains regarding the environment was the process of raising awareness regarding the conservation of natural resources. The small scale of CBT operations and low capacity to accommodate visitors was seen as a limitation of the model.
Spenceley ( 2012 ) compiled case studies of community-based tourism in countries in southern Africa, including Botswana, Madagascar, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. In this volume, authors characterize community-based and nature-based tourism development projects in the region and demonstrate how community participation in planning and decision-making has generated benefits for local residents and supported conservation initiatives. They contend that responsible tourism practices are of particular importance in the region because of the rich biological diversity, abundant charismatic wildlife, and the critical need for local economic development and livelihood strategies.
In Kenya, CBT enterprises were not perceived to have made a significant impact on poverty reduction at an individual household level, in part because the model relied heavily on donor funding, reinforcing dependency and poverty (Manyara & Jones, 2007 ). The study identified several critical success factors for CBT enterprises, namely, awareness and sensitization, community empowerment, effective leadership, and community capacity building, which can inform appropriate tourism policy formulation in Kenya. The impacts of CBT on economic development and poverty reduction would be greatly enhanced if tourism initiatives were able to emphasize independence, address local community priorities, enhance community empowerment and transparency, discourage elitism, promote effective community leadership, and develop community capacity to operate their own enterprises more efficiently.
Pro-Poor Tourism
Pro-poor tourism is a model of tourism development that brings net benefits to people living in poverty (Ashley et al., 2001 ; Harrison, 2008 ). Although its theoretical foundations and development objectives overlap to some degree with those of community-based tourism and other models of AT, the key distinctive feature of pro-poor tourism is that it places poor people and poverty at the top of the agenda. By focusing on a very simple and incontrovertibly moral idea, namely, the net benefits of tourism to impoverished people, the concept has broad appeal to donors and international aid agencies. Harnessing the economic benefits of tourism for pro-poor growth means capitalizing on the advantages while reducing negative impacts to people living in poverty (Ashley et al., 2001 ). Pro-poor approaches to tourism development include increasing access of impoverished people to economic benefits; addressing negative social and environmental impacts associated with tourism; and focusing on policies, processes, and partnerships that seek to remove barriers to participation by people living in poverty. At the local level, pro-poor tourism can play a very significant role in livelihood security and poverty reduction (Ashley & Roe, 2002 ).
Rogerson ( 2011 ) argues that the growth of pro-poor tourism initiatives in South Africa suggests that the country has become a laboratory for the testing and evolution of new approaches toward sustainable development planning that potentially will have relevance for other countries in the developing world. A study of pro-poor tourism development initiatives in Laos identified a number of favorable conditions for pro-poor tourism development, including the fact that local people are open to tourism and motivated to participate (Suntikul et al., 2009 ). The authors also noted a lack of development in the linkages that could optimize the fulfilment of the pro-poor agenda, such as training or facilitation of local people’s participation in pro-poor tourism development at the grassroots level.
Critics of the model have argued that pro-poor tourism is based on an acceptance of the status quo of existing capitalism, that it is morally indiscriminate and theoretically imprecise, and that its practitioners are academically and commercially marginal (Harrison, 2008 ). As Chok et al. ( 2007 ) indicate, the focus “on poor people in the South reflects a strong anthropocentric view . . . and . . . environmental benefits are secondary to poor peoples’” benefits (p. 153).
Harrison ( 2008 ) argues that pro-poor tourism is not a distinctive approach to tourism as a development tool and that it may be easier to discuss what pro-poor tourism is not than what it is. He concludes that it is neither anticapitalist nor inconsistent with mainstream tourism on which it relies; it is neither a theory nor a model and is not a niche form of tourism. Further, he argues that it has no distinctive method and is not only about people living in poverty.
Slow Tourism
The concept of slow tourism has emerged as a model of sustainable tourism development, and as such, it lacks an exact definition. The concept of slow tourism traces its origin back to some institutionalized social movements such as “slow food” and “slow cities” that began in Italy in the 1990s and spread rapidly around the world (Fullagar et al., 2012 ; Oh et al., 2016 , p. 205). Advocates of slow tourism tend to emphasize slowness in terms of speed, mobility, and modes of transportation that generate less environmental pollution. They propose niche marketing for alternative forms of tourism that focus on quality upgrading rather than merely increasing the quantity of visitors via the established mass-tourism infrastructure (Conway & Timms, 2010 ).
In the context of the Caribbean region, slow tourism has been promoted as more culturally sensitive and authentic, as compared to the dominant mass tourism development model that is based on all-inclusive beach resorts dependent on foreign investment (Conway & Timms, 2010 ). Recognizing its value as an alternative marketing strategy, Conway and Timms ( 2010 ) make the case for rebranding alternative tourism in the Caribbean as a means of revitalizing the sector for the changing demands of tourists in the 21st century . They suggest that slow tourism is the antithesis of mass tourism, which “relies on increasing the quantity of tourists who move through the system with little regard to either the quality of the tourists’ experience or the benefits that accrue to the localities the tourist visits” (Conway & Timms, 2010 , p. 332). The authors draw on cases from Barbados, the Grenadines, Jamaica, and Trinidad and Tobago to characterize models of slow tourism development in remote fishing villages and communities near nature preserves and sea turtle nesting sites.
Although there is a growing interest in the concept of slow tourism in the literature, there seems to be little agreement about the exact nature of slow tourism and whether it is a niche form of special interest tourism or whether it represents a more fundamental potential shift across the industry. Conway and Timms ( 2010 ) focus on the destination, advocating for slow tourism in terms of a promotional identity for an industry in need of rebranding. Caffyn ( 2012 , p. 77) discusses the implementation of slow tourism in terms of “encouraging visitors to make slower choices when planning and enjoying their holidays.” It is not clear whether slow tourism is a marketing strategy, a mindset, or a social movement, but the literature on slow tourism nearly always equates the term with sustainable tourism (Caffyn, 2012 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Oh et al., 2016 ). Caffyn ( 2012 , p. 80) suggests that slow tourism could offer a “win–win,” which she describes as “a more sustainable form of tourism; keeping more of the economic benefits within the local community and destination; and delivering a more meaningful and satisfying experience.” Research on slow tourism is nascent, and thus the contribution of slow tourism to sustainable development is not well understood.
Impacts of Tourism Development
The role of tourism in sustainable development can be examined through an understanding of the economic, environmental, and social impacts of tourism. Tourism is a global phenomenon that involves travel, recreation, the consumption of food, overnight accommodations, entertainment, sightseeing, and other activities that simultaneously intersect the lives of local residents, businesses, and communities. The impacts of tourism involve benefits and costs to all groups, and some of these impacts cannot easily be measured. Nevertheless, they have been studied extensively in the literature, which provides some context for how these benefits and costs are distributed.
Economic Impacts of Tourism
The travel and tourism sector is one of the largest components of the global economy, and global tourism has increased exponentially since the end of the Second World War (UNWTO, 2020 ). The direct, indirect, and induced economic impact of global travel accounted for 8.9 trillion U.S. dollars in contribution to the global gross domestic product (GDP), or 10.3% of global GDP. The global travel and tourism sector supports approximately 330 million jobs, or 1 in 10 jobs around the world. From an economic perspective, tourism plays a significant role in sustainable development. In many developing countries, tourism has the potential to play a unique role in income generation and distribution relative to many other industries, in part because of its high multiplier effect and consumption of local goods and services. However, research on the economic impacts of tourism has shown that this potential has rarely been fully realized (Liu, 2003 ).
Numerous studies have examined the impact of tourism expenditure on GDP, income, employment, and public sector revenue. Narayan ( 2004 ) used a computable general equilibrium model to estimate the economic impact of tourism growth on the economy of Fiji. Tourism is Fiji’s largest industry, with average annual growth of 10–12%; and as a middle-income country, tourism is critical to Fiji’s economic development. The findings indicate that an increase in tourism expenditures was associated with an increase in GDP, an improvement in the country’s balance of payments, and an increase in real consumption and national welfare. Evidence suggests that the benefits of tourism expansion outweigh any export effects caused by an appreciation of the exchange rate and an increase in domestic prices and wages.
Seetanah ( 2011 ) examined the potential contribution of tourism to economic growth and development using panel data of 19 island economies around the world from 1990 to 2007 and revealed that tourism development is an important factor in explaining economic performance in the selected island economies. The results have policy implications for improving economic growth by harnessing the contribution of the tourism sector. Pratt ( 2015 ) modeled the economic impact of tourism for seven small island developing states in the Pacific, the Caribbean, and the Indian Ocean. In most states, the transportation sector was found to have above-average linkages to other sectors of the economy. The results revealed some advantages of economies of scale for maximizing the economic contribution of tourism.
Apergis and Payne ( 2012 ) examined the causal relationship between tourism and economic growth for a panel of nine Caribbean countries. The panel of Caribbean countries includes Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Grenada, St. Kitts and Nevis, St. Lucia, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, and Trinidad and Tobago. The authors use a panel error correction model to reveal bidirectional causality between tourism and economic growth in both the short run and the long run. The presence of bidirectional causality reiterates the importance of the tourism sector in the generation of foreign exchange income and in financing the production of goods and services within these countries. Likewise, stable political institutions and adequate government policies to ensure the appropriate investment in physical and human capital will enhance economic growth. In turn, stable economic growth will provide the resources needed to develop the tourism infrastructure for the success of the countries’ tourism sector. Thus, policy makers should be cognizant of the interdependent relationship between tourism and economic growth in the design and implementation of economic policy. The mixed nature of these results suggest that the relationship between tourism and economic growth depends largely on the social and economic context as well as the role of tourism in the economy.
The economic benefits and costs of tourism are frequently distributed unevenly. An analysis of the impact of wildlife conservation policies in Zambia on household welfare found that households located near national parks earn higher levels of income from wage employment and self-employment than other rural households in the country, but they were also more likely to suffer crop losses related to wildlife conflicts (Richardson et al., 2012 ). The findings suggest that tourism development and wildlife conservation can contribute to pro-poor development, but they may be sustainable only if human–wildlife conflicts are minimized or compensated.
Environmental Impacts of Tourism
The environmental impacts of tourism are significant, ranging from local effects to contributions to global environmental change (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). Tourism is both dependent on water resources and a factor in global and local freshwater use. Tourists consume water for drinking, when showering and using the toilet, when participating in activities such as winter ski tourism (i.e., snowmaking), and when using swimming pools and spas. Fresh water is also needed to maintain hotel gardens and golf courses, and water use is embedded in tourism infrastructure development (e.g., accommodations, laundry, dining) and in food and fuel production. Direct water consumption in tourism is estimated to be approximately 350 liters (L) per guest night for accommodation; when indirect water use from food, energy, and transport are considered, total water use in tourism is estimated to be approximately 6,575 L per guest night, or 27,800 L per person per trip (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). In addition, tourism contributes to the pollution of oceans as well as lakes, rivers, and other freshwater systems (Gössling, 2002 ; Gössling et al., 2011 ).
The clearing and conversion of land is central for tourism development, and in many cases, the land used for tourism includes roads, airports, railways, accommodations, trails, pedestrian walks, shopping areas, parking areas, campgrounds, vacation homes, golf courses, marinas, ski resorts, and indirect land use for food production, disposal of solid wastes, and the treatment of wastewater (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). Global land use for accommodation is estimated to be approximately 42 m 2 per bed. Total global land use for tourism is estimated to be nearly 62,000 km 2 , or 11.7 m 2 per tourist; more than half of this estimate is represented by land use for traffic infrastructure.
Tourism and hospitality have direct and indirect links to nearly all aspects of food production, preparation, and consumption because of the quantities of food consumed in tourism contexts (Gössling et al., 2011 ). Food production has significant implications for sustainable development, given the growing global demand for food. The implications include land conversion, losses to biodiversity, changes in nutrient cycling, and contributions to greenhouse emissions that are associated with global climate change (Vitousek et al., 1997 ). Global food use for tourism is estimated to be approximately 39.4 megatons 1 (Mt), about 38% than the amount of food consumed at home. This equates to approximately 1,800 grams (g) of food consumed per tourist per day.
Although tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, nonextractive option for economic development, (Gössling, 2000 ), assessments reveal that such pursuits have a significant carbon footprint, as tourism is significantly more carbon intensive than other potential areas of economic development (Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Tourism is dependent on energy, and virtually all energy use in the tourism sector is derived from fossil fuels, which contribute to global greenhouse emissions that are associated with global climate change. Energy use for tourism has been estimated to be approximately 3,575 megajoules 2 (MJ) per trip, including energy for travel and accommodations (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). A previous estimate of global carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) emissions from tourism provided values of 1.12 gigatons 3 (Gt) of CO 2 , amounting to about 3% of global CO 2 -equivalent (CO 2 e) emissions (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). However, these analyses do not cover the supply chains underpinning tourism and do not therefore represent true carbon footprints. A more complete analysis of the emissions from energy consumption necessary to sustain the tourism sector would include food and beverages, infrastructure construction and maintenance, retail, and financial services. Between 2009 and 2013 , tourism’s global carbon footprint is estimated to have increased from 3.9 to 4.5 GtCO 2 e, four times more than previously estimated, accounting for about 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions (Lenzen et al., 2018 ). The majority of this footprint is exerted by and within high-income countries. The rising global demand for tourism is outstripping efforts at decarbonization of tourism operations and as a result is accelerating global carbon emissions.
Social Impacts of Tourism
The social impacts of tourism have been widely studied, with an emphasis on residents’ perceptions in the host community (Sharpley, 2014 ). Case studies include research conducted in Australia (Faulkner & Tideswell, 1997 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Tovar & Lockwood, 2008 ), Belize (Diedrich & Garcia-Buades, 2008 ), China (Gu & Ryan, 2008 ), Fiji (King et al., 1993 ), Greece (Haralambopoulos & Pizam, 1996 ; Tsartas, 1992 ), Hungary (Rátz, 2000 ), Thailand (Huttasin, 2008 ), Turkey (Kuvan & Akan, 2005 ), the United Kingdom (Brunt & Courtney, 1999 ; Haley et al., 2005 ), and the United States (Andereck et al., 2005 ; Milman & Pizam, 1988 ), among others. The social impacts of tourism are difficult to measure, and most published studies are mainly concerned with the social impacts on the host communities rather than the impacts on the tourists themselves.
Studies of residents’ perceptions of tourism are typically conducted using household surveys. In most cases, residents recognize the economic dependence on tourism for income, and there is substantial evidence to suggest that working in or owning a business in tourism or a related industry is associated with more positive perceptions of tourism (Andereck et al., 2007 ). The perceived nature of negative effects is complex and often conveys a dislike of crowding, traffic congestion, and higher prices for basic needs (Deery et al., 2012 ). When the number of tourists far exceeds that of the resident population, negative attitudes toward tourism may manifest (Diedrich & Garcia-Buades, 2008 ). However, residents who recognize negative impacts may not necessarily oppose tourism development (King et al., 1993 ).
In some regions, little is known about the social and cultural impacts of tourism despite its dominance as an economic sector. Tourism is a rapidly growing sector in Cuba, and it is projected to grow at rates that exceed the average projected growth rates for the Caribbean and the world overall (Salinas et al., 2018 ). Still, even though there has been rapid tourism development in Cuba, there has been little research related to the environmental and sociocultural impacts of this tourism growth (Rutty & Richardson, 2019 ).
In some international tourism contexts, studies have found that residents are generally resentful toward tourism because it fuels inequality and exacerbates racist attitudes and discrimination (Cabezas, 2004 ; Jamal & Camargo, 2014 ; Mbaiwa, 2005 ). Other studies revealed similar narratives and recorded statements of exclusion and socioeconomic stratification (Sanchez & Adams, 2008 ). Local residents often must navigate the gaps in the racialized, gendered, and sexualized structures imposed by the global tourism industry and host-country governments (Cabezas, 2004 ).
However, during times of economic crisis, residents may develop a more permissive view as their perceptions of the costs of tourism development decrease (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ). This increased positive attitude is not based on an increase in the perception of positive impacts of tourism, but rather on a decrease in the perception of the negative impacts.
There is a growing body of research on Indigenous and Aboriginal tourism that emphasizes justice issues such as human rights and self-empowerment, control, and participation of traditional owners in comanagement of destinations (Jamal & Camargo, 2014 ; Ryan & Huyton, 2000 ; Whyte, 2010 ).
Sustainability of Tourism
A process or system is said to be sustainable to the extent that it is robust, resilient, and adaptive (Anderies et al., 2013 ). By most measures, the global tourism system does not meet these criteria for sustainability. Tourism is not robust in that it cannot resist threats and perturbations, such as economic shocks, public health pandemics, war, and other disruptions. Tourism is not resilient in that it does not easily recover from failures, such as natural disasters or civil unrest. Furthermore, tourism is not adaptive in that it is often unable to change in response to external conditions. One example that underscores the failure to meet all three criteria is the dependence of tourism on fossil fuels for transportation and energy, which are key inputs for tourism development. This dependence itself is not sustainable (Wheeller, 2007 ), and thus the sustainability of tourism is questionable.
Liu ( 2003 ) notes that research related to the role of tourism in sustainable development has emphasized supply-side concepts such as sustaining tourism resources and ignored the demand side, which is particularly vulnerable to social and economic shocks. Tourism is vulnerable to both localized and global shocks. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to localized shocks include disaster vulnerability in coastal Thailand (Calgaro & Lloyd, 2008 ), bushfires in northeast Victoria in Australia (Cioccio & Michael, 2007 ), forest fires in British Columbia, Canada (Hystad & Keller, 2008 ); and outbreak of foot and mouth disease in the United Kingdom (Miller & Ritchie, 2003 ).
Like most other economic sectors, tourism is vulnerable to the impacts of earthquakes, particularly in areas where tourism infrastructure may not be resilient to such shocks. Numerous studies have examined the impacts of earthquake events on tourism, including studies of the aftermath of the 1997 earthquake in central Italy (Mazzocchi & Montini, 2001 ), the 1999 earthquake in Taiwan (Huan et al., 2004 ; Huang & Min, 2002 ), and the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake in western Sichuan, China (Yang et al., 2011 ), among others.
Tourism is vulnerable to extreme weather events. Regional economic strength has been found to be associated with lower vulnerability to natural disasters. Kim and Marcoullier ( 2015 ) examined the vulnerability and resilience of 10 tourism-based regional economies that included U.S. national parks or protected seashores situated on the Gulf of Mexico or Atlantic Ocean coastline that were affected by several hurricanes over a 26-year period. Regions with stronger economic characteristics prior to natural disasters were found to have lower disaster losses than regions with weaker economies.
Tourism is extremely sensitive to oil spills, whatever their origin, and the volume of oil released need not be large to generate significant economic losses (Cirer-Costa, 2015 ). Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to the localized shock of an oil spill include research on the impacts of oil spills in Alaska (Coddington, 2015 ), Brazil (Ribeiro et al., 2020 ), Spain (Castanedo et al., 2009 ), affected regions in the United States along the Gulf of Mexico (Pennington-Gray et al., 2011 ; Ritchie et al., 2013 ), and the Republic of Korea (Cheong, 2012 ), among others. Future research on the vulnerability of tourist destinations to oil spills should also incorporate freshwater environments, such as lakes, rivers, and streams, where the rupture of oil pipelines is more frequent.
Significant attention has been paid to assessing the vulnerability of tourist destinations to acts of terrorism and the impacts of terrorist attacks on regional tourist economies (Liu & Pratt, 2017 ). Such studies include analyses of the impacts of terrorist attacks on three European countries, Greece, Italy, and Austria (Enders et al., 1992 ); the impact of the 2001 terrorist attacks on the United States (Goodrich, 2002 ); terrorism and tourism in Nepal (Bhattarai et al., 2005 ); vulnerability of tourism livelihoods in Bali (Baker & Coulter, 2007 ); the impact of terrorism on tourist preferences for destinations in the Mediterranean and the Canary Islands (Arana & León, 2008 ); the 2011 massacres in Olso and Utøya, Norway (Wolff & Larsen, 2014 ); terrorism and political violence in Tunisia (Lanouar & Goaied, 2019 ); and the impact of terrorism on European tourism (Corbet et al., 2019 ), among others. Pizam and Fleischer ( 2002 ) studied the impact of acts of terrorism on tourism demand in Israel between May 1991 and May 2001 , and they confirmed that the frequency of acts of terrorism had caused a larger decline in international tourist arrivals than the severity of these acts. Most of these are ex post studies, and future assessments of the underlying conditions of destinations could reveal a deeper understanding of the vulnerability of tourism to terrorism.
Tourism is vulnerable to economic crisis, both local economic shocks (Okumus & Karamustafa, 2005 ; Stylidis & Terzidou, 2014 ) and global economic crisis (Papatheodorou et al., 2010 ; Smeral, 2010 ). Okumus and Karamustafa ( 2005 ) evaluated the impact of the February 2001 economic crisis in Turkey on tourism, and they found that the tourism industry was poorly prepared for the economic crisis despite having suffered previous impacts related to the Gulf War in the early 1990s, terrorism in Turkey in the 1990s, the civil war in former Yugoslavia in the early 1990s, an internal economic crisis in 1994 , and two earthquakes in the northwest region of Turkey in 1999 . In a study of the attitudes and perceptions of citizens of Greece, Stylidis and Terzidou ( 2014 ) found that economic crisis is associated with increased support for tourism development, particularly out of self-interest. Economic crisis diminishes residents’ concern for environmental issues. In a study of the behavior of European tourists amid an economic crisis, Eugenio-Martin and Campos-Soria ( 2014 ) found that the probability of households cutting back on travel expenditures depends largely on the climate and economic conditions of tourists’ home countries, and households that do reduce travel spending engage in tourism closer to home.
Becken and Lennox ( 2012 ) studied the implications of a long-term increase in oil prices for tourism in New Zealand, and they estimate that a doubling of oil prices is associated with a 1.7% decrease in real gross national disposable income and a 9% reduction in the real value of tourism exports. Chatziantoniou et al. ( 2013 ) investigated the relationship among oil price shocks, tourism variables, and economic indicators in four European Mediterranean countries and found that aggregate demand oil price shocks generated a lagged effect on tourism-generated income and economic growth. Kisswani et al. ( 2020 ) examined the asymmetric effect of oil prices on tourism receipts and the sensitive susceptibility of tourism to oil price changes using nonlinear analysis. The findings document a long-run asymmetrical effect for most countries, after incorporating the structural breaks, suggesting that governments and tourism businesses and organizations should interpret oil price fluctuations cautiously.
Finally, the sustainability of tourism has been shown to be vulnerable to the outbreak of infectious diseases, including the impact of the Ebola virus on tourism in sub-Saharan Africa (Maphanga & Henama, 2019 ; Novelli et al., 2018 ) and in the United States (Cahyanto et al., 2016 ). The literature also includes studies of the impact of swine flu on tourism demand in Brunei (Haque & Haque, 2018 ), Mexico (Monterrubio, 2010 ), and the United Kingdom (Page et al., 2012 ), among others. In addition, rapid assessments of the impacts of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 have documented severe disruptions and cessations of tourism because of unprecedented global travel restrictions and widespread restrictions on public gatherings (Gössling et al., 2020 ; Qiu et al., 2020 ; Sharma & Nicolau, 2020 ). Hotels, airlines, cruise lines, and car rentals have all experienced a significant decrease globally because of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the shock to the industry is significant enough to warrant concerns about the long-term outlook (Sharma & Nicolau, 2020 ). Qiu et al. ( 2020 ) estimated the social costs of the pandemic to tourism in three cities in China (Hong Kong, Guangzhou, and Wuhan), and they found that most respondents were willing to pay for risk reduction and action in responding to the pandemic crisis; there was no significant difference between residents’ willingness to pay in the three cities. Some research has emphasized how lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic can prepare global tourism for an economic transformation that is needed to mitigate the impacts of climate change (Brouder, 2020 ; Prideaux et al., 2020 ).
It is clear that tourism has contributed significantly to economic development globally, but its role in sustainable development is uncertain, contested, and potentially paradoxical. This is due, in part, to the contested nature of sustainable development itself. Tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, nonextractive option for economic development, particularly for developing countries (Gössling, 2000 ), and many countries have managed to increase their participation in the global economy through development of international tourism. Tourism development has been viewed as an important sector for investment to enhance economic growth, poverty alleviation, and food security, and the sector provides an alternative opportunity to large-scale development projects and extractive industries that contribute to emissions of pollutants and threaten biodiversity and cultural values. However, global evidence from research on the economic impacts of tourism has shown that this potential has rarely been realized (Liu, 2003 ).
The role of tourism in sustainable development has been studied extensively and with a variety of perspectives, including the conceptualization of alternative or responsible forms of tourism and the examination of economic, environmental, and social impacts of tourism development. The research has generally concluded that tourism development has contributed to sustainable development in some cases where it is demonstrated to have provided support for biodiversity conservation initiatives and livelihood development strategies. As an economic sector, tourism is considered to be labor intensive, providing opportunities for poor households to enhance their livelihood through the sale of goods and services to foreign tourists.
Nature-based tourism approaches such as ecotourism and community-based tourism have been successful at attracting tourists to parks and protected areas, and their spending provides financial support for biodiversity conservation, livelihoods, and economic growth in developing countries. Nevertheless, studies of the impacts of tourism development have documented negative environmental impacts locally in terms of land use, food and water consumption, and congestion, and globally in terms of the contribution of tourism to climate change through the emission of greenhouse gases related to transportation and other tourist activities. Studies of the social impacts of tourism have documented experiences of discrimination based on ethnicity, gender, race, sex, and national identity.
The sustainability of tourism as an economic sector has been examined in terms of its vulnerability to civil conflict, economic shocks, natural disasters, and public health pandemics. Most studies conclude that tourism may have positive impacts for regional development and environmental conservation, but there is evidence that tourism inherently generates negative environmental impacts, primarily through pollutions stemming from transportation. The regional benefits of tourism development must be considered alongside the global impacts of increased transportation and tourism participation. Global tourism has also been shown to be vulnerable to economic crises, oil price shocks, and global outbreaks of infectious diseases. Given that tourism is dependent on energy, the movement of people, and the consumption of resources, virtually all tourism activities have significant economic, environmental, and sustainable impacts. As such, the role of tourism in sustainable development is highly questionable. Future research on the role of tourism in sustainable development should focus on reducing the negative impacts of tourism development, both regionally and globally.
Further Reading
- Bramwell, B. , & Lane, B. (1993). Sustainable tourism: An evolving global approach. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 1 (1), 1–5.
- Buckley, R. (2012). Sustainable tourism: Research and reality. Annals of Tourism Research , 39 (2), 528–546.
- Butler, R. W. (1991). Tourism, environment, and sustainable development. Environmental Conservation , 18 (3), 201–209.
- Butler, R. W. (1999). Sustainable tourism: A state‐of‐the‐art review. Tourism Geographies , 1 (1), 7–25.
- Clarke, J. (1997). A framework of approaches to sustainable tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 5 (3), 224–233.
- Fennell, D. A. (2020). Ecotourism (5th ed.). Routledge.
- Gössling, S. (2002). Global environmental consequences of tourism. Global Environmental Change , 12 (4), 283–302.
- Honey, M. (2008). Ecotourism and sustainable development: Who owns paradise? (2nd ed.). Island Press.
- Inskeep, E. (1991). Tourism planning: An integrated and sustainable development approach . Routledge.
- Jamal, T. , & Camargo, B. A. (2014). Sustainable tourism, justice and an ethic of care: Toward the just destination. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 22 (1), 11–30.
- Liburd, J. J. , & Edwards, D. (Eds.). (2010). Understanding the sustainable development of tourism . Oxford.
- Liu, Z. (2003). Sustainable tourism development: A critique. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 11 (6), 459–475.
- Sharpley, R. (2020). Tourism, sustainable development and the theoretical divide: 20 years on. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 28 (11), 1932–1946.
- Adams, W. M. (2009). Green development: Environment and sustainability in a developing world (3rd ed.). Routledge.
- Andereck, K. L. , Valentine, K. M. , Knopf, R. A. , & Vogt, C. A. (2005). Residents’ perceptions of community tourism impacts. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (4), 1056–1076.
- Andereck, K. , Valentine, K. , Vogt, C. , & Knopf, R. (2007). A cross-cultural analysis of tourism and quality of life perceptions. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 483–502.
- Anderies, J. M. , Folke, C. , Walker, B. , & Ostrom, E. (2013). Aligning key concepts for global change policy: Robustness, resilience, and sustainability . Ecology and Society , 18 (2), 8.
- Apergis, N. , & Payne, J. E. (2012). Tourism and growth in the Caribbean–evidence from a panel error correction model. Tourism Economics , 18 (2), 449–456.
- Arana, J. E. , & León, C. J. (2008). The impact of terrorism on tourism demand. Annals of Tourism Research , 35 (2), 299–315.
- Ashley, C. , & Roe, D. (2002). Making tourism work for the poor: Strategies and challenges in southern Africa. Development Southern Africa , 19 (1), 61–82.
- Ashley, C. , Roe, D. , & Goodwin, H. (2001). Pro-poor tourism strategies: Making tourism work for the poor: A review of experience (No. 1). Overseas Development Institute.
- Baker, K. , & Coulter, A. (2007). Terrorism and tourism: The vulnerability of beach vendors’ livelihoods in Bali. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (3), 249–266.
- Baral, N. , Stern, M. J. , & Bhattarai, R. (2008). Contingent valuation of ecotourism in Annapurna conservation area, Nepal: Implications for sustainable park finance and local development. Ecological Economics , 66 (2–3), 218–227.
- Becken, S. , & Lennox, J. (2012). Implications of a long-term increase in oil prices for tourism. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 133–142.
- Beckerman, W. (1994). “Sustainable development”: Is it a useful concept? Environmental Values , 3 (3), 191–209.
- Bhattarai, K. , Conway, D. , & Shrestha, N. (2005). Tourism, terrorism and turmoil in Nepal. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (3), 669–688.
- Blewitt, J. (2015). Understanding sustainable development (2nd ed.). Routledge.
- Brouder, P. (2020). Reset redux: Possible evolutionary pathways towards the transformation of tourism in a COVID-19 world. Tourism Geographies , 22 (3), 484–490.
- Brunt, P. , & Courtney, P. (1999). Host perceptions of sociocultural impacts. Annals of Tourism Research , 26 (3), 493–515.
- Buckley, R. (2011). Tourism and environment. Annual Review of Environment and Resources , 36 , 397–416.
- Butler, R. W. (1980). The concept of a tourist area cycle of evolution: Implications for management of resources. Canadian Geographer/Le Géographe canadien , 24 (1), 5–12.
- Butler, R. , & Hinch, T. (Eds.). (2007). Tourism and indigenous peoples: Issues and implications . Routledge.
- Cabezas, A. L. (2004). Between love and money: Sex, tourism, and citizenship in Cuba and the Dominican Republic. Signs: Journal of Women in Culture and Society , 29 (4), 987–1015.
- Caffyn, A. (2012). Advocating and implementing slow tourism. Tourism Recreation Research , 37 (1), 77–80.
- Cahyanto, I. , Wiblishauser, M. , Pennington-Gray, L. , & Schroeder, A. (2016). The dynamics of travel avoidance: The case of Ebola in the US. Tourism Management Perspectives , 20 , 195–203.
- Calgaro, E. , & Lloyd, K. (2008). Sun, sea, sand and tsunami: Examining disaster vulnerability in the tourism community of Khao Lak, Thailand. Singapore Journal of Tropical Geography , 29 (3), 288–306.
- Castanedo, S. , Juanes, J. A. , Medina, R. , Puente, A. , Fernandez, F. , Olabarrieta, M. , & Pombo, C. (2009). Oil spill vulnerability assessment integrating physical, biological and socio-economical aspects: Application to the Cantabrian coast (Bay of Biscay, Spain). Journal of Environmental Management , 91 (1), 149–159.
- Cater, E. (1993). Ecotourism in the Third World: Problems for sustainable tourism development. Tourism Management , 14 (2), 85–90.
- Ceballos-Lascuráin, H. (1987, January). The future of “ecotourism.” Mexico Journal , 17 , 13–14.
- Chase, L. C. , Lee, D. R. , Schulze, W. D. , & Anderson, D. J. (1998). Ecotourism demand and differential pricing of national park access in Costa Rica. Land Economics , 74 (4), 466–482.
- Chatziantoniou, I. , Filis, G. , Eeckels, B. , & Apostolakis, A. (2013). Oil prices, tourism income and economic growth: A structural VAR approach for European Mediterranean countries. Tourism Management , 36 (C), 331–341.
- Cheong, S. M. (2012). Fishing and tourism impacts in the aftermath of the Hebei-Spirit oil spill. Journal of Coastal Research , 28 (6), 1648–1653.
- Chok, S. , Macbeth, J. , & Warren, C. (2007). Tourism as a tool for poverty alleviation: A critical analysis of “pro-poor tourism” and implications for sustainability. Current Issues in Tourism , 10 (2–3), 144–165.
- Cioccio, L. , & Michael, E. J. (2007). Hazard or disaster: Tourism management for the inevitable in Northeast Victoria. Tourism Management , 28 (1), 1–11.
- Cirer-Costa, J. C. (2015). Tourism and its hypersensitivity to oil spills. Marine Pollution Bulletin , 91 (1), 65–72.
- Coccossis, H. , & Nijkamp, P. (1995). Sustainable tourism development . Ashgate.
- Coddington, K. (2015). The “entrepreneurial spirit”: Exxon Valdez and nature tourism development in Seward, Alaska. Tourism Geographies , 17 (3), 482–497.
- Cohen, E. (1978). The impact of tourism on the physical environment. Annals of Tourism Research , 5 (2), 215–237.
- Conway, D. , & Timms, B. F. (2010). Re-branding alternative tourism in the Caribbean: The case for “slow tourism.” Tourism and Hospitality Research , 10 (4), 329–344.
- Corbet, S. , O’Connell, J. F. , Efthymiou, M. , Guiomard, C. , & Lucey, B. (2019). The impact of terrorism on European tourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 75 , 1–17.
- Daly, H. E. (1990). Toward some operational principles of sustainable development. Ecological Economics , 2 (1), 1–6.
- Deery, M. , Jago, L. , & Fredline, L. (2012). Rethinking social impacts of tourism research: A new research agenda. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 64–73.
- Diedrich, A. , & Garcia-Buades, E. (2008). Local perceptions of tourism as indicators of destination decline. Tourism Management , 41 , 623–632.
- Durbarry, R. (2004). Tourism and economic growth: The case of Mauritius. Tourism Economics , 10 , 389–401.
- Elliott, S. M. , & Neirotti, L. D. (2008). Challenges of tourism in a dynamic island destination: The case of Cuba. Tourism Geographies , 10 (4), 375–402.
- Enders, W. , Sandler, T. , & Parise, G. F. (1992). An econometric analysis of the impact of terrorism on tourism. Kyklos , 45 (4), 531–554.
- Eugenio-Martin, J. L. , & Campos-Soria, J. A. (2014). Economic crisis and tourism expenditure cutback decision. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 53–73.
- Farrell, B. , & McLellan, R. (1987). Tourism and physical environment research. Annals of Tourism Research , 14 (1), 1–16.
- Faulkner, B. , & Tideswell, C. (1997). A framework for monitoring community impacts of tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 5 (1), 3–28.
- Fennell, D. A. , & Eagles, P. F. (1990). Ecotourism in Costa Rica: A conceptual framework. Journal of Park and Recreation Administration , 8 (1), 23–34.
- Fullagar, S. , Markwell, K. , & Wilson, E. (Eds.). (2012). Slow tourism: Experiences and mobilities . Channel View.
- Garau-Vadell, J. B. , Gutierrez-Taño, D. , & Diaz-Armas, R. (2018). Economic crisis and residents’ perception of the impacts of tourism in mass tourism destinations. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management , 7 , 68–75.
- Garrod, B. , & Fyall, A. (1998). Beyond the rhetoric of sustainable tourism? Tourism Management , 19 (3), 199–212.
- Ghimire, K. B. (Ed.). (2013). The native tourist: Mass tourism within developing countries . Routledge.
- Goodrich, J. N. (2002). September 11, 2001 attack on America: A record of the immediate impacts and reactions in the USA travel and tourism industry. Tourism Management , 23 (6), 573–580.
- Gössling, S. (1999). Ecotourism: A means to safeguard biodiversity and ecosystem functions? Ecological Economics , 29 , 303–320.
- Gössling, S. (2000). Tourism–sustainable development option? Environmental Conservation , 27 (3), 223–224.
- Gössling, S. (2002). Global environmental consequences of tourism. Global Environmental Change , 12 , 283–302.
- Gössling, S. , & Peeters, P. (2015). Assessing tourism’s global environmental impact 1900–2050. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 23 (5), 639–659.
- Gössling, S. , Peeters, P. , Hall, C. M. , Ceron, J.‑P. , Dubois, G. , Lehman, L. V. , & Scott, D. (2011). Tourism and water use: Supply, demand and security, and international review. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 16–28.
- Gössling, S. , Scott, D. , & Hall, C. M. (2020). Pandemics, tourism and global change: A rapid assessment of COVID-19. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 29 (1), 1–20.
- Gössling, S. , Scott, D. , Hall, C. M. , Ceron, J. P. , & Dubois, G. (2012). Consumer behaviour and demand response of tourists to climate change. Annals of Tourism Research , 39 (1), 36–58.
- Gray, N. J. , & Campbell, L. M. (2007). A decommodified experience? Exploring aesthetic, economic and ethical values for volunteer ecotourism in Costa Rica. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 463–482.
- Grober, U. (2007). Deep roots—a conceptual history of “sustainable development” (Nachhaltigkeit) . Wissenschaftszentrum Berlin für Sozialforschung.
- Gu, H. , & Ryan, C. (2008). Place attachment, identity and community impacts of tourism—the case of a Beijing hutong. Tourism Management , 29 (4), 637–647.
- Gursoy, D. , Chi, C. G. , & Dyer, P. (2010). Locals’ attitudes toward mass and alternative tourism: The case of Sunshine Coast, Australia. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (3), 381–394.
- Haley, A. J. , Snaith, T. , & Miller, G. (2005). The social impacts of tourism a case study of Bath, UK. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (3), 647–668.
- Hall, C. M. , & Lew, A. A. (2009). Understanding and managing tourism impacts: An integrated approach . Routledge.
- Hall, C. M. , & Lew, A. A. (Eds.). (1998). Sustainable tourism: A geographical perspective . Longman.
- Haque, T. H. , & Haque, M. O. (2018). The swine flu and its impacts on tourism in Brunei. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management , 36 , 92–101.
- Haralambopoulos, N. , & Pizam, A. (1996). Perceived impacts of tourism: The case of Samos. Annals of Tourism Research , 23 (3), 503–526.
- Harrison, D. (2008). Pro-poor tourism: A critique. Third World Quarterly , 29 (5), 851–868.
- Hearne, R. R. , & Salinas, Z. M. (2002). The use of choice experiments in the analysis of tourist preferences for ecotourism development in Costa Rica. Journal of Environmental Management , 65 (2), 153–163.
- Hetzer, N. D. (1965). Environment, tourism, culture. Links , 1 (2), 1–3.
- Höhler, S. (2015). Spaceship earth in the environmental age, 1960–1990 . Routledge.
- Honey, M. , & Gilpin, R. (2009). Tourism in the developing world: Promoting peace and reducing poverty . United States Institute for Peace.
- Huan, T. C. , Beaman, J. , & Shelby, L. (2004). No-escape natural disaster: Mitigating impacts on tourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 31 (2), 255–273.
- Huang, J. H. , & Min, J. C. (2002). Earthquake devastation and recovery in tourism: The Taiwan case. Tourism Management , 23 (2), 145–154.
- Hunter, C. (1995). On the need to re-conceptualise sustainable tourism development. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 3 (3), 155–165.
- Hunter, C. , & Green, H. (1995). Tourism and the environment. A sustainable relationship? Routledge.
- Huttasin, N. (2008). Perceived social impacts of tourism by residents in the OTOP tourism village, Thailand. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research , 13 (2), 175–191.
- Hystad, P. W. , & Keller, P. C. (2008). Towards a destination tourism disaster management framework: Long-term lessons from a forest fire disaster. Tourism Management , 29 (1), 151–162.
- Katircioglu, S. (2009). Tourism, trade and growth: The case of Cyprus. Applied Economics , 41 (21), 2741–2750.
- Katircioglu, S. (2010). Testing the tourism-led growth hypothesis for Singapore: An empirical investigation from bounds test to cointegration and Granger causality tests. Tourism Economics , 16 (4), 1095–1101.
- Khan, M. M. (1997). Tourism development and dependency theory: Mass tourism vs. ecotourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 24 (4), 988–991.
- Kim, H. , & Marcouiller, D. W. (2015). Considering disaster vulnerability and resiliency: The case of hurricane effects on tourism-based economies. The Annals of Regional Science , 54 (3), 945–971.
- King, B. , Pizam, A. , & Milman, A. (1993). Social impacts of tourism: Host perceptions. Annals of Tourism Research , 20 (4), 650–665.
- Kisswani, K. M. , Zaitouni, M. , & Moufakkir, O. (2020). An examination of the asymmetric effect of oil prices on tourism receipts. Current Issues in Tourism , 23 (4), 500–522.
- Kuvan, Y. , & Akan, P. (2005). Residents’ attitudes toward general and forest-related impacts of tourism: The case of Belek, Antalya. Tourism Management , 26 (5), 691–706.
- Lai, P. H. , & Nepal, S. K. (2006). Local perspectives of ecotourism development in Tawushan Nature Reserve, Taiwan. Tourism Management , 27 (6), 1117–1129.
- Lanouar, C. , & Goaied, M. (2019). Tourism, terrorism and political violence in Tunisia: Evidence from Markov-switching models. Tourism Management , 70 , 404–418.
- Lee, C. C. , & Chang, C. P. (2008). Tourism development and economic growth: A closer look at panels. Tourism Management , 29 , 180–192.
- Lenzen, M. , Sun, Y. Y. , Faturay, F. , Ting, Y. P. , Geschke, A. , & Malik, A. (2018). The carbon footprint of global tourism. Nature Climate Change , 8 (6), 522–528.
- Lian Chan, J. K. , & Baum, T. (2007). Ecotourists’ perception of ecotourism experience in lower Kinabatangan, Sabah, Malaysia. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 574–590.
- Liu, A. , & Pratt, S. (2017). Tourism’s vulnerability and resilience to terrorism. Tourism Management , 60 , 404–417.
- Manyara, G. , & Jones, E. (2007). Community-based tourism enterprises development in Kenya: An exploration of their potential as avenues of poverty reduction. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (6), 628–644.
- Maphanga, P. M. , & Henama, U. S. (2019). The tourism impact of Ebola in Africa: Lessons on crisis management. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure , 8 (3), 1–13.
- Mathieson, A. , & Wall, G. (1982). Tourism, economic, physical and social impacts . Longman.
- May, V. (1991). Tourism, environment and development—values, sustainability and stewardship. Tourism Management , 12 (2), 112–124.
- Mazzocchi, M. , & Montini, A. (2001). Earthquake effects on tourism in central Italy. Annals of Tourism Research , 28 (4), 1031–1046.
- Mbaiwa, J. E. (2005). The socio-cultural impacts of tourism development in the Okavango Delta, Botswana. Journal of Tourism and Cultural Change , 2 (3), 163–185.
- McKercher, B. (1993a). Some fundamental truths about tourism: Understanding tourism’s social and environmental impacts, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 1 (1), 6–16.
- McKercher, B. (1993b). The unrecognized threat to tourism: Can tourism survive “sustainability”? Tourism Management , 14 (2), 131–136.
- Meadows, D. H. , Meadows, D. L. , Randers, J. , & Behrens, W. W. (1972). The limits to growth . Universe Books.
- Miller, G. A. , & Ritchie, B. W. (2003). A farming crisis or a tourism disaster? An analysis of the foot and mouth disease in the UK. Current Issues in Tourism , 6 (2), 150–171.
- Milman, A. , & Pizam, A. (1988). Social impacts of tourism on central Florida. Annals of Tourism Research , 15 (2), 191–204.
- Monterrubio, J. C. (2010). Short-term economic impacts of influenza A (H1N1) and government reaction on the Mexican tourism industry: An analysis of the media. International Journal of Tourism Policy , 3 (1), 1–15.
- Narayan, P. K. (2004). Economic impact of tourism on Fiji’s economy: Empirical evidence from the computable general equilibrium model. Tourism Economics , 10 (4), 419–433.
- Nash, D. , & Butler, R. (1990). Towards sustainable tourism. Tourism Management , 11 (3), 263–264.
- Novelli, M. , Burgess, L. G. , Jones, A. , & Ritchie, B. W. (2018). “No Ebola . . . still doomed”—the Ebola-induced tourism crisis. Annals of Tourism Research , 70 , 76–87.
- Oh, C. (2005). The contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy. Tourism Management , 26 , 39–44.
- Oh, H. , Assaf, A. G. , & Baloglu, S. (2016). Motivations and goals of slow tourism. Journal of Travel Research , 55 (2), 205–219.
- Okumus, F. , & Karamustafa, K. (2005). Impact of an economic crisis evidence from Turkey. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (4), 942–961.
- Page, S. , Song, H. , & Wu, D. C. (2012). Assessing the impacts of the global economic crisis and swine flu on inbound tourism demand in the United Kingdom. Journal of Travel Research , 51 (2), 142–153.
- Papatheodorou, A. , Rosselló, J. , & Xiao, H. (2010). Global economic crisis and tourism: Consequences and perspectives. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (1), 39–45.
- Peeters, P. (2012). A clear path towards sustainable mass tourism? Rejoinder to the paper “Organic, incremental and induced paths to sustainable mass tourism convergence” by David B. Weaver. Tourism Management , 33 (5), 1038–1041.
- Pennington-Gray, L. , London, B. , Cahyanto, I. , & Klages, W. (2011). Expanding the tourism crisis management planning framework to include social media: Lessons from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill 2010. International Journal of Tourism Anthropology , 1 (3–4), 239–253.
- Pizam, A. , & Fleischer, A. (2002). Severity versus frequency of acts of terrorism: Which has a larger impact on tourism demand? Journal of Travel Research , 40 (3), 337–339.
- Pratt, S. (2015). The economic impact of tourism in SIDS. Annals of Tourism Research , 52 , 148–160.
- Prideaux, B. , Thompson, M. , & Pabel, A. (2020). Lessons from COVID-19 can prepare global tourism for the economic transformation needed to combat climate change. Tourism Geographies , 22 (3), 667–678.
- Qiu, R. T. , Park, J. , Li, S. , & Song, H. (2020). Social costs of tourism during the COVID-19 pandemic . Annals of Tourism Research , 84 , 102994.
- Rátz, T. (2000). Residents’ perceptions of the socio-cultural impacts of tourism at Lake Balaton, Hungary. Tourism and Sustainable Community Development , 7 , 36.
- Ribeiro, L. C. D. S. , Souza, K. B. D. , Domingues, E. P. , & Magalhães, A. S. (2020). Blue water turns black: Economic impact of oil spill on tourism and fishing in Brazilian Northeast . Current Issues in Tourism , 1–6.
- Richardson, R. B. , Fernandez, A. , Tschirley, D. , & Tembo, G. (2012). Wildlife conservation in Zambia: Impacts on rural household welfare. World Development , 40 (5), 1068–1081.
- Richardson, R. B. , & Loomis, J. B. (2004). Adaptive recreation planning and climate change: A contingent visitation approach. Ecological Economics , 50 (1), 83–99.
- Richardson, R. B. , & Witkowski, K. (2010). Economic vulnerability to climate change for tourism-dependent nations. Tourism Analysis , 15 (3), 315–330.
- Ritchie, B. W. , Crotts, J. C. , Zehrer, A. , & Volsky, G. T. (2013). Understanding the effects of a tourism crisis: The impact of the BP oil spill on regional lodging demand. Journal of Travel Research , 53 (1), 12–25.
- Rogerson, C. M. (2011). Urban tourism and regional tourists: Shopping in Johannesburg, South Africa. Tijdschrift voor economische en sociale geografie , 102 (3), 316–330.
- Rutty, M. , & Richardson, R. (2019). Tourism research in Cuba: Gaps in knowledge and challenges for sustainable tourism. Sustainability , 11 (12), 3340–3346.
- Ryan, C. , & Huyton, J. (2000). Who is interested in Aboriginal tourism in the Northern Territory, Australia? A cluster analysis. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 8 (1), 53–88.
- Salinas, E. , Mundet, L. , & Salinas, E. (2018). Historical evolution and spatial development of tourism in Cuba, 1919–2017: What is next? Tourism Planning & Development , 15 (3), 216–238.
- Sanchez, P. M. , & Adams, K. M. (2008). The Janus-faced character of tourism in Cuba. Annals of Tourism Research , 35 , 27–46.
- Scott, D. , Hall, C. M. , & Gössling, S. (2012). Tourism and climate change: Impacts, adaptation and mitigation . Routledge.
- Seetanah, B. (2011). Assessing the dynamic economic impact of tourism for island economies. Annals of Tourism Research , 38 (1), 291–308.
- Sharma, A. , & Nicolau, J. L. (2020). An open market valuation of the effects of COVID-19 on the travel and tourism industry . Annals of Tourism Research , 83 , 102990.
- Sharpley, R. (2000). Tourism and sustainable development: Exploring the theoretical divide. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 8 (1), 1–19.
- Sharpley, R. (2014). Host perceptions of tourism: A review of the research. Tourism Management , 42 , 37–49.
- Smeral, E. (2010). Impacts of the world recession and economic crisis on tourism: Forecasts and potential risks. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (1), 31–38.
- Southgate, C. R. (2006). Ecotourism in Kenya: The vulnerability of communities. Journal of Ecotourism , 5 (1–2), 80–96.
- Spenceley, A. (Ed.). (2012). Responsible tourism: Critical issues for conservation and development . Routledge.
- Stabler, M. (Ed.). (1997). Tourism and sustainability: Principles to practice . Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International.
- Stronza, A. (2007). The economic promise of ecotourism for conservation. Journal of Ecotourism , 6 (3), 210–230.
- Stylidis, D. , & Terzidou, M. (2014). Tourism and the economic crisis in Kavala, Greece. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 210–226.
- Suntikul, W. , Bauer, T. , & Song, H. (2009). Pro-poor tourism development in Viengxay, Laos: Current state and future prospects. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research , 14 (2), 153–168.
- Swarbrooke, J. (1999). Sustainable tourism management . CABI.
- Tovar, C. , & Lockwood, M. (2008). Social impacts of tourism: An Australian regional case study. International Journal of Tourism Research , 10 (4), 365–378.
- Tsartas, P. (1992). Socioeconomic impacts of tourism on two Greek isles. Annals of Tourism Research , 19 (3), 516–533.
- Turner, L. , & Ash, J. (1975). The golden hordes: International tourism and the pleasure periphery . Constable.
- United Nations . (2015). Transforming our world: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development . Division for Sustainable Development Goals.
- United Nations World Tourism Organization . (2002). Tourism and poverty alleviation . United Nations World Tourism Organization.
- United Nations World Tourism Organization . (2020). UNWTO world tourism barometer . United Nations World Tourism Organization.
- Viner, D. (2006). Tourism and its interactions with climate change. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 14 (4), 317–322.
- Vitousek, P. M. , Mooney, H. A. , Lubchenco, J. , & Melillo, J. M. (1997). Human domination of Earth’s ecosystems. Science , 277 (5325), 494–499.
- World Commission on Environment and Development . (1987). Our common future . Oxford University Press.
- Weaver, D. (2007). Towards sustainable mass tourism: Paradigm shift or paradigm nudge? Tourism Recreation Research , 32 (3), 65–69.
- Weaver, D. B. (2012). Organic, incremental and induced paths to sustainable mass tourism convergence. Tourism Management , 33 (5), 1030–1037.
- Weaver, D. B. (2014). Asymmetrical dialectics of sustainable tourism: Toward enlightened mass tourism. Journal of Travel Research , 53 (2), 131–140.
- Wheeller, B. (2007). Sustainable mass tourism: More smudge than nudge the canard continues. Tourism Recreation Research , 32 (3), 73–75.
- Whitford, M. , & Ruhanen, L. (2016). Indigenous tourism research, past and present: Where to from here? Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 24 (8–9), 1080–1099.
- Whyte, K. P. (2010). An environmental justice framework for indigenous tourism. Environmental Philosophy , 7 (2), 75–92.
- Wolff, K. , & Larsen, S. (2014). Can terrorism make us feel safer? Risk perceptions and worries before and after the July 22nd attacks. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 200–209.
- Yang, W. , Wang, D. , & Chen, G. (2011). Reconstruction strategies after the Wenchuan earthquake in Sichuan, China. Tourism Management , 32 (4), 949–956.
- Young, G. (1973). Tourism—blessing or blight? Penguin.
- Zapata, M. J. , Hall, C. M. , Lindo, P. , & Vanderschaeghe, M. (2011). Can community-based tourism contribute to development and poverty alleviation? Lessons from Nicaragua. Current Issues in Tourism , 14 (8), 725–749.
1. One megatonne (Mt) is equal to 1 million (10 6 ) metric tons.
2. One megajoule (MJ) is equal to 1 million (10 6 ) joules, or approximately the kinetic energy of a 1-megagram (tonne) vehicle moving at 161 km/h.
3. One gigatonne (Gt) is equal to 1 billion (10 9 ) metric tons.
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Environmental Science. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 14 September 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|185.66.14.236]
- 185.66.14.236
Character limit 500 /500

20 Reasons You Should Integrate Tourism into Your Development Agenda
Louise twining-ward, damien shiels.

Senior Private Sector Specialist

Global Product Specialist
Join the Conversation
- Share on mail
- comments added

What is the impact of tourism on development?

Image: Passengers walk across an air bridge as they disembark a flight at Changi Airport in Singapore. REUTERS/Vivek Prakash.
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} John Perrottet

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Economic Progress is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, travel and tourism.
Tourism is growing, and growing fast. After surpassing 1 billion international visitors in 2012, we are expecting 1.8 billion by 2030. Tourism is growing faster than the global economy and, for the first time, the statistics for 2015 are expected to show that there were more trips taken to the developing world than to the developed world. But what does this actually mean? Growth, on its own, is not enough. Destinations and their stakeholders are responsible for ensuring that growth is well-managed; that benefits are maximized; and that any negative externalities are minimized. This requires a continuous process of planning and management that evolves and that can be measured over time. For the World Bank Group, our clients and our development partners, this process of planning and management is a central interest. How can we help these processes to deliver more and better development impact? What kinds of interventions or types of assistance will deliver the best results? How do you define the best results – for whom? – and how do we measure them? Being able to demonstrate how the tourism sector contributes to the Bank Group’s twin goals of eliminating extreme poverty and promoting shared prosperity is an imperative for all stakeholders. It’s relevant for national governments, sub-national state agencies, businesses (both multinationals and SMEs), multilateral development banks, NGOs, academics and think tanks. Moreover, it’s vital in helping guide future planning and development, gaining access to and applying for funding, and demonstrating progress to constituents at all levels.
Despite the great breadth and depth of existing impact information, however, serious concerns remain about the accuracy, complexity, gaps, comparability and sustainability of the types of the impact analyses that have been carried out. The Bank Group’s Sustainable Tourism Global Solutions Group recently convened a thought-leadership event in Washington to begin a preliminary discussion about how all stakeholders can come together to try and address some of the current shortcomings. During the “ Measuring for Impact in Touris m” event, we heard about a wide range of challenges for those working in this area and we began to map out the greatest gaps and issues. As Anabel Gonzalez, the Senior Director of the Trade and Competitiveness Global Practice, said at that conference: “We want to be better at monitoring and evaluating our impact, we want to learn from others, and we want to contribute more effectively to tourism development. I believe these are goals most of you will share. We invite you to join this discussion – and be frank, open and provocative.”The findings can be found in our report, “ Towards More Effective Impact Measurement in the Tourism Sector: Observations and Key Issues ,” which highlights a number of priorities. Some of those challenges concern the availability, quality and consistency of data; the high cost of impact measurement for SMEs; the proliferation of different systems; issues of attribution; quantifying notions of “value”; and the ability to communicate effectively to a wide range of audiences. Some key areas for immediate follow-up and further analysis were also identified. They include:
-Exploring the theory of change by examining more closely the proposition that, when tourism growth occurs, those living in extreme poverty benefit and by digging deeper into what tourism growth really means for the poor, especially in terms of employment.
-Assessing the impact value of different types of tourism.
-Assessing and developing the role of technology for data collection, impact measurement and communication.
-Evaluating the use of training for better communication – including assessing what has been tried and what has worked and considering how it could be scaled up.
-Analyzing the necessity and practicality of improving collaboration among various actors, and assessing the alignment of frameworks along with proposals for greater alignment.
-Developing ideas and proposals for the enhanced sharing and pooling of impact data.
-Developing ideas and proposals for greater inclusion of SMEs.
The Bank Group is committed to advancing this agenda . As an international organization heavily invested in the sector, with a deep motivation to deliver change for the world’s poorest people, we aim to take a leading role in a number of key areas. Other major stakeholders have also shown their support. Harvard University and the University of Sussex have asked to host follow-up events. Wyndham Hotels, the World Trade Organization, the United Nations Environment Program, the World Wildlife Fund and Sustainable Travel International have sought specific collaboration and partnership opportunities. The Bank Group will continue to convene meetings, promote dialogue, conduct research and publish relevant information – focusing our interventions on those areas where we’re well-placed to fulfill the twin goals of eliminating extreme poverty and promoting shared prosperity.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Economic Growth .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

The 'middle-income trap' is holding back over 100 countries. Here's how to overcome it
Spencer Feingold
September 4, 2024

Ray Dalio: Here are 5 trends shaping the global economy
Simon Torkington
August 30, 2024

6 trends shaping financial advice in the fintech era
Andrea Willige
August 6, 2024

Access to credit: The silent issue hampering growth and development in emerging economies
Omair Ansari and Manahil Javaid

A third of India's economy relies on nature: here’s why corporates need to invest more in natural climate solutions
August 5, 2024

How do we ensure the green transition doesn't penalize the poorest?
Tarini Fernando and Nadia Shamsad
July 18, 2024
Sustainable tourism
Related sdgs, promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable ....

Description
Publications.
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States (SIDS) and coastal least developed countries (LDCs) (see also: The Potential of the Blue Economy report as well as the Community of Ocean Action on sustainable blue economy).
The World Tourism Organization defines sustainable tourism as “tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment and host communities".
Based on General assembly resolution 70/193, 2017 was declared as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development.
In the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development SDG target 8.9, aims to “by 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism is also highlighted in SDG target 12.b. which aims to “develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”.
Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “by 2030, increase the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries” as comprised in SDG target 14.7.
In the Rio+20 outcome document The Future We want, sustainable tourism is defined by paragraph 130 as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities by supporting their local economies and the human and natural environment as a whole. ” In paragraph 130, Member States also “call for enhanced support for sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building in developing countries in order to contribute to the achievement of sustainable development”.
In paragraph 131, Member States “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small- and medium-sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”. In this regard, Member States also “underline the importance of establishing, where necessary, appropriate guidelines and regulations in accordance with national priorities and legislation for promoting and supporting sustainable tourism”.
In 2002, the World Summit on Sustainable Development in Johannesburg called for the promotion of sustainable tourism development, including non-consumptive and eco-tourism, in Chapter IV, paragraph 43 of the Johannesburg Plan of Implementation.
At the Johannesburg Summit, the launch of the “Sustainable Tourism – Eliminating Poverty (ST-EP) initiative was announced. The initiative was inaugurated by the World Tourism Organization, in collaboration with UNCTAD, in order to develop sustainable tourism as a force for poverty alleviation.
The UN Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD) last reviewed the issue of sustainable tourism in 2001, when it was acting as the Preparatory Committee for the Johannesburg Summit.
The importance of sustainable tourism was also mentioned in Agenda 21.
For more information and documents on this topic, please visit this link
UNWTO Annual Report 2015
2015 was a landmark year for the global community. In September, the 70th Session of the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a universal agenda for planet and people. Among the 17 SDGs and 169 associated targets, tourism is explicitly featured in Goa...
UNWTO Annual Report 2016
In December 2015, the United Nations General Assembly declared 2017 as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development. This is a unique opportunity to devote a year to activities that promote the transformational power of tourism to help us reach a better future. This important cele...
Emerging Issues for Small Island Developing States
The 2012 UNEP Foresight Process on Emerging Global Environmental Issues primarily identified emerging environmental issues and possible solutions on a global scale and perspective. In 2013, UNEP carried out a similar exercise to identify priority emerging environmental issues that are of concern to ...
Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
This Agenda is a plan of action for people, planet and prosperity. It also seeks to strengthen universal peace in larger freedom, We recognize that eradicating poverty in all its forms and dimensions, including extreme poverty, is the greatest global challenge and an indispensable requirement for su...
15 Years of the UNWTO World Tourism Network on Child Protection: A Compilation of Good Practices
Although it is widely recognized that tourism is not the cause of child exploitation, it can aggravate the problem when parts of its infrastructure, such as transport networks and accommodation facilities, are exploited by child abusers for nefarious ends. Additionally, many other factors that contr...
Towards Measuring the Economic Value of Wildlife Watching Tourism in Africa
Set against the backdrop of the ongoing poaching crisis driven by a dramatic increase in the illicit trade in wildlife products, this briefing paper intends to support the ongoing efforts of African governments and the broader international community in the fight against poaching. Specifically, this...
Status and Trends of Caribbean Coral Reefs: 1970-2012
Previous Caribbean assessments lumped data together into a single database regardless of geographic location, reef environment, depth, oceanographic conditions, etc. Data from shallow lagoons and back reef environments were combined with data from deep fore-reef environments and atolls. Geographic c...
Natural Resources Forum: Special Issue Tourism
The journal considers papers on all topics relevant to sustainable development. In addition, it dedicates series, issues and special sections to specific themes that are relevant to the current discussions of the United Nations Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD)....
Thailand: Supporting Sustainable Development in Thailand: A Geographic Clusters Approach
Market forces and government policies, including the Tenth National Development Plan (2007-2012), are moving Thailand toward a more geographically specialized economy. There is a growing consensus that Thailand’s comparative and competitive advantages lie in amenity services that have high reliance...
Road Map on Building a Green Economy for Sustainable Development in Carriacou and Petite Martinique, Grenada
This publication is the product of an international study led by the Division for Sustainable Development (DSD) of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA) in cooperation with the Ministry of Carriacou and Petite Martinique Affairs and the Ministry of Environment, Foreig...
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal (NRF)
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal, seeks to address gaps in current knowledge and stimulate relevant policy discussions, leading to the implementation of the sustainable development agenda and the achievement of the Sustainable...
UN Ocean Conference 2025
Our Ocean, Our Future, Our Responsibility “The ocean is fundamental to life on our planet and to our future. The ocean is an important source of the planet’s biodiversity and plays a vital role in the climate system and water cycle. The ocean provides a range of ecosystem services, supplies us with
UN Ocean Conference 2022
The UN Ocean Conference 2022, co-hosted by the Governments of Kenya and Portugal, came at a critical time as the world was strengthening its efforts to mobilize, create and drive solutions to realize the 17 Sustainable Development Goals by 2030.
58th Session of the Commission for Social Development – CSocD58
22nd general assembly of the united nations world tourism organization, world tourism day 2017 official celebration.
This year’s World Tourism Day, held on 27 September, will be focused on Sustainable Tourism – a Tool for Development. Celebrated in line with the 2017 International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, the Day will be dedicated to exploring the contribution of tourism to the Sustainable Deve
World Tourism Day 2016 Official Celebration
Accessible Tourism for all is about the creation of environments that can cater for the needs of all of us, whether we are traveling or staying at home. May that be due to a disability, even temporary, families with small children, or the ageing population, at some point in our lives, sooner or late
4th Global Summit on City Tourism
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and the Regional Council for Tourism of Marrakesh with support of the Government of Morroco are organizing the 4th Global Summit on City Tourism in Marrakesh, Morroco (9-10 December 2015). International experts in city tourism, representatives of city DMOs, of
2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and Ulsan Metropolitan City with support of the Government of the Republic of Korea are organizing the 2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference, in Ulsan, Republic of Korea (14 - 16 October 2015). Under the title “Paving the Way for a Bright Future for Mounta
21st General Assembly of the United Nations World Tourism Organization
Unwto regional conference enhancing brand africa - fostering tourism development.
Tourism is one of the Africa’s most promising sectors in terms of development, and represents a major opportunity to foster inclusive development, increase the region’s participation in the global economy and generate revenues for investment in other activities, including environmental preservation.
- January 2017 International Year of Tourism In the context of the universal 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the International Year aims to support a change in policies, business practices and consumer behavior towards a more sustainable tourism sector that can contribute to the SDGs.
- January 2015 Targets 8.9, 12 b,14.7 The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development commits Member States, through Sustainable Development Goal Target 8.9 to “devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism, as a driver for jobs creation and the promotion of local culture and products, is also highlighted in Sustainable Development Goal target 12.b. Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “increase [by 2030] the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries”, through Sustainable Development Goals Target 14.7.
- January 2012 Future We Want (Para 130-131) Sustainable tourism is defined as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities” as well as to “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small and medium sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”.
- January 2009 Roadmap for Recovery UNWTO announced in March 2009 the elaboration of a Roadmap for Recovery to be finalized by UNWTO’s General Assembly, based on seven action points. The Roadmap includes a set of 15 recommendations based on three interlocking action areas: resilience, stimulus, green economy aimed at supporting the tourism sector and the global economy.
- January 2008 Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria The Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria represent the minimum requirements any tourism business should observe in order to ensure preservation and respect of the natural and cultural resources and make sure at the same time that tourism potential as tool for poverty alleviation is enforced. The Criteria are 41 and distributed into four different categories: 1) sustainability management, 2) social and economic 3) cultural 4) environmental.
- January 2003 WTO becomes a UN specialized body By Resolution 453 (XV), the Assembly agreed on the transformation of the WTO into a United Nations specialized body. Such transformation was later ratified by the United Nations General Assembly with the adoption of Resolution A/RES/58/232.
- January 2003 1st Int. Conf. on Climate Change and Tourism The conference was organized in order to gather tourism authorities, organizations, businesses and scientists to discuss on the impact that climate change can have on the tourist sector. The event took place from 9 till 11 April 2003 in Djerba, Tunisia.
- January 2002 World Ecotourism Summit Held in May 2002, in Quebec City, Canada, the Summit represented the most important event in the framework of the International Year of Ecosystem. The Summit identified as main themes: ecotourism policy and planning, regulation of ecotourism, product development, marketing and promotion of ecotourism and monitoring costs and benefits of ecotourism.
- January 1985 Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code At the World Tourism Organization Sixth Assembly held in Sofia in 1985, the Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code were adopted, setting out the rights and duties of tourists and host populations and formulating policies and action for implementation by states and the tourist industry.
- January 1982 Acapulco Document Adopted in 1982, the Acapulco Document acknowledges the new dimension and role of tourism as a positive instrument towards the improvement of the quality of life for all peoples, as well as a significant force for peace and international understanding. The Acapulco Document also urges Member States to elaborate their policies, plans and programmes on tourism, in accordance with their national priorities and within the framework of the programme of work of the World Tourism Organization.

Why tourism planning is important
Tourism planning should be an integral part of any destination’s tourism development plan in order to achieve the best results and satisfy all stakeholders. Tourism planning is key to maintaining sustainable tourism and whilst some destinations do this very well, others (often developing countries), fail the recognise the importance of effective tourism development planning.
In this post I will explain why tourism planning is so important and recommend some literature for further reading on this topic. This information on tourism planning should be helpful to a number of tourism stakeholders, including business entrepreneurs, Government bodies and tourism workers. It is also useful for those studying travel and tourism as well as those who have a general interest in the subject. For an introduction to the concept of tourism policy and planning visit this post- ‘ The different levels of tourism policy and planning ‘.
Wait! Before you read on, take a look at the short video that I created all about the importance of tourism planning!
What is tourism planning?
Tourism development refers to the growth and maintenance of the tourism industry in a given locality. And, of course, tourism planning is a very important part of this.
On a basic level, tourism development can be defined as creating strategies and plans to increase/develop/encourage tourism for a destination. The fundamental reason behind planning and implementing strategies for developing the tourism sector is primarily to make money and to subsequently increase the GDP of a country/area.
You might also be interested in my post- ‘ What is tourism? A definition of tourism ‘
Tourism development consists of many elements including, but not limited to: developing and managing private-public partnerships, assessing the competitors to gain competitive advantage, ensuring responsible and sustainable development, viewing tourism as an interconnected system and a demand-driven sector, assessing private sector investment and international cooperation, tourism clustering and involvement by the Government.
According to Williams cited in Mason (2003);
‘The aim of modern planning is to seek optimal solutions to perceived problems and that it is designed to increase and, hopefully maximise development benefits, which will produce predictable outcomes’.
And Getz (1987) cited in Pearce (1989) defines tourism planning as;
“A process, based on research and evaluation, which seeks to optimise the potential contribution of tourism to human welfare and environmental quality”
Tourism development planning should be an integral part of any destination’s tourism plan in order to achieve the best results and satisfy all stakeholders. Tourism development planning is key to maintaining sustainable tourism and whilst some destinations do this very well, others (often developing countries), fail the recognise the importance of effective tourism development planning.
What is tourism development planning?
Tourism development refers to the growth and maintenance of the tourism industry in a given locality. And, of course, planning is a very important part of this.
Basic stages in tourism development planning
Tourism development planning is no simple task and there are many variables to consider. There are also different levels of tourism planning and policy . Fortunately , destinations can learn lessons from other areas which have been successful or otherwise. Take for example, over dependence on tourism in Egypt as I explain in this post- Why Unpaid Business is Better than No Business: The Case of the Egyptian Boatman. It is also worthwhile to look at the tourism policies of similar destinations. Some strong examples include Jamaica and Cape Town .
On a basic level, the main stages in tourism development planning include: the analysis of previous tourist development; evaluation of the position of tourism in the area including competition; formulation of relevant tourism policy by Government; the defining of a development strategy and the formation of a programme of action.

The benefits of tourism development
Tourism development planning enables a range of benefits to all stakeholders involved, for example:
- It increases income and jobs from tourist spending
- It helps preserve cultural and natural heritage for tourists
- It increases understanding of other cultures
- It builds new facilities such as sewage for whole communities or new roads
The costs of tourism development
There are also some costs which must be considered and planned for, which include:
- Costs of implementing tourist facilities can be costly
- The environment can be destructed to make room for hotels etc. to be built
- Social standards may be undermined e.g. topless women in Dubai
- The natural environment may be polluted
Formulating an approach to tourism policy and planning
There are six ‘golden rules’ that should be applied when formulating an approach to tourism policy and planning, as outlined by Inskeep (1991).

- Goal oriented
Clear recognition of tourism’s role in achieving broad national and community goals
- Integrative
Incorporating tourism policy and planning into the mainstream of planning for the economy, land use and infrastructure, conservation and environment
- Market driven
Planning for tourism development that trades successfully in a competitive global marketplace
- Resource driven
Developing tourism which build on the destination’s inherent strengths whilst protecting and enhancing the attributes and experiences of current tourism assets
- Consultative
Incorporating the wider community attitudes, needs and wants to determine what is acceptable to the population
Drawing on primary or secondary research to provide conceptual or predictive support for planners including the experiences of other tourism destinations
Why tourism development planning is important
Tourism development planning really can make or break a destination. If done well, it can ensure the longevity of the tourism industry in the area, take good care of the environment, have positive economic outcomes and a positive benefit to the community.
If done badly , tourism development can destroy the very environment or culture that it relies on. It can disrupt local economies, cause inflation and negative effects to local people and businesses. Unfortunately, developing countries tend to suffer the most from negative impacts such as these, largely as a result of limited education and experience in contrast with Western nations. For more on this topic, you can read this post.
If you wish to cite any of the content in the post please use reference ‘Stainton, Hayley. (2018) Lifeasabutterfly .’
§§cs§§
For more on what constitutes tourism planning I recommend that you refer to the texts Tourism Policy and Planning: Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow by Edgell and Swanson and Tourism Planning and Destination Marketing by Camilleri .
Tourism development planning is no simple task and there are many variables to consider. There are also different levels of tourism planning and policy. Fortunately, destinations can learn lessons from other areas which have been successful or otherwise. Take for example, over dependence on tourism in Egypt as I explain in this post- Why Unpaid Business is Better than No Business: The Case of the Egyptian Boatman. It is also worthwhile to look at the tourism policies of similar destinations. Some strong examples include Jamaica and Cape Town .

You might also be interested in my post- ‘ Best Universities In The UK To Study Travel and Tourism ‘
There are six ‘golden rules’ that should be applied when formulating an approach to tourism planning and policy, as outlined by Inskeep (1991).

You might also be interested in my post- ‘ What is ‘begpacking’ and why is it so bad ?’
Tourism planning really can make or break a destination. If done well, it can ensure the longevity of the tourism industry in the area, take good care of the environment, have positive economic outcomes and a positive benefit to the community.
If done badly, tourism development can destroy the very environment or culture that it relies on. It can disrupt local economies, cause inflation and negative effects to local people and businesses. Unfortunately, developing countries tend to suffer the most from negative impacts such as these, largely as a result of limited education and experience in contrast with Western nations.
For more on this topic, I recommend the following texts:
Tourism Policy and Planning: Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow
Tourism Planning and Destination Marketing
Leisure, Sport and Tourism, Politics, Policy and Planning
Tourism Planning: Policies, Processes and Relationships
What Is Sustainable Tourism and Why Is It Important?
Sustainable management and socioeconomic, cultural, and environmental impacts are the four pillars of sustainable tourism
- Chapman University
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/HaleyMast-2035b42e12d14d4abd433e014e63276c.jpg)
- Harvard University Extension School
- Sustainable Fashion
- Art & Media
What Makes Tourism Sustainable?
The role of tourists, types of sustainable tourism.
Sustainable tourism considers its current and future economic, social, and environmental impacts by addressing the needs of its ecological surroundings and the local communities. This is achieved by protecting natural environments and wildlife when developing and managing tourism activities, providing only authentic experiences for tourists that don’t appropriate or misrepresent local heritage and culture, or creating direct socioeconomic benefits for local communities through training and employment.
As people begin to pay more attention to sustainability and the direct and indirect effects of their actions, travel destinations and organizations are following suit. For example, the New Zealand Tourism Sustainability Commitment is aiming to see every New Zealand tourism business committed to sustainability by 2025, while the island country of Palau has required visitors to sign an eco pledge upon entry since 2017.
Tourism industries are considered successfully sustainable when they can meet the needs of travelers while having a low impact on natural resources and generating long-term employment for locals. By creating positive experiences for local people, travelers, and the industry itself, properly managed sustainable tourism can meet the needs of the present without compromising the future.
What Is Sustainability?
At its core, sustainability focuses on balance — maintaining our environmental, social, and economic benefits without using up the resources that future generations will need to thrive. In the past, sustainability ideals tended to lean towards business, though more modern definitions of sustainability highlight finding ways to avoid depleting natural resources in order to keep an ecological balance and maintain the quality of environmental and human societies.
Since tourism impacts and is impacted by a wide range of different activities and industries, all sectors and stakeholders (tourists, governments, host communities, tourism businesses) need to collaborate on sustainable tourism in order for it to be successful.
The World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) , which is the United Nations agency responsible for the promotion of sustainable tourism, and the Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) , the global standard for sustainable travel and tourism, have similar opinions on what makes tourism sustainable. By their account, sustainable tourism should make the best use of environmental resources while helping to conserve natural heritage and biodiversity, respect the socio-culture of local host communities, and contribute to intercultural understanding. Economically, it should also ensure viable long-term operations that will provide benefits to all stakeholders, whether that includes stable employment to locals, social services, or contributions to poverty alleviation.
The GSTC has developed a series of criteria to create a common language about sustainable travel and tourism. These criteria are used to distinguish sustainable destinations and organizations, but can also help create sustainable policies for businesses and government agencies. Arranged in four pillars, the global baseline standards include sustainable management, socioeconomic impact, cultural impacts, and environmental impacts.
Travel Tip:
The GSTC is an excellent resource for travelers who want to find sustainably managed destinations and accommodations and learn how to become a more sustainable traveler in general.
Environment
Protecting natural environments is the bedrock of sustainable tourism. Data released by the World Tourism Organization estimates that tourism-based CO2 emissions are forecast to increase 25% by 2030. In 2016, tourism transport-related emissions contributed to 5% of all man-made emissions, while transport-related emissions from long-haul international travel were expected to grow 45% by 2030.
The environmental ramifications of tourism don’t end with carbon emissions, either. Unsustainably managed tourism can create waste problems, lead to land loss or soil erosion, increase natural habitat loss, and put pressure on endangered species . More often than not, the resources in these places are already scarce, and sadly, the negative effects can contribute to the destruction of the very environment on which the industry depends.
Industries and destinations that want to be sustainable must do their part to conserve resources, reduce pollution, and conserve biodiversity and important ecosystems. In order to achieve this, proper resource management and management of waste and emissions is important. In Bali, for example, tourism consumes 65% of local water resources, while in Zanzibar, tourists use 15 times as much water per night as local residents.
Another factor to environmentally focused sustainable tourism comes in the form of purchasing: Does the tour operator, hotel, or restaurant favor locally sourced suppliers and products? How do they manage their food waste and dispose of goods? Something as simple as offering paper straws instead of plastic ones can make a huge dent in an organization’s harmful pollutant footprint.
Recently, there has been an uptick in companies that promote carbon offsetting . The idea behind carbon offsetting is to compensate for generated greenhouse gas emissions by canceling out emissions somewhere else. Much like the idea that reducing or reusing should be considered first before recycling , carbon offsetting shouldn’t be the primary goal. Sustainable tourism industries always work towards reducing emissions first and offset what they can’t.
Properly managed sustainable tourism also has the power to provide alternatives to need-based professions and behaviors like poaching . Often, and especially in underdeveloped countries, residents turn to environmentally harmful practices due to poverty and other social issues. At Periyar Tiger Reserve in India, for example, an unregulated increase in tourists made it more difficult to control poaching in the area. In response, an eco development program aimed at providing employment for locals turned 85 former poachers into reserve gamekeepers. Under supervision of the reserve’s management staff, the group of gamekeepers have developed a series of tourism packages and are now protecting land instead of exploiting it. They’ve found that jobs in responsible wildlife tourism are more rewarding and lucrative than illegal work.
Flying nonstop and spending more time in a single destination can help save CO2, since planes use more fuel the more times they take off.
Local Culture and Residents
One of the most important and overlooked aspects of sustainable tourism is contributing to protecting, preserving, and enhancing local sites and traditions. These include areas of historical, archaeological, or cultural significance, but also "intangible heritage," such as ceremonial dance or traditional art techniques.
In cases where a site is being used as a tourist attraction, it is important that the tourism doesn’t impede access to local residents. For example, some tourist organizations create local programs that offer residents the chance to visit tourism sites with cultural value in their own countries. A program called “Children in the Wilderness” run by Wilderness Safaris educates children in rural Africa about the importance of wildlife conservation and valuable leadership development tools. Vacations booked through travel site Responsible Travel contribute to the company’s “Trip for a Trip” program, which organizes day trips for disadvantaged youth who live near popular tourist destinations but have never had the opportunity to visit.
Sustainable tourism bodies work alongside communities to incorporate various local cultural expressions as part of a traveler’s experiences and ensure that they are appropriately represented. They collaborate with locals and seek their input on culturally appropriate interpretation of sites, and train guides to give visitors a valuable (and correct) impression of the site. The key is to inspire travelers to want to protect the area because they understand its significance.
Bhutan, a small landlocked country in South Asia, has enforced a system of all-inclusive tax for international visitors since 1997 ($200 per day in the off season and $250 per day in the high season). This way, the government is able to restrict the tourism market to local entrepreneurs exclusively and restrict tourism to specific regions, ensuring that the country’s most precious natural resources won’t be exploited.
Incorporating volunteer work into your vacation is an amazing way to learn more about the local culture and help contribute to your host community at the same time. You can also book a trip that is focused primarily on volunteer work through a locally run charity or non profit (just be sure that the job isn’t taking employment opportunities away from residents).
It's not difficult to make a business case for sustainable tourism, especially if one looks at a destination as a product. Think of protecting a destination, cultural landmark, or ecosystem as an investment. By keeping the environment healthy and the locals happy, sustainable tourism will maximize the efficiency of business resources. This is especially true in places where locals are more likely to voice their concerns if they feel like the industry is treating visitors better than residents.
Not only does reducing reliance on natural resources help save money in the long run, studies have shown that modern travelers are likely to participate in environmentally friendly tourism. In 2019, Booking.com found that 73% of travelers preferred an eco-sustainable hotel over a traditional one and 72% of travelers believed that people need to make sustainable travel choices for the sake of future generations.
Always be mindful of where your souvenirs are coming from and whether or not the money is going directly towards the local economy. For example, opt for handcrafted souvenirs made by local artisans.
Growth in the travel and tourism sectors alone has outpaced the overall global economy growth for nine years in a row. Prior to the pandemic, travel and tourism accounted for an $9.6 trillion contribution to the global GDP and 333 million jobs (or one in four new jobs around the world).
Sustainable travel dollars help support employees, who in turn pay taxes that contribute to their local economy. If those employees are not paid a fair wage or aren’t treated fairly, the traveler is unknowingly supporting damaging or unsustainable practices that do nothing to contribute to the future of the community. Similarly, if a hotel doesn’t take into account its ecological footprint, it may be building infrastructure on animal nesting grounds or contributing to excessive pollution. The same goes for attractions, since sustainably managed spots (like nature preserves) often put profits towards conservation and research.
Costa Rica was able to turn a severe deforestation crisis in the 1980s into a diversified tourism-based economy by designating 25.56% of land protected as either a national park, wildlife refuge, or reserve.
While traveling, think of how you would want your home country or home town to be treated by visitors.
Are You a Sustainable Traveler?
Sustainable travelers understand that their actions create an ecological and social footprint on the places they visit. Be mindful of the destinations , accommodations, and activities you choose, and choose destinations that are closer to home or extend your length of stay to save resources. Consider switching to more environmentally friendly modes of transportation such as bicycles, trains, or walking while on vacation. Look into supporting locally run tour operations or local family-owned businesses rather than large international chains. Don’t engage in activities that harm wildlife, such as elephant riding or tiger petting , and opt instead for a wildlife sanctuary (or better yet, attend a beach clean up or plan an hour or two of some volunteer work that interests you). Leave natural areas as you found them by taking out what you carry in, not littering, and respecting the local residents and their traditions.
Most of us travel to experience the world. New cultures, new traditions, new sights and smells and tastes are what makes traveling so rewarding. It is our responsibility as travelers to ensure that these destinations are protected not only for the sake of the communities who rely upon them, but for a future generation of travelers.
Sustainable tourism has many different layers, most of which oppose the more traditional forms of mass tourism that are more likely to lead to environmental damage, loss of culture, pollution, negative economic impacts, and overtourism.
Ecotourism highlights responsible travel to natural areas that focus on environmental conservation. A sustainable tourism body supports and contributes to biodiversity conservation by managing its own property responsibly and respecting or enhancing nearby natural protected areas (or areas of high biological value). Most of the time, this looks like a financial compensation to conservation management, but it can also include making sure that tours, attractions, and infrastructure don’t disturb natural ecosystems.
On the same page, wildlife interactions with free roaming wildlife should be non-invasive and managed responsibly to avoid negative impacts to the animals. As a traveler, prioritize visits to accredited rescue and rehabilitation centers that focus on treating, rehoming, or releasing animals back into the wild, such as the Jaguar Rescue Center in Costa Rica.
Soft Tourism
Soft tourism may highlight local experiences, local languages, or encourage longer time spent in individual areas. This is opposed to hard tourism featuring short duration of visits, travel without respecting culture, taking lots of selfies , and generally feeling a sense of superiority as a tourist.
Many World Heritage Sites, for example, pay special attention to protection, preservation, and sustainability by promoting soft tourism. Peru’s famed Machu Picchu was previously known as one of the world’s worst victims of overtourism , or a place of interest that has experienced negative effects (such as traffic or litter) from excessive numbers of tourists. The attraction has taken steps to control damages in recent years, requiring hikers to hire local guides on the Inca Trail, specifying dates and time on visitor tickets to negate overcrowding, and banning all single use plastics from the site.
Traveling during a destination’s shoulder season , the period between the peak and low seasons, typically combines good weather and low prices without the large crowds. This allows better opportunities to immerse yourself in a new place without contributing to overtourism, but also provides the local economy with income during a normally slow season.
Rural Tourism
Rural tourism applies to tourism that takes place in non-urbanized areas such as national parks, forests, nature reserves, and mountain areas. This can mean anything from camping and glamping to hiking and WOOFing. Rural tourism is a great way to practice sustainable tourism, since it usually requires less use of natural resources.
Community Tourism
Community-based tourism involves tourism where local residents invite travelers to visit their own communities. It sometimes includes overnight stays and often takes place in rural or underdeveloped countries. This type of tourism fosters connection and enables tourists to gain an in-depth knowledge of local habitats, wildlife, and traditional cultures — all while providing direct economic benefits to the host communities. Ecuador is a world leader in community tourism, offering unique accommodation options like the Sani Lodge run by the local Kichwa indigenous community, which offers responsible cultural experiences in the Ecuadorian Amazon rainforest.
" Transport-related CO 2 Emissions of the Tourism Sector – Modelling Results ." World Tourism Organization and International Transport Forum , 2019, doi:10.18111/9789284416660
" 45 Arrivals Every Second ." The World Counts.
Becken, Susanne. " Water Equity- Contrasting Tourism Water Use With That of the Local Community ." Water Resources and Industry , vol. 7-8, 2014, pp. 9-22, doi:10.1016/j.wri.2014.09.002
Kutty, Govindan M., and T.K. Raghavan Nair. " Periyar Tiger Reserve: Poachers Turned Gamekeepers ." Food and Agriculture Organization.
" GSTC Destination Criteria ." Global Sustainable Tourism Council.
Rinzin, Chhewang, et al. " Ecotourism as a Mechanism for Sustainable Development: the Case of Bhutan ." Environmental Sciences , vol. 4, no. 2, 2007, pp. 109-125, doi:10.1080/15693430701365420
" Booking.com Reveals Key Findings From Its 2019 Sustainable Travel Report ." Booking.com.
" Economic Impact Reports ." World Travel and Tourism Council .
- Costa Rica’s Keys to Success as a Sustainable Tourism Pioneer
- How to Be a Sustainable Traveler: 18 Tips
- Regenerative Travel: What It Is and How It's Outperforming Sustainable Tourism
- What Is Ecotourism? Definition, Examples, and Pros and Cons
- What Is Experiential Tourism?
- What Is Community-Based Tourism? Definition and Popular Destinations
- 3 More Rules for Sustainable Tourism
- What Is Overtourism and Why Is It Such a Big Problem?
- How to Become a Geo-Traveler
- What Is Voluntourism? Does It Help or Harm Communities?
- The World Doesn't Want Your Inukshuk
- 8 Incredible Rainforest Destinations Around the World
- 'Scattered Hotels' Are Saving Historic Villages in Italy and Beyond
- 15 Travel Destinations Being Ruined by Tourism
- How to Make Travel More Sustainable
- What's Special About the Faroe Islands

- Get Connected
- globalEDGE Blog
The Importance of Tourism on Economies and Businesses
Published: 3/26/2019 12:21:08 PM

Image Source
Tourism is vital for the success of many economies around the world. There are several benefits of tourism on host destinations. Tourism boosts the revenue of the economy, creates thousands of jobs, develops the infrastructures of a country, and plants a sense of cultural exchange between foreigners and citizens.
The number of jobs created by tourism in many different areas is significant. These jobs are not only a part of the tourism sector but may also include the agricultural sector, communication sector, health sector, and the educational sector. Many tourists travel to experience the hosting destination’s culture, different traditions, and gastronomy. This is very profitable to local restaurants, shopping centers, and stores. Melbourne, Australia ’s population is greatly affected by tourism. It has a population of around 4 million people and around 22,000 citizens are employed by the tourism sector only.
Governments that rely on tourism for a big percentage of their revenue invest a lot in the infrastructure of the country . They want more and more tourists to visit their country which means that safe and advanced facilities are necessary. This leads to new roads and highways, developed parks, improved public spaces, new airports, and possibly better schools and hospitals. Safe and innovative infrastructures allow for a smooth flow of goods and services. Moreover, local people experience an opportunity for economic and educational growth.
Tourism creates a cultural exchange between tourists and local citizens. Exhibitions, conferences, and events usually attract foreigners. Organizing authorities usually gain profits from registration fees, gift sales, exhibition spaces, and sales of media copyright. Furthermore, foreign tourists bring diversity and cultural enrichment to the hosting country.
Tourism is a great opportunity for foreigners to learn about a new culture, but it also creates many opportunities for local citizens . It allows young entrepreneurs to establish new products and services that would not be sustainable on the local population of residents alone. Moreover, residents experience the benefits that come with tourism occurring in their own country.
To learn about the countries earning the most from international tourist arrivals, click on the link below!
Countries Earning the Most from International Tourism
Share this article

December 2022 - You are accessing an archived version of our website. This website is no longer maintained or updated. The Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform has been migrated here: https://sdgs.un.org/
You will be redirected to the new Partnership Platform in 10 seconds.
- A/70/472 - Sustainable development: report of the Second Committee [Arabic] [Chinese] [English] [French] [Russian] [Spanish]
- A/RES/70/193 - International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, 2017 [Arabic] [Chinese] [English] [French] [Russian] [Spanish]
- A/RES/70/196 - Sustainable tourism and sustainable development in Central America [Arabic] [Chinese] [English] [French] [Russian] [Spanish]
- A/RES/70/200 - Global Code of Ethics for Tourism [Arabic] [Chinese] [English] [French] [Russian] [Spanish]
- Compendium of Best Practices in Sustainable Tourism

- Hispanoamérica
- Work at ArchDaily
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
The Tourism Effect: Reshaping Cities, Landscapes, and Infrastructure

- Written by Olivia Poston
- Published on September 10, 2024
This summer, over one million visitors, spectators, and athletes are expected to gather in the streets of Paris for the 2024 Summer Olympic Games . The preparation for the event included massive investments into upgrading infrastructure, venues, and public spaces throughout the city and country. In addition to the restoration of Grande New de I'Île-des-Vannes venue , the Georges-Callerey Swimming Pool, and the Poissonniers Sports Center , the city has revealed new typologies of public services and a master plan for the Olympic Athletes Village by Dominique Perrault Architecture .

While the event of the 2024 Summer Olympics will garner an incredible amount of attention, Paris is not the only city that is bracing for a strained season of tourism this year. Venice continues to navigate a tumultuous relationship with the negative effects of over-tourism, the residents of Barcelona are voicing their concerns of displacement and economic exploitation, and cities throughout Southeast Asia continue to see correlating numbers of tourists and biodiversity loss. The impacts of over-tourism, cultural commodification, and environmental harm from tourism development are universal concerns, shared by dense urban centers and rural communities alike.

Fortunately, there are many creative designers, planners, and policymakers who integrate spaces and networks of tourism into the built environment with the support of the local residents. Since the development of tourism undeniably impacts the infrastructure, planning, economy, and local ecology of the surrounding environment, there is a unique opportunity to invest in the public spaces and infrastructures of the existing context.
Related Article
Complementing historic monuments with contemporary architecture.

Sitting at the foot of the Athens Acropolis, the New Acropolis Museum , designed by Bernard Tschumi Architects , bridges multiple key archeological sites in modern-day Athens to the iconic campus of the Greek Acropolis. Acting as a narrative aid to the Parthenon, the exhibition space of the museum unites collections spanning thousands of years to tell a story of human presence on the Acropolis. Without attempting to overshadow the presence of the Parthenon on the Acropolis, the museum injects a historical, social, and cultural context of the site throughout the years of development and evolution, enhancing the iconic environment of contemporary Athens.

Urban environments are in constant states of change. By blending contemporary architectural moments with historical monuments, designers and planners can maintain a cohesive urban fabric to elevate the image of the city. Although contemporary architectural spaces contrast with historically preserved monuments, such as the Athens Acropolis, this form of architectural intervention prevents spatial fragmentation into strictly old versus new areas of the city. When coupled with contemporary projects, historic monuments are not frozen in time, but become relevant, functional, and engaged with the current cultural and technological contexts.
Unified Images in Tourism Networks

Completed in 2016, the network of tourism pavilions throughout the capital city of Madrid are strategically situated to complement the sites with the greatest traffic from tourism crowds. Designed by the offices of Irene Brea and José Manuel Sanz Arquitectos , the iconic form of the pavilion series is quickly recognizable to the visitor in need of direction, guidance, or information, but the materiality seamlessly blends into the existing fabric of the city. Adhering to the primary guiding design principles of transparency and lightness, those in the interior of the centers are included in the activity of the city while the passing pedestrians can interact with the workers and information on the inside.

Without a clear vision for the visitor experience of discovering the city, the tourist will tire easily, become disoriented, or grow disengaged, altogether. The opportunity to design a network of pavilions throughout the urban environment transforms the purposes of the architectural spaces from strictly informative purposes, to a unified network for rest, orientation, and energy. By ensuring that the day of sightseeing, walking, and wandering through the city is cohesive and enjoyable, a tourism network can encourage longer stays and leave a positive lasting impression of the city and its sites.
Serving Local Communities through Tourism

Located in the small village of Pai Town in Linzhi, the southeastern part of Tibet autonomous region , the Tibet Namchabawa Visitor Center celebrates the cultural history of the village and the extraordinary beauty of the Mount Namchabawa and Yaluntzangpu Grand Canyon. While servicing the backpackers that embark on the networks of hiking, the Visitor Center has transformed into a "town center" for the residents, as well. While the design team of standard architecture included necessary elements to service the backpacking travelers, such as a supply store, medical aid, and a reception desk, the town center holds a water reservation tank and a central electrical switch house for the residents of the village. While fulfilling the needs of the visitor, the design team successfully elevated the quality of life for the permanent residents of the Yaluntzangpu Canyon region.

From examples in Barcelona, Paris , and countless others, the tourism industry can exacerbate existing inequalities if the benefits, resources, and profits from welcoming visitors are not distributed well among the existing residents. By including the community members in the planning and design processes, the conversation will include a sustainable approach to distributing resources. Since the local community has a profound understanding of the cultural and ecological context, they are valuable stakeholders to ensure that development is sustainable and responsible. If the residents are able to shape the strategies for development in conjunction with tourism, there is a lower risk of cultural exploitation, displacement from gentrification, and environmental degradation. These enhancements to the tourism industry can act as an opportunity to serve the needs of the community when meaningfully included in the design and planning stages.
Short-term visions for tourism development will amplify the negative consequences of over-tourism, fragmented city planning, environmental degradation, cultural commodification, and an increased pressure on local resources. The goal of architecture and infrastructure serving these tourism developments should not be concentrated on a singular event or experience, but rather on how to strengthen the relationship between the visitor, the resident, and the environment. In this context, the impact of design and planning decisions extends far beyond the original program of promoting a tourism event or experience. There is an opportunity with developing networks and sites of tourism to integrate local knowledge, invest in the infrastructure or local neighborhoods for the area, and build resilient communities.
Image gallery

- Sustainability
世界上最受欢迎的建筑网站现已推出你的母语版本!
想浏览archdaily中国吗, you've started following your first account, did you know.
You'll now receive updates based on what you follow! Personalize your stream and start following your favorite authors, offices and users.
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
UN report Underscores Importance of Tourism for Economic Recovery in 2022
- All Regions
- 13 Jan 2022
The important role that tourism will play in the recovery of national economies and global trade has been highlighted in the 2022 edition of the World Economic Situation and Prospects (WESP) report by the United Nations. Drawing on data from the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), WESP underlines the sector’s importance for the world economy and particularly for developing economies, including Small Island Developing States (SIDS).
After a global contraction of 3.4% in 2020 and a rebound of 5.5% in 2021, the world economy is projected to grow by 4% in 2022 and then 3.5% in 2023. Given its importance as a major export category (prior to the pandemic tourism was the third largest in the world, after fuels and chemicals), and recognizing its role as a source of employment and economic development , the sector’s recovery is expected to drive growth in every world region.
UNWTO Secretary-General Zurab Pololikashvili said: “The sudden halt in international tourism caused by the pandemic has emphasized the sector’s importance to both national economies and individual livelihoods. The flagship UN report makes use of UNWTO data and analysis to assess the cost of declining tourism and illustrates just how important restarting tourism will be in 2022 and beyond.”
Jobs, economic growth and equality all hit
The sudden halt in international tourism caused by the pandemic has emphasized the sector’s importance to both national economies and individual livelihoods
The latest edition of the UN World Economic Situation and Prospects report uses key UNWTO data on international tourist arrivals and tourism receipts to illustrate how the pandemic’s impact has been felt beyond the sector itself . International tourist arrivals plunged by 73% in 2020, dropping to levels not seen for 30 years. And while tourism did record a modest improvement in the third quarter of 2021, international arrivals between January-September 2021 were still 20% below 2020 levels and 76% below 2019 levels (full year 2021 results to be released by UNWTO on 18 January).
The crisis has had a devastating impact on employment, including in hospitality, travel services and retail trade. It has disproportionately affected vulnerable groups, including youth and migrant workers, as well as workers with lower educational attainment and skills. Exacerbation of the gender divide is evident, especially in developing countries, with women seeing greater declines in employment and labour force participation than men.
Diversification for recovery
Further analysing the sector’s role in economic recovery, the UN report notes that many destinations, in particular tourism-dependent countries, will need to diversify their tourism throughout 2022 and beyond. Again drawing on UNWTO analysis , the publication shows how many destinations are developing domestic and rural tourism to help local economies in rural and depressed areas to boost job creation and protect natural resources and cultural heritage , while at the same time empowering women, youth and indigenous peoples. Additionally, the report notes how Small Island Developing States can take steps to ensure local businesses and workers retain more of the economic benefits that international tourism brings, noting for example that that “tourism leakage” amounts to an estimated 80% of all money spent by tourists in the Caribbean region.
Related links
- Download the news release in PDF
- UNWTO Market Intelligence
- UNWTO Tourism Data Dashboard
- Rural Tourism
- World Economic Situation and Prospects 2022
Related Content
Global conference on wine tourism celebrates heritage a..., un tourism launches investment guidelines for armenia, un tourism’s committee on tourism and sustainability co..., un tourism in kazakhstan: working together to put susta....

Analysis of the Impact of Cultural Components on the Development of Creative Urban Tourism in the Historical Textures the Case Study A Tabriz Historical Bazaar
Document Type : Article extracted From phd dissertation
- Hasan Satari Sarban Qoli
- Arash Saghafi Asl
Department of Architecture and Urban Planning, Tabriz Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tabriz, Iran
- Handicraft Development
- Urban Creative Tourism
- Historical Bazaar of Tabriz
- Amini, A & Zaidi, Z. (2014). The cultural effects of tourism in rural areas from the perspective of the local community (case study: Abyaneh village). Geographical Research Quarterly , 30 (2), 13-32. [In Persian]
- Bakas, F. E., Duxbury, N., & de Castro, T. V. (2019). Creative tourism: Catalysing artisan entrepreneur networks in rural Portugal. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research , 3(12), 102-123. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJEBR-03-2018-0177
- Bayliss, D. (2017). The rise of the creative city: Culture and creativity in Copenhagen. European planning studies , 15(7), 889-903. https://doi.org/10.1080/09654310701356183.
- Bazrafshan, J., & bameri, A. (2018). Study and analysis of the status of creative tourism in Zahedan. Regional Planning , 8(31), 167-180. https://dorl.net/dor/20.1001.1.22516735.1397.8.31.12.4 [In Persian]
- Carvalho, R. M. F., da Costa, C. M. M., & Ferreira, A. M. A. P. (2019). Review of the theoretical underpinnings in the creative tourism research field . Tourism & Management Studies , 15(1SI), 11-22.
- Doosti, F., Zaal, M. H., & Ramezanzadeh Lasbouee, M. (2019). Assessing the Capacities of Creative Tourism in Tabriz City. Journal of Urban tourism , 6(2), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.22059/jut.2018.253316.461 [In Persian].
- Eshaghiye Firoozabadi, E., salehi, S. M., & rashidi, M. M. (2019). Assessing the potential of culture-led regeneration in Fahadan district of Yazd with the aim of developing tourism in the district. Journal of urban tourism , 6 (3), 59-74. https://doi.org/10.22059/jut.2019.260083.499 [In Persian]
- Eyisi, A., Lee, D., & Trees, K. (2021). Facilitating collaboration and community participation in tourism development: The case of South-Eastern Nigeria. Tourism and Hospitality Research , 21(3), 275-288. https://doi.org/10.1177/1467358420966035
- Fernandez, J. A. S.& Azevedo, P. S.& Martín, J. M. M. & Martín, J. A. R. (2020) Determinants of tourism destination competitiveness in the countries most visited by international tourists: Proposal of a synthetic index. Tourism Management Perspectives , 33(3),435-450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2019.100582
- Golrk, SH., & Motaharian, M. (2019). Acceptance for Creative Tourism by citizens and tourists in Tourism- Supporting Cities; the case of Yasouj. Journal of Fine Arts: Architecture & Urban Planning , 24 (4), 83-92. https://doi.org/10.22059/jfaup.2019.270831.672173 [In Persian].
- Haq Parast, F; Asefi, M & Abizadeh, E. (2018). The effect of place identity components on the sense of belonging to the place; A study of the historical market of Tabriz. Geographical Research , 34(3), 303-312. [In Persian].
- Henriques, C., & Moreira, M. C. (2019). Creative tourism and urban sustainability: the cases of Lisbon and Oporto. Revista Portuguesa de Estudos Regionais , 51, 93-114.
- Hong, H. U. I., Bin, T. A. N. G., & Yang, J. I. N. G. (2010). A Study on Cultural Reasons for Difference on Community Participation in Tourism Development in Different Nations. In Tourism Forum. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2023.101127.
- Kim, H. (2016). The concept and strategy of creative tourism. Policy of Korean Tourism ,2(6), 8-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2020.102922
- Lee, T. H. (2013). Influence analysis of community resident support for sustainable tourism development. Tourism management , 34, 37-46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2012.03.007
- McManus, C., & Carruthers, C. (2014) Cultural quarters and urban regeneration: The caseof cathedral quarter Belfast. International Journal of Cultural Policy , 20 (1), 78–98. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286632.2012.737322
- Mohajer, B., shafiee, Z., khaje ahmad attari, A., & toghraee, M. T. (2020). Identifying the key components of child-based creative tourism, (Case study: Isfahan, the creative city of handicrafts). Motaleate Shahri , 9(35), 75-86. https://doi.org/10.34785/J011.2021.395 [In Persian].
- Panahi, A & Dadash Pourmoghadam, M. (2018). Analysis of the role of creative city indicators in the development of urban tourism (case study of Isfahan city). Shabak , 5(1), 77-96. [In Persian].
- Phillips, M.R. & House, C. (2009) an evaluation of priorities for beach tourism: Case studies from South Wales, UK. Tourism Management , 30 (1), 176-183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2008.05.012
- Richards, G. (2011). Creativity and tourism: The state of the art. Annals of tourism research , 38(4), 1225-1253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2011.07.008
- Richards, G. (2018). Cultural tourism: A review of recent research and trends. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management , 36, 12-21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2018.03.005
- Romana, K. V. (2013), Enforcing sustainability principles in tourism via creative tourism development. Journal of Tourism Challenges and trends , 6(1), 35-57.
- Salaripour, A., Hesam, M., Baradaran sagharloo, A., & Hamidi, A. (2020). Explaining the Creative Tourism Development Strategies of Rasht City. Journal of Urban tourism , 7(3), 127-142. https://doi.org/10.22059/jut.2020.303292.801 [In Persian].
- Shatrian, M., Heydari Sureshjani, R., & Varfinejad, J. (2016). The effects of tourism power in expanding infrastructure and creating a creative city, a case study: Kermanshah city. Geography , 5(52), 201-216. [In Persian].
- Sinclair-Maragh, G., & Gursoy, D. (2016). A conceptual model of residents’ support for tourism development in developing countries. Tourism Planning & Development , 13(1), 1-22. https://doi.org/10.1080/21568316.2015.1047531
- Stylidis, D., Biran, A., Sit, J., & Szivas, E. M. (2014). Residents' support for tourism development: The role of residents' place image and perceived tourism impacts. Tourism management , 45, 260-274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2014.05.006
- Than, T. T., Kiu, T. P. H., PHAM, T. A. D., HOANG, T. C. V., TRAN, T. H., NGUYEN, H. D., & DAO, T. K. (2020). Impact of community attachment and resident's support on destination sustainability: Evidence from spiritual and community destination in Vietnam. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics, and Business , 7(8), 361-369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2023.104796

Volume 10, Issue 2 April 2023 Pages 75-91
How to cite.
- Article View: 188
- PDF Download: 197
Zare, E., Satari Sarban Qoli, H., & Saghafi Asl, A. (2023). Analysis of the Impact of Cultural Components on the Development of Creative Urban Tourism in the Historical Textures the Case Study A Tabriz Historical Bazaar. urban tourism , 10 (2), 75-91. doi: 10.22059/jut.2023.352590.1098
Elham Zare; Hasan Satari Sarban Qoli; Arash Saghafi Asl. "Analysis of the Impact of Cultural Components on the Development of Creative Urban Tourism in the Historical Textures the Case Study A Tabriz Historical Bazaar", urban tourism , 10, 2, 2023, 75-91. doi: 10.22059/jut.2023.352590.1098
Zare, E., Satari Sarban Qoli, H., Saghafi Asl, A. (2023). 'Analysis of the Impact of Cultural Components on the Development of Creative Urban Tourism in the Historical Textures the Case Study A Tabriz Historical Bazaar', urban tourism , 10(2), pp. 75-91. doi: 10.22059/jut.2023.352590.1098
Zare, E., Satari Sarban Qoli, H., Saghafi Asl, A. Analysis of the Impact of Cultural Components on the Development of Creative Urban Tourism in the Historical Textures the Case Study A Tabriz Historical Bazaar. urban tourism , 2023; 10(2): 75-91. doi: 10.22059/jut.2023.352590.1098

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
THE IMPORTANCE OF TOURISM FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT. Sustainability is a concept that has been gaining social and political recognition, not least due to the coordinated launch of the Millennium Development Goals in 2000, and now with the 2030 Agenda and its 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDG). Established in 2015 and promoted by the ...
By the early 21st century, international tourism had become one of the world's most important economic activities, and its impact was becoming increasingly apparent from the Arctic to Antarctica.The history of tourism is therefore of great interest and importance. That history begins long before the coinage of the word tourist at the end of the 18th century.
To date, rural tourism in many places has become an important new element of the regional rural economy; it is increasing in importance as both a strategic sector and a way to boost the ...
The contribution of tourism to economic well-being depends on the quality and the revenues of the tourism offer. UN Tourism assists destinations in their sustainable positioning in ever more complex national and international markets. As the UN agency dedicated to tourism, UN Tourism points out that particularly developing countries ...
10 Nov 2023. Tourism has again been identified as a key driver of economic recovery and growth in a new report by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). With UNWTO data pointing to a return to 95% of pre-pandemic tourist numbers by the end of the year in the best case scenario, the IMF report outlines the positive impact the sector's rapid ...
Background. Tourism is one of the world's largest industries, and it has linkages with many of the prime sectors of the global economy (Fennell, 2020).As a global economic sector, tourism represents one of the largest generators of wealth, and it is an important agent of economic growth and development (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018).Tourism is a critical industry in many local and national ...
Showcased along 23 case studies from around the world, this two-volume report examines the role of tourism in each of the five pillars of the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, 2017: 1. Sustainable economic growth; 2. Social inclusiveness, employment and poverty reduction; 3. Resource efficiency, environmental protection ...
7. Promotes Inclusive Growth: Tourism is labor intensive and has the potential to reach and benefit large numbers of people thanks to its wide supply chain. 8. Strengthens Rural Communities: Rural tourism supports economic diversification and creates jobs for rural youth and ethnic minorities. 9.
After surpassing 1 billion international visitors in 2012, we are expecting 1.8 billion by 2030. Tourism is growing faster than the global economy and, for the first time, the statistics for 2015 are expected to show that there were more trips taken to the developing world than to the developed world. But what does this actually mean?
Description. PDF. Tourism and the Sustainable Development Goals - Journey to 2030 serves as a guide to how the tourism sector can contribute towards the implementation and achievement of the 17 SDGs. It aims to inspire governments, policymakers and tourism companies to incorporate relevant aspects of the SDGs into policy and financing ...
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States ...
Showcased along 23 case studies from around the world, this two-volume report examines the role of tourism in each of the five pillars of the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, 2017: 1. Sustainable economic growth; 2. Social inclusiveness, employment and poverty reduction; 3. Resource efficiency, environmental protection ...
Revitalisation of Culture and Art. Preservation of Heritage. Empowering communities. The importance of tourism: Environmental gains. Protecting nature. The importance of tourism: Political gains. Why tourism is important: To conclude. The importance of tourism: Further reading.
Tourism development refers to the growth and maintenance of the tourism industry in a given locality. And, of course, tourism planning is a very important part of this. On a basic level, tourism development can be defined as creating strategies and plans to increase/develop/encourage tourism for a destination.
One of the most important and overlooked aspects of sustainable tourism is contributing to protecting, preserving, and enhancing local sites and traditions. These include areas of historical ...
Tourism and the Sustainable Development Goals Description PDF Article / Chapter Tools. Add to Favorites; Email to a Friend; Send to Citation Mgr; Track Citations; Download PDF; Subscription Options. UN Tourism Publications | UN Tourism Home | Terms & Conditions | ... UN Tourism is a specialized agency of the United Nations ...
ABSTRACT. Tourism has long been explored through the lens of development theory. David Harrison was one of the earlier academics to do so, subsequently turning his attention to critiquing the relevance of such theory to tourism, concluding that although much tourism research has been framed within it, development theory has contributed little if anything to knowledge and understanding of the ...
There are several benefits of tourism on host destinations. Tourism boosts the revenue of the economy, creates thousands of jobs, develops the infrastructures of a country, and plants a sense of cultural exchange between foreigners and citizens. The number of jobs created by tourism in many different areas is significant. These jobs are not ...
In the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development SDG target 8.9, aims to "by 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products". The importance of sustainable tourism is also highlighted in SDG target 12.b. which aims to "develop and implement tools to monitor ...
A joint effort by UNWTO, UNDP and other partners, Tourism and the Sustainable Development Goals - Journey to 2030 aims to build knowledge, and empower and inspire tourism stakeholders to take necessary action to accelerate the shift towards a more sustainable tourism sector by aligning policies, business operations and investments with the ...
Sustainable tourism development requires the informed participation of all relevant stakeholders, as well as strong political leadership to ensure wide participation and consensus building. Achieving sustainable tourism is a continuous process and it requires constant monitoring of impacts, introducing the necessary preventive and/or corrective ...
Since the development of tourism undeniably impacts the infrastructure, planning, economy, and local ecology of the surrounding environment, there is a unique opportunity to invest in the public ...
Introduction. In recent years, tourism has emerged as a crucial sector that significantly contributes to the economic advancement of nations. It plays an important role in boosting GDP, providing employment opportunities, and promoting development (Ali, Citation 2015).Ecotourism is recognized as a leading development industry that aims to diversify the economies of countries, stimulate ...
After a global contraction of 3.4% in 2020 and a rebound of 5.5% in 2021, the world economy is projected to grow by 4% in 2022 and then 3.5% in 2023. Given its importance as a major export category (prior to the pandemic tourism was the third largest in the world, after fuels and chemicals), and recognizing its role as a source of employment ...
In the meantime, the tourism industry plays an important role in the economic dynamics of this city; Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to tourism as the main policy of urban development. The use of creative tourism dimensions in all urban areas and among the historical contexts of Tabriz city can be a perfect lever for promoting this ...
Biodiversity, the variety of life on Earth, plays a crucial role in sustainable development by providing essential ecosystem services, supporting livelihoods, and fostering resilience to environmental changes. This comprehensive review explores the significance of biodiversity in sustainable development through an examination of its ecological, economic, and socio-cultural dimensions. The ...