
- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7

Types of Travel Agents: A Comprehensive Guide
This blog explains who a Travel Agent is, what the different Types of Travel Agents are, and how they function in the tourism industry. It also provides some examples of each type of Travel Agent and their advantages and disadvantages for Travellers.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Communication and Influencing skill Training
- Effective Communication Skills
- Call Centre Training
- Cross Cultural Communications Training
- Negotiation Skills Training

Thus, understanding these different Types of Travel Agents can empower Travellers to make informed decisions. Moreover, it will ensure a more personalised and stress-free Travel experience that aligns perfectly with their unique needs and preferences. So, let’s delve in to learn more! In this blog, you will learn who a Travel Agent is, the different Types of Travel Agents and their roles and responsibilities in great detail.
Table of Contents
1) Who is a Travel Agent?
2) What are the different Types of Travel Agents?
a) Independent Travel Agents
b) Online Travel Agents
c) Visitor information centres
d) High street Travel Agents
e) Business Travel Agents
f) Call centre Travel Agents
g) Multiple Travel Agents
h) Miniple Travel Agents
3) Conclusion
Who is a Travel Agent?
A Travel Agent is a person or a firm that arranges Travel products and services for customers. These Agents can work as intermediaries or organisers. An intermediary Travel Agent acts for another party, such as an airline, a hotel, or a tour operator. They then plan a journey or a stay for a customer in return for a price. They also offer many services or a series of services, such as transportation, accommodation, sightseeing, and activities.

What are the different Types of Travel Agents?
There are many Types of Travel Agents in the tourism industry, each with its own characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. Let’s explore their different types:
1) Independent Travel Agents
Independent Travel Agents are self-employed or work for a small agency that is not affiliated with any larger network or organisation. They have more flexibility and autonomy in choosing their suppliers, products, and services. They can also offer more personalised and customised services to their customers, such as the following:
1) Tailor-made itineraries
2) Special deals
3) Niche products
Independent Travel Agents can operate online or offline and can specialise in a particular destination, market segment, or type of Travel. But such specialisations require possessing Specialised Travel Agents Skills .
However, Independent Travel Agents may also face some challenges, such as limited resources, higher costs, lower commissions, and less bargaining power with suppliers. They may also have less visibility and credibility in the market and may struggle to compete with larger and more established Travel Agents.
2) Online Travel Agents
Online Travel Agents are Agents who operate exclusively on the internet, using websites, mobile apps, or social media platforms to offer and sell Travel products and services. Online Travel Agents have many advantages, such as the following:
1) Lower overheads
2) Wider reach
3) 24/7 availability
4) More convenience
5) Choice for customers
Online Travel Agents can also use technology to enhance their services, such as online booking systems, chatbots, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Big Data. Online Travel Agents can offer a variety of products and services, such as flights, hotels, car rentals, tours, cruises, and packages. Some examples of online Travel Agents are Expedia, Booking.com, Skyscanner, and Airbnb. However, online Travel Agents also face some challenges, such as the following:
1) High competition
2) Low customer loyalty
3) Security and privacy issues
4) Lack of human interaction
5) Personal touch
Master the art of persuasion with our Negotiation Skills Training – Sign up now!
3) Visitor information centres
Visitor information centres are Travel Agencies that provide information and advice to tourists at the destination. They are usually located at airports, train stations, bus terminals, city centres, or tourist attractions.
Visitor information centres can help travellers with maps, brochures, guides, timetables, bookings, reservations, and local tips. These centres can also promote and sell local products and services, such as souvenirs, crafts, tours, events, and activities.
Some examples of visitor information centres are Visit Britain and Tourism Australia. Visitor information centres have the advantage of being close to the customers and having firsthand knowledge of the destination. However, visitor information centres may also have limited resources, staff, and products and may depend on the seasonality and popularity of the destination.
4) High street Travel Agents
High street Travel Agents operate from physical shops or offices on the streets or shopping centres of towns and cities. High street Travel Agents can offer a range of products and services, such as the following:
1) Flights
2) Hotels
3) Car rentals
4) Tours
5) Cruises
6) Holiday packages
They can also provide face-to-face consultation, customer service, and after-sales support. Some examples of high street Travel Agents are Thomas Cook, TUI, and Flight Centre.
High street Travel Agents have the advantage of having a strong brand presence, a loyal customer base, and experienced staff. However, high street Travel Agents also face some challenges, such as high rent, overheads, staff costs, low margins and commissions, and competition from online Travel Agents and direct suppliers.
5) Business Travel Agents
Business Travel Agents specialise in arranging Travel products and services for corporate clients, such as companies, organisations, or government agencies. Business Travel Agents can offer products and services that meet the specific needs and preferences of business travellers, such as the following:
1) Flexible fares
2) Convenient schedules
3) Premium seats
4) Airport lounges
5) Meeting rooms
6) Corporate discounts
Business Travel Agents can also provide account management, reporting, invoicing, and Travel policy compliance. Some examples of business Travel Agents are American Express Global Business Travel, BCD Travel, and CWT.
These Agents have the advantage of having a stable and profitable market segment, long-term contracts, and high-value customers. However, business Travel Agents also face some challenges, such as high expectations, complex regulations, and changing Travel trends and technologies.
6) Call centre Travel Agents
Call centre Travel Agents are professionals who operate from a centralised office or facility that handles a large volume of phone calls from customers. Call centre Travel Agents can offer and sell travel products and services over the phone, using a computerised reservation system and a script. Call centre Travel Agents can also provide customer service, support, and assistance.
Some examples of call centre Travel Agents are Expedia, Priceline, and Travelocity. Call centre Travel Agents have the advantage of having lower costs, wider reach, and faster response than high street Travel Agents. However, they also face some challenges, such as high staff turnover, low customer satisfaction, and communication barriers.
Redefine customer interactions with our Call Center Training – sign up today!
7) Multiple Travel Agents
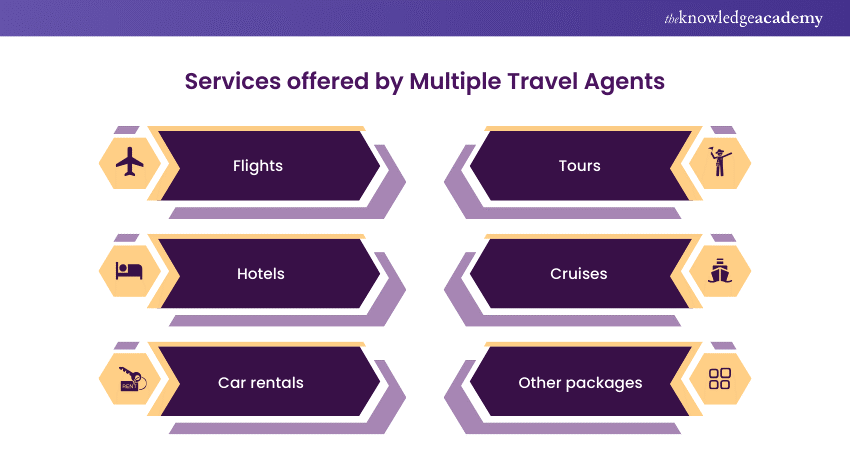
They can also benefit from economies of scale, bulk buying, and brand recognition. Some examples of multiple Travel Agents are TUI, Thomas Cook, and Flight Centre. These Agents have the advantage of having a dominant market position, loyal customer base, and extensive distribution network. However, multiple Travel Agents also face some challenges, such as the following:
1) High overheads
2) Staff costs
3) Competition from Online Travel Agents and direct suppliers
8) Miniple Travel Agents
Miniple Travel Agents operate as part of a small or medium-sized chain or group that has a few branches or outlets across different locations. They can offer a variety of products and services, such as flights, hotels, car rentals, tours, cruises, and packages. They can also provide more personalised and customised services, such as the following:
1) Niche products
3) Local expertise
Some examples of miniple Travel Agents are Trailfinders, STA Travel, and Hays Travel. Miniple Travel Agents have the advantage of having a flexible and adaptable business model, a loyal customer base, and competitive prices. However, they also face some challenges, such as limited resources, bargaining power, and brand awareness.
Conclusion
We hope you read and understand the different Types of Travel Agents. The world of Travel Agents is diverse, catering to a wide range of traveller preferences and needs. From traditional brick-and-mortar agencies to online platforms and specialised niche Agents, there's a Travel Agent for everyone. Choosing the right one can enhance your Travel experience, making your journey smoother and more enjoyable.
Transform your passion for Travel into a thriving career with our Travel Agent Training – sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming business skills resources batches & dates.
Fri 28th Jun 2024
Fri 25th Oct 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

Download WP Travel
Please enter your email to download WP Travel and also get amazing WP Travel offers and Newsletters.
What is a Travel Agency? Types, Purpose, Function, Services
Home » Blog » What is a Travel Agency? Types, Purpose, Function, Services
The travel agency business is now something that most people want to do.
The main purpose of a travel agency is to make planning a trip easier and more useful for their customers by giving them information and making reservations .
Flights, hotels, transportation, trips, and other events can all be booked through the travel company.
If you learn about tour-related ideas and get knowledge from these articles, you’ll be able to start your travel agency in the travel industry.
Table of contents
What is a travel agency, 1. traditional travel agencies, 2. online travel agencies, 3. corporate travel operators, 4. consolidators, 5. franchise travel services, 1. convenience, 2. expertise and advice, 3. access to deals and discounts, 4. risk management, 5. customer services, 1. travel planning, 2. booking services, 3. customized itineraries, 4. travel documentation, 5. emergency support, 6. customer services, services offered by travel agency, 1. booking services, 2. information and advice, 3. customer services, 4. negotiation and coordination, differences between travel agency and travel agent.

A travel agency is a business that helps people and groups choose, plan, and book travel-related services . Flights, hotels, rides, trips, sports, and other things can be a part of these services.
Most travel companies know about a lot of different trips that their clients can take that fit their wants and budgets.
A lot of travel and tour operators also hire people called tour agents who know a lot about important things like visa rules, places to visit, and travel trends.
They plan and organize everything so that their clients’ trips are as easy, fun, and stress-free as possible.
Explore the beginner’s guide to launch your travel agency
Types of Travel Agency

Several types of travel agencies meet the wants and tastes of different travelers.
These are the most common travel agencies related to the travel industry:
These agencies are physical office companies where customers can go and talk to the tour planners. They give specialized services and often a wide range of trip needs.
Online Travel Agencies(OTAs) run the online trip business, where their websites or mobile apps provide tourists with book flights, rooms, rental cars, and other trip services. Expedia and Booking.com are some examples.
The corporate travel service makes trip plans for companies and groups. They take care of bookings for businesses, make deals, and offer services like keeping track of costs.
Consolidators buy a large number of plane tickets at a discount, they sell them at a lower price to travel companies or directly to customers.
Franchise companies work under a bigger brand name and use marketing, technology, and support systems in the travel industry that have already been set up.
Within the franchise network, owners of travel companies get the training and tools they need to run their businesses.
Purposes of Travel Agency
The main purpose of travel agencies is to facilitate and enhance the tour experiences for individuals and groups.
Travel companies try to make planning a trip easier by letting people book flights, hotels, transportation, events, and other services related to travel all in one place.
Trip planners hire knowledgeable agents who can offer expert advice and recommendations based on their suggestions of different places or destinations.
Similarly, travel agents shared their experiences of various destinations, travel trends, visa requirements and more.
Airlines, hotels, ship lines, tour operators, and other travel companies often offer deals, discounts, and packages that only travel agencies can get.
They can help customers get the most for their money and save money on their trip costs by taking advantage of deals.
Travel agencies help mitigate risks associated with travel by giving travelers information or knowledge on safety, health issues, and security in different places.
Travel agencies or companies make sure their clients are happy by giving each one of them high-quality service and individual care.
Overall, the travel company’s main goal is to make planning a trip easier, more fun, and less stressful for their costumes by giving them advice, making things easier.
What does Travel Agency do?

Many services travel agencies offer to make it easier and better for people and groups to trip.
One of the things that a travel agency does is the following:
Travel agencies support the client in planning their trips by talking about their tastes, hobbies, income, and any special requirements they may have.
These companies are called travel agents that help people book flights, hotels, rental cars, airport transfers, trips, events, and other services related to travel.
They can use online tools and scheduling systems to get reservations for their clients.
Most tour operators make personalized trip plans based on what their clients want and what they’re interested in.
It supports you on trip documents like passports, visas, travel insurance, and any other paperwork that is needed is available from travel companies.
Before a client leaves on a trip, they make sure that all of their paperwork is in order.
Travel companies are there to help their customers in case of accidents or other problems that come up during their trip.
In this case, they might rebook flights, arrange alternative accommodations, or give advice on medical help or legal issues.
Tour Operators prioritize customer happiness first by giving each client great services and individual care.

There are a lot of services travel agencies provide to meet the news and preferences of travelers.
Trip planner aims to ease the trip planning process, provide expert advice and support, and ensure a smooth and enjoyable travel experience for their clients.
These are some common services provided by travel agencies.
- Flight Booking
- Accommodation Booking
- Transportation Services
- Tour Packages
- Cruise Booking
- Travel Insurance
- Visa Assistance
- Destination Recommendations
- Emergency Assistance
Overall, the travel agency’s purpose is to ease the trip schedule process, deliver expert advice and support, and provide smooth and enjoyable trip experiences for their customers.
Let’s launch your travel booking website today
Functions of the Travel Agency
The main function of a travel agency revolves around assisting and arranging various parts of travel and people and groups.
The purpose of a travel agency is to ease the trip planning process, provide expert advice and support, and improve the entire trip experience for their customers.
Here’s an overview of the key tasks of a travel agency:
Travel agencies handle the planning process for flights, lodgings, transportation, trips, events, and other travel-related services.
Most travel agency provides guidance and formation on different parts of the travel, visa requirements, and health and safety measures.
Travel companies put customer happiness first by giving each client great service and individual care.
The travel agencies deal with tour operator suppliers, including airlines, trip suppliers, and hotel and tour operators to secure good terms and rates for their clients.
A trip agency is a business company that offers other-related services, while a trip agent is a person hired by or connected with a tour operator who helps clients with their trip planning and bookings.
These are some key differences between a travel agency and a travel agent:
In summary, travel agencies may have multiple trip agents working under their umbrella to help the clients, while a tour agent may work separately as a part of a bigger company.
Travel companies are essential businesses in the travel industry, acting as intermediaries between tourists and travel providers. They offer a range of services to ease trip planning and booking.
These companies can take the form of standard brick-and-mortar businesses, or online-based platforms.
Each type of service responds to different tastes and wants, providing accessibility to a wide range of travel-related customers.
Regardless of their form, the primary goal of travel companies stays consistent: to provide ease, knowledge, and support throughout the trip process.
They give personalized systems to help, access to exclusive deals, and 24/7 assistance before, during, and after the trip.
By offering personalized solutions and reducing travel risks, travel companies play a crucial role in allowing enjoyable and stress-free travel experiences for individuals and groups.
There are two types of agencies, retail tour operators and wholesale travel agencies. These travel companies, as well as tour providers, operate as intermediaries. The main goal is the buying and selling process in the travel business.
The global market size of the travel agency industry is estimated at nearly 296 billion U.S. dollars as of January 2024. ( Source )
Overall, roughly 589 thousand travel companies operated in the tourism industry, with employment reaching approximately three million.

Yam Bahadur Chhetri is a content writer and vivid contributor to the WordPress community and a WordPress enthusiast with an experience of 7+ years in the relative field. He also loves to develop WordPress Themes, Plugins, and custom WordPress development for clients.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get WP Travel Pro
Create Stunning , SEO friendly and Fully functional Travel website within minutes . No Coding Required !
Suitable for any
- Travel Agency
- Tour Booking Services
- Travel Bloggers
Drive more Sales and Revenues from today !
$ 99 99 USD per year

📢 Santa has sent the gift for Christmas and New Year sales on all WP Travel Pro plans. 🛍️ Use coupon code "XMAS_NEWYEAR2024" at checkout.
Related posts

51 Tourism and Travel Business Ideas to Start in 2024

How To Translate Strings in WP Travel Plugin?

How to contribute to WP Travel translation?
Wp travel modules.
Need more features to save your time and to boost your travel business? WP Travel Pro comes with more powerful modules . While our core travel plugin provides almost all the features that a travel and trekking websites generally needs, our add-ons boost it’s capacity further to make it the best travel engine on WordPress. Whether you want to add new payment method to your site or brush up your trekking listings with beautiful maps show casing your trips, we have all your imagination covered. See all our add ons below to boost your travel website’s features further.

Weather Forecast

Import Export

Partial Payment
Connect with wp travel to join the travel conversation, documentation →.
Explore More
Customer Support →
We are here to help.
Facebook Group →
User Community Forum
Follow On Twitter →
Connect with us on Twitter

- Business Concierge
- Buy Gift Card
Award Winning

Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
- Amendments, refund & cancellation-policy
Exploring the Different Types of Travel Agents
Apr 29, 2024 | Travel , Travel Agent

Table of Contents
The days of travel agencies operating out of little booths in malls are over. Travel agents come in all shapes and sizes, and you can find them on almost every website these days. Everyone, no matter what their location, may now easily book tours and travel. Tours and activities can be reserved in a variety of easy methods, including through online travel agencies, global distribution systems, independent agents, and visitor centers. For that reason, we will explain the many kinds of travel agents and walk you through the most common kinds of travel agents so you can understand who does what.
What Is the Precise Definition of a Travel Agent?
A travel agent is an individual employed by a public service organization or private retailer who offers advice and services pertaining to travel and tourism. Travel agents provides various forms of travel agency packages for their clients on behalf of travel suppliers (such as hotels, transportation companies, travel concierge services , travel insurance providers, and tour operators). They will coordinate the logistical aspects of travel for their clients while operating as intermediaries between various travel service providers.
What Are the Different Types of Travel Agents?
Independent Travel Agents
A travel agent who is considered independent either works by themselves or for a smaller agency that is not part of a bigger network. When it comes to selecting vendors, goods, and services, they have greater leeway and independence. Additionally, they have the option to provide clients with services that are more tailored to their specific needs, like:
- Customized itineraries
- One-time offers
- Specialty products
Online Travel Agents
Online travel agents are those who conduct business exclusively via the internet, offering and selling travel products and services via websites, mobile applications, or social media platforms. Online travel agencies offer numerous benefits, including the subsequent:
- Decreased overhead
- Greater reach
- Constant availability
- Enhanced convenience
- Options for clients
Technology can be leveraged by online travel agencies to improve their services through the implementation of chatbots, artificial intelligence (AI), online booking systems, and big data. A variety of goods and services, including flights, hotels, vehicle rentals, tours, cruises, and packages, may be provided by online travel agents. Online travel agencies include Airbnb, Expedia, Booking.com, and Skyscanner.
Visitor Information Centers
Travel agencies that offer information and guidance to visitors at the location are known as visitor information centers. Locations such as airports, rail stations, bus terminals, city centers, and tourist attractions often house these.
Visitors information centers are a treasure trove of useful information for vacationers, including maps, brochures, guides, schedules, reservations, and insider tips. Local goods and services, including arts and crafts, excursions, events , and activities, can also be promoted and sold at these places.
Multiple Travel Agents
Multiple travel agents is one of the Types of Travel Agents that function as components of a larger conglomerate or organization that maintains numerous branches or locations. They may provide the following products and services, among others:
- Car rentals
Miniple Travel Agents
These Types of Travel Agents typically have a limited number of locations within a specific region. One advantage of these businesses is the personalized service they provide, which includes impartial recommendations for vacation packages. Another perk is that they can take use of economies of scale to a greater extent than independents can as they just have to pay a single licensing charge for all of their branches, as opposed to an independent who isn’t part of a branch paying a single price for their business.
High street Travel Agents
Physical locations where High Street Travel Agents conduct business, such as shops or offices in retail centers or main streets of cities and towns. High street travel agents may provide the following products and services, among others:
- Holiday packages
Call Center Travel Agents
Call center is one the Types of Travel Agents who function from a centralized office or center that manages a substantial influx of customer phone inquiries. The call facility Travel agents have the capability to provide and market travel-related goods and services via telephone by utilising a script and an automated reservation system. The call center Travel agents may also offer support, assistance, and customer service.
Business Travel Agents
Corporate clientele, including businesses, organizations, and government agencies, are the specialty of business travel agents. The following are examples of the kinds of products and services that corporate travel agents can provide to cater to the demands and tastes of their clients:
- Fare flexibility
- Flexible appointment times
- First-class seats
- Lounges at airports
- Rooms for meetings
- Discounts for businesses
Read more about How airssist Play Roll In The Corporate Travel Industry
Choosing the Right Travel Agent for You
Planning a trip can be an exciting but overwhelming task, especially with the abundance of information and options available online. That’s where a travel agent can come to your rescue. A reliable travel agent can save you time, provide expert advice, and help ensure a smooth and enjoyable travel experience. However, not all Types of Travel Agents are created equal, and it’s important to choose the right one for your specific needs. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting a travel agent:
Specialization:
Consider the specific Types of Travel Agents you’re interested in, such as leisure vacations, adventure travel, cruises, or corporate travel. Look for a travel agent who specializes in the type of trip you want to take. Specialization ensures that the agent has in-depth knowledge, established connections, and access to exclusive deals within that particular niche.
Experience:
A travel agent’s experience can make a significant difference in the quality of service they provide. Find out how long the agent has been in the industry and inquire about their personal travel experiences. An experienced agent will have firsthand knowledge of various destinations, understand potential challenges, and have a network of reliable contacts to rely on.
Reputation:
Research the reputation of the travel agent or the agency they work for. Read reviews and testimonials from past clients to get an idea of their level of customer satisfaction. You can also ask friends, family, or colleagues for recommendations based on their personal experiences. A reputable travel agent will have a track record of delivering excellent service and ensuring client satisfaction.
Service fees:
Inquire about the travel agent’s fee structure upfront. Some travel agents charge a flat fee for their services, while others earn commissions from the travel suppliers they work with. Make sure you understand the fees involved and what services are covered. While price shouldn’t be the sole determining factor, it’s important to ensure that the agent’s fees are reasonable and align with the value they provide.
Online presence:
In today’s digital age, a travel agent’s online presence is crucial. Look for an agent who has a professional website or presence on reputable travel platforms. A well-designed website can provide valuable information about their services, destination expertise, and contact details. Additionally, check if they are active on social media platforms, as this can give you insights into their knowledge, responsiveness, and engagement with clients.
It’s also essential to have a conversation with the travel agent before making a final decision. Ask them about their approach to trip planning, how they handle emergencies or changes, and what level of personalized attention they offer. A good travel agent will listen to your needs, provide tailored recommendations, and be responsive to your queries.
Travel Agent Fees vs. Value
Remember to have open and transparent communication with your travel agent to understand their fee structure and the services included, ensuring you receive the best possible value for your travel investment.
How airssist Could Make Travel Agents Client Happy
By utilizing airssist services for travel agents they will offer personalized assistance to their clients. This includes services such as airport Meet & Greet, Airport Greeter, Baggage Handling, And Private Lounge Access, also:
- save customers’ time by making the booking process very simple and easy.
- airssist is proactive with travel agent communication, and swift with its resolutions.
- We present wherever customers are to make their trips better, easier, less stressful,
- airssist deep personalization.
In Conclusion,
exploring the different types of travel agents can help you find the one that best suits your travel needs and preferences. Whether you’re planning a leisure vacation, an adventure trip, or corporate travel, there are specialized travel agents available to assist you.
Note : Please note that the information on this page is generic & subject to change due to fluctuations in airport services. Kindly confirm service availability with our team, as offerings may vary daily.
Send Inquiry
01. welcome.
airssist offers a stress-free airport experience through personalized Airport VIP Services.
02. SEARCH BY CITY
03. latest entries.
- The Importance of Securing Your Corporate Limousine Service June 5, 2024
- Difference Between Fast Track, Clear Airport Security, and TSA Pre Check June 4, 2024
- Eco tourism VS Sustainable Tourism June 4, 2024
- All You Need to Know About Conscious Travelling June 4, 2024
Need help? Call +971 4 456 1940
[email protected]
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Meet & Greet
VIP Terminal
List With Us
Amendments, Refund & Cancellation Policy
Typically replies within minutes
Any questions related to Exploring the Different Types of Travel Agents?
WhatsApp Us
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us

9 Different Types of Travel Agents
Posted on June 24, 2022
Categories Travel

There are three main categories of travel agents: business, special interest, and leisure, and they fall into six types. These are:
- Global distribution systems
- Online travel agents
- Guest information centers
- Hotel and concierge agents
- Inbound tour operators
- Independent travel agents
Remember when we had to go to a travel agency and sit for a long time to book a trip or a tour? Those days are long gone. There are travel agents just about anywhere, from online to hotels and even independent agents.
Some people think they don’t need a travel advisor until their plans begin to go awry. Plus, tour operators need them. Travel agents were and still are relevant today. Let’s look at the different types of travel agents, their role, and their relevance.
Types of Travel Agents
Here are the six different types of travel agents:
Global Distribution Systems
One of the many ways that tourists can get their travel needs met is through a global distribution system. A corporation manages the computerized network system, which makes online reservations possible through the facilitation of transactions.
Global distribution systems will be used by both online and offline agents to reserve current travel experiences at a certain location. The most popular global distribution helps you boost your digital delivery and acquire more bookings.
These systems want to cooperate with tour operators who make their activities and excursions available for convenient internet booking. The majority of global distribution systems rely on real-time inventory from service providers.
Online Travel Agents

A web-based system where tourists may organize and make travel arrangements straight from their internet sites is known as an online travel agency (OTA). They depend on the simplicity and comfort of the Internet to construct bundles for their customers.
As a result, a growing number of vacationers are searching for the best ways to plan all-inclusive vacations that cover everything from transportation to lodging and activities.
Travel and tour companies can expand their digital delivery by building ties with online travel agents. A commission can be earned by utilizing an online booking system, which enables online travel agents to book directly with you and receive compensation.
Centers for Tourist Information
A tourist information station is a one-stop store where tourists may buy souvenirs and get free advice on things to do, places to stay, maps, and other useful information about the area. With this, they are a popular location for tourists who are new to the area and want to learn more about the local culture.
Tourist information centers, which are frequently run by local governments, confer legitimacy on the advice and assistance they provide.
If you want your local tourist information center to book your trips and activities for you, let them know. As a result, they’ll be more likely to spread the word about your products.
Independent Travel Agents

For most passengers, independent travel agencies are the preferred retail travel agents.
To incorporate travel experiences that their clientele is interested in, travel agents, whether offline or online, want to tailor the itinerary they provide for them.
You may enhance your online distribution by working with individual travel agencies and utilizing distribution technology entities. To make it easier for agents to promote your service.
The commission percentages for independent travel agents will vary from one agent to the next. Between 15% and 25% is typical for independent agencies that schedule your events.
Organizers of Outbound Tours
Inbound tour operators, are regarded as specialists in a certain location and are aware of the best excursions and activities in the area.
Working with these advisors to sell your products is advantageous because they advocate these outings to their clientele. They are more likely to recommend safe, exciting trips that are simple to book if they have worked with them before.
Travel Agent Categories
Here are the three travel agent categories:
1. Business Travel Agents

Work or business-related travelers. This group of commuters heads to and from work every day from their homes.
Commuters need to concentrate on efficiency and timeliness when they travel. It’s not uncommon for business travelers to plan their entire journey around a single event or meeting.
To stay productive when traveling, they chose workstations in the hotel rooms with high-speed web access. To make things easier, guests should be able to walk or use public transportation to and from their place of business.
Openings for Travel Agents
Business tourism is a multi-trillion-dollar industry, and travel agents may capitalize on this opportunity. Every day, up to 1.1 million individuals in the United States travel for work. This group of tourists is looking for a hassle-free journey. As a result, you’ll be called upon.
Travelers on business trips prefer to concentrate on their job rather than on the details of their journey. An excellent opportunity to select a hotel room with luxuries that will let the client forget they are even outside their hometowns is presented by the travel agent. As a result, understanding what a booking system is and how to utilize it effectively is critical.
Breakfast in the am, espresso in the foyer, and a fitness center are among the amenities that business travelers look for while they’re on the road for long periods. If your team manages to arrange appropriate lodging for a business traveler, you’ll have a satisfied and productive customer.
To get to and from work, commuters are more likely to be on the road. Loyalty programs are a terrific way to keep customers coming back to your business over and over again. Travelers will want to utilize your firm more often as their royalties grow, which will keep them invested in your brand.
In the event you play your chips properly as a travel agent and schedule hundreds of trips for a corporation, there are risks involved. But if something goes awry, it may suddenly turn from countless business visits to booking for one firm to none. In the travel agency industry, you need to be aware of the potential dangers.
Whenever it comes to corporate travel, there is no margin for error, since most appointments may not wait for a tardy attendee. Before the start of the project, everything must be planned out and accounted for. If the client is late for a business meeting, the meeting may be canceled, resulting in lost revenue, time, and labor for the business traveler.
If you’re going on a trip, it’s important to think about possible health concerns. A business vacation is not a time to put off illness, accidents, or catastrophes. You may want to recommend that the company purchase Business Travel Accident (BTA) insurance to fully safeguard the firm’s travelers.
The traveler must be satisfied if your travel agency provides a journey that emphasizes punctuality and convenience.
2. Special Tourism Agents

This type of travel caters to the interests and desires of the individual traveler. When it comes to special interest tourism, the goal is to get an exceptional experience that directly relates to the preferences of the traveler.
Special interest travelers have a wide range of features, as they are all based on the preferences of the individual traveler. There are a wide number of possibilities, including gourmet tours, religious travel, cultural trips, and more.
The underlying denominator among these travelers is a great passion for something and a desire to travel the world to further explore this obsession.
Determine the purpose of the trip – Is it to unwind and relax? Is the purpose of this journey to learn and grow? Is the goal to see as many of the big tourist destinations as possible? Accommodations can be made once the purpose of the trip has been determined.
Create tour offers that will pique your client’s interest when it comes to customizing a trip for them. Packages appeal to special interest visitors since they are cost-effective and focus on what they want to see and do.
An adventure package is a traditional special-interest package. All of the area’s top places to visit would be included in this itinerary. People who are willing to take risks will be drawn to your website if you offer zip-lining, whitewater rafting, and rock climbing. You can guarantee that your consumers will have the vacation of a lifetime if you provide them with the most exciting options.
A rapidly growing segment of the travel industry is wellness tourism. These tours are specifically designed to focus on health, focusing on both physical and emotional well-being.
Travel companies will make reservations for these customers based on their preferences for health and well-being, including staying in hotels with exercise facilities, eating at restaurants with organic options, and staying in places with plenty of greenery.
A travel agent may be contacted by someone in need of medical treatment. Because the patient doesn’t live in an area where medical aid is needed, medical tourism is a necessity.
In any case, the patient already has a lot on their plate, and they don’t want the excessive strain of travel or hotel reservations on top of everything else. The treatment isn’t accessible in their homeland, or there may be better doctors abroad.
Due to needing to function as the liaison between the customer and the many tour operators, excursions, and activities, there is some risk for travel agents. Because of this, many people rely on the services of travel host agencies.
The client has placed their trust in you and your organization, and this is where tour operators come into play. The customer will come to you if something turns out badly.
Therefore, keep communication open between the two of you. To serve your customers with the highest service, you should have a list of organizations you can rely on.
To avoid a last-minute withdrawal from either side, you should plan . You should specify the dates by which cancellations are accepted and whether or not there will be a fee for doing so. There must be no misunderstandings when the day of the scheduled events approaches if you provide all the relevant information.
Unexpected medical concerns are another issue for tourists with specialized interests. Terrible events might occur when a trip is centered on being adventurous, tasting new foods, or getting medical treatment done.
Travel insurance is the right strategy to avoid any potential issues. This will protect your traveler in the event of an emergency, but ideally, it will never be needed.
3. Travel Agencies for the Leisure Traveler

Travelers who want to get away from the daily grind. Those that travel for leisure are more concerned about having fun and having a good time.
People who go on vacation tend to be alone or with a small group of relatives and friends. All of these tours are geared toward leisure, exploration, and fun.
There are several aspects of a leisure trip that include eating at fine restaurants, staying in luxury hotels, lounging by the pool or beach, and seeing tourist attractions.
Those who prefer a more authentic travel experience, however, may choose to backpack around a new location, overnight in hostels, steer clear of the most popular tourist attractions, and learn about the history and culture of the place they’re visiting. Online travel agencies can only provide this level of service.
There are numerous options for the travel agent to personalize a client’s journey while they are going for pleasure. An experienced traveler can help you get the most out of your vacation.
With a cruise, you don’t have the burden of choosing your itinerary, so you can relax and unwind. In one transaction, a cruise provides transportation, meals, amusement, and a place to stay. If a family is looking for a getaway from their bustling daily routine, this kind of trip is an excellent option.
In most cases, a customer will know where they want to go, but they will need assistance working out how to fill their days. A seasoned traveler can provide their recommendations for the must-see attractions, the best restaurants, and fun activities for the entire group. To ensure that your customers get the most value for their money, your travel firm can put together a well-thought-out itinerary.
When the word “leisure” is used, the first thing that comes up is sitting by a pool, reading a book, and wearing floppy hats. Travel agents that can propose a variety of resorts to potential customers are more likely to get the best deal. Travelers will love a hotel that is located close to a beautiful beach, has an on-site spa, and has a fitness facility.
There are few risks involved in working with leisure visitors. If something goes wrong, it usually doesn’t have a major impact on the holiday because the timetable is so slack.
There is an increasing trend for clients to submit evaluations on web forums. Internet sites like TripAdvisor make it easy for customers to sing your firm’s praises while also calling it out when it makes a mistake in the public eye.
Image and reputation may be ruined in a matter of minutes thanks to the power of the internet, and dissatisfied consumers are quick to spread the word.

Types of Travel Agency
Types of Travel Agency: The travel agencies play a pivotal role in the tourism & hospitality Industry. Significantly, travel agency is a crucial constituent of the tourism & hospitality Industry. As a vital component of tourism industry, travel agency has faced many operational and managerial changes over recent years and needs to constantly evolve in order to continue to meet the needs of tourists and diversity of distribution channels in the volatile tourism marketplace. Thus, understanding how a travel agency operates, remains competitive and meets the needs of customers is essential for any employee of a travel agency and those who want to join this vital sector as career. It is important that learners appreciate the complexity of working within a agency organisation and therefore the wealth of skills and knowledge needed to achieve success during this vital component of the industry. This module aims to develop an understanding about different types of travel agencies operating in the tourism industry. This module also appraises the students to know in brief activities and importance of different types of travel agencies.

Various types of travel agencies
The Travel agencies are classified on the following basis:
On the basis of distribution chain
According to the International Institute for the Unification of Private law (UNIDROIT), a travel agency can be of two types. An Intermediary Travel Agency: This type of travel agency undertakes as intermediary to act for another, in obtaining either a journey or a sojourn possible in return for the price for the services.
An Organizing agency : An organizing Travel Agency undertakes to arrange for the general public , a journey or sojourn comprising a series of services.
On the basis of Functions
Retail Travel agency : Retailing mean to sell in small quantity of product / service to the end users. Retailing refers to all or any the transactions which involve sale of products or services to the last word consumers. A retail travel agency is a middleman between producers and tourists who procures goods from the producers /wholesalers and sells it to the final consumers. They form a vital link in the channel of distribution of products/ services because without travel agency the products/ services would not sell nor would it is possible for consumers to buy services of their choice. They have a way stronger personal relation with the consumers and deal directly with the people of various tastes and temperaments. They form the last link in the chain of distribution and give the final selling price to the product/ service. Thus, the retail travel agencies provide important services and solve the problems of the producers and wholesalers on one hand and the tourists on the other hand.
Wholesale Travel agency: As the name indicates, a wholesale travel agency operates at large scale and deals in bulk purchase of products/ services and retail through the retail travel agency. Wholesaler may be defined as the middleman who operates between the producers (from whom they purchase goods) and the retailers (to whom they sell goods). Wholesaler refers to any individual or business firm selling goods/ services in relatively large quantities to buyers (retailers) other than the ultimate consumers. Thus, the producers who sell their products directly to retailers may also be regarded as wholesalers. The specialized knowledge and skill of wholesalers increase the efficiency of the distribution network. The wholesalers provide important services and solve the issues of both the manufacturers and therefore the retailers.
On the basis of Tourism flows:
On the basis of tourism flow types of travel agency are as: Outbound Travel Agency: The outbound travel agencies are those travel agencies which provide product and services to tourists want to visit abroad. Generally, these travel agencies provide convenient location for the purchase of travel product/ service besides offering expert product knowledge and ancillary services.
Handling Travel Agency / Inbound Travel Agency: This is very old form of travel agency which is specialized at a particular destination or location. This travel agency plans and executes of travel packages at destination level. In fact, a handling travel agency represents tour operators at a destination and supervises the delivery of local suppliers.
On the basis of Business or leisure
Travel agencies can be categories on the basis of business or leisure such as: Leisure Travel Agency: These types of travel agencies manly serve holidaymakers with package tours.
Business Travel agency: Today, business travel has become core area for many travel agencies. Business travel agency arrange travel for business travelers and corporations and provide extra services such as reporting and travel management.
You may read this book
On basis of level of specialization.
Niche Travel agency: Due to the emergence of new form of tourism like ecotourism, Niche travel agencies have evolved. Niche travel agencies and usually small independent travel agencies and specialized in certain products or certain suppliers.
Mass Travel agency: Mass travel agencies are big travel agencies often large scale/ multinational travel companies. These travel agencies generally offer wide range of destinations and products/services having large supplier network. These travel agencies operate on economies of scale.
On the premise of Geographical coverage
Travel agencies is categories on the idea of geographical coverage like Multinational: Multinational travel companies present in many countries, either through own outlets or partnerships. A multinational travel company is one which is incorporated in one country (called the house country); but whose operations extend beyond the house country and which carries on business in other countries (called the host countries) additionally to the house country. Generally, multinational travel company has it’s headquarter within the home country.
National: agency is serving the requirementsof shoppers nationwide. In fact, when a travel company conducts its affairs in its home country is thought as national agency . A national agencyis commonly taxed differently than a distantagencyand should be required to pay duties or fees on the importation of its products/ services. Typically, a national agencyis in a positionto work business in other states or other parts of the country as per the articles of association.
Regional: when a agencyis working at regional level is usuallycalled regional agency . These travel agencies are specialized in certain countries and offer both leisure and business products/ services.
On the idea of Number of outlets
Travel agencies may be categories on the idea of number of outlets like Multiples : Multiples travel agencies are those travel agencies which operate nationwide and owned by large agency . These travel agencies are large scale and think about package holidays. These travel agencies have a sequence of establishments spread throughout the country under one name. Thus, these travel agencies have a large number of clients.

Mintiples : Mintiples travel agencies targeta selected region with multiple business line . These travel agencies have number of branches scattered throughout the local area but sometimes operate under different trade names. These have head offices and will acquire independent firms to show them into one in all their outlets.
Independent Agencies: Independent travel agencies usually cater for a special or niche market. Independent agencies have one outlet and frequently specialized in niche markets. These travel agencies and frequently small travel agencies and specialized in certain products or certain suppliers like eco-tour package, adventure tour package or others.
On the idea of Business Model
Travel agencies are often categories on the idea of business model like Offline Travel Agency: the sort of agencyis that the oldest sort ofagency . Generally, offline travel agencies operate through physical offices and face to face customer service/product.
Online Travel Agency: Online agency serving customers through World Wide Web channels. Online agency (OTAs) could be a relatively recent innovation and may be a major growth sector within the global distribution system. OTAs are a style of distribution mechanism where an oversized number of sellers and buyers are connected via an online site provided by an independent third party. The leading international OTAs are:
• Travelocity, owned by Sabre. Travelocity includes the brands lastminute.com, World Choice Travel and Zuji. within the corporate market, Sabre operates through the GetThere.com and TravelocityBusiness.com OTAs • Orbitz which operates the subsequent OTA leisure brands:
1. CheapTickets.com 2. Ebookers.com 3. HotelClub.com 4. RatesToGo.comOn the premise of Size
On the idea of business size travel agencies are often categories like
Small Scale Travel Agency: the little scale travel agencies are those agencies which treat small scale, restricted to a little segment of the tourism market and to a narrow range of products. Small scale travel agencies are very large in number but account for atiny low portion of the overall retail tourism business.
Medium Scale Travel Agency: Medium-scale agency business is that the outgrowth of a successful small scale agency. A agency business with 50 or fewer employees is mostly considered small, while one with 50-150 employees is taken into account to be medium-sized. Large scale Travel Agency: Large scale agency is that business operation whose operates at large scale, having an outsized segment of the market and have a good range of products/ services. .
On the idea of Form
On the premise of business forms travel agencies may be categories like Sole Proprietorship: when a agency business is owned, managed and financed by one man, it’s known sole proprietorship agency. In fact, its debt, obligations and taxes, are the owner’s personal liabilities, and income from a proprietorship is taken into account the owner’s income. this kind of agency is straightforward to begin and simple to dissolve.
Partnership : agency being seen on a partnership basis is jointly owned by two or more individuals. In other words, when two or more persons agreed to contribute money or money’s worth and sharing profit/ loss as per the agreement is knowledge partnership. The partnership style of agency business organization enjoys the subsequent advantages: a. easy formation: Partnership is easy to create, inexpensive to ascertain and straightforward to control. No legal formalities are involved and no formal documents are to be prepared. Only an agreement is required. . b. Combined abilities and judgment: The skill and knowledge of all the partners are pooled together. Combined judgment of several persons helps reduce errors of judgment. c. Direct motivation: there’s no difference between owner and management. In fact, ownership and management of business are vested within the same persons. Thus, every partner is motivated to figure hard and to make sure the success of the firm. d. Close supervision: Every partner is anticipated to require personal interest within the affairs of the business. Different partners can maintain personal contacts with employees and customers. e. Flexibility of operations: Partnership business is free from legal restrictions and government control. Partners can make changes within the size of business, capital and managerial structure with none approval. The activities of partnership business may be adapted easily to changing conditions within the market. f. Corporate: Unlike a proprietorship or partnership a company is taken into account to own its own identity, break free its owners. a company agency is owned by shareholders/ stockholders who are represented by a board of directors. the company variety of agency is incorporated under the businesses Act. the company has differing types of merits like indebtedness perpetual existence, which implies it’s a separate person within the eyes of the law and simple to transfer ownership interests in an exceedingly corporation. The board of directors can authorize the problem of shares of stock in exchange for investors’ capital infusion into the corporate.
On the Bases of Services
On the idea of services travel agencies is categories like
Full-Service agency : A full-service agency could be a agency which offers s all services / products to both international and domestic tourists. Its operation includes every kind of tour packages like holiday and business travel on individual or group based. Further, a full-service agency is also small or large scale concentrating on both leisure travel and business travel.
Corporate/ Business agency : A Corporate/ Business agency are specialized solely in servicing the travel needs of the business or corporate clients. Generally, the merchandise line of corporate agency includes business / MICE and incentive travel.
In-House agency: In-House Travel Agencies are growing these days; and in house agency is simply diversification of product of the many large scale companies to help the corporate to prepare MICE / incentive travel. However, these travel agencies are differ from the company agency within the sense that they work with only 1 corporate account doing mainly business travel but also handling the leisure side for corporate clients. The Ashok Tour and Travel is that the best example of in-house travel of ITDC.
Speciality Agencies: A speciality Agency because the name indicates is specialised in an exceedingly particular market, destination or product. These travel agencies are the results of specific market needs, serving the wants of market segments like senior citizens, incentive groups or adventure travellers. Generally, these travel agencies are intermediaries between the retail travel agencies and also the tourists and are referred to as specialty channelers. These travel agencies may represent either the customer or the supplier and include incentive travel firms, MICE planners/ association executives, and company travel offices. Moreover, incentive travel companies put together and sell travel as an incentive to extend sales. Sometimes these travel agencies sell their ability to style, promote, and manage incentive travel programs.
Types of Travel Agency Types of Travel Agency Types of Travel Agency
Types of travel agency types of travel agency, you may be interested to read this travel agents and tour operators, you might also like.

Top Indian Casinos

World Federation of Tourist Guide Associations (WFTGA)

International Air Transport Organization (IATA)

What does a travel agent do?
Would you make a good travel agent? Take our career test and find your match with over 800 careers.
What is a Travel Agent?
A travel agent assists individuals or groups in planning, organizing, and booking various aspects of their travel arrangements. They act as intermediaries between travelers and travel suppliers, such as airlines, hotels, car rental companies, and tour operators. Travel agents have in-depth knowledge of different destinations, travel options, and industry trends, which they leverage to provide personalized recommendations and advice to their clients.
One of the primary roles of a travel agent is to help clients navigate the complex world of travel. They listen to their clients' preferences, budget constraints, and desired experiences, and then work towards creating a tailored itinerary that meets their needs. Travel agents handle tasks such as booking flights, accommodations, ground transportation, and excursions, ensuring that all the necessary arrangements are made smoothly. They can also provide valuable insights on visa requirements, travel insurance, and local customs, helping travelers make informed decisions and avoid potential pitfalls.
What does a Travel Agent do?

Travel agents possess extensive knowledge and expertise in the travel industry, including destinations, transportation options, accommodations, and activities. This expertise allows them to provide valuable advice and guidance to travelers, helping them make informed decisions and create well-planned itineraries that meet their specific needs and preferences. They also have access to a wide range of resources and tools that enable them to efficiently search for the best deals, discounts, and promotions available. They can often secure exclusive rates and packages, saving their clients both time and money.
Duties and Responsibilities Here are some common tasks and responsibilities associated with being a travel agent:
- Client Consultation: Travel agents engage in thorough consultations with clients to understand their travel preferences, requirements, and budget. They ask relevant questions to gather necessary information and provide personalized recommendations based on the client's needs.
- Itinerary Planning: Based on client preferences, travel agents create detailed travel itineraries that include destinations, transportation options, accommodations, and activities. They consider factors like travel dates, budget constraints, and any specific requests from clients.
- Reservation and Booking: Travel agents handle the booking process for flights, hotels, rental cars, and other travel-related services. They ensure that all bookings are made accurately and efficiently, securing the best available rates and deals for their clients.
- Travel Documentation and Logistics: Travel agents assist clients in obtaining necessary travel documents such as passports, visas, and travel insurance. They provide guidance on the documentation process and ensure that clients have all the required paperwork in order. Agents also handle logistical aspects like seat assignments, baggage allowances, and transportation arrangements.
- Knowledge of Destinations: Travel agents possess extensive knowledge about various destinations, including popular attractions, local customs, weather conditions, and safety considerations. They provide valuable information and recommendations to clients, enabling them to make well-informed decisions about their travel plans.
- Customer Service: Travel agents offer exceptional customer service throughout the entire travel process. They address client inquiries, resolve any issues or concerns that may arise, and provide support during the trip. Agents act as a point of contact for emergencies and assist clients in making alternative arrangements if necessary.
- Stay Up-to-Date with Industry Trends: To provide the best service to clients, travel agents stay updated with the latest industry trends, travel regulations, and changes in travel technology. They attend industry conferences, participate in training programs, and conduct research to ensure their knowledge is current.
- Sales and Marketing: Some travel agents engage in sales and marketing activities to attract new clients and promote travel packages and services. They may participate in trade shows, develop promotional materials, and utilize online platforms to reach a wider audience.
- Financial Management: Travel agents handle financial transactions related to travel bookings, including processing payments, issuing refunds, and managing invoices. They maintain accurate records of financial transactions and ensure compliance with accounting procedures.
- Continuous Learning: Travel agents continuously enhance their skills and knowledge by staying updated on travel industry trends, new destinations, and emerging technologies. They actively seek opportunities for professional development to provide the best possible service to their clients.
Types of Travel Agents There are various types of travel agents, each specializing in different aspects of travel and catering to specific clientele. Here are some common types of travel agents and what they do:
- Leisure Travel Agents: Leisure travel agents focus on organizing vacations and leisure trips for individuals, families, or groups. They assist clients in planning and booking all aspects of their leisure travel, including flights, accommodations, tours, and activities. Leisure travel agents may specialize in specific types of travel, such as beach vacations, cruises, adventure travel, or luxury travel.
- Corporate Travel Agents: Corporate travel agents primarily cater to business travelers and companies. They handle the complex travel needs of corporate clients, including booking flights, arranging accommodations, managing itineraries, and coordinating travel logistics. Corporate travel agents are familiar with business travel policies, negotiated rates, and preferred vendors to ensure cost-effective and efficient travel arrangements for their clients.
- Group Travel Agents: Group travel agents specialize in organizing travel for large groups, such as family reunions, weddings, school trips, or corporate retreats. They handle group bookings for flights, accommodations, transportation, and activities, negotiating group rates and coordinating logistics to accommodate the specific needs and preferences of the group.
- Tour Operators: Tour operators design and operate pre-packaged tours and travel itineraries. They create comprehensive tour packages that include transportation, accommodations, guided tours, and activities. Tour operators often work with travel agents to sell their tour packages, providing them with a ready-made product to offer their clients.
- Destination Specialists: Destination specialists focus on specific regions, countries, or cities. They have in-depth knowledge of the destination's culture, attractions, local experiences, and logistical considerations. Destination specialists provide expert advice and create customized itineraries for travelers seeking in-depth exploration of a particular destination.
- Online Travel Agents (OTAs): Online travel agents operate through internet platforms and websites, offering a wide range of travel services. They allow customers to search, compare, and book flights, hotels, rental cars, and other travel services online. Online travel agents may also provide customer support and assistance through online chat or call centers.
- Niche Travel Agents: Niche travel agents specialize in specific types of travel, catering to niche markets or specialized interests. Examples include adventure travel agents, luxury travel agents, honeymoon specialists, culinary travel agents, or eco-tourism experts. These agents have extensive knowledge and expertise in their niche area, curating unique experiences and tailored itineraries for clients with specific interests.
Are you suited to be a travel agent?
Travel agents have distinct personalities . They tend to be enterprising individuals, which means they’re adventurous, ambitious, assertive, extroverted, energetic, enthusiastic, confident, and optimistic. They are dominant, persuasive, and motivational. Some of them are also conventional, meaning they’re conscientious and conservative.
Does this sound like you? Take our free career test to find out if travel agent is one of your top career matches.
What is the workplace of a Travel Agent like?
The workplace of a travel agent can vary depending on their specific employment arrangement. Some travel agents work in traditional brick-and-mortar travel agencies, which may be part of a larger travel company or operate independently. In these settings, travel agents typically have a physical office space with workstations, computers, and travel industry resources such as brochures, destination guides, and reservation systems. They may have a reception area to welcome clients and conduct in-person consultations.
With the increasing prevalence of remote work and online booking platforms, many travel agents now have the flexibility to work from home or in virtual offices. They utilize technology, such as laptops, smartphones, and high-speed internet, to communicate with clients, access travel resources, and make online bookings. Virtual travel agents often communicate with clients via phone, email, or video conferencing, offering the convenience of remote consultations.
Travel agents also frequently visit destinations, attend industry conferences, and participate in familiarization trips organized by travel suppliers. These opportunities allow them to gain firsthand experience, build relationships with suppliers, and stay updated on the latest travel trends. While travel agents spend a significant amount of time working at their desks, they also have the chance to explore and experience the destinations they recommend to their clients.
In terms of work hours, travel agents may have a standard office schedule, working weekdays during regular business hours. However, they may also need to be flexible, accommodating clients in different time zones or assisting with emergency situations outside of regular office hours. The workload of travel agents can vary throughout the year, with peak periods during holiday seasons or when there are significant events or festivals happening in popular destinations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Pros and cons of being a travel agent.
Being a travel agent can be an exciting and rewarding career for individuals who are passionate about travel and enjoy helping others create memorable experiences. However, like any profession, there are pros and cons to consider.
- Travel Opportunities: One of the major advantages of being a travel agent is the exposure to diverse travel opportunities. Travel agents often have the chance to visit destinations, experience different cultures, and explore new places as part of their job. This firsthand experience not only enhances their knowledge but also allows them to provide valuable insights and recommendations to clients.
- Personal Satisfaction: For individuals who are passionate about travel and helping others, being a travel agent can be personally fulfilling. The ability to create personalized itineraries and witness the joy and excitement of clients as they embark on their dream trips can be highly rewarding.
- Knowledge and Expertise: Travel agents develop a deep understanding of destinations, travel products, and industry trends. They stay up-to-date with the latest information, including visa requirements, safety advisories, and emerging travel destinations. This expertise allows them to provide valuable advice and recommendations to clients, ensuring they have well-planned and memorable travel experiences.
- Building Relationships: Travel agents have the opportunity to build strong relationships with clients, travel suppliers, and industry professionals. They can establish a network of contacts that can enhance their business and open doors for collaboration and future opportunities.
- Industry Changes and Competition: The travel industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies, online booking platforms, and dynamic pricing models. Travel agents must stay updated with these changes and adapt their business practices accordingly. The rise of online travel agencies and self-booking options has increased competition, requiring travel agents to differentiate themselves and provide added value to their clients.
- Workload and Time Management: The travel industry can be demanding, especially during peak travel seasons. Travel agents may need to work long hours, including evenings and weekends, to accommodate client needs and handle emergencies. Proper time management skills are essential to balance the workload and maintain a healthy work-life balance.
- Pressure for Exceptional Customer Service: Travel agents are expected to deliver outstanding customer service consistently. They must handle client inquiries, resolve issues, and manage expectations throughout the travel process. This level of customer service can be challenging, particularly when dealing with unforeseen circumstances or dissatisfied clients.
- Commission-Based Income: While some travel agents receive a salary or hourly wage, others rely on commission-based income. This means their earnings are directly tied to the bookings they secure for clients. It can take time to build a client base and establish a steady income stream, especially in the early stages of a travel agent's career.
Travel Agents are also known as: Travel Consultant
What is a Travel Agent?
Learn about the role of Travel Agent, what they do on a daily basis, and what it's like to be one.
- What is a Travel Agent
- How to Become
- Certifications
- Tools & Software
- LinkedIn Guide
- Interview Questions
- Work-Life Balance
- Professional Goals
- Resume Examples
- Cover Letter Examples
Start Your Travel Agent Career with Teal
Definition of a Travel Agent
What does a travel agent do, key responsibilities of a travel agent.
- Consulting with clients to understand their travel preferences, needs, and budget constraints.
- Designing and organizing travel itineraries tailored to clients' specifications, including booking flights, hotels, tours, and other travel services.
- Providing clients with destination information, including travel advisories, visa requirements, and vaccination protocols.
- Utilizing specialized travel software to research and secure the best travel deals for clients.
- Offering recommendations on travel insurance options and assisting with the purchase process.
- Handling travel-related issues or emergencies, offering support and solutions to clients as needed.
- Staying current with industry trends, destination knowledge, and travel regulations to provide accurate advice and service.
- Building and maintaining relationships with travel suppliers, such as tour operators, airlines, and hotel chains, to ensure favorable terms and client satisfaction.
- Managing bookings and travel documentation, ensuring accuracy and timely delivery to clients.
- Monitoring changes in travel schedules or services and communicating these to clients promptly.
- Assisting clients with special requests, such as dietary needs, accessibility accommodations, or cultural experiences.
- Following up with clients post-travel to gather feedback and foster repeat business through excellent service and relationship management.
Day to Day Activities for Travel Agent at Different Levels
Daily responsibilities for entry level travel agents.
- Booking standard travel arrangements such as flights, hotels, and car rentals
- Assisting clients with travel documentation and providing basic travel advice
- Processing payments and handling booking confirmations
- Responding to client inquiries via phone or email under supervision
- Learning about destinations, travel products, and industry regulations
- Performing general office duties and maintaining client files
Daily Responsibilities for Mid Level Travel Agents
- Designing and selling tailored travel packages and itineraries
- Building and maintaining relationships with clients to understand their travel needs
- Providing expert travel advice and destination knowledge
- Handling travel emergencies or changes with minimal supervision
- Networking with vendors and suppliers to negotiate better rates for clients
- Developing niche expertise in areas such as luxury, adventure, or business travel
Daily Responsibilities for Senior Travel Agents
- Overseeing complex travel arrangements and VIP client accounts
- Setting sales targets and strategies for the travel agency or branch
- Leading and mentoring junior agents, and providing advanced training
- Establishing and maintaining relationships with key industry partners
- Contributing to marketing and promotional strategies to attract new business
- Analyzing market trends to adapt the agency's offerings and stay competitive
Types of Travel Agents
Leisure travel agent, corporate travel agent, luxury travel agent, adventure travel agent, destination specialist travel agent, group travel agent, cruise specialist travel agent, what's it like to be a travel agent , travel agent work environment, travel agent working conditions, how hard is it to be a travel agent, is a travel agent a good career path, faqs about travel agents, how do travel agents collaborate with other teams within a company, what are some common challenges faced by travel agents, what does the typical career progression look like for travel agents.
How To Become a Travel Agent in 2024

Related Career Paths
Creating memorable guest experiences, driving service excellence in the hospitality sector
Driving customer satisfaction, resolving issues with empathy and efficiency
Fostering customer loyalty and business growth through personalized relationship management
Driving customer satisfaction and loyalty through proactive relationship management
Ensuring passenger safety and comfort, creating memorable travel experiences
Crafting unforgettable journeys, tailoring travel experiences to individual desires

What does a travel agency do?
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
What does a travel agency do? You will almost definitely have heard of travel agencies if you have ever booked a holiday or have an interest in the tourism industry. But what exactly is a travel agency, and what do they do?
What is a travel agency?
Independent travel agents, online travel agencies , visitor information centres, other types of travel agency, what can a travel agency book, big names in the travel agency industry, travel agency business model, a brief timeline of travel agencies, further reading.
A travel agency is essentially the ‘middle man’ between travel companies and the general public i.e consumers. They book all sorts of travel-related experiences for customers on behalf of larger companies.
The main aim of a travel agency is to make the booking process simpler for the public, who might lack the time or confidence to book trips themselves.
Types of travel agencies
So what does a travel agency do? It mostly depends on what type of travel agency you’re looking at. This can be broken down into the following types…

An independent travel agent is the type you’ll see on Instagram or with their own Facebook pages, their feeds full of snaps from Amsterdam, Bali , or New York City. They tend to partner with a ‘host agency’, who will take a portion of the agents’ commission themselves in exchange for letting them use the company software and access their commission. Travel agents are also able to recruit other people, and in turn get a cut of their commission too. In this way, independent travel agencies tend to be a type of multi-level marketing scheme.
Online travel agencies are much more consumer-focused. They allow individual customers to book their own travel, but as a package or with the added protection from ATOL and ABTA. They act as a broker, allowing you to input your dates, desired destination(s), what board basis you wish to travel and so on. The site then pulls together a package deal, allowing you to book everything in one go with access to booking details so you can make amendments and keep up to date with any changes.
While these don’t offer flights and hotels generally, visitor or tourist information centres are found within cities or tourist destinations. They provide advice, maps, discounts and booking services for tours and excursions such as open top bus tours. These are usually run by local or national governments, or specific tourist boards. They are great for recommendations when travelling somewhere new!
Hotel concierge services work in this same way, often getting commission for booking trips for guests.
I won’t go into too much detail here, but there are other types of travel agencies too. You can learn more in this post about the different types of travel agents .
Overall, what does a travel agency do?
A travel agency does a multitude of things. During non-peak times, they will mostly spend their days researching new or upcoming tourist destinations and what makes them so great, advertising them as somewhere people can book future holidays to.
Travel agencies are also required to keep up to date with safety information for various destinations. They do plenty of research meaning they can tell customers about the best places to go, what they can do while they’re there, what documents they need and so on. This is particularly important now, as travel advice is ever-changing with regards to political conflicts and public health.
But during peak times and in the run-up to these times, travel agents will be busy actually booking trips. Nowadays they mostly do everything via the computer, using the internet to put holiday packages together which include at least the basics – flights and accommodation – for one price. However, they also call travel companies directly in order to get better deals or to see if there are rooms or seats available which might not be showing online for whatever reason. Because of this, travel agencies and agents tend to have great relationships with particular brands.

Travel agents can book much more than just flights and accommodation. Not all of them can book all of these experiences or features, but it is definitely worth asking if you are using a travel agency to book your next vacation.
- Flights – short haul, long haul, & various classes
- Accommodation – hotels, apartments, and villas
- Airport transfers
- Executive airport lounges
- Airport parking
- Cruises – river and ocean
- Car rentals
- Travel insurance
- Excursions and tours
- Taxi services
- Currency exchange
- Train tickets
- Theme park & water park tickets e.g Disneyworld and Universal in Orlando, Florida
They will also advise on public transport services and timetables, as well as arranging for medical items to be delivered and any access requests you have.
Most travel agencies are actually online, and many of us use them regularly. There are still some in-store travel agencies, but with the impact of both modernisation and the Covid-19 pandemic the majority are online now. Below are some big names within the industry which you will likely recognise.
Expedia – founded by Microsoft in 2001
Cruise.com – specifically for booking cruises
American Express Travel – allows you to earn & use points when booking
Audley Travel – the largest operator in tailor-made travel
loveholidays – a British company founded in 2012
Lastminute.com – offering cheaper travel when you book last minute
Kiwi.com – specifically for booking air and ground transport
Booking Holdings – these are a travel technology company who own Booking.com, Cheapflights, OpenTable and more
Now we’ve looked at the question of ‘ what is a travel agency’, let’s take a look at the generic business model. Generally, travel agencies work in one of two ways. The first way is by receiving commission from the companies they book experiences with for customers. For example, if you were to use a travel agency to book your next holiday which included flights, a hotel stay and a transfer to and from the airport this is three separate components which will be booked through three different companies. The travel agency will receive commission from each of the three companies. There may be other benefits and incentives offered by the travel companies. Commission rates and these benefits mean that travel agencies are more likely to use some companies more so than others who might offer them less in exchange.
Alternatively, travel agencies will charge a fee for their services. This makes it more expensive for consumers to book trips through travel agents and agencies than it would to book themselves. However, as some people don’t feel confident booking themselves, many are happy to pay this additional cost. Holidays booked through travel agencies often come with the added benefit of being ATOL and ABTA protected.
- Cox & Kings were the first travel agency, was established in 1758
- Abreu Agency was the first public travel agency, was established in 1840
- Thomas Cook , one of the most famous travel agencies, was founded in 1841
- Brownwell Travel, the first travel agency in the US, was established in 1895
- Nippon Travel Agency was the first travel agency in Japan, established in 1905
- Intourist became the official state travel agency of the Soviet Union in 1929
- The first travel agency in Australia which went on to become Helloworld Travel, was established in 1951
- Henderson Travel Service became the first Black-owned travel agency, taking Black tourists to various African countries, in 1955
- American Airlines’ Sabre unit created a direct-to=consumer booking tool for flights, hotels and cars in the early 1980s
- Mode Tour became the first travel agency in South Korea, established in 1989
- Hotel Reservations Network, which went on to become Hotels.com, was established in 1991 – at this point, hotels didn’t pay a lot of commission so it didn’t take off
- Travelweb.com, the first online hotel directory, launched in 1994
- The Internet Travel Network sold the first airline ticket online in 1995
- Expedia launched in 1996, funded by Microsoft, and are now one of the biggest travel agencies
- In 2007, as the iPhone was released, more bookings were made online because mobile apps were now in use
- Airbnb was established in 2008
- HotelTonight, specifically for instant same-day hotel room bookings, was launched in 2011
If you enjoyed this article explaining what does a travel agency do, then I am sure you will enjoy these articles too-
- What is a tour operator and how does it work?
- The 3 types of travel and tourism organisations
- 150 types of tourism! The ultimate tourism glossary
- The 9 types of tourist destinations
- 50 fascinating facts about the travel and tourism industry
Liked this article? Click to share!
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
travel agent
Definition of travel agent
Examples of travel agent in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'travel agent.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
1885, in the meaning defined above
Articles Related to travel agent

Is it ‘traveling’ or...
Is it ‘traveling’ or ‘travelling’?
A tale of two variants
Dictionary Entries Near travel agent
travel agency
Cite this Entry
“Travel agent.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/travel%20agent. Accessed 10 Jun. 2024.
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
What's the difference between 'fascism' and 'socialism', more commonly misspelled words, commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - june 7, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, 9 superb owl words, 10 words for lesser-known games and sports, your favorite band is in the dictionary, games & quizzes.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 7. Travel Services
7.1 Components of Travel Services
The travel services sector helps travellers arrange and reserve their vacation or business trips (StatsCan, 2018). This sector is made up of businesses and organizations that work in a coordinated effort to provide travellers with seamless arrangements to maximize their travel experience. Go2HR describes travel services experiences and employment opportunities as follows:
Within this sector, you have the flexibility of working in various capacities with event and conference planning organizations, travel companies and organizations, as well as associations, government agencies and companies that specialize in serving the needs of the tourism sector as a whole. (go2HR, Essential Tips – Travel Services, 2020)
Before we move on, let’s explore the term travel services a little more. As detailed in Chapter 1 , Canada, the United States, and Mexico have used the NAICS guidelines, which define the tourism industry as consisting of transportation, accommodation, food and beverage, recreation and entertainment, and travel services (Tourism HR Canada, 2020). These five sectors are defined and further detailed in B.C. by the B.C. government (BC Government, 2014) and go2HR on their website (go2HR, Career Explorer, 2020).
For many years, however, the tourism industry was classified into eight sectors: accommodations, adventure and recreation, attractions, events and conferences, food and beverage, tourism services, transportation, and travel trade (Yukon Department of Tourism and Culture, 2020; go2HR, 2020, What is Tourism? – Travel Services).
Tourism services support industry development and the delivery of guest experiences, and some of these are missing from the NAICS classification. To ensure you have a complete picture of the tourism industry in BC, this chapter will cover both the NAICS travel services activities and some additional tourism services.
First, we’ll review the components of travel services as identified under NAICS, as well as exploring popular careers within:
- Travel agencies (brick and mortar)
- Online Travel Agencies/OTA
- Tour operators
- Destination marketing organizations (DMOs)
Other Organizations
Following these definitions and descriptions, we’ll take a look at some other support functions that fall under tourism services. These include sector organizations, tourism and hospitality human resources organizations, training providers, educational institutions, government branches and ministries, economic development and city planning offices, and consultants.
Finally, we’ll look at issues and trends in travel services, both at home, and abroad.
While the application of travel services functions are structured somewhat differently around the world, there are a few core types of travel services in every destination. Essentially, travel services are those processes used by guests to book components of their trip. Let’s explore these services in more detail.
Travel Agencies

A travel agency is a business that operates as the intermediary between the travel industry (supplier) and the traveller (purchaser). Part of the role of the travel agency is to market prepackaged travel tours and holidays to potential travellers. The agency can further function as a broker between the traveller and hotels, car rentals, and tour companies (Goeldner & Ritchie, 2003). Travel agencies can be small and privately owned or part of a larger entity.
A travel agent is the direct point of contact for a traveller who is researching and intending to purchase packages and experiences through an agency. Travel agents can specialize in certain types of travel including specific destinations; outdoor adventures; and backpacking, rail, cruise, cycling, or culinary tours, to name a few. These specializations can help travellers when they require advice about their trips. Some travel agents operate at a fixed address and others offer services both online and at a bricks-and-mortar location. Travellers are then able to have face-to-face conversations with their agents and also reach them by phone or by email. To promote professionalism within the travel industry, travel counsellors can apply for a specialized diploma or certificate in travel from ACTA (ACTA, 2020a; go2HR, 2020a).
Today, travellers have the option of researching and booking everything they need online without the help of a travel agent. As technology and the internet are increasingly being used to market destinations, people can now choose to book tours with a particular agency or agent, or they can be identified as seeking Domestic Independent Travel (DIT) or Foreign Independent Travel (FIT) , by creating their own itineraries from a number of suppliers.
Online Travel Agents (OTAs)
Increasing numbers of travellers are turning to online travel agents (OTAs), companies that aggregate accommodations and transportation options and allow users to choose one or many components of their trip based on price or other incentives. Examples of OTAs include iTravel2000, Booking.com, Expedia.ca, Hotwire.com, and Kayak.com. OTAs continue to gain popularity with the travelers; in 2012, they reported online sales of almost $100 billion (Carey, Kang, & Zea, 2012) and almost triple that figure, upward of $278 billion, in 2013 ( The Economist , 2014).
In early 2015 Expedia purchased Travelocity for $280 million, merging two of the world’s largest travel websites. Expedia became the owner of Hotels.com, Hotwire, Egencia, and Travelocity brands, facing its major competition from Priceline (Alba, 2015).
Although OTAs can provide lower-cost travel options to travellers and the freedom to plan and reserve when they choose, they have posed challenges for the tourism industry and travel services infrastructure. As evidenced by the merger of Expedia and Travelocity, the majority of popular OTA sites are owned by just a few companies, causing some concern over lack of competition between brands. Additionally, many OTAs charge accommodation providers and operators a commission to be listed in their inventory system. Commission-based services, as applied by Kayak, Expedia, Hotwire, Hotels.com, and others, can have an impact on smaller operators who cannot afford to pay commissions for multiple online inventories (Carey, Kang & Zea, 2012). Being excluded from listings can decrease the marketing reach of the product to potential travellers, which is a challenge when many service providers in the tourism industry are small or medium-sized businesses with budgets to match.
While the industry and communities struggle to keep up with the changing dynamics of travel sales, travellers are adapting to this new world order. One of these adaptations is the ever-increasing use of mobile devices for travel booking. The Expedia Future of Travel Report found that 49% of travellers from the millennial generation (which includes those born between 1980 and 1999) use mobile devices to book travel (Expedia Inc., 2014), and these numbers are expected to continue to increase. Travel agencies are reacting by developing personalized features for digital travellers and mobile user platforms (ETC Digital, 2014). With the number of smartphone users expected to reach 1.75 billion in 2014 (CWT Travel Management Institute, 2014) these agencies must adapt as demand dictates.

A key feature of travel agencies’ (and to a growing extent transportation carriers) mobile services includes the ability to have up-to-date itinerary changes and information sent directly to consumers’ phones (Amadeus, 2014). By using mobile platforms that can develop customized, up-to-date travel itineraries for clients, agencies and operators are able to provide a personal touch, ideally increasing customer satisfaction rates.
Take a Closer Look: PATA — The Future of Travel is Personalisation at Scale
“The industry has changed monumentally over the past decade. The rise of meta-search websites and sharing economy services like Airbnb is giving travellers more control and choice than ever before. However, this is nothing compared to the changes that are on the horizon as technologies like mobile, AR, AI, and VR become mainstream.
One thing is certain; the pace of change is accelerating. Against this backdrop, the travel industry as a whole will need to fundamentally shift its focus to continuous innovation.” (PATA, 2019)
Despite the growth and demand for OTAs, brick and mortar travel agencies are still in demand by travellers (IBISWorld, 2019) as they have both an online presence and physical locations. The COVID-19 pandemic may see an increase in travellers relying on personal contact with brick and mortar travel agencies but at a distance through mail and phone.
Tour Operators

A tour operator packages all or most of the components of an offered trip and then sells them to the traveller. These packages can also be sold through retail outlets or travel agencies (CATO, 2020; Goeldner & Ritchie, 2003). Tour operators work closely with hotels, transportation providers, and attractions in order to purchase large volumes of each component and package these at a better rate than the traveller could if purchasing individually. Tour operators generally sell to the leisure market.
Inbound, Outbound, and Receptive Tour Operators
Tour operators may be inbound, outbound, or receptive:
- Inbound tour operators bring travellers into a country as a group or through individual tour packages (e.g., a package from China to visit Canada).
- Outbound tour operators work within a country to take travellers to other countries (e.g., a package from Canada to the United Kingdom).
- Receptive tour operators (RTOs) are not travel agents, and they do not operate the tours. They represent the various products of tourism suppliers to tour operators in other markets in a business-to-business (B2B) relationship. Receptive tour operators are key to selling packages to overseas markets (Destination BC, 2020) and creating awareness around possible product.
Destination Marketing Organizations
Destination marketing organizations (DMOs) include national tourism boards, state/provincial tourism offices, and community convention and visitor bureaus around the world. DMOs promote “the long-term development and marketing of a destination, focusing on convention sales, tourism marketing and service” (Destinations BC, 2020).
Spotlight On: Destinations International
Destinations International is the global trade association for official DMOs. It is made up of over 600 official DMOs in 15 countries around the world. DMAI provides its members with information, resources, research, networking opportunities, professional development, and certification programs. For more information, visit the Destinations International website.
With the proliferation of other planning and booking channels, including OTA s, today’s DMOs are shifting away from travel services functions and placing a higher priority on destination management components.
Working Together
One way tour operators, DMOs, and travel agents work together is by participating in familiarization tours (FAMs for short). These are usually hosted by the local DMO and include visits to different tour operators within a region. FAM attendees can be media, travel agents, RTO representatives, and tour operator representatives. FAMs are frequently low to no cost for the guests as the purpose is to orient them to the tour product or experience so they can promote or sell it to potential guests.
The majority of examples in this chapter so far have pertained to leisure travellers. There are, however, specialty organizations that deal specifically with business trips.
Spotlight On: Global Business Travel Association (GBTA) Canada
“GBTA Canada is the voice of the Canadian business travel industry. We believe in providing the business travel and meetings community with a global platform to serve as a resource library for their peers, to implement world-class Conferences, workshops and virtual meetings, and to foster an interactive network of innovation and support.” The GBTA state that their economic impact contributes $23.5 billion CAD in Canadian business travel (Economic Impact Study) and “$435+ billion CAD of business travel and meetings expenditures represented globally.” Visit the GBTA website .
Business Travel Planning and Reservations
Unlike leisure trips, which are generally planned and booked by end consumers using their choice of tools, business travel often involves a travel management company, or its online tools. Travel managers negotiate with suppliers and ensure that all the trip components are cost effective and comply with the policies of the organization.
Many business travel planners rely on global distribution systems (GDS) to price and plan components. GDS combine information from a group of suppliers, such as airlines. In the past, this has created a chain of information from the supplier to GDS to the travel management company. Today, however, there is a push from airlines (through the International Air Transport Association’s Resolution 787) to dissolve the GDS model and forge direct relationships with buyers (BTN Group, 2014).
Destination Management Companies
According to the Association of Destination Management Executives International (ADMEI), a destination management company (DMC) specializes in designing and implementing corporate programs, and “is a strategic partner to provide creative local experiences in event management, tours/activities, transportation, entertainment, and program logistics” (ADMEI, 2020). The packages produced by DMCs are extraordinary experiences rather than general business trips. These are typically used as employee incentives, corporate retreats, product launches, and loyalty programs. DMCs are the one point of contact for the client corporation, arranging for airfare, airport transfers, ground transportation, meals, special activities, and special touches such as branded signage, gifts, and decor (ADMEI, 2020). The end user is simply given (or awarded) the package and then liaises with the DMC to ensure particular arrangements meet his or her needs and schedule.
As you can see, travel services range from online to personal, and from leisure to business applications. Now that you have a general sense of the components of travel services, let’s look at some examples in Canada and BC.
Under NAICS, businesses and functions that assist with planning and reserving components of the visitor experience.
Other services that work to support the development of tourism and the delivery of guest experiences.
A business that provides a physical location for travel planning requirements.
An individual who helps the potential traveller with trip planning and booking services, often specializing in specific types of travel.
A trade organization established in 1977 to ensure high standards of customer service, engage in advocacy for the trade, conduct research, and facilitate travel agent training.
A service that allows the traveller to research, plan, and purchase travel without the assistance of a person, using the internet on sites such as Expedia.ca or Hotels.com.
An operator who packages suppliers together (hotel + activity) or specializes in one type of activity or product.
An operator who packages products together to bring visitors from external markets to a destination.
An operator who packages and sells travel products to people within a destination who want to travel abroad.
Someone who represents the products of tourism suppliers to tour operators in other markets in a business-to-business (B2B) relationship.
Also known as a destination management organization; includes national tourism boards, state/provincial tourism offices, and community convention and visitor bureaus.
Tours provided to overseas travel agents, travel agencies, RTOs, and others to provide information about a certain product at no or minimal cost to participants. The short form is pronounced like the start of the word "family" (not as each individual letter).
A company that creates and executes corporate travel and event packages designed for employee rewards or special retreats.
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC - 2nd Edition Copyright © 2015, 2020, 2021 by Morgan Westcott and Wendy Anderson, Eds is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
6 types of agents tours and activities can partner with to improve business

By Rezdy — 12 Aug 2018
agent bookings distribution tour operator
Updated June 2022 – The days of travel agents being limited to independent storefronts in shopping malls are far behind us. There are numerous different types of travel agents nowadays across a variety of platforms. This makes travel and tour bookings accessible for everyone, no matter where they are in the world. From online travel agents and global distribution systems, to independent agents and visitor centers: tours and travel activities can be booked in numerous convenient ways. This means that tour operators must extend their presence across these different types of travel agency platforms to compensate for all of the many types of bookings.
In order to grow their business and increase online bookings, tour and activity operators need to form relationships with travel agents from across the industry. A travel agency partnership will dramatically boost the visibility of your tour business and help drive bookings.
Don’t know where to begin or how to present your business to a potential travel agent partner? Here’s everything you need to know about the different types of travel agency platforms to ensure that you know what exactly to look for in an ideal agency partner.
What exactly is a travel agent?
A travel agent is a person working for a private retailer or public service organization that provides travel and tourism-related advice and services. Travel agents work on the behalf of travel suppliers (i.e. hotels, transport companies, travel insurance, tour operators) to supply different types of travel agency packages to their clients. They will arrange the logistics of travel for their clients while simultaneously acting as an ‘agent’ to different travel service suppliers. If you are a tour operator, travel agents are key to unlocking visibility amongst tourists that are traveling to your destination. As they are representing your company, travel agents will require a fee or commission for their services. This fee will differ depending on the travel agent’s policies.
What are the different types of travel agents that tour operators can work with?
Here are the 6 types of travel agents tour operators can work with in building mutually beneficial relationships.
1. Independent travel agents

Most travelers prefer independent travel agents as their go-to type of retail travel agent.
Both offline and online travel agents want to customize the travel itineraries for their clients in order to include tours and activities that interest them.
By partnering with independent travel agents and using distribution technology like Rezdy, you can increase your online distribution. Making it easy for agents to recommend your products.
Independent travel agent commission percentages will differ from agent to agent. Typically, independent agents can earn a commission between 15 and 25 percent for booking your activities.
2. Online travel agents

You’ve probably already heard the acronym OTA, but exactly what is an OTA in travel ?
Online travel agents (OTAs) are web-based platforms where travelers can plan and book travel products directly from their websites. OTAs rely on the convenience and ease of the Internet in order to create packages for their clients. Today, many travelers want to find the best way to book travel packages that include not only transportation and accommodations but also excursions, tours and activities.
By forming relationships with online travel agents, tour and activity operators can increase their online distribution. Through Rezdy’s online booking system , online travel agents can book with you directly and earn a commission at the same time.
3. Visitor information centers

A visitor information center provides travelers with a centralized location to shop for souvenirs and access free advice on the local area’s attractions, accommodations, maps, and other key information. This makes them a popular destination for travelers who are unfamiliar with the region and want to gain knowledge about local activities.
Local governments often operate visitor information centers, which give their advice and services a level of authority.
Let your local visitor information center know that they can easily book your tours and activities online. This will ensure that they will be more apt to recommend your products.
4. Hotel and concierge services

With the rise of mobile technology, the role of the concierge has changed. However, concierges remain an important source of personalized, local recommendations. Hotel concierge services can play a key role in increasing the visibility of your business as they offer real-time and instant information.
Operators should work with concierges in their region to let them know how convenient it is to book their tours. In addition, they will be pleased to know they will receive a fair commission for quickly booking with you.
5. Inbound tour operators

Inbound tour operators are considered experts in a given destination, and they are aware of the best tours and activities in any region. They recommend these excursions to their clients, so it’s beneficial to work with these agents to promote your products. They will be more apt to recommend reliable, exciting tours that are easy to reserve.
6. Global distribution systems

A global distribution system is a worldwide conduit between travelers and travel providers. The computerized network system is operated by a company that enables online reservations by enabling transactions. Online and offline agents will utilize global distribution systems to automatically reserve available tours and activities in a particular destination.
Working with global distribution systems, such as Amadeus and Sabre, will help you increase your online distribution and help you secure more bookings. These systems prefer to work with tour providers who offer easy online booking for their activities and tours. Global distribution systems mainly work with service providers that offer real-time inventory.
Want to boost your visibility to tour agents?
Building rapport with travel agents involves more than just a single conversation. A successful partnership will rely upon constant communication and a clear outline of everyone’s roles and responsibilities. You and your agent should benefit from your partnership, so measuring and monitoring its success is important.
Travel agencies will have special requirements and processes for the partnerships they form. Therefore, it’s important that your company is in its best shape before contacting the different types of travel agents. You should also be aware of what type of travel agent will best promote our business. Your travel agent partner should have characteristics that make them the right fit for your specific company. If you doubt that your target customers would utilize a certain type of travel agent platform, then it’s best to focus your attention elsewhere.
Now that you know who you can partner up with, here’s how to get travel agents to sell your tours.
Start your free trial today
Rezdy streamlines your booking software to accommodate bookings that are finalized through a variety of different types of travel agency platforms. As a booking software customer, you’ll also have instant access to Rezdy Channel Manager . An online distribution platform designed for tour and activity operators – with over 25,000 resellers that includes the different types of travel agents listed above.
Sign up for a free 21-day trial or book a demo with Rezdy today to experience how simple your tour operator booking processes can be with an all-in-one platform.
If you enjoyed this article, then follow the Rezdy blog . There are a lot of marketing tools and resources designed with businesses like yours in mind.
Want to learn more?

Enjoy 21 days to take a look around and see if we are a good fit for your business.
No obligations, no catches, no limits, nada

- Travel Terms Glossary
We have provided a glossary for your use. The travel industry is replete with jargon and acronyms and we hope you find this glossary/dictionary of travel terms useful when you run across a term you are not familiar with. We encourage our clients to submit any words or concepts they would like defined or clarified to us on the Contact Us page and we will be happy to reply by email with a definition and include the term or clarification in our glossary/dictionary of travel terms for other clients benefit as well.
A la carte – referring to meals, an indication that each dish is priced separately; also that a choice of meals may be vailable, such as on a tour.
A la Carte Bar – Also known as a “Cash Bar,” a bar located within one’s hotel room that is pre-stocked with an assortment of snacks and beverages.
ABC – a reference to the Caribbean islands of Aruba, Bonaire, and Curacao, in the Netherlands Antilles, just off the northern coast of South America (Venezuela). Fabulous for diving, snorkeling and all manner of watersports.
Abeam – A directional term, used on ships and aircraft, which describes something off to the side of the vessel, such as the wings.
Accessible Tourism – Travel that ensures that there is high availability in destinations, accommodations, attractions, products, and services to all people.
Accessible Travel – Travel that ensures that there is high availability in destinations, accommodations, attractions, products, and services to all people.
Actual Time of Arrival – Literally, the actual time of arrival. As opposed to the ETA (Estimated Time of Arrival).
Add-on – an option, usually at extra cost, added to travel arrangements.
Adjoining rooms – Two hotel or accommodation rooms that have a door connecting them from the inside, allowing the guests to combine the two rooms into one larger room.
Adoption Rate – the percentage of tickets issued through an online booking system compared to the traditional booking channel of agent-assisted reservations.
ADT – Atlantic Daylight Time; Alaska Daylight Time. Advance Purchase Fare – airfare that requires the traveler to purchase the ticket a minimum number of days prior to departure.
Advance Purchase Requirement – APR, or Advance Purchase Requirement, is the requirement that a ticket must be purchased a minimum number of days before the flight departs.
Adventure tour – A tour designed around an adventurous activity such as rafting, hiking, or mountain climbing.
Adventure travel – adventure travel is category of travel involving exploration or travel with perceived (and possibly actual) risk, and potentially requiring specialized skills and physical exertion.
Adventure Traveler – Adventure travelers travel to destinations with the specific purpose of active physical participation and exploration of new experiences.
Affinity Card – These are credit or debit cards issued by a banking institution in partnership and co-branded with a particular frequent traveler program.
Affinity group – A group of people that share a common hobby, interest, or activity, or that are united through regular participation in shared outings. Also see preformed group.
Aft – toward the rear of a ship.
After-departure charge – Charges that do not appear on the guest’s bill at checkout such as telephone or dining charges.
Agent – A person who has the power to act as the representative for another person. Most frequently in travel, a specific kind of agent such as a travel agent.
AIO variables – Activities, interests, and opinions-used to measure and categorize customer lifestyles.
Air mile – a distance of approx. 6076 feet.
Air Traffic Control – Usually refers to the control tower at the airport, but may also be a control center somewhere else in charge of controlling a large area of sky.
Air Travel Card – a credit card sponsored by the airlines, for the purchase of air travel only.
Air Travel – air travel is the action or process of making a journey by aircraft.
Air/sea – a term referring to tickets, trips, fares, etc. that include both air and land-based travel arrangements, such as a cruise package with air included.
Aircraft – Generally speaking, any machine capable of flight. However, in the travel industry, these often mean airplanes.
Airline Alliance – These are agreements of cooperation between groups of airlines. Alliances offer airlines more flexibility and larger networks.
Airline fare – Price charged for an airline ticket. Several types of fares exist and can change with market conditions.
Airlines Reporting Corporation (ARC) – An organization that provides a method of approving authorized agency locations for the sale of transportation and cost-effective procedures for processing records and funds of such sales to carrier customers.
Airport access fee – a fee paid by the car rental companies to the airport authority, for the use of shuttle vehicles, etc. – usually passed on to the consumer.
Airport transfer – a transport service to/from an airport to hotel, etc., normally prepaid as part of a package tour, but available separately as well.
Air-Sea – A cruise or travel package in which one or more transportation elements are provided by air and one or more by sea. The package is usually combined with local lodging.
All Inclusive – sold for one price that includes charges and fees that are often added separately.
All-inclusive package – A tour package in which most travel elements are purchased for set price. Also called an all-expense package.
Alternative Tourism – Travel that is not conventional in nature, though that is hard to define. It can be a niche kind of tourism.
Alternative Travel – Travel that is not conventional in nature, though that is hard to define. It can be a niche kind of tourism.
Alumni tour – A tour created for customers who have previously traveled with a tour operator. Also called a reunion tour.
Ambassador – The head of a state’s diplomatic mission in another state, usually with offices inside the main embassy.
Amenities – a desirable or useful feature or facility of a building or place
Amenity package – A cluster of special features, such as complimentary shore excursions, bar or boutique credit, or wine at dinner offered to clients on a given tour or cruise, usually as a bonus or extra feature. Usually used to induce clients to book through a particular travel agency or organization.
Amenity – The facilities and features of a property, usually cruise ship, airline or destination accommodation.
American plan – a hotel’s meal plan that usually includes all three meals each day.
AMEX – American Express (AX).
Amidships – toward the middle of a ship – usually the most stable part of the vessel.
Anniversary travel – a type of milestone travel celebrating a date that is remembered or celebrated because a special or notable event occurred on that date in a previous year, such as a wedding anniversary.
Antebellum – describes a building and/or period of time prior to the Civil War, such as an antebellum mansion on a cotton plantation in the southern US.
APEX – an airline term meaning “advance purchase excursion fare” – normally the least expensive fares.
Apron – The area surrounding the gate areas of a terminal, generally used for parking and maintenance of planes.
ARC – Airline Reporting Corporation- the agency that regulates ticket sales and reports to the airlines for travel agencies.
Archipelago – An archipelago is a grouping of islands, essentially. Indonesia and Japan are both archipelago countries.
ARTA – Association of Retail Travel Agents – professional trade group of travel agents only.
ASC Fee – Administrative Service Charge. Usually it’s the same as the change fee, or the fee to exchange the ticket for future travel.
AST – Atlantic (or Alaska) Standard Time.
ASTA – American Society of Travel Agents – trade group consisting of travel agencies, travel agents, and allied members (suppliers, etc.).
ATO – Airline Ticket Office – becoming rarer these days, as carriers continue to reduce customer service.
Attractions – An item or specific interest to travelers, such as natural wonders, manmade facilities and structures, entertainment, and activities.
Autobahn – high-speed equivalent to the US interstate highway system, in Germany and a few other European countries.
Availability – The total number of seats allowed to be sold at a particular rate.
Average room rate – The total guest room revenue for a given period divided by the number of rooms occupied for the same period.
B&B – A bed and breakfast home or guest house that a proprietor has converted into accommodation(s) for the public. Each room becomes a separate unit for rent and typically breakfast and/or other meals are served as part of the fare.
Babymoon – A relaxing and romantic vacation or getaway taken by parents-to-be before their baby is born.
Back to back – A term used to describe tours operating on a consistent, continuing basis. For instance, a motor coach arriving in a city from a cross-country tour may conclude the first tour upon arrival, then transport a second group back along the same route to the origination city of the first tour.
Back-to-back ticket(ing) – an against-the-rules practice whereby an air ticket is issued round-trip with only one portion to be used. Another is then issued roundtrip, again with only one portion to be used. In effect, this amounts to using one ticket for the outbound part of a trip, and the other for the return. The normal Saturday night stay requirement is then avoided – useful only when two roundtrip tickets are less than the cost of a single ticket with no Saturday night stayover.
Baggage Allowance – The amount of baggage a passenger may transport without having to pay extra charges, determined by carrier.
Baggage handler – See porter.
Baggage master – The person who controls baggage handling on a ship.
Balcony – sometimes called a verandah – an outside “porch ” that is usually private, just outside your ship’s cabin. Great for relaxing and port arrivals!
Barge cruising – pleasure cruising along a canal system, such as in upstate New York or in Europe, in converted barges or new ships that resemble them.
Base fare – the basic price of an airline ticket, before ANY taxes, surcharges, airport fees, etc.
Base – Flight crew term for their home airport; where the flights originate from and terminate at.
Beam – a ship’s width at its widest point; determines whether or not a vessel can pass through the Panama Canal.
Bed and breakfast (B&B) – Overnight accommodations usually in a private home or boarding house, often with a full American-style or Continental breakfast included in one rate.
Bell captain – The person in charge of luggage at a hotel.
Bellboy – Also called “Bellboy” or “Bellman,” a person that is hired by the hotel to assist guests, such as with luggage, running errands, etc.
Bellman – a person who carries one’s luggage to a hotel room.
Benelux – term for the countries of Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg.
Berth – usually refers to the bed in a ship’s cabin; also the space at which a ship is docked.
Bespoke tour – a tour that is customized, personalized and tailor-made for the traveler.
Biking Trips and tours – Bicycle trips and touring means self-contained cycling trips or pleasure, adventure and autonomy rather than sport, commuting or exercise. Touring can range from single to multi-day trips, getaways or vacations.
Birthday travel – a type of milestone travel celebrating a birthday, quite often marking decade birthday milestones such as 40 th , 50 th , 60 th , 70 th etc. birthdays.
Blackout dates – Specific dates in which special fares or promotions do not apply. Typically exist around holidays or special events.
Block – A number of rooms, seats, or space reserved in advance, usually by wholesalers, tour operators, or receptive operators who intend to sell them as components of tour packages.
Blocked space – seats, rooms, and/or cabins held on airlines, in hotels, or aboard ships. Usually held speculatively and made available at reduced rates.
Boarding pass – a receipt with a seat number, now issued only at check-in at the airport. A ticket is not valid unless a boarding pass has been issued. A Boarding Pass is not a ticket, but allows you to board a plane or ship or other mode of transportation.
Boarding Pass – Bonded – protected or guaranteed by a bond, usually referring to the protection of passenger’s funds.
Booking form – A document which purchasers of tours must complete to give the operator full particulars about who is buying the tour. It states exactly what is being purchased (including options) and must be signed as acknowledgment that the liability clause has been read and understood.
Boutique Hotel – A boutique hotel is a type of hotel, usually smaller and more intimate than a chain hotel, which conforms to a niche.
Bow – Bow is a directional term. Front of a ship or the nose of an aircraft; specifically, the foremost point of the hull of the craft.
Breakage – Expenses budgeted for a tour but not used or expended, thus resulting in additional profit to the tour operator. Examples include meals budgeted but not consumed, currency fluctuations in favor of the tour operator, or the tour selling to much larger numbers of passengers than expected.
Break-even point (BEP) – The point at which revenues and expenses are the same. For example, the BEP is the number of products (or seats, cabins, tickets, etc.) that must be sold for a company to break even. The BEP is calculated as fixed costs divided by the selling price less variable costs. See reasonable number.
Break-even pricing – Pricing a product based on a forecast of the break-even point and the cost of achieving the break-even point.
Bridge – the navigational center of a ship.
Bucket list destinations – Bucket list travel is a list of destinations a person wants to travel to and experience before reaching a certain age or dying.
Bulk contract – An agreement whereby an airline sells large blocks of seats at a discount for resale by a third party.
Bulk fare – A reduced fare for purchases of a large number of tickets.
Bulkhead Seat – Seats located directly behind a bulkhead wall separator. As these seats don’t have the benefit of a seatback in front of them.
Bulkhead – A partitioning wall, usually referring to one within the cabin of an aircraft, or perhaps on another mode of transportation.
Bumping – the airline practice of denying boarding to confirmed passengers who hold tickets on a specific flight, due to an oversold condition. The carrier will ask for volunteers to take later flights, and will normally provide some sort of compensation in the form of vouchers or tickets for future travel. Rules for when compensation must be provided are complicated; ask the ticket agent for a copy of that carrier’s rules, as each has their own set of guidelines.
Business class – While amenities vary based on the airline, business class generally falls between first class and coach.
Cabin – the passenger area on an aircraft; the stateroom aboard a cruise ship.
Cabin Crew – The collective group of flight attendants and the purser as a whole. The cabin crew is responsible primarily for handling the duties within the cabin.
Cabin steward – the person responsible for maintaining/cleaning the cabins aboard ship.
Cabin-(Aircraft) – The section of the aircraft in which passengers travel.
Cabin – A sleeping room on a ship.
Cancellation penalty – the monetary penalty due when travel plans are cancelled, usually after final payment has been made.
Cape – A small version of a peninsula, usually long and narrow, that juts far out into a body of water.
Captain – (Aircraft-The captain is the pilot in command (PIC), which is the person in the cockpit sitting on the left with 4 stripes on their shoulder.
Card mill – a “business “that sells potentially fake travel agent ID cards, usually in a sort of pyramid scheme, whereby the buyer intends only to partake of any legitimate agent benefits.
Carrier – generic term for any company that transports passengers and/or freight.
Carry-on – currently, there are no uniformly enforced airline restrictions concerning carry-on luggage.
Cashless cruising – a term that applies to the system of onboard payment used for most all cruises; the final bill for any such purchases is presented against a credit card or cash deposit given upon check-in. The final statement itemizes the purchases of all passengers in a cabin, such as drinks, shore tours, etc.
Casual research – A form of marketing research that is used to test cause-and-effect relationships between a marketing program and customers.
Cay – pronounced “key” – term for a small island, used primarily in the Caribbean, such as Princess Cay.
Celebrity Travel – celebrity and high net worth travel is an ultra-luxurious travel category describing the highly demanding travel requirements of celebrity and high net worth travelers characterized by the ultra-luxurious travel modalities and destinations with attention to privacy, security and confidentiality.
Certified Tour Professional (CTP) – A designation conferred upon tour professionals who have completed a prescribed course of academic study, professional service, tour employment, and evaluation requirements. The CTP program is administered by the National Tour Association (Lexington, KY) and is open to individuals employed in any segment of the tourism industry.
Certified Travel Associate – (CTA) – a travel professional certified by the Institute of Certified Travel Agents, who has passed a series of rigorous tests, assuring the traveling public of professional competence.
Certified Travel Counselor (CTC) – A designation attesting to professional competence as a travel agent. It is conferred upon travel professionals with five or more years of industry experience who compete a two-year graduate-level travel management program administered by the Institute of Certified Travel Agents (Wellesley, MA).
Certified Travel Industry Specialist (CTIS) – A designation conferred upon American Bus Association member company employees who successfully complete five correspondence courses (three) required and two electives and written evaluation of eight marketplace seminars.
Chain-ratio method – A method for forecasting market demand by multiplying a base market figure by a series of consumption constraints.
Chamber of commerce – A DMO that operates at the local level and is comprised of businesses that are not necessarily associated with the tourism industry.
Chancery – The physical building that houses an embassy and its diplomatic delegation.
Change of equipment – when a flight, with a single flight number, lands and changes the type of airplane used before continuing on to its destination. Sometimes referred to as a change of gauge.
Charter service – The transportation of preformed groups (organized by someone other than the carrier), which have the exclusive use of the vehicle.
Charter – To hire the exclusive use of any aircraft, motorcoach, or other vehicle.
Chauffer driven tours – a chauffeur tour is a tour driven by a chauffeur employed to drive a passenger motor vehicle, especially a luxury vehicle such as a large sedan or limousine.
Chunnel – slang for the tunnel beneath the English Channel, from England to France, through which the Eurostar train passes.
Circle itinerary – A travel routing design that overnights in different locations and returns to the point of departure without retracing the travel route.
Circle trip – any trip that involves more than a single destination, but which returns to the initial point of departure.
City guide – A tour guide who points out and comments on the highlights of a city, usually from a motor coach or van.
City Pair – The departure and destination points of an air or rail journey.
City tour – A sightseeing trip through a city, usually lasting a half day or a full day, during which a guide points out the city’s highlights.
Class of Service – The inventory in which a passenger is booked according to the fare purchased. (E.g. a full fare coach class cabin is usually Y class of service)
CLIA – Cruise Lines International Association, located in New York City, NY.
Client list – A printout of the names of all tour participants.
Client mix – Objectives set by companies to achieve percentages of customers from different market segments.
Closed-end question – A question for which the answers are provided for the respondent, who chooses only from those answers.
Closeout – Finalization of a tour, cruise, or similar group travel project after which time no further clients are accepted. Any unsold air or hotel space is released, and final lists and payments are sent to all suppliers.
Coach – the “economy ” section of an aircraft, which may have literally scores of different fares for the same flight.
Collision damage waiver-(CDW) – Optional insurance provided by car rental companies that eliminates all responsibility of the driver in case of an accident. Car rental insurance covering any damage to a rental vehicle (CDW) many credit card companies cover their clients in this area if they use that card to pay for the rental. Check with you credit card company to see if you are covered and to what extent.
Commission – Money paid to a travel agency or ARC number by suppliers for generating bookings.
Commission cap – The limit placed on commissions paid to travel agents for the sale of air tickets, regardless of their price; designed to allow airlines to increase their profits at the expense of their primary distribution system – the travel agents.
Commissionable tour – A tour available through retail and wholesale travel agencies which provides for a payment of an agreed-upon sales commission to the retailer or wholesale seller.
Common carrier – Any person or organization that offers transportation for a fee.
Commuter – term referring to the small, regional airlines, sometimes called puddle-jumpers.
Comp policy – Arrangements for free tickets, rooms, meals, etc.
Complimentaries (comps) – Items provided free of charge, such as rooms, meals, tickets, airfare, gifts, souvenirs, etc.
Computerized reservation system (CRS) – An automated system used by travel agents that contains pricing, availability and product descriptions for hotels, car rentals, cruises, and air transportation.
Concierge – a hotel employee who provides additional advice, recommendations, and other services to guests, such as restaurant reservations. An employee of the hotel whose primary task is to serve as the liaison between the hotel and non-hotel attractions, facilities, services, and the guest.
Concierge Level – special service level normally offered at higher grade hotels that provide the guest additional amenities and information, typically at a higher rate.
Conditions – The section or clause of a transportation or tour contract that specifies what is not offered and that may spell out the circumstances under which the contract may be invalidated (in whole or in part).
Configuration – The interior arrangement of a vehicle, particularly an airplane. The same airplane, for example, may be configured for 190 coach-class passengers, or it may hold 12 first-class passengers and 170 coach passengers, or any other combination within its capacity.
Confirmed reservation – An oral or written statement by a supplier that he has received and will honor a reservation. Oral confirmation have virtually no legal weight. Even written or faxed confirmations have specified or implied limitations. For example, a hotel is usually not obliged to honor a reservation if a guest arrives after 6 p.m., unless late arrival has been guaranteed.
Confluence – A confluence, also known as a conflux, is the meeting point of two flowing bodies of water, such as streams or rivers; the place where they come together.
Conflux – A confluence, also known as a conflux, is the meeting point of two flowing bodies of water, such as streams or rivers; the place where they come together.
Connecting Flight – A flight that makes a stop at an intermediate point where travelers must change planes in order to connect to another flight to reach their destination. (I.e. San Francisco to Chicago and Chicago to New York).
Connecting room – Two rooms that are connected to each other by a door.
Consolidation – Cancellation by a charter tour operator of one more flights associated with a specific charter departure or departure period, with the transfer of passengers to another charter flight or flights to depart on or near the same day. Also, selling the same tour with identical departure dates through a number of wholesalers, cooperatives, or other outlets in order to increase sales and reduce the possibility of tour cancellations.
Consolidator – A wholesaler who purchases airline tickets in bulk and re-sells them to individuals and travel agencies at a discounted rate. These fares tend to have complex restrictions, but can be cheaper than buying direct from the airline. Consolidator fares are found to have the most savings on international flights.
Consortium – A collection of organizations made up of independently owned and managed agencies who band together to increase their buying power.
Consulate – Essentially a satellite office of the embassy, but its roles are limited in scope.
Consul – Head diplomat of the consulate.
Consumer protection plan – A plan offered by a company and/or association that protects the customer’s deposits and payments from loss in the event of company bankruptcy.
Consumer – The actual user of a product or service. See also customer.
Consumption constraints – Issues that limit the number of people in a market who will purchase a product.
Continental breakfast – At a minimum, a beverage (coffee, tea, or milk) and rolls and toast, with fruit juice sometimes included.
Continent – Large landmasses that the world is divided into, by convention, although it is generally-accepted that there are seven.
Contract – A legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties.
Control Tower – Often referred to as simply the tower, the people in the Control Tower oversee aircraft movements at the airport, including ground traffic.
Convenience sample – A collection of research subjects who are the easiest for the researcher to select.
Convention and Visitors Bureau (CVB) – A nonprofit DMO that operates at the county and city level. A CVB typically encourages groups to hold meetings, conventions, and trade shows in its city.
Co-op tour – Selling a tour through a number of wholesalers, cooperatives, or other outlets in order to increase sales and reduce the possibility of tour cancellations.
Cooperative (co-op) advertising – An agreement between two parties to share the cost of placing an advertisement.
Corporate agency – A travel agency that usually caters to medium-large sized businesses.
Corporate Rate – a hotel rate that is designed to appeal to the needs of the business traveler. It is not necessarily a discounted rate or the minimum rate offered by the hotel. Corporate rates normally guarantee the best available room at a fixed cost for a specific period of time, typically outlined in a contract between the hotel and company.
Corporate Travel – Corporate Travel is travel arranged by a business for business purposes. A division or department of a travel agency devoted to such travel.
Costing – The process of itemizing and calculating all the costs the tour operator will pay on a given tour.
Cost-plus pricing – See markup pricing.
Couchette – the sleeping compartment of a train that can contain up to 6 beds.
Coupon – See voucher.
Cruise Tour – A land and sea vacation, which combines a cruise with a multi-night land tour to inland destinations that the ship can’t reach.
Cruise – A cruise is a voyage on a ship or boat taken for pleasure or as a vacation and usually docking at several port destinations.
CST – Central Standard Time.
CTA – Certified Travel Associate.
CTC – Certified Travel Counselor – the ultimate in travel professionals, CTC certification can be compared to the “Master’s Degree “of the industry.
Cuisin e – a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes associated with a specific culture or geographic region.
Culinary Tourism – Culinary tourism is defined as the pursuit of unique and memorable eating and drinking experiences. By combining travel with these edible experiences, culinary tourism offers both locals and tourists alike an authentic taste of a specific culture or geographic region.
Cultural Tourism – Cultural tourism is the category or tourism concerned with a country or region’s culture, specifically the lifestyle of the people in those geographical areas, the history of those people, their art, architecture, religion(s), and other elements that helped shape their way of life.
Cultural Travel – This is travel with regard to a region’s culture and history.
Culture – Similar shared traits or characteristics unique to an ethnic group, region, or nation.
Custom tour – A travel package created specifically for a preformed group or niche market.
Customer – The buyer of a product or service. See consumer.
Customized tours – a customized tour is a tour category where an independent travel plan is designed and arranged just for the traveler’s needs, goals and desires. This type of travel includes private airport/hotel transfers, hotels, internal airfare, trains, cruises, performances, events, activities and privately guided tours.
Customs – The common term for U.S. Customs Service, the federal agency charged with collecting duty on specified items imported into the country. The agency also restricts the entry of forbidden items.
CVB – Convention and Visitor’s Bureau (generic term).
Database – A computerized, organized collection of individual customer information.
Day rate – Also called a day room. A reduced rate granted for the use of a guest room during the daytime, not overnight occupancy. Usually provided on a tour when a very late-night departure is scheduled.
Day tour – An escorted or unescorted tour that lasts less than 24 hours and usually departs and returns on the same day. See sightseeing tour.
Deadheading – Making a trip or a segment of a trip without passengers, such as driving an empty motor coach somewhere.
Debark – to get off an airplane or passenger ship.
Deck – the floor area of a ship. Some cruise liners have as many as 11 to 14 decks or more.
Deck plan – the drawing representing the location of the decks, public rooms, cabins, etc. of a cruise ship.
Demand generators – Strategies and programs developed by DMOs and suppliers to generate destination demand. Examples include festivals, events, cultural tours, and consumer promotion.
Demands – A consumer’s wants backed by the ability to purchase.
Demographics – Population measures, such as age, gender, income, education, race/ethnicity, religion, marital status, household size, and occupation.
Denied-boarding compensation – that payment and/or voucher given those bumped from a flight; may be somewhat negotiable – always ask! See “bumping”.
Department of State – the US government agency that, among other things, issues cautions and warnings concerning travel to many points worldwide. Connect to the Department of State for the latest updates for the areas you are interested in.
Departure point – The location or destination from which a tour officially begins.
Departure tax – Fee collected from a traveler by the host country at the time of departure.
Deplane -To disembark, or get off, a plane.
Deposit policy – A specified amount or a percentage of the total bill due on a specified date prior to arrival.
Deposit – An advance payment required to obtain and confirm space.
Descriptive research – a form of marketing research that is used to provide detailed answers about customer markets.
Destination alliance – A DMO that operates as a for-profit association of select suppliers who form a paid-membership network to promote their services to travelers.
Destination management company (DMC) – A for-profit company that operates similar to a CVB by providing planning and execution services for the convention and meeting market.
Destination marketing organization (DMO) – An organization that promotes a location (city, region, state province, country) as a travel destination.
Destination Weddings – a destination wedding a category of travel where couples celebrate their marriage at a destination of their choosing away from home.
Destination – The geographic place to which a traveler is going.
Dine-around-plan – A meal plan, usually prepaid, that allows one to dine at various restaurants in an area.
Direct access – Refers to a travel agent’s ability to get directly into an airlines database to get true last-seat availability and correct pricing – a big difference between internet fare ” quotes ” and an agent’s CRS ( Computer Reservations System ).
Direct Flight – A flight that goes from a traveler’s origin to their final destination with one or more intermediate stops. No change in aircraft occurs. (I.e. San Francisco to New York with a stop in Chicago)
Direct marketing – Sales and marketing communication that feature direct interaction between a company and its customers without any distribution intermediaries.
Disaster Tourism – Travel when tourists go to an area that may be or may have been affected by natural disasters, civil strife, or warfare.
Disclaimer – a legal document that advises clients that a travel agent acts only as a middleman in the sale of travel products; any liability ultimately lies with the supplier, i.e. airline, hotel, car rental company, tour operator, railway, etc.
DMC – Destination Management Company
Docent – A tour guide who works free of charge at a museum.
Domestic fare – a fare charged for travel within a country.
Double booking – a not-nice practice of holding reservations to the same destination for the same times/days, on the same carriers but through different travel agencies, when only one reservation will ultimately be used.
Double Double – A room with two double beds.
Double occupancy – the way in which almost all cruise fares and tour packages are quoted, that is, based on two people traveling together. Most hotel rooms are quoted based on two adults to a room.
Double-occupancy rate – The price per person for a room to be shared with another person; the rate most frequently quoted in tour brochures.
Double-room rate – The full price of a room for two people (twice the double-occupancy rate.)
Downgrade – To move to a lesser level of accommodations or a lower class of service.
Driver guided tours – A driver guided tour is a tour guided by an individual that operates a vehicle while providing commentary in a front-line position who leads participants (individual or groups) on tours, ensures that itineraries are followed, provides commentary in an informative and entertaining manner, and creates positive experiences for tour participants.
Driver-guide – A tour guide who does double duty by driving a vehicle while narrating.
Drop-off charge – the fee added to a car rental when the vehicle is returned to a city other than where it was originally rented. In some states, there is no drop off fee most of the time, such as in Florida.
Duty-free imports – Item amounts and categories specified by a government that are fee of tax or duty charges when brought into the country.
Early Check-In – A perk that allows a guest to check in at an earlier time than the standard check-in time.
Eco/Sustainable Tourism – Eco or Sustainable Tourism is tourism directed toward exotic, often threatened, natural environments, especially to support conservation efforts and observe wildlife.
Eco-Conscious Travel – Though often interchangeable, being “eco-conscious” literally means that one is simply aware of their environmental impact.
Eco-Friendly Travel – Though often interchangeable, being “eco-conscious” literally means that one is simply aware of their environmental impact.
Economic impact study – Research into the dollars generated by an industry and how these dollars impact the economy through direct spending and the indirect impact of additional job creation and the generation of income and tax revenue.
Ecotour – A tour designed to focus on preserving the environment, or to environmentally sensitive areas.
Ecotourism – Tourism directed at exotic and/or endangered destinations while fostering an environmental understanding and conservation.
Educational tour – A tour designed around an educational activity, such as studying art.
Elder hostel – hostel catering to seniors – see “hostel”.
Electronic ticket – a “paperless” airline ticket allowing one to check-in and fly with just proper photo ID. What may look like a ticket is actually just a paper passenger receipt. E-tickets cannot be lost, or used by anyone else, so they are safer than standard paper tickets, which may soon become extinct. One drawback is that e-tickets on one carrier cannot be honored by another, so in a cancelled-flight snafu, the original carrier must print hard copy tickets before another airline can accept them. This presents major paperwork problems for the affected carrier.
Embark – to board a plane or cruise ship.
End suite – in the hotel industry, indicates that a certain feature(s) is directly in the room, or adjacent to that room.
English breakfast – basic meal of cereal, juice, eggs, meats, and other beverages. Common with most hotels in the UK/Great Britain.
Environmental scanning – The process of monitoring important forces in the business environment for trends and changes that may impact a company.
Errors and Omissions Insurance – Insurance coverage equivalent to malpractice insurance, protecting an agent’s or operator’s staff if an act of negligence, an error, or an omission occurs that causes a client great hardship or expense.
Escort – See tour director.
Escorted group tour – A group tour that features a tour director who travels with the group throughout the trip to provide sightseeing commentary and coordinate all group movement and activities.
Escrow accounts – Funds placed in the custody of licensed financial institutions for safekeeping. Many contracts in travel require that agents and tour operators maintain customers’ deposits and prepayments in escrow accounts.
ES T – Eastern Standard Time.
Estimated Time of Arrival – Literally, the estimated time of the transport’s arrival. As opposed to the ATA (Actual Time of Arrival), the ETA is the time that the flight or transport arrives.
Estuary – A body of water connecting a flowing river and a larger body, such as a sea or ocean. Because it is the transition point.
ETA – estimated time of arrival.
ETD – estimated time of departure.
Ethnicity – A term that groups people together with a similar cultural identity; unlike terms such as nationality, ethnicity is more ambiguous.
Ethno-Tourism – Focusing on exploration of indigenous populations and their respective culture and traditions.
E-Ticket – Regarding transportation, especially on airlines, an electronic ticket, or e-ticket, is the digital version of a paper ticket, issued via email.
Eurailpass – a special fare ticket that allows either unlimited train travel, or travel for a certain number of days/weeks, in many European countries (except in Britain, where the Britrailpass offers similar travel in England, Scotland, and Wales).
European pla n – a rate at a hotel that includes no meals.
Exchange order – See voucher.
Exclusive fare – Discounted airfares offered by travel consolidators.
Excursion – a side trip from a main destination, usually at added cost and optional.
Excursion Fare – special airline fares with restrictions such as minimum and maximum stays.
Exotic Travel – Exotic travel refers to a category of travel that is strikingly, excitingly and mysteriously different or unusual. Exotic travel is travel that is completely different than what a traveler is accustomed to and is highly subjective in nature.
Experiential Travel – Experiential travel is also known as immersion travel and is a form of tourism in which people focus on experiencing a country, city or particular place by connecting to its history, people and culture.
Exploratory research – A form of marketing research that’s used to obtain preliminary information and clues. It is most often used when the marketing problem is ambiguous.
Extension – A fully arranged sub-tour offered optionally at extra cost to buyers of a tour or cruise.
Extensions may occur before, during, or after the basic travel program.
FAM (familiarization) tour – A free or reduced-rate trip offered to travel professionals to acquaint them with what a destination, attraction, or supplier has to offer.
Familiarity Tour – A familiarity tour as used in the travel industry it is a tour of a travel destination, travel accommodation, travel activity or travel mode (airline, cruise, ground transportation) to familiarize a travel advisor and provide knowledge and direct experience with the product or service so they can better serve their clients.
Family plan – offered by most hotels, allow children to stay in the same room as parents, at no additional charge. Age requirements vary between hotels.
Family Vacation – a family vacation is a travel category referring to travel involving family members. It is also commonly referred to as multi-generational travel.
Familymoon – A neologism term used to describe a type of honeymoon a newlywed couple can make along with their children from previous relationships.
Fare Aggregator – Fare aggregators’ redirect the users to an airline, cruise, hotel, or car rental site or online travel agent for the final purchase of a ticket. Aggregators’ business models include getting feeds from major OTAs, then displaying to the users all of the results on one screen. The OTA then fulfills the ticket. Aggregators generate revenues through advertising and charging OTAs for referring clients.
Fare Basis – the letters and numbers assigned to a specific fare like an identification number.
Fare basis (code) – The code that determines the price of an airline ticket.
Final Boarding Call – Last call to board before the jet bridge closes and the flight departs, leaving late passengers stranded.
First class – The class which offers the most premium service. Enhanced seating, meal selection, and drink offerings staples of this services.
First Officer – Pilot who is second in command. The pilot in the cockpit sitting on the right with 3 stripes.
Fishing Trips and tours – a fishing trip or fishing tour is a travel tour category where groups of fisherman are provided guided tours and typically lodging with the overall purpose of catching fish.
FIT – foreign independent tour – actually used generically now for a travel package put together by a travel agent from separate components such as car, hotel and airfare, adjusted exactly as the traveler wishes. May include city tours, theater tickets, and other “independent ” options, and may also include custom mapping/routing to accomplish the client’s goals. It now is more commonly used as an acronym for Flexible Independent Travel. It describes a type of travel or tourism that does not incorporate a packaged tour but is nonetheless customized by a travel-selling professional.
Fjord – a narrow inlet from the ocean, usually bounded by cliffs, and with spectacular scenery. Most are located in Alaska, Norway, and New Zealand.
Flight Attendant – Commonly referred to as stewards/stewardesses and air hosts/hostesses, flight attendants are available to ensure the safety and comfort of the passengers of an aircraft.
Flight Crew – Sometimes called the aircrew, the flight crew consists of everyone hired by the airlines on a flight, including pilots, pursers, and flight attendants.
Fly/drive tour – An F.I.T. package that always includes air travel and a rental car and sometimes other travel components.
Fly-drive package – a travel package featuring airfare, rental car, and perhaps hotels. Usually less expensive than booking each separately.
Folio – An itemized record of a guest’s charges and credits which is maintained in the front office until departure. Also referred to as a guest bill or guest statement.
Fore – Directional term. Towards the front of the craft, lengthwise, such as the bow of a ship or the nose of a plane. Opposite of aft.
Frequent Flier Program – A program that a traveler can enroll in that earns them rewards such as free flights on a particular airline for being a loyal customer of that airline.
Frequent Flier – One who flies frequently.
Frequent Independent travel (F.I.T.) – A custom-designed, prepaid travel package with many
Full house – A hotel with all guest rooms occupied.
Full service hotel – a hotel with restaurant facilities.
Function room – A special room that is used primarily for private parties, banquets, and meetings. Also called banquet rooms.
Funnel flight – a flight, such as on a regional or commuter carrier that “feeds “larger planes which continue on to other destinations. Also, the use of a single flight number for an itinerary that really involves a connection with two separate flight numbers, thus making the itinerary appear to be a direct flight with a change of aircraft as opposed to a connection. Just call it a connection and be done with it.
Fuselage – The aircraft’s main body section, the cylindrical, central piece that contains the cabin and holds the crew and cargo.
Galley – The kitchen/kitchenette area of a plane or train or ship. On a plane, the galley may be a small affair with a simple arrangement and a few carts.
Gate-Airport – The specific area in an airport where passengers board a plane for a flight. Gates are located in concourses.
Gateway – City, airport, or area from which a flight or tour departs.
GDS – Global Distribution Systems – A system containing information about availability, prices, and related services for Airlines, Car Companies, Hotel Companies, Rail Companies, etc. and through which reservations can be made and tickets can be issued. A GDS also makes some or all of these functions available to subscribing travel agents, booking engines, and airlines. The GDS leaders are Amadeus, Apollo/Galileo/Worldspan, Sabre.
Geotourism – this is “tourism that sustains or enhances the distinctive geographical character of a place.
Global distribution system (GDS) – An international computer reservation system that accesses many databases of suppliers, airlines, etc. in different countries, such as Sabre.
Graduation travel – graduation travel is a milestone category of travel which refers to travel celebrating a graduation typically from high school or college.
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) – solar based time in Greenwich, England, fun which time in all other time zones in the world is based.
Gross Registered Tonnage (GRT) – a measurement of the enclosed space in a ship. Cruise ships in the 70,000 ton range are considered “superliners”.
Ground operator – See receptive operator.
Group – several persons, usually 10 or more, traveling together. Group travel is often available at discounted rates.
Group leader – An individual who has been given the responsibility of coordinating tour and travel arrangements for a group. The group leader may act as a liaison to a tour operator or may develop a tour independently (and sometimes serve as the tour director).
Group Rate – A negotiated rate on travel, perhaps a stay or vacation plan, that incentivizes for a large crowd or group that books together.
Group tour – A travel package for an assembly of travelers that has a common itinerary, travel date, and transportation. Group tours are usually prearranged, prepaid, and include transportation, lodging, dining, and attraction admissions. See also escorted group tour.
Group Travel – group travel refers to a category of travel with a group arranged by an outside company or organization or travel with a group of friends and family that you have organized yourself. Some groups are small, private and escorted, while others large.
GST – Goods and Services Tax, such as levied in Canadian Provinces.
Guaranteed share – a cruise term that promises that a companion will be found for a single passenger, at a special rate. That rate will be honored even if the cruise line is unable to find a cabin mate. The rate is usually the going double-rate at that time, and is much less than the single person rate for that cabin.
Guaranteed tour – A tour guaranteed to operate unless canceled before an established cutoff date (usually 60 days prior to departure).
Guest account – See folio.
Guest houses – a guest house is a private house offering accommodations to paying guests.
Guest ranch – a guest ranch, also known as a dude ranch, is a type of ranch oriented towards visitors or tourism. It is considered a form of agritourism.
Guide or guide service – A person or company qualified to conduct tours of specific localities or attractions.
Guided tour – A local sightseeing trip conducted by a guide.
Half pension – a hotel rate that includes breakfast and one other meal, usually dinner. Sometimes called Modified American Plan (MAP) or demi-pension.
Hard-copy – a printed version of a document, such as an airline ticket or hotel voucher.
Head tax – Fee charged for arriving and departing passengers in some foreign countries.
Hidden-city ticketing – another airline no-no; buying a ticket from A to C with a stop in B. The passenger gets off at B, which was the intended destination anyway. The ticket is purchased because the fare from A to C is LESS than A to B.
High season – the time of year when a destination gets the greatest crowds, and thus can increase hotel and rental car rates, etc. As an example, summertime is high season for travel to Europe (just check the airfares!).
High season – See peak season.
Hiking Trips and tours – a hiking trip or hiking tour is a category of travel vacation or getaway where the traveler is walking or hiking as the major mode of transportation.
Honeymoon Travel – Honeymoon travel is a category of travel where a newly married couple travels while celebrating their marriage.
Hosted group tour – A group tour that features a representative (the host) of the tour operator, destination, or other tour provider, who interacts with the group only for a few hours a day to provide information and arrange for transportation. The host usually does not accompany the group as it travels.
Hostel – an inexpensive accommodation, usually dormitory style, popular with the student crowd – thus the term “youth hostel”.
Hotel – a hotel is an establishment providing accommodations, meals, and other services for travelers and tourists.
House – A synonym used for hotel.
Hub – an airport or city in which an airline has a major presence and many flights to other destinations. As an example, Delta has a hub in Atlanta. Many carriers use the hub-and-spoke system to maximize profits by keeping the aircraft in the air as much as possible. Flights to the hub are many, and from there flights too many other destinations are scheduled.
Hub-and-spoke itinerary – A travel routing design that uses a central destination as the departure and return point for day trips to outlying destinations and attractions.
Hurricane season – in the Caribbean primarily, and the Southeastern US, a period from June through October during which such storms are likely to occur.
IATA – International airline industry trade group, headquartered in Montreal, Canada, with executive offices in Geneva, Switzerland.
IATAN – International Airlines Travel Agent Network – administers the IATAN card, the only widely accepted form of legitimate travel agent identification.
In season – meaning only available at certain times of the year.
In transit – en route; in the process of traveling.
Inbound operator – A receptive operator that usually serves groups arriving from another country.
Inbound tour – A tour for groups of travelers whose trip originates in another location, usually another country.
Incentive or incentive commission – See override.
Incentive tour – A trip offered as a prize, particularly to stimulate the productivity of employees or sales agents.
Incentive trave l – travel as a reward for an employee’s outstanding performance.
Incidental Charge – Items and services billed to a room after their use, such as movies, phone calls, etc.
Incidentals – Charges incurred by the participants of a tour, but which are not included in the tour price.
Inclusive tour – a package tour that bundles transportation, accommodations, transfers, sightseeing, possibly some meals, etc.
Inclusive tour – See all-inclusive package.
Independent tour – A travel package in which a tour operator is involved only with the planning, marketing, and selling of the package, but is not involved with the passengers while the tour is in progress.
In-flight Service – Entertainment (movies, television, etc.), meals, beverages and other items made available during a flight for the convenience of the passenger.
Inside cabin – a stateroom aboard ship that has no window. Sometimes smaller, but at times the same size as an outside cabin.
Intercontinental – Having to do with two continents. In travel, transit from one continent to another. Not to be confused with transcontinental.
interline connection – a flight on one airline that connects to a flight on another carrier – these tickets are usually more expensive than flying all on one carrier but may be the only way to get to a destination in some cases.
Intermodal tour – A tour that uses several forms of transportation, such as a plane, motorcoach, cruise ship, and train.
International Air Transport Association – International airline industry trade group, headquartered in Montreal, Canada, with executive offices in Geneva, Switzerland.
International Date Line – at 180 degrees longitude, the date on one side of this imaginary line, running from the north to the South Pole, is different from the other. The line runs through the Pacific Ocean, and because of it, it is possible to leave one destination on one day, and arrive in another the day before
International Rate Desk – Utilizes all available resources to ensure the lowest fare for your selected itinerary, including splitting tickets, consolidator fares, and available discounts.
Involvement device – An element of direct mail that gets the reader involved in the process of evaluating and/or responding to the solicitation.
Itinerary – A list of a tour’s or entire trip’s schedule and major travel elements.
Jet Bridge – An enclosed, movable connector which extends from a terminal gate to a plane, allowing passengers to board and disembark without having to go outside.
Jet lag – an upset of one’s biological clock, due to travel across many time zones; not all folks are affected by it.
Jones Act – a law dating back to 1886, that forbids foreign-flagged ships from carrying passengers between US ports with no foreign port stops in-between.
Judgment sample – A sample based on the researcher’s choice of subjects for a study.
Jump Seat – A flight term referring to an auxiliary (extra) seat for persons who are not operating the aircraft, such as the cabin crew or perhaps a trainee.
Kilometer – a measure of distance used in almost all other countries, at about 5/8 mile.
King room – a hotel room with a king bed.
Knot – a nautical measure of speed equaling approx. 1.5 mph. A ship traveling at 15 knots is traveling at about 22 mph.
Kph – kilometers-per-hour – land speed measurement in most other countries. 60 kph equals approx. 36 miles-per-hour.
Land arrangements – all the details of a land portion of a trip (hotel, car, tours, sightseeing, etc.).
Land Destinations – A land destination or travel destination is a place to which one is journeying, typically for its inherent or exhibited natural or cultural value, historical significance, natural or built beauty, offering leisure, adventure and amusement.
Land operator – See receptive operator.
Land Transfers – travel by train, bus, limo or taxi to and from an accommodation, plane or cruise ship.
Land-only – a rate that does NOT include airfare; usually includes most other land-based charges such as accommodations, transfers, taxes, and perhaps other optional items like theme park tickets, rental care, etc.
Last-seat availability – the ability of a travel agent to get, literally, the ” last seat ” for you on a particular flight, either at a certain fare or actually the last remaining seat on an aircraft. See “direct access”.
Late booking fee – a fee due if travel arrangement are made at the last minute. Normally covers express delivery of documents and other last-minute arrangements that may have to be made by a tour operator.
Late Checkout – A more exclusive perk for some guests that allow a few extra hours to check out from the normal hours.
Latitude – imaginary horizontal lines of angular distance, measured in degrees north or south of the equator.
Layover – a period of time spent during a trip, sometimes overnight, while waiting for a transportation connection – usually a change of planes.
Layover – The period of time spent between connecting flights.
LDW – loss damage waiver – additional insurance pertaining to car rentals, covering theft and vandalism in addition to accident damage.
Lead-in price – the lowest available price for a travel product, often pertaining to cabins on a cruise ship. Usually, there are only a few staterooms available on board each cruise liner in this category, but often better accommodations are only slightly higher in price. Rock-bottom price shoppers normally insist on these rates, though they sell out quickly.
Leeward – the side of a ship or an island that is located opposite from the direction of the prevailing wind -the “Leeward Islands” in the Caribbean for example.
Leg – Portion of a journey between two scheduled stops.
Leisure travel – Usually signifies traveling for relaxation, vacation, or to visit friends/family. Travel for pleasure as opposed to business.
Letter of agreement – A letter from the buyer to the supplier accepting the terms of the proposal. This may also be the supplier’s first proposal that has been initialed by the buyer.
Lido deck – usually the deck on a cruise ship that surrounds the pool area.
Limited service hotel – a hotel property without a restaurant.
List broker – A seller of mail lists for direct marketing.
Load factor – The number of passengers traveling on a vehicle, vessel, or aircraft compared to the number of available seats or cabins.
Locater map – A map of an area or a city, showing locations of attractions and hotels.
Lodging – Any establishment that provides shelter and overnight accommodations to travelers.
Logistics – Management of the details of an operation.
Low season – the period when a destination experiences its lowest prices and the fewest number of guests.
Low season – See off peak.
Lower (bed) – in a cruise stateroom, the bed(s) on the floor as opposed to the higher bunks (uppers), if any. On many ships, two lowers can be arranged to make a king or queen bed.
Lowest available fare – the current, lowest airfare available for purchase right then.
Lowest available fare – The most inexpensive flight currently available.
Lowest fare – the lowest published airfare between two cities; may not have seats available at that fare, as the airlines usually have a limited number of those seats on any given flight.
Luxury class – the most expensive, high-class accommodations or category of fare.
Luxury Cruise – Luxury cruises are the most comfortable and convenient way to see the world. Ships are usually smaller in size so the ratio of crew and staff to guests is generally higher than other cruise ships offering that premium service and attention to detail to be expected of exquisite vacations.
Luxury Ocean Cruise – a luxury ocean cruise is an ocean cruise on a luxury cruise ship or luxury cruise liner or passenger ship used for pleasure voyages, where the voyage itself and the ship’s amenities are a part of the experience, as well as the different destinations along the way.
Luxury River Cruise – a luxury river cruise is a river cruise on a luxury cruise ship or luxury passenger ship used for pleasure voyages, where the voyage itself and the ship’s amenities are a part of the experience, as well as the different destinations along the way.
Luxury travel – while luxury travel is completely subjective to the traveler, it can be loosely defined at travel that constitutes the state of great comfort and extravagant living.
Luxury vacations – a luxury vacation is a vacation that encompasses a state of great comfort and extravagant living.
Macro-environment – The broad forces in society and the business world that impact most companies.
Management Company – A firm that owns several lodging properties.
Manifest – Final official listing of all passengers and/or cargo aboard a transportation vehicle or vessel.
Market demand – The amount of a specific product or service that may be purchased during a certain period of time in a particular geographic area.
Market forecast – The realistic demand within a given time period for the products produced by all companies within a certain industry or product category.
Market – All existing and potential customers for a product or service.
Marketing mix – The 4 Ps of marketing- product, price, promotion, place (distribution).
Marketing plan – A written report that details marketing objectives for a product or service, and recommends strategies for achieving these objectives.
Marketing research – The function that links the consumer, customer, and public to the marketer through the systematic gathering and analyzing of information.
Markup pricing – Pricing a product by adding a standard markup to costs. Also called cost-plus pricing.
Markup – A percentage added to the cost of a product to achieve a selling price.
Master account – The guest account for a particular group or function that will be paid by the sponsoring organization. See folio.
Maximum stay – The longest period of time a traveler can stay at a particular destination and still qualify for the promotion or discounted fare.
Media – Communications channel such as broadcast (radio, TV), print (newspapers, magazines, direct mail), outdoor (billboards), and multimedia (Internet).
Meet-and-greet service – A pre-purchased service for meeting and greeting clients upon arrival in a city, usually at the airport, pier, or rail station, and assisting clients with entrance formalities, collecting baggage, and obtaining transportation.
Meeting/conference tour – A tour designed around a specific meeting or conference for the participants.
Microenvironment – Those forces close to a company that impact operations and marketing programs.
Midships – Directional term. Amidships, sometimes termed midships, is the center of the vessel or aircraft.
Minimum connect time – defined as the minimum time necessary between connecting flights – 30 minutes domestically, usually – ideally, at least an hour. The shortest time required in order to successfully transfer to a connecting flight. It is recommended to select a connecting flight that exceeds the minimum connection time.
Mission statement – The concise description of what an organization is, its purpose, and what it intends to accomplish.
Modified American plan (MAP) – meal plan that includes two daily meals, usually breakfast and dinner.
Motorcoach tour operators – Tour operators that own their own motorcoaches.
Motorcoach Tour – A tour that features the motorcoach as the form of transportation to and from destinations.
Motorcoach – A large, comfortable bus that can transport travelers and their luggage long distances.
MST – Mountain Standard Time.
Multi-day tour – A travel package of two or more days. Most multi-day tours are escorted, all-inclusive packages.
Multigenerational Travel – multigenerational travel is a travel category referring to travel with parents, siblings, kids, grandkids, and assorted family members with the goal to broaden horizons, provide opportunities to reconnect and provide an enriching assortment of shared experiences.
Murder-mystery tour – A tour that features a staged “murder” and involves travelers in solving the crime.
Mystery tour – A journey to unpublicized destinations in which tour takers aren’t told where they will be going until en route or upon arrival.
NACTA – National Association of Career Travel Agents – trade group representing primarily independent and home-based agents, now part of ASTA.
National tourism organization (NTO) – A federal-government-level DMO that promotes country as a travel destination.
Nautical Mile – Unit of length that is about one minute of arc of latitude along any meridian, but is approximately one minute of arc of longitude. Air-Sea distance measurement of approx. 1.1 statute miles.
Negotiated Rate – A discounted rate offered to a company based on the volume of business you agree to provide the selected vendor.
Net fare, net rate – Implies the commission has already been added to the price of the fare.
Net wholesale rate – A rate usually slightly lower than the wholesale rate, applicable to groups of individuals when a hotel is specifically mentioned in a tour brochure. The rate is marked up by wholesale sellers of tours to cover distribution and promotion costs.
Niche market – A highly specialized segment of the travel market, such as an affinity group with a unique special interest.
No show – a passenger who doesn’t show for a flight, hotel, or rental car booking. A guest with confirmed reservations who does not arrive and whose reservation was not canceled.
Non Stop Flight – Do not land in between your departure and arrival destinations. (I.e. San Francisco to New York)
Non-Changeable Ticket – A ticket that cannot be exchanged for a different route or flight once it’s been purchased.
Non-refundable – a fare that cannot be refunded either in cash or via a credit card credit; very seldom is there an exception.
Non-Refundable Ticket – A ticket that cannot be returned for cash or credit once it’s been purchased, but may be changeable for a fee.
Nonstop – A flight that travels directly to its destination without connections or layovers.
Non-transferable – A ticket that can only be used by the person who was originally scheduled to fly at the time of purchase.
NTSB – National Transportation Safety Board; investigates accidents and other incidents related to public transportation.
Objective and task method – A process for creating a promotion budget that sets objectives first, then defines the tasks needed to achieve those objectives, and then commits funds necessary to perform the tasks.
Occupancy rate – the percent of hotel rooms expected to be filled during a specific time period.
Occupancy – The percentage of available rooms occupied for a given period. It is computed by dividing the number of rooms occupied for a period by the number of rooms available for the same period.
Ocean view cabin – a cabin aboard a cruise ship with a window, such as a porthole or picture-window, and perhaps a balcony/verandah.
OCV – ocean view, usually in reference to a hotel room.
Offline connection – a change of aircraft also involving a change of carriers.
Off-peak – A less expensive time to travel as result of lower consumer volume during these periods.
On-site guide – A tour guide who conducts tours of one or several hours’ duration at a specific building, attraction, or site.
Onsite – An on-site is an expert travel provider that lives in the country they serve and has firsthand knowledge and long-standing relationships with all aspect of travel in their country.
Open jaw – a trip in during which there is no travel by air between two cities, such as a flight to Washington DC, then travel by rental car to Charlotte, NC, then a return by air from Charlotte back to the original departure city.
Open return – an air ticket with no return date specified. Rarely done these days, usually quite expensive and not allowed on most discounted fares.
Open-end question – A question that allows the respondent to provide a free-response answer.
Open-jaw itinerary – A travel routing design that departs from one location and returns to another. For example, travelers may fly into one city and depart from another one. Or a traveler may purchase round-trip transportation from the point of origin to one destination, at which another form of transportation is used to reach a second destination, where the traveler resumes the initial form of transportation to return to the point of origin.
Operations – Performing the practical work of operating a tour or travel program.
Operator – a company providing transportation or travel related services (airline, cruise line, railway, hotel, car Rental Company, etc.).
Operator – See Tour Operator.
Option date – drop dead date on which a reservation must be deposited or cancellation will result.
Optionals – Optional tour features that are not included in the base tour price, such as sightseeing excursions or special activities.
OTA – Online travel agencies, examples include Priceline, Expedia and Orbitz
Outbound – the departure leg of a journey.
Outbound operator – A company that takes groups from a given city or country to another city or country.
Outbound tour – A tour that takes travelers out of the area, usually from a domestic city to another country.
Outside cabin – see “ocean view ” cabin.
Outside salesperson – job description of a travel agency employee who sells travel but is not based primarily in the agency location most of the time.
Overbook – Accepting reservations for more space than is available.
Overbooking – the practice of selling more airline seats than are available on a specific flight, to make up for no-shows. Usually backfires on the carrier and at times can create much consumer ill-will. Requires passengers to be “bumped” – not always voluntarily. To some extent, happens in the hotel industry as well.
Overhead – Those fixed costs involved in regular operations, such as rent, insurance, management salaries, and utilities.
Override – A commission over and above the normal base commission percentage.
Packaged travel – A package in combination of two or more types of tour components into a product which is produced, assembled, promoted and sold as a package by a tour operator for an all-inclusive price.
Passenger facility charge (PFC) – a fee for the use of many airports, added in to the cost of an air ticket – another name for an additional tax on travelers.
Passenger name record (PNR) – The official name of one’s reservation in a computer reservation system (CRS).
Passenger vessel – Ships, yachts, ferries, boats, etc.
Passport/visa service – a service that will take your passport and hand carry, if necessary, to the appropriate embassy in order to expedite a visa. Can be expensive if you have waited until the last minute to obtain a travel visa.
Patronage Program – A program that rewards the customer for loyalty and repeat purchase, such as frequent-flyer programs.
Peak season – A destination’s high season when demand is strong. Also called the high season.
Peninsula – A piece of land that is connected to a mainland or larger piece of land on only one side, while the other sides are surrounded by water.
Per Diem – “by the day;” in the cruise industry, the per-day cost of a cruise, per person.
Per-capita costs – Per-person costs.
Per-capita tour – See scheduled tour.
Perceived value – The ratio of perceived benefits to perceived price.
Personal effects coverage – Additional car rental insurance covering loss of personal property from the rented vehicle.
Point-to-point – refers to the fares between two cities; the service between two cities without additional segments or any continuation.
Port – the place where a ship docks; a place visited by cruise ship; the left side of a vessel.
Port charges/taxes – fees levied by local authorities upon the cruise lines for each passenger visiting a port of call, normally added to the total cruise fare.
Port of Debarkation – Port of Debarkation is the geographic point where personnel arrive on a cruise vessel
Port of Embarkation – Port of Embarkation is the geographic point where personnel depart on a cruise vessel
Port of entry – Destination providing customs and immigration services.
Port-Directional – When facing forward, the side of the ship or aircraft that is on the left.
Porter – A person who handles luggage at an airport, train station, etc.; also called skycap or baggage handler.
Porthole – usually a round, sealed window in a shipboard stateroom.
Posada – a small country hotel (Spanish).
Positioning strategy – The development of a clear, unique, and attractive image for a company and/or product in the minds of target customers.
Positive space – space aboard a ship or aircraft that can be confirmed ahead of time.
Post-Cruise Vacation – a post-cruise vacation is a vacation or getaway prior to a cruise in the town or region of the port of debarkation of the cruise.
PPDO – per person, double occupancy. Most tours and cruises are quoted this way; the average cost to stay in a particular location per day.
Pre- and post-trip tour – An optional extension or side trip package before and/or after a meeting, gathering, or convention.
Pre-Cruise Vacation – a vacation or getaway prior to a cruise in the town or region of the port of embarkation of the cruise.
Pre-deduct commission – When a distributor such as a travel agent takes up front the commission on a sale and sends the supplier the balance of the sales price.
Preferred Supplier – The selection of specific supplier(s) for priority promotion to customers and/or integration in travel packages in exchange for reduced rates and/or higher commission.
Preferred Vendor – The vendor(s) a company specifies as their first choice for travelers.
Preformed group – A pre-existing collection of travelers, such as affinity groups and travel clubs, whose members share a common interest or organizational affiliation.
Prepaid ticket advice – a form used when purchasing an air ticket to be picked up and used by someone else at another airport. E-tickets have reduced the need for this greatly.
Primary research – The collection of data specifically to solve the marketing problem at hand.
Prix fixe – meals offered at a fixed price, usually fairly low, consisting of several courses with no substitutions allowed. Common in Europe.
Profit margin – A dollar value that represents the markup of a product’s price over its costs.
Promotion mix – Promotion tools including advertising, direct marketing, sales promotion, and public relations.
Promotional group tour – A travel package composed of tour elements that match the specific needs and wants of niche customers who aren’t part of an organized or preformed group.
Promotional partnership – The combination of two or more companies to offer special incentives to customers.
Prop – referring to propeller-driven aircraft.
Property – A specific lodging structure, such as a hotel, and the ground on which it is built.
Property – A general term that may be used by a place of accommodation that denotes the facility.
Protection overbooking – The practice of blocking space that will likely be in excess of what will actually be needed.
Pseudo-agent – someone claiming to be a travel agent who really isn’t. They often produce bogus ID cards, and can disappear when problems arise!
PST – Pacific Standard Time.
Psychographics – Measures of a person’s lifestyle. See also AIO variables.
Public relations (PR) – A management function that determines the attitudes and opinions of an organization’s publics, identifies its policies with the interests of its publics, and formulates and executes a program of action to earn public understanding and goodwill.
Public tours – See scheduled tour.
Published fare – an airfare that is listed in the carrier’s tariff.
Pull strategy – A marketing approach that creates demand at the customer level by generating awareness, interest, and desire so customers pull a product through a distribution channel by demanding it.
Purser – aboard ship, the person responsible for providing a wide array of services such as information, making change, stamps, etc. Found at the purser’s desk.
Purser-(Airline) – On a flight, the purser is the head flight attendant, responsible for overseeing the attendants and making sure travelers’ needs are met.
Push strategy – A marketing approach that creates demand at the distributor level by providing resellers with an incentive to push (sell) a product to end consumers.
Quad – a room suitable for four persons.
Quay – a pier – pronounced the same as “key”.
Query – The process of sorting and retrieving information from a database.
Quid – a monetary term for a British pound sterling.
Quota sample – A research sample that involves forming groups based on certain characteristics. A random sample can then be selected form the quota segments.
Rack rate – The published (brochure) rate for a travel component. The price of a hotel prior to discount.
Rate desk – the office of an air carrier that calculates fares for passengers and travel agents.
Reach – The measure of how many people in a market will be exposed to a certain advertisement via a specific medium.
Reasonable number – A forecast of the break-even point for a tour.
Rebate (ing) – the practice of returning part of an agency’s commission on a scale back to the client in the form of a rebate or “discount.” The trade-off is usually little or no personal/customer service. This is practiced often by “800 ” number travel sellers and others who deal in huge volume.
Receptive operator – A local tour company that specializes in services for incoming visitors, often for tour operator groups.
Reconfirm – to double-check a reservation.
Record locator – The number assigned to a reservation in the airlines number. This number is unique, as it will never be assigned again.
Record locator – the number assigned to one’s reservation in an airline’s computer system.
Red-eye flight – An overnight flight that leaves at night and arrives early the next morning.
Referral agent/agency – an ” agent ” that refers business to a travel agency in return for a commission or fee – often as part of a card mill operation
Registry – the formal registration of a ship’s ownership, and the country it is registered in (such as Panama, Liberia, Norway, etc.).
Reissue – the generation of a new ticket that is exchanged for another, due to a change of plans, dates, flights, etc. May involve additional fare, penalties and fees.
Relationship marketing – The process of building and nurturing ongoing, solid relationship with customers.
Repositionin g – the moving of a cruise ship to another home port for all of part of a season, such as the repositioning of ships to Alaska for the summer. Often these cruises are excellent bargains, but will involve one-way airfare home from the port of debarkation.
Res – short for “reservation”.
Research constraints – Those issues, such as cost and timing that will limit the scope of marketing research.
Reseller – See retailer and wholesaler.
Reservation fee – A customer payment for a certain percentage of the travel package price that’s made immediately after booking.
Responsible Tourism – Travel that extends beyond being merely environmentally responsible, to being culturally-conscious and economically-aware, locally.
Retail price – The actual price a customer pays for a travel element or tour.
Retail tour – See scheduled tour.
Retailer – A middleman, such as a travel agent, who sells directly to the customer.
Retirement travel – retirement travel is a category of travel referring to when a traveler is has retired from a career and commences to travel. Travel done after retirement age.
Rollaway – a cot or other bedding that can be added to a hotel room to accommodate another guest. There is often an extra charge for this.
Romantic Destinations – romance destination and romance travel is a category of travel that involves travel involving a feeling of excitement and mystery associated with love and often refers to travel associated with a wedding, honeymoon, wedding anniversary, babymoon or another type of romantic getaway.
Room Night – In the hotel (hospitality) industry, a room night, room/night occupancy, is a measure of occupancy where a room is the unit of measure.
Room Occupancy – In the hotel (hospitality) industry, a room night, room/night occupancy, is a measure of occupancy where a room is the unit of measure.
Room rates – The various rates used by lodging properties to price rooms. These include- day rate (usually one half the regular rate for a room used by a guest during the day up to 5 p.m.-sometimes called a use rate), flat rate (a specific room rate for a group agreed upon by the hotel and group in advance), group rate (same as flat rate), net group rate ( a wholesale rate for group business to which an operator may add a markup if desired), net wholesale rate ( a rate usually lower than the group rate and applicable to groups or individuals when a hotel is specifically mentioned in a tour folder), and published rate ( a full rate available to or advertised to the public-also called the rack rate.)
Rooming list – A printout of the names of all tour participants that also lists special lodging requests and provides a spot for the hotel or cruise ship to fill in the passenger’s room number.
Round trip – A flight to a single destination and a return.
Run-of-house (ROH) – refers to a hotel room, the type of which is assigned at the discretion of the hotel shortly before you arrive. Usually, the rates are lower.
Run-of-ship – cabin is assigned at the last moment, giving the cruise line the ability to shift accommodations as needed. Usually, you are guaranteed a minimum category of cabin, and sometimes get an upgraded stateroom at no additional cost. Most upgrades are from inside-to-inside cabins, or from outside-to-outside but occasionally an inside-to-ocean view upgrade will occur. It is not always worth the gamble though.
Run-of-the-house rate – A flat rate for which a lodging property agrees to offer any of its available rooms to a group. Final assignment of the rooms is at the discretion of lodging management.
Sabre® – A computerized travel reservation system.
Safaris – Today the negative hunting connotations of the word ‘safari’ are being rapidly replaced by more modern associations with socially and environmentally responsible travel. Safari travel typically implies that the journey will include game viewing and some time spent in wilderness areas (game reserves and national parks). A traditional is usually focused on seeing wildlife, but safaris are definitely not limited to game viewing. Safaris are now for admiring wildlife and birds in the wild, along with a host of other adventures. Safaris have largely developed into vacation trips that actually benefit the wildlife by supporting local conservation efforts and wildlife sanctuaries. As opposed to hunting the animals, visitors get to encounter them and help make a difference in protecting the species. Safari companies either actively contribute towards conservation projects or help generate tourism revenue which is used to manage wildlife projects and game reserves. The modern safari is also a socially responsible journey designed to interact ethically with local communities and have a positive impact on local economies. The cultural interactions offered by reputable safari operators do not exploit local people. The local communities benefit from sustainable tourism through employment and financial gains from selling goods and services.
Sales margin – A term used by resellers to describe profit as a percentage of sales revenue.
Sample – The portion of a population chosen to represent the population being studied for research.
Saturday night stay – A requirement by the airlines that your travel must involve a Saturday night stay over in order to obtain our lowest fare.
Saturday night stay – In order to receive a specialty fare, a Saturday stay over is sometimes required.
Scandals tour – A light-hearted history tour that shows locations where interesting scandals took place.
Scheduled carrier – An airline that offers regularly scheduled flights between destinations.
Scheduled flights – Air flights that are publicly scheduled and promoted by major airlines.
Scheduled tour – A tour that’s set in a tour operator’s regular schedule of tour departures and that’s often sold to the general public. Also called public tour or retail tour.
Sea bands – a product resembling a bracelet that is worn on the wrists and operates via acupressure.
Wearers claim that seasickness can be avoided by their use, thus eliminating the need for drugs such as Dramamine, etc.
Sea legs – the ability to move around on a ship without losing balance and without sea sickness.
Secondary information – Research data that was collected by another company or person and usually for a purpose that’s different than the research objectives and tasks at hand.
Sectioning system (GPS) – system of satellites that allows miniature radio receivers on earth to pinpoint one’s location within a few feet. Most cruise ships make use of this system to navigate the world’s oceans.
Segment – a “leg” or part of a journey, usually in reference to an air itinerary. One take-off and landing during air travel constitutes a “segment”.
Segment – One leg or portion of a trip. The segment begins when you board the plane and ends when you de-board the plane. (I.e. A connecting flight from San Francisco to New York through Chicago equals 2 segments)
Self-drive – a rental car (British term).
Service non comprise – in French, meaning “service not included”.
Shells – Preprinted brochures with photos, illustrations, and graphics but no text; also called slicks.
Shore excursio n – tours that are purchased as an option when visiting ports of call while on a cruise; can sometimes be bought before you cruise.
Shore excursion – A land tour, usually available at ports of call, sold by cruise lines or tour operators to cruise passengers.
Shoulder season – a period of time between high and low seasons, where prices at a destination are between their highest and lowest, and the crowds are thinner.
Shoulder season – Those periods between the peak and off season when destination demand is moderate.
Sightseeing companies – Organizations that provide local guided tours.
Sightseeing guide – See driver/guide.
Sightseeing tour – Short excursions of usually a few hours that focus on sightseeing and/or attraction visits.
Simple random sample – A sample that draws a group of respondents randomly from all members of the population.
Single Room – A room that is only guaranteed to comfortably accommodate one guest. May also be called a “Standard Room.”
Single Supplement – An additional charge added to a solo traveler, when prices were originally quoted for dual occupancy.
Sleeper – the sleeping compartment aboard a train.
Soft adventure – an outdoor travel experience that is not especially physically demanding, such as a canyon horseback trail ride or a hot-air balloon flight.
Sommelier – A wine professional, usually hired by the most upscale restaurants and establishments, on staff to primarily suggest wine and food pairing to patrons.
Spa – a resort area centered around a mineral springs, hot springs and the like, typically where one can find massage, hydrotherapy, exercise, steam baths, etc.
Special event tour – A travel package that features major happenings, such as concerts or sporting events, as the reason for the journey.
Special fare – Any fare that deviates from normal pricing (typically discounted).
Special interest tour – a tour catering to the needs of a specific interest, such as bird-watching, whale-watching, river rafting, mountain biking, rain forest exploration among many others.
Split itinerary – An itinerary in which part of the group does one thing while the other part does something else.
Split Ticket – Issuing multiple tickets for one round-trip journey. This is done to reduce the total cost of the entire reservation.
Sports Tourism – sports tourism refers to travel which involves either observing or participating in a sporting event staying apart from their usual environment.
Stabilizer – a device on most all cruise vessels, to reduce pitch and roll when at sea – the movement that can cause seasickness. Stabilizers are often pulled in at night in order to allow faster speeds when traveling between ports of call.
Standby – Referring to a passenger who does not have a confirmed seat on the intended flight.
Star Service – a critical guide describing in detail many hotel and cruise ship properties. Can be subjective, as it is based on someone’s opinion, but provides a travel agent with a non-commercial point-of-view.
Starboard – the right side of a ship.
Stateroom – A private cabin or compartment with sleeping accommodations on a ship or train.
Step-on guide – A tour guide who boards a motorcoach to give detailed, expert commentary about the city or area being visited.
Stern – the rear of a ship.
Stopover – a planned stayover in a city for a day or more, while enrooted to another destination. Sometimes adds significantly to the cost of an air ticket.
Strategic plan – A report that describes a company’s mission statement, goals, objectives and strategic actions.
Student visa – permission to enter a country, issued to a student, normally for the purpose of attending school in that country.
Subcontractor – A local operator who provides services for a wholesaler.
Suite – a hotel accommodation with more than one room, or sometimes a single room with distinct sleeping and living areas and often a kitchenette. A suite in a hotel or other public accommodation denotes a class of accommodations with more space and amenities than a typical accommodation room. Luxury or upscale accommodations often have a scaled range of suites progressively increasing in size, luxury and amenities starting with a junior suite and culminating in the largest and most luxurious suite which is often called a presidential or royal suite.
Supplier – any company that supplies travel and/or related services to the traveling public. The actual producer and seller of travel components.
Surface – travel over land that does not involve an aircraft.
SWOT analysis – A summary of a company’s strengths and weaknesses, and the environmental opportunities and threats that will most influence it.
T&E – Travel and Entertainment expenses.
Target market – The group of customers who will be the focus of a company’s marketing efforts.
Tariff – a schedule of prices/fares.
Telemarketing – Direct marketing via the telephone.
Tender – a small boat or ferry that carries passengers from an anchored cruise ship to the pier at a port of call. Many ships are too large for existing port facilities at some destinations, and so they anchor just off shore and “tender “their passengers in for their visit.
Terminal – A building where clients report for trips via train, plane, etc.; also called a depot or a station.
TGV – the term applied to the French high-speed train system.
Theme cruise – a cruise devoted to a specific interest, such as big bands, country western, Star Trek, exercise and weight-loss, cooking and cuisine, and many more. There is usually a theme cruise to suit just about any interest.
Theme tour – A tour that’s designed around a concept of specific interest to the tour takers, such as history or sports.
Through passenger – a passenger who is not disembarking at a particular stop while enrooted to the final destination.
Ticket stock – Blank airline tickets.
Tickler system – A method for monitoring reservations and payments that’s arranged by date and points out late payments so customers can be contacted.
Tiered override pla n – When commissions rise proportionately with a corresponding increase in sales.
Tiered pricing – When suppliers offer different prices to receptive operators, tour operators, and group leaders, so each party can earn a profit by marking up the supplier’s price while still offering a fair price to customers.
Tour broker – See tour operator.
Tour catalog – A publication by tour wholesalers listing their tour offerings. Catalogs are distributed to retail agents who make them available to their customers. Bookings by retail agents are commissionable.
Tour Company – A tour company or tour operator typically combines tour and travel components to create a packaged vacation. They advertise and produce brochures to promote their products, vacation and itineraries.
Tour conductor – the person who accompanies and is in charge of a tour, often on a motor coach tour. See tour director.
Tour departure – The date of the start by any individual or group of a tour program or, by extension, the entire operation of that single tour.
Tour director – Also called tour manager, tour conductor, and tour escort. The person who is responsible for a group on tour and for most aspects of a tour’s execution.
Tour escort – See tour director.
Tour guide – A person qualified (and often certified) to conduct tours of specific locations or attractions.
See also step-on guide, city guide, on-site guide, and docent.
Tour manager – See tour director.
Tour manual – A compendium of facts about a destination, tour procedures, forms, and other information that a tour operator gives to its tour directors.
Tour menu – A menu that limits group clients to two or three choices.
Tour operator – A person or company that contracts with suppliers to create and/or market a tour and/or subcontract their performance.
Tour order – A voucher given to the purchaser of a tour package that identifies the tour, the seller, and the fact that the tour is prepaid. The purchaser then uses this form as proof of payment and receives vouchers for meals, porterage, transfers, entrance fees, and other expenses. See also voucher.
Tour planner – A person who researches destinations and suppliers, negotiates contracts, and creates itineraries for travel packages.
Tour rate – See group rate.
Tour series – Multiple departures to the same destination throughout the year.
Tour – A prearranged, prepaid journey to one or more destinations that generally returns to the point of origin, is usually arranged with an itinerary of leisure activities, and includes at least two travel elements.
Tourism – The business of providing marketing services and facilities for leisure travelers.
Tourist card – a card issued to a visitor in lieu of a visa, usually for a short duration visit.
Tourist – This is the majority of adult travelers, when not vacationing. Tourists may be couples, families, or just a person or two who visit locations.
Tours – a tour is a journey for pleasure which includes the visiting of a number of places in sequence, especially with an organized group often led by a guide.
Tracking study – A survey of customers before and after implementing a promotion campaign to assess changes in consumer behavior.
Trans-canal – passing through the Panama Canal.
Transcon – Having to do with crossing a continent. For example, travel of this sort would be from one end of a continent to another.
Transcontinental – Having to do with crossing a continent. For example, travel of this sort would be from one end of a continent to another.
Transfer – Local transportation and porterage from one carrier terminal to another, from a terminal to a hotel, or from a hotel to an attraction.
Transient Occupancy Tax – Also known as a Bed Tax, it is a City or County tax added to the price of the room.
Transient – A person who stays in a place for just a short while; not a permanent resident, such as a visitor or tourist.
Transit visa – A visa allowing the holder to stop over in a country or make a travel connection or a brief visit.
Transportation – Any method of moving travelers from one point in a journey to another, such as air, ship, rail, and motor coach travel.
Travel advisor – a travel advisor simplifies the time-consuming and complicated process of planning travel for their customers in addition to providing consultation services and entire travel packages. They may book flights, cruises, rental cars and hotels, as well as resort stays and events. Agents cater to a wide demographic, serving both individuals and corporations. They may also concentrate in a special segment of travel; many advisors specialize in leisure, business or group travel, or destination-specific journeys.
Travel advisory – a travel warning issued by the US Department of State, indicating a special caution should be taken in a country due to political unrest, natural disaster, or other special situation. These can be obtained from any good travel agent, on any area you are considering visiting.
Travel agency – Usually used in the travel industry to refer to an ARC-appointed storefront retailer.
Travel agent – A person or firm qualified to arrange for lodging, meals, transportation, cruises, tours, and other travel elements, typically on a commission basis. A travel agent simplifies the time-consuming and complicated process of planning travel for their customers in addition to providing consultation services and entire travel packages. They may book flights, cruises, rental cars and hotels, as well as resort stays and events. Agents cater to a wide demographic, serving both individuals and corporations. They may also concentrate in a special segment of travel; many agents specialize in leisure, business or group travel, or destination-specific journeys.
Travel component – Transportation, lodging, dining, attractions, entertainment, guide services, and other travel elements offered as part of a travel package.
Travel Destination – a place to which one is journeying.
Travel Experience – A travel experience or experiential travel (also known as immersion travel) as it is commonly referred to, is a form of tourism in which people focus on experiencing a country, city or particular place by connecting to its history, people and culture.
Travel Institute – the primary educational and certification arm of the travel industry. Was formerly the “Institute of Certified Travel Agents” (ICTA), located in Wellesley, Mass.
Travel Insurance – Travel insurance is insurance that is intended to cover medical expenses, trip cancellation, lost luggage, flight accident and other losses incurred while traveling, either internationally or within one’s own country.
Travel Itinerary – a travel itinerary is a travel plan or organization of your travel and involves all of the details, times and dates concerning things like airline, cruises and train transportation confirmations, hotel, villa and accommodation reservations, rental car information, restaurant reservations and much more.
Travel Policy – A fluid internal document, pertinent to the company’s culture that outlines the guidelines for business travel and expenses within a company.
Travel rewards – Travel reward programs are often referred to as a loyalty rewards program, and they are generally a campaign devised to generate repeat customers for a particular company by offering a point gratification system for the customers’ business. They are also meant to provide customers with a “thank you” for their loyalty to a company’s product or service. That benefit is typically some sort of discount on certain items or services. Travel specialist – a travel specialist is a travel agent or travel advisor that concentrates in a special segment of travel; many travel agents or travel advisors specialize in leisure, group or business travel, or destination specific travel.
Travel Tours – a travel tour is a journey for pleasure which includes the visiting of a number of places in sequence, especially with an organized group often led by a guide.
Traveler – One who travels.
Travelogues – Many travel websites are online travelogues or travel journals, usually created by individual travelers and hosted by companies that generally provide their information to consumers for free. These companies generate revenue through advertising or by providing services to other businesses. This medium produces a wide variety of styles, often incorporating graphics, photography, maps, and other unique content.
Trip director – An escort for an incentive company. Larger companies reserve this title for the person who directs all personnel and activities for a particular incentive trip.
Trundle Bed – Bed that stores itself under another bed, usually on casters. Often found in smaller hotel rooms or in cramped transport accommodations.
Turn – Airline parlance. A flight that leaves base and returns back to base in the same day. Also known as a turnaround.
Turnaway – A potential reservation that couldn’t be satisfied because the tour (or hotel, ship, etc.) was fully booked.
Twenty-four hour time – used extensively in Europe and other countries, 1pm becomes 1300 hours, 4pm is 1500 hours, etc., up to 2359 ( 1159pm ). Midnight is then considered 2400 or “zero ” hours. 1-20am is then 0120 or “one hour, twenty minutes “and so on. Most schedules and timetables in the majority of other countries are listed in the 24-hour format.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites – a UNESCO World Heritage Site is a place (such as a building, city, complex, desert, forest, island, lake, monument, or mountain) that is listed by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) as being of special cultural or physical significance.
Unlimited mileage – No mileage restriction when renting a car.
Unrestricted fare – an airfare that has no special advance purchase, Saturday stay or certain days to travel requirements, and is usually refundable. Many full coach and most first-class fares are unrestricted. An airfare with no limitations. It is typically refundable and has no blackout days.
Upgrade – To move to a better accommodation or class of service.
USTOA – United States Tour Operators Association – a trade association which requires its members to be very financially stable and to have a million dollars or more in funds set aside for consumer protection against defaults. Visit www.ustoa.com for more information.
Value added tax (VAT) – a tax on goods in Europe, which under certain circumstances can be refunded.
Value season – similar to shoulder or low season, when pricing is lower. See off season.
Value – The relationship between the benefits associated with a product or service and the costs of obtaining the product or service. See also perceived value.
Value-added tax (VAT) – A type of tax system which adds a fixed percentage of taxation on products and services at each step of production or service delivery.
Value-based pricing – Pricing a product based on buyer perceptions of value rather than actual product costs.
Variable costs – Costs that change with sales or production levels.
Variance report – A summary of how much a company has gone above or below budget.
Verandah – a roofed-porch, such as connected to a cruise ship stateroom.
VIA rail – the Canadian railway system.
Villas – a large and luxurious country residence. A villa is a fancy vacation home. The word has been around ever since ancient Roman times to mean “country house for the elite.” In Italian, villa means “country house or farm.” Most villas include a large amount of land and often barns, garages, or other outbuildings as well.
VIP experiences – a VIP Experience is the most exclusive way to go behind the scenes or experience a travel destination, accommodation or mode of transportation.
Visa – usually a stamp in a passport allowing entry into a country for a specific purpose and a finite amount of time.
Visa service – a service that can expedite the processing of a visa, sometimes even at the last minute. A fee is charged that varies, depending on the nature of the service needed. Visas are usually stamped into the pages of a valid passport and are issued for varying reasons and periods of time. Not all countries require them, especially for United States Citizens.
Volume incentive – See override.
Volume purchase – The purchase of large quantities of a product or service.
Voucher – Documents that are exchanged for goods and service to substantiate payment that will be or already has been made.
Voyage – a voyage is a long journey involving travel by sea or in space.
Waitlist – A list of clients awaiting transportation or accommodations at times when they are not available. Waitlisted clients are confirmed as a result of subsequent cancellations.
Waiver – a written acknowledgement that a passenger has declined something, such as insurance coverage for a trip, for example. Also, the formal acknowledgement of the waiving or dismissal of a requirement, such as a waiver of a penalty for late booking, etc.
Waiver – A written acknowledgement that a passenger has declined something.
Walk-up – one who purchases an air ticket at the last moment, usually at the airport ticket counter.
Wants – Ways in which a person satisfies a basic need.
Wellness Travel – wellness travel is a category of travel for the purpose of promoting health and well-being through physical, psychological, or spiritual activities
Wet bar – the area of a hotel room that has a bar or other counter space with running water, used for the preparation of drinks.
Wholesale – Sale of travel products through an intermediary in exchange for a commission or fee generally at reduced tariffs.
Word-of-mouth promotion – Personal communication about a product or service from one customer to another.
World Travel Guide – a yearly publication that provides detailed information on most every country in the world, with entries on currency, transportation, climate, visa and passport requirements, sightseeing opportunities, etc. A primary book of knowledge for the professional travel agent.
Yield management – Calculating and analyzing the profits earned per customer.

World Travel Agency, LLC is owned and operated by Michael and Cheryl LaBaw. We are a husband and wife team dedicated to working together with our clients to insure they travel well. World Travel Agency, LLC is an independent affiliate of Andavo Travel, a Virtuoso® Member. Travel should be more than just a journey, it should be a series of unforgettable experiences. We work hard to ensure our clients’ trips are always stimulating, authentic and – above all else – fun... READ MORE

- Recent Blog Posts
- Luxury Ocean Cruise
- Luxury River Cruises
- Land Destinations
- Group Travel
- Corporate Travel
- Family Vacation
- Adventure Travel
- Celebrity Travel
- Travel Experience
- Wellness Travel
- Romantic Destinations
- Destination Weddings
- Value of an Adviser
- Mission Statement
- Publications
- Travel Photos
- Travel Videos
- Distinctive Travel Offers
- Travel Tips & Ideas

The Role of a Travel Agent

In 2022, the role of a Travel Agent is more important than ever, are you ready for the challenge?
Contributed By: The Travel Institute
What does it mean to be a travel agent? Well, your role starts and ends with you being a professional. An understanding of professionalism in the travel workplace is a necessity for all those who wish to call themselves travel agents, counselors, advisors, experts, or other terms conveying expertise.
Let’s start with, what is the definition of Professionals ? These are people who earn their living by practicing some skill or engaging in some activity that requires expertise. True Travel Professionals demonstrate a commitment to the ethics and standards of the occupation and to the interests of the client.

Are You Exhibiting Ethical Behavior?
Professionalism implies a commitment to ethical behavior, which means following certain principles of proper conduct. If you earn a reputation for unethical behavior, you forgo the trust of clients and are likely to lose their business. Therefore, it is imperative that you create and follow a code of conduct.
A code of conduct is a useful tool to standardize ethical behavior for a group of professionals. It shouldn’t be viewed only on a new hire’s first day of work. For a code to be effective, it must be reviewed and practiced by all members of the organization, at all organizational levels. Travel organizations, large or small, can benefit from a written code of conduct explaining the company’s policy regarding ethical challenges most likely to occur. These codes should incorporate the core values—those guiding principles and fundamental beliefs—that make up the heart of the organization. These can include things in a Role of a Travel Agent like:
- Excellence in service —To ensure clients receive your best efforts and customized products of the highest quality before, during, and after a transaction
- Honesty and integrity —To exhibit ethical, truthful, and honorable behavior and to exercise good judgment
- Passion —To love what you do and to inspire excitement in your clients
- Commitment —To be loyal, dedicated, and devoted to your clients, the organization, the community, and the profession
- Individual responsibility —To hold yourselves accountable, to deliver what you promise and to own up to your mistakes
- Efficiency and accuracy —To do things correctly the first time and without wasting time, effort, or resources
- Communication —To respond quickly, accurately, and honestly to clients, vendors, suppliers, supervisors, and coworkers
- Currency and knowledge —To constantly research current trends, methods, and destinations to best serve the client and the organization.
Why Does a Client Need You?
Sometimes it’s good to step back and look at all the things you bring to the table as a travel counselor. You demonstrate your worth every day, and you certainly have proven your value by stepping up for your clients over the past several months. If the thought of “Do clients need me?” crosses your mind, you must watch this clip on CNBC’s Seema Mody .
A large percentage of your value lies in doing the things the customer cannot do. Every day, you
- reduce the stress of planning a vacation
- lessen the risk that something will be forgotten and that things will go wrong
- remove obstacles that get in the way of what the client wants to do
- add convenience by relieving the client from doing all the work
- provide travel options that are good, better, and best
- rescue the client from difficult situations
- be your client’s advocate ALWAYS.
As you can see, there is much to being a travel professional, and it all starts with your education. To learn more visit www.thetravelinstitute.com
- All Inclusive Resort
- Association and Events
- Host Agency
- Hotel and Resort
- River Cruising
- Tour Operator
- Sales and Marketing
- Your Travel Business
- Suppliers and Destinations
- Trade Associations and Events
- Free Downloads
- Your Travel Agency
- Destination
- Host Agency List
Add Travel Professional NEWS® to your Homescreen!

The Complete Guide to Booking Travel Online
What is an online travel agency, and what are the best sites and apps to use to search for hotels and flights we break it all down for you..
- Copy Link copied

There’s a lot to navigate when researching and booking travel online.
Photo by Rawpixel.com/Shutterstock
My first travel adventure was to Venezuela. I booked the ticket with a travel agent over a pay phone. The agent searched a dozen flight itineraries over a few days, all so I could save $15.
Times have changed. Today, flight searches start online , often on your mobile device. Passengers book either directly with the airline or hotel or with online travel agencies. Rarely do we get on the phone. In fact, American Airlines and United Airlines charge $25 to make a domestic flight booking by phone. And pay phones hardly exist anymore.
So, what is the best way to book online? Here is our complete guide to online travel agencies, search tools, and the variety of booking options available on both mobile devices and desktops.
What is an OTA?
An online travel agency, or OTA, is a website or mobile app that allows users to search for and book travel services such as flights, hotels, car rentals, cruises, and activities. The booking is made directly with the online travel agency but confirmed by the service provider, such as an airline or a hotel. As a customer, your relationship is with the OTA.
What are the main OTAs?
Many online travel agencies nowadays are owned by two main companies: Expedia and Priceline. The Expedia Group is the largest online travel agency in the United States with 70 percent market share, according to travel data firm Phocuswright. Expedia Group operates Expedia.com , Orbitz, Hotels.com , Trivago, CheapTickets , Hotwire , Vrbo , and Travelocity .
Priceline is a major competitor to Expedia, with global revenues larger than the Expedia Group. The company owns Priceline.com, Booking.com, Cheapflights, Momondo, and Kayak—the latter two being metasearch engines (more on that below).
There are also independent newcomers such as Hopper (a mobile-only booking tool) and Kiwi.com (which allows you to book flights on air carriers that don’t normally have a commercial relationship).
Are OTA fares lower than booking directly?
Generally, no. The fares that are displayed by an OTA will be similar if not slightly more expensive when compared to an airline’s website. They’re usually only a few dollars higher or lower. The OTAs charge a booking fee to the airlines, and often that fee is passed directly to consumers. For example, Lufthansa tacks on an additional $18 to any booking made through an OTA for Lufthansa flights. The same flights are exactly $18 cheaper on the airline’s website.
Where you can score a good travel deal through an OTA is when booking a last-minute hotel and flight package. Many OTAs have cut agreements with airlines allowing last-minute travelers to access lower rates than are typically available when passengers book a flight alone.
Are all airlines available to be booked through OTAs?
No. Many OTAs do not display flights from some of the low-fare leaders. For example, Southwest and Allegiant flights are not available through OTAs; the same goes for Ryanair in Europe. And, earlier this year United Airlines threatened to pull out of Expedia altogether, only recently signing a multi-year agreement to stay in. The airlines would rather not lose any margin to online travel agencies in an already low-margin industry and would rather maintain a direct relationship with the customer.
Are smaller OTAs safe to use?
Expedia and Priceline are the two largest players in the online booking space, but there are dozens of independent OTAs, such as CheapOAir, OneTravel, JustFly, and SmartFares. Confusingly, you might actually stumble on ads for these OTAs while using Expedia or Priceline sites. That’s because the larger OTAs earn revenue through advertising, sending passengers to smaller OTAs and charging those OTAs for the favor.
Buyer beware: some of these lesser-known OTAs are masters at hidden fees. For example, a flight search on JetBlue allows for free seat selection in many instances. If you perform the same search on FlightNetwork, an independent OTA, and select a seat, you will be charged an additional $25—despite the fact that JetBlue doesn’t charge a seat selection fee if you book directly.
What if you need to change your itinerary?
Itinerary changes are often a pain. If your plans change, it won’t matter whether you’ve booked directly with an airline or with an OTA—you’re going to pay fees for the privilege, if you can even change your ticket at all.
For example, CheapTickets.com, which is part of the Expedia Group, charges $25 to change or cancel a ticket if that change is requested after 24 hours of making the booking—it is free if you do so within 24 hours of booking. However, the fees go up from there. JustFly, an independent OTA, charges a $75 fee for changes to domestic flights in addition to airline change fees, plus the difference in fare, for tickets that can be changed. For an international trip, the fee rises to $200. That means to change an international flight with Delta (which charges a $100 change fee) booked through JustFly, you’ll be assessed $300 in fees, plus the difference in fare. At that rate, you may as well book a new flight. FlightNetwork indicates in its terms of service that changes may incur a change fee but doesn’t specify what those fees are. That hardly makes the few dollars you saved by booking with the OTA in the first place worth it.
What is an OTA price match policy?
To assure travelers that they are getting the lowest fare possible, many OTAs have a price match policy. The rules vary and so do the benefits.
For example, if you book with Orbitz and find a less expensive flight, car rental, or activity on any U.S.-based website within 24 hours of your booking, Orbitz will refund you the difference you paid. And it works: I have personally found a flight in the same class, on the same airline, for the same origin and destination cities, and requested Orbitz to refund the difference of around $35. Within a few weeks, I received a check in the mail. A similar program applies for CheapOAir, but there’s a catch—the price difference must be found on a major OTA such as Expedia or Travelocity.
Expedia has a particularly good price match policy, but you have to pay extra for it at the time of booking. Expedia offers the price match option as an add-on that costs between $5 and $30 when you book. With the price match applied, if the airfare on Expedia drops between 120 days of the flight and up to six hours before the flight, Expedia will automatically refund you the difference in fare. Unfortunately, fares generally do not drop substantially as the travel date approaches, so while this might give you peace of mind, it’s probably not worth the expense.
How do Google Flights and other travel metasearch engines work?
Frequent fliers are likely familiar with websites such as Google Flights, Kayak, Momondo, or Skyscanner. On these websites, passengers search on the site but are redirected to the service provider to complete the booking, such as an airline, rental car company, or hotel.
Metasearch started with a product called ITA Matrix, which is a tool for searching airfares online but not for actually booking online. ITA Matrix allows for multi-city searching, such as setting two different departure or arrival airports, and for offering a calendar view of fares for easier comparison. That company was acquired by Google in 2011, and savvy travelers swear by it to help find the least expensive fares online. Most consumers are more familiar with Google Flights, which has gained traction more recently not least because it has the benefit of being displayed first in search results on Google.
Metasearch engines receive distribution fees from the airlines for sending traffic to the supplier websites. There are no additional hidden fees for using a metasearch engine because you’re booking directly with the airline or hotel.
A major benefit of the metasearch engines is their price tracking tool, which lets users know whether the displayed fares are low, average, or high for the flight, allowing travelers to make a more informed decision on whether to book a flight or not . Google Flights and Kayak, for instance, both have price tracking tools.
Why not just book directly?
The airlines would definitely much rather you book directly with them. Over the past five years, they have gotten much better at marketing and selling their product directly to consumers online and through mobile sites and apps. But in the past, they weren’t so good at it. In fact, Delta, Northwest, United, American, and Continental got together to invest $145 million to launch Orbitz in 1999 to counter the threat from Expedia. Now Orbitz is owned by Expedia.
The airlines also try to encourage customers to book directly so that they can maintain a closer relationship with them. It allows carriers to connect bookings with loyalty programs and create special offers and discounts catered to individual passengers.
There is another benefit to booking directly. The U.S. Department of Transportation requires carriers to hold a reservation at the quoted fare for 24 hours without payment or allow a reservation to be cancelled within 24 hours without penalty, so long as the booking is made at least seven days before travel. The law applies, however, only to U.S. and foreign air carriers that have websites marketed to U.S. consumers. This means that, in theory, an online travel agency does not have to offer such a policy, although most OTAs do.
What are the options for booking on your mobile device?
Airlines and the major OTAs all have apps to help you book and manage your trip on your mobile device, but their functionality is lacking compared to these websites’ desktop editions. For example, Expedia’s app doesn’t allow you to view flights on a month-view calendar. Kayak has an app with more bells and whistles and a better user interface, including a month-view calendar with color-coded pricing. It also has a handy “augmented reality” function to help you see if your carry-on bag will fit in the overhead bin (a feature originally developed by KLM). Point your phone’s camera at the luggage, and it’ll give you the dimensions.
While apps are improving and gaining in popularity, you still might find it easier to locate the best deals on flights and hotels by using your desktop, where you can have multiple tabs open and have all the available search tools at your disposal. Apps are fine for booking directly with an airline once you know which flights you want to book.
If you’re determined to use your mobile device, you may want to look into Hopper. Hopper is a mobile-first flight booking tool that has a solid price prediction tool. You can research travel options and book directly on the app. Another benefit of Hopper: Of its team of 300 employees, nearly half are dedicated to customer support and are based in Canada versus some OTAs and airlines that outsource much of their customer service further afield.
The bottom line?
Like many travelers, I enjoy a flight deal as much as the next person, but I also don’t like any added hassle. I typically start my travel searches using the ITA Matrix or Google Flights to get a general sense of the fares. It helps to know what is a good deal and what is expensive for a particular route. I do my research, typically on a desktop computer. When I’m ready to book, I’ll book directly with the airline. I’ve found that customer service is better when booking directly with the service provider. But I’ve also saved money by using OTAs and have booked with them, too. Whichever way you choose to book, you can be safe in the knowledge that finding and purchasing travel online is a lot easier today than searching for a deal with a travel agent on a pay phone.
>> Next: How to Get the Best Last-Minute Travel Deals

The Travel Glossary - find the best Terms, Definitions and Acronyms
Travel terms, glossary, definitions and acronyms of the travel industry from A – Z. Click on a letter to see the terms and descriptions in our glossary.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Add-collect, adjoining room.
Average Daily Rate. A hotel industry term used to calculate average hotel room rate. Equal to room revenue divided by rooms sold.
advance purchase
The advance time before travel that a fare requires a ticket to be issued, normally 3,7,14 or 21 days.
Agent Error. An incorrect entry made by a consultant during the reservation process.
AEA (see “Association of European Airlines”)
A US based travel agency that has entered into an agreement with BCD Travel to use the BCD Travel trademarks and provide travel services to customers in the affiliate’s territory.
Airlines Reporting Corporation (ARC)
An independent corporation jointly owned by most of the major United States airlines; ARC collects payments for tickets sold by travel agencies and distributes the monies to the airlines; ARC also governs appointment of travel agencies to sell domestic air transportation.
airport code
The three-letter code used by airlines and the air travel industry to identify airports around the world, e.g. LHR=London Heathrow, JFK=New York John F. Kennedy. http://www.world-airport-codes.com/
airport security check
Airport security checks are procedures and measures for screening passengers and baggage to ensure security against terrorist threats and other dangers. Find out how to get through quickly
airport tax
Tax levied by certain airports throughout the world. In many cases this can be built into the total ticket price, although some airlines will not co-operate, thus making payable locally by the passenger.
On outbound journey’s, airside includes all those areas of the airport terminal after you have passed through passport control. On inbound journey’s, airside includes all those areas of the terminal before you pass through passport control.
A short-hop aircraft for up to 20 passengers, usually flying unscheduled services with a 200 / 500-mile range.
all-inclusive
A hotel program which usually includes all meals, snacks, beverages and activities.
A joint partnership between specified carriers which may include, but not limited to, interlining, code-sharing, joint frequent flyer program participation, and even equity participation of stock ownership.
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, a government-subsidized corporation that operates all passenger train service in the United States.
Automatic Number Identification. A contact center term for a telephone network feature that passes that number of the phone the caller is using to the contact center, real-time.
American Plan. A hotel rate that includes breakfast and dinner, sometimes lunch.
Asia Pacific. A geographical term used interchangeably with ASPAC and often used in reference to the entire Asian market.
Advance Purchase Excursion Fare
applicable fare
The fare to be applied.
Accounts Receivable. Money which is owed by a customer to a company for products or services provided on credit.
ARC (see “Airlines Reporting Corporation”)
An eight-digit identification number issued by ARC to travel agencies who have met accreditation standards.
Arrival Unknown. An ARNK is added to a reservation when there is a break in the itinerary and continuity is not recognized; it does count as a segment when ticketing.
Around-the-world
A continuous journey circumnavigating the globe in one general west-to-east or east-to-west direction in which both the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans are crossed not more than once each.
ARR (see “Average room rate”)
Asia South Pacific. A geographic term used interchangeably with APAC.
Automated Ticket & Boarding Pass. IATA standard transportation ticket and combined boarding pass which features a magnetic strip containing passenger and journey details.
Average Ticket Price. The average price of all tickets purchased; domestic and international are sometimes calculated separately.
availability
The total number of seats allowed to be sold at a particular rate.
average room rate (ARR)
Ratio of hotel’s sales revenue to the number of occupied rooms.
back-to-back ticketing
An against-the-rules practice whereby a traveler books a return ticket nested inside another return ticket to avoid minimum stay requirements for the purpose of saving money. For example, the traveler uses the first ticket to fly from origin to destination on Monday in week 1, then he uses the second ticket to fly from destination to origin on Friday in week 1 and back to destination on Monday in week 2, and then he uses the first ticket again to fly back to origin on Friday in week 2. The normal Saturday night stay requirement is then avoided. While this will sometimes save money, most airlines do not allow this practice and doing so might result in penalties.
backtracking
Having to return to your original airport of entry in a country to make the return trip home. A time-consuming and costly procedure to overcome by arranging an op-jaw itinerary, which allows you to fly out to one point and return from another.
Carry-on-baggage and checked baggage have many restrictions. Most notable are the number and size of the baggage. Many airlines allow only 1 carry-on bag, plus one personal item (purse, back-pack, computer bag). For checked baggage restrictions and fees, refer to the carrier’s website for details.
banker’s buying rate (BBR)
Exchange rate used to convert from one currency to another; called the ‘buying rate’ because it is the rate used when banks purchase currency from an individual
banker’s selling rate (BSR)
Exchange rate used to convert from one currency to another; called the ‘buying rate’ because it is the rate used when banks sell currency to an individual
Best Available Rate. A hotel industry pricing method for yielding room rates (floating) based on demand while ensuring the best rate is presented for sale to agents, consumers.
A fare without tax.
Measurement of hotel occupency.
blackout dates
Certain dates or periods when travel on specific fares is not permitted (usually holidays).
blocked space
Multiple reservations, often subject to deposit forfeiture, which wholesalers or travel agents make with a supplier in anticipation of resale.
boarding pass
A permit to board a ship, plane, or other form of transportation. In the case of air travel, the card indicates boarding gate and aircraft seat number.
booking code
A letter code used to make an airline reservation at a particular fare level in a computerized reservation system. (CRS/GDS)
Bank Settlement Plan. Outside the USA, a system by which the travel agent community pays carriers for tickets it issues.
Business Travel Account. If a company has a corporate credit card program where certain purchases such as air, rail, and associated transaction fees are centrally billed to one “master” credit card number, this is referred to as the Business Travel Account (BTA). This account allows for the purchase of certain air travel expenses for corporate employees without the need to issue individual credit cards to each traveler for the designated expenses. Because the account has no physical card, it’s often called a “ghost card.”
BTC (see “Business Travel Center”)
Business Travel News. A travel industry publication that delivers news and research to the corporate travel population.
bucket shop
An unlicensed, unbonded travel agency used by some airlines to dispose of excess capacity seats that are available on certain flights.
buffer zone
For taxation purposes, an extension of the US border 225 miles north into Canada and 225 miles south into Mexico border; all cities within this area are assessed the 7.5% US domestic tax when tickets are purchased and sold in the US.
A net fare contract for certain number of seats. Similar to blocked space except that the tour operator, wholesaler, or travel agent usually contracts for airline seats at a low, non-commissioned price without the option of releasing space back to the airline.
A partition (usually a wall) on an airplane separating compartments.
Travel slang for the removal of a passenger from a flight through overbooking; usually applied to those holding concessionary tickets.
bundled pricing
A pricing proposal, always a transaction fee, where elements other than air (e.g. car hire, hotel, rail) are included in the fee with the air transaction.
business class
Level of airline service between First class and Economy class. On European routes business class has now replaced first class as premier service level. Most airlines have their own brand names. (e.g. British Airways – Club World and Club Europe: Air France – Le Club etc.)
Business Travel Center (BTC)
Standard full service and online service in a local call center, undedicated, team environment.
Business Travel Management
Business travel management is the process of planning, organizing, and overseeing business travel for an organization. This includes booking travel arrangements, managing expenses, and developing policies and procedures for business travel.
cancellation policy
The advance time a hotel requires a booking to be canceled by to avoid being billed for the room
carrier (CXR)
Another term for airline.
Credit Card. A system of payment whereby the issuer of the card grants a line of credit to the cardholder, to be used to make payment to a merchant or to withdraw cash.
Collision Damage Waiver. An industry term for optional insurance provided by car rental companies that eliminates all responsibility of the driver in an accident.
centralized billing
System under which a travel supplier, credit card company, agency or other supplier consolidates all costs/charges incurred by different employees or departments into one total invoice.
change of equipment
Also known as “change of gauge”. A single flight number used to represent flights on two different aircraft; usually on international destinations.
Notification to an airline or hotel that a traveler has arrived to take a flight or stay at a hotel; some airlines provide curbside check-in while others only allow check-in at the ticket counter.
Advice to a hotel that a guest is leaving the property and usually includes payment for the stay.
A traveler who has had his/her second birthday, but not yet his/her twelfth birthday (this definition may vary by carrier).
Churning refers to any repeated booking or canceling of the same itinerary in the same class or different classes of service in one or more PNRs or GDS.
circle pacific
Travel from IATA Area 1 (North and/or South America) to IATA Area 3 (Asia, Australia, South Pacific) by way of the North Pacific Ocean in one direction, via the South Pacific Ocean in the opposite direction, and at least one flight within IATA Area 3 that crosses the Equator.
circle trip (CT)
A journey from origin to destination with a return to origin in a continuous, circuitous route using two or more fare components
The orgin (from) and arrival (to) points of a trip, usually by air or train.
city terminal
Airline office, usually city center, where passengers may check-in, receive seating details and board special bus/ taxi/ helicopter/ rail/ shuttle services to the airport.
class of service
The interior of an aircraft is divided into sections, each with a different level of service and amenities; common classes of service are first, business, and economy.
Cruise Lines International Association. An association dedicated to the promotion and growth of the cruise industry.
Section of a hotel offering higher security and special facilities either for a premium payment or as an incentive/ privilege for frequent users.
club ticket
Fully flexible, redeemable business class ticket valid one year from date of issue. Phrase used primarily in the U.K.
Another term for bus.
Close of Business. A term meaning the end of the business day.
A marketing agreement between two airlines (very common amongst airlines that have an alliance) where a seat is purchased on one airline (the selling carrier), but the flight is actually operated by a different airline (the operating carrier).
combination
Two or more fares shown separately in a fare calculation.
Computerized Reservation System
System used to book and process travel reservations, also known as a Global Distribution System (GDS).
A hotel employee who attends to guests’ needs for special information, theater and restaurant reservations, and any other special requests.
connecting flight
A flight which the passenger must change aircraft.
A stop in a given city for less than 4 hours (domestic US); less than 12 hours (domestic US as part of an international journey); less than 24 hours (international); continuing on the next applicable flight to an onward destination; designated by X/ in a linear fare construction line.
conjunction ticket
Two or more tickets concurrently issued to a passenger and which together constitute a single contract of carriage.
connecting rooms
Two rooms that are side-by-side that have a common connecting interior door.
consolidation fare
A group inclusive tour fare available to travel agents and other operators to construct packages to destinations which are inclusive of accomodation. Consolidation fares, although group fares, are for sale to individual passengers.
consolidator
A person or company which forms groups to travel on charter or at group fares on scheduled flights to increase sales, earn override commissions or reduce the chance of tour cancellations.
A group of independent companies that join together to gain greater profits.
construction point
A city through which fares have been combined for the purpose of pricing an itinerary; a destination city or a turnaround point; a fare break shown on the ticket.
A contact center term for an individual who is calling or visiting your company by phone or through the website, and who is requesting an interaction with an agent.
contact center
An umbrella term that generally refers to reservations centers, help desks, information lines or customer service centers, regardless of how they are organized or what types of transactions they handle.
continental breakfast
A light breakfast of such things as coffee, pastry and sometimes juice.
contract fare / contract discount
A discounted fare agreed upon by the client and a carrier; contract fares require a client give the carrier a certain percentage of its business in all markets.
corporate fare
A discounted airfare for business travelers.
corporate rate
A special rate negotiated between a supplier (hotel or car for example) and a company.
corporate hotel rate
Learn how to get corporate hotel rates .
Corporate Travel Department (CTD)
A CTD (Corporate Travel Department) establishes a direct purchasing relationship between the company and its travel suppliers. The accrediting body, ARC (Airline Reporting Corporation) authorizes the company to function as its own “travel agency” and control it’s financial settlement.
co-terminals
A group of cities/airports considered to be the same point; example: JFK/LGA/EWR.
country of commencement (COC)
The country in which a journey begins; the base fare is converted from NUCs into the currency of the Country of Commencement by using the IATA ROE.
country of payment (COP)
The country in which a ticket is being purchased; the base fare is converted from the currency of the Country of Commencement into the currency of the country of payment using the Bank Rate if the countries are not the same.
Cost Per Mile. A calculation of the average price paid per mile.
Cost Per Transaction. A calculation of the total cost a company incurs for generating a customer transaction.
Customer Relationship Management. A term used for a database that is used to house and maintain customer information.
CRS (see “Computerized Reservation System”)
Corporate Social Responsibility . A concept whereby companies consider the impact to society and the environment of their actions.
Central Security Record. A hotel industry term for the name of the Viewership Management Table used to maintain a list of offices authorized to access a client’s negotiated hotel rates.
Central Standard Time. A time zone in the US, also known as Central Time or CT.
Corporate Travel Department. A company’s in-house travel agency that purchases air transportation and related travel services on behalf of its own employees.
Computer Telephony Integration. A contact center term for the software, hardware, and programming necessary to integrate computers and telephones so they can work together seamlessly and intelligently.
A checkpoint at which imported goods are verified for legality and value.
Data Release Authorization (DRA)
Under a DRA, Client instructs, as of the date specified, BCD Travel to receive, process, and/or transfer certain personal travel data from Client’s travelers, including, but not limited to, transactional ticket-level, segment-level, and traveler-level information, which may include, without limitation, traveler name and address, origination and destination, corporate and/or personal credit card number, passport number, drivers license, travel preferences, and other special needs or any other sensitive data as may be provided by or behalf of the travelers (“Travel Data”).
Decision Source (DS)
A BCD Travel product that allows our customers to interact with their reservation data.
delegate rate
An inclusive rate for meetings on a daily basis. Twenty-four hour delegate rate also includes accommodation. Phrase primarily used in the U.K.
denied boarding compensation (DBC)
Commonly called “bumping,” – When more passengers arrive to take a flight than can actually fit on the plane; although legal, the carrier is only responsible for providing compensation to a traveler if he/she has a confirmed reservation and is checked in and has arrived at the departure gate within a pre-determined time period; compensation may be in cash or in a voucher for future travel; passengers who voluntarily relinquish their seats are compensated with a cash payment or voucher towards a future trip and are then accommodated on the next available flight; if an airline delivers a bumped passenger to his/her destination within an hour of the originally-scheduled time, no compensation is required.
deregulation
Originally applied to American air travel: in 1978, federal law phased out the civil Aeronautics Board and stopped government intervention or regulation of airline routes and fares.
destination
The final stopping place as shown on the ticket; the furthest point on a fare component used to price an itinerary.
Destination Management Company
Company, possibly an incoming tour operator, who organizes local ground services at destination.
differential
The difference between the fares for two different classes of service between two cities; this fare construction principle is only used internationally.
direct fare
The fare for one-way or half round-trip travel visa the shortest route operated between two cities.
direct flight
A flight from origin to destination that makes one or more intermediate stops, but passengers do not change planes.
directional fare
Fare valid only in a specified direction of travel.
discount fare
Transportation fare lower than the full published tariff for an airline’s route. A discount fare usually entails certain stipulations regarding purchase or travel (space availbility).
DMC (see “Destination Management Company”)
Domestic travel.
Travel wholly within any one country; typically used to designate intra-US travel.
A hotel room with two double beds and/or accommodating 2-4 people.
double booking
The practice of making reservations for two or more flights, cars or hotels as a type of backup; considered to be unethical.
double occupancy
The way in which almost all cruise fares and tour packages are quoted, that is, based on two people traveling together. Most hotel rooms are quoted based on two adults to a room, as well.
double open jaw (DOJ)
Travel in which the outbound departure point and arrival and the inbound point of departure and arrival are not the same.
To move a passenger to a lower class of service or accommodation.
drop-off charge
A fee charged for dropping a rental car at a different location from where it was picked up.
Being exempt from any import tax.
economy class
The rear area of the aircraft in which passengers having paid one of the lower fare types are seated.
electronic miscellaneous document – Associated (EMD-A)
Document that allows for the fulfillment of all flight related services and fees (such as bags, seats, meals, etc.). An EMD or EMD-A is linked to a specific eticket coupon in the airline’s database.
electronic miscellaneous document – Standalone (EMD-S)
Non-flight related services (such as lounge access or change fee collection) a stand alone EMD, a EMD-S is issued. To issue an EMD-S a manually created service segment must be in the PNR. Specific services that can be charged on an EMD-S is dependent on the airline’s own requirements.
electronic ticket (eticket)
An airline transportation ticket that is entirely in a GDS; no physical ticket is required for travel.
EMD (see “electronic miscellaneous document”)
Endorsement.
Permission from the plating carrier, the ticketed carrier or the carrier losing air space for the traveler to use the flight coupon(s) for travel on another airline at no additional cost; usually only required for international tickets.
end-on-end combination
A special type of combination in which two round trip fares are combined to produce a complete itinerary.
In this example, the passenger buys a round trip ticket from AAA to BBB (Rule 1), and a separate round trip fare from BBB to CCC (Rule 2). The net effect is to travel from AAA to CCC, but breaking the fare at BBB, which may in some cases be less expensive than the round trip (through) fare from AAA to CCC.
equivalent fare paid
An amount converted into the currency of the country of payment when the published fare is in a currency other than that of the country of payment.
ERA (see “European Regions Airline Association”)
Eastern Standard Time. A time zone in the US, also known as Eastern Time or ET.
Electronic System for Travel Authorization. ESTA is a free, automated system that determines the eligibility of visitors to travel to the U.S. under the Visa Waiver Program. The ESTA application collects the same information collected on Form I-94W. ESTA applications may be submitted at anytime prior to travel, though it is recommended travelers apply when they begin preparing travel plans.
Estimated Time of Arrival. A measure of when an object is expected to arrive at a certain place.
Estimated Time of Departure or Delivery. The expected start time of a particular journey or the expected delivery of a good or service.
e-ticket (see “electronic ticket”)
Electronic Ticket Record.

European Regions Airline Association
Association which aims to identify, protect and promote the interests of regional air transport in Europe. Over 170 memebers including airlines, aircraft manufacturers and airports. www.eraa.org
excess baggage
Baggage in excess of the allowable number, size or weight.
The process of reissuing a ticket due to a change of flight, fare basis, dates or routing.
excursion fare
Round-trip fare with restrictions, such as minimun and maximum stays and the need to purchase well in advance.
executive card
Types of privilege cards available to frequent users of airlines, hotel chains, car rental companies, etc. Most carry benefits and have their own brand names, e.g. British Airways Executive Blue, Executive Silver, Executive Gold and Premier.
executive room
Higher grade than standard room and usually slightly larger, the executive room often has additional facilities for the business traveler such as trouser press, desk etc. and may be located on a separate Executive Club Floor.
Expatriot (or expat)
An expatriate (in abbreviated form, expat) is a person temporarily or permanently residing in a country and culture other than that of the person’s upbringing or legal residence.
explant/ outplant/ offsite
Branch office dedicated to serving a single client that is not located on the client’s premises, but rather operates as a separate part of a BTC.
familiarization tour
A complimentary or reduced-rate travel program for travel agents, airline or rail employees, which is designed to acquaint participants with specific destinations. Often known as “Fam-Trips”.
family plan
A hotel rate that allows children to stay free with adults in the same room.
A combination of letters and numbers used to identify a fare type which may also indicate the rules of the fare
fare component
A fare between two points.
fare ladder
A vertically-written fare construction that includes fare components, surcharges and additional amounts collected.
- fee – bundled air transaction fee An air transaction fee that includes the costs associated with servicing air, hotel and car transactions. Therefore, hotel and car only bookings (not to exceed XX% of air bookings) are not charged a transaction fee.
- fee – management fee Fee assessed in addition to direct costs. Covers primarily overhead and profit. Can be assessed as % of sales, per transaction or fixed amount.
- fee – management fee structure (formerly cost plus offering) Client fee arrangement whereby direct expenses are passed through to the client in addition to management fee. Management fee could be % of sales, fixed fee, or per transaction.
- fee – online booking tool fee (PNR fee) Charged per unique reserved PNR. Additional fees may be assessed for transactions booked on a website accessed via the online booking tool.
- fee – online transaction fee (e-fulfillment fee) Charged per online transaction – that excludes any ‘flow through costs’ charged by the online booking tool provider.
- fee – transaction fee structure Client fee arrangement whereby client is billed per transaction for all major program costs including direct expenses and contribution to overhead and profit, usually at POS.
- fee – unbundled (menu) transaction fee Separately charged per each type of transaction, e.g. hotel, car, rail and air. AM and MIS costs might also be charged separately.
final destination
The last point on an itinerary/fare component.
first class
The cabin on an aircraft where there are fewer seats, more elaborate service and amenities.
FIT (see “Fully Independent Traveler”)
Flag carrier.
The airline that internationally represents a given country; sometimes financed or owned by the government.
flight coupon
A section of an airline ticket; one flight coupon is required to take each flight.
flight/time specific
A fare rule that requires a to fly on a specific flight or at a specific time of day.
FOI (see “Form of Indemnity”)
Form of Payment. The method of payment for a transaction.
form of indemnity
A form that needs to be completed by the passenger in order to claim refund in respect of an air ticket that has been misplaced or stolen.
frequent flyer number
Find out what a frequent flyer number is and how to get one
frequent flyer program
An airline loyalty program that provides awards to travelers who use an airline or its partners.
frequent guest program
A hotel loyalty program that provides awards to guests who use a hotel chain.
frequent renter program
A car rental loyalty program that provides services (such as fast pickup) to those who use a car rental vendor.
front office (FO)
An industry term used for products associated with customer-facing activities. The GDS is a front office system.
fuel surcharge
A surcharge assessed for fuel use applicable for travel between specified points and/or for departure from a specified city.
Hotel rate with accommodation, breakfast, lunch and dinner included.
full economy
This is a fully flexible, fully refundable ticket which is valid for one year from date of issue in economy class.
full exchange
Change an already ticketed reservation, with no flown flight segments.
full to full exchange
Change to a ticketed reservation when no segments are flown and the change is to any segment other than the outbound flights. Or when a segment has been flown and there is a change to a remaining flight segment. In either of these instances, the FULL value of the original ticket must be exchanged for the ‘combined’ FULL value of the new ticket.
fully independent traveler
A traveler / tourist not part of a tour group.
One of the world’s CRSs (GDSs).
Area in an airport where passengers for a flight gather before boarding their flight or deplane on arrival.
gateway city
The last domestic city from which a passenger departs prior to arriving at an international destination; the first point of arrival in a given country (e.g., on the journey SFO-CHI-FRA-MUC, CHI and FRA are gateway cities).
GDS (see “ Global Distribution System “)
Gds operations (gdso).
An industry term for computer reservation systems that book and sell tickets for multiple airlines.
GEBTA (see “Guild of European Business Travel Agents)
In the credit card industry a system used by corporations whereby travel related charges made through designated travel agencies are centrally billed but no plastic card actually exists. Often referred to as “Lodge card” in Europe.
global distribution system
An industry term for computer reservation systems that book and sell tickets for multiple airlines. Learn more
global indicator
Two-letter code used to identify the direction of travel applicable to a given fare.
governing carrier
The airline whose fares and rules are used on a given itinerary.
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)
Solar based time in Greenwich, England, from which time in all other time zones in the world is based.
ground time
The time not flying.
A booking solution that allows the booking and managing of all ground transportation services, such as limousines, executive sedans, taxis, vans and parking services.
A fare that offers discounts to groups of varying minimum sizes in selected markets, with various conditions, and usually require round trip travel within a specified time limit.
guaranteed hotel reservations
This means that the hotel will hold the room all night. However if the room is not required, failure to cancel will result in a charge. Where reservations are made on an ad hoc basis, rather than through a regular account arrangement, a credit card number will be required to effect this guaranteed reservation.
Hotel rate for accommodation, breakfast and one other meal.
half round trip fare
Half of a fare designated for use on round-trip journeys.
Fee or tax some countries or cities levy on arriving or departing travelers.
Half of the globe; the North and South hemispheres are divided by the Equator; the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans divide the East and West hemispheres.
higher intermediate point (HIP)
A pair of cities within a one-way or half round-trip fare component that has a direct fare higher than the direct fare between the origin and destination of the fare component; this fare construction principle is only used internationally.
hotel sourcing
Hotel sourcing or procurement is the process of identifying, negotiating and contracting with hotels to secure accommodations for a specific group, event or organization.
An airport at which an airline centers many of its schedules, particularly connecting flights to smaller destinations.
(see “International Air Transport Association”)*
IATA Number (see “ARC Number”)
Iata rate of exchange (roe).
Rates of exchange designated by IATA to convert local currency to NUCs and to convert NUCs into the currency of commencement of travel.
ICAO (see “International Civil Aviation Organization”)
Interline e-ticket. An interline agreement between airlines that allow e-ticketing on each other’s flights. Interline agreement between airlines permitting travel service cooperation in areas such as: baggage transfer services, guaranteed connection times.
IGK (see “International Gatekeeper”)
Immigration.
Area at which a traveler’s documentation (e.g., Passport and Visa) are verified to ensure the traveler may enter the country.
implant (on-site)
Dedication operational team, based within an office of the client.
implementation
Phase of launching a new relationship, including e.g. opening a new location, training staff, installing technical equipment, and informing clients, travelers and travel arrangers.
inbound travelers
Travelers coming into a specified location are considered inbound. Travelers departing from the location are considered outbound.
A traveler who has not yet reached his/her second birthday.
Term used in the U.S. to describe an implant.
international departure taxes
Taxes levied on all travelers departing a country on an international journey that are, typically collected at the airport at the time of departure.
Between two airlines; TUS-HP-DEN-UA-LON is an interline journey.
interline baggage agreement
An agreement between two air carriers that a carrier will transfer baggage to the other carrier.
interline connection
When a passenger changes airlines as well as aircraft during a journey (same as off-line connection).
interline ticketing agreement
An agreement between two air carriers that permits air travel of one carrier to be on a ticket issued and/or ‘plated’ on another carrier.
intermediate point
A ticketed point of an international journey at which there is no fare break; an intermediate point may be a stopover or connection.
intermediate stop
An enroute stop at a city between the origin and destination (see also Direct Flight).
International Air Transport Association
The world trade association of international air carriers; appoints travel agencies to sell tickets; determines rules and regulations for international carriers. www.iata.org
International Civil Aviation Organization
Specialed agency of the United Nations with responsibility for civil aviation action in standardization, technical co-operation and the formulation of international aviation law. www.iaco.int
A chronological plan showing a traveler’s booked arrangement.
A special through fare (usually only internationally) that permits travel on two or more different airlines.
The origin to final destination of a fare construction.
BCD Travel provides support for KDS. KDS provides an online booking platform for the confirmation of air, car, hotel and rail itineraries.
On outbound journeys, landside includes all those areas of the terminal before you arrive at passport control. On inbound journeys, landside includes all those areas of the terminal after you’re through passport control.
last date of purchase
The date by which a ticket must be issued – fares are not guaranteed until tickets are issued.
last room availability (LRA)
A hotel industry term for ensuring a negotiated rate is always available when standard inventory is available or when the room type negotiated is available.
LDW (see “Loss Damage Waiver”)
One flight; one part of an entire journey.
Lowest Fare Routing. The least expensive airfare available to a destination.
local currency fare (LCF)
See Country Of Payment (COP).
locator reference
Unique identifying booking number used within a computer reservations system as part of a booking file.
In the credit card industry a system used by corporations whereby travel related charges made through designated travel agencies are centrally billed but no plastic card actually exists. Often referred to as “Ghost Card” in the U.S.
Loss Damage Waiver
Additional insurance pertaining to car rentals, covering theft and vandalism in addition to accident damage.
low cost carrier (LCC)
An airline that offers generally low fares in exchange for eliminating many traditional passenger services.
lowest combination principle
Construction of a fare using a particular combination of sector fares to provide the lowest fare when there is no published fare between two points.
Marine Travel
Specialized travel services, available 24/7, provides travel arrangements (including helicopters and charter aircraft) for marine personnel.
Market Number (MK)
A code all online booking tools (OBTs) add at the time each reservation is made, as a way to track PNRs for online adoption and fulfillment purposes. It should never be removed once added to the PNR.
Married Segments
Two or more connecting flight segments joined, or “married,” meaning that these segments are inseparable and the subsequent rebooking or cancellation of any one flight segment must, at the same time, be applied to the connecting flight segment.
maximum permitted mileage (MPM)
The number of miles that may be flown on a published direct fare between origin and destination; this fare construction principle is only used internationally.
maximum stay
The maximum amount of time a traveler may stay at a destination before return is required.
MCO (see “Miscellaneous Change Order”)
Meetings, Incentives and Corporate Events. An industry term for a department within a company that offers meeting planning services to customers. BCD Travel’s department is called BCD M&E
midoffice (MO)
An industry term for the management information (MIS) portion of a travel agency’s system.
mileage fare
A fare based on the total miles flown from the origin to destination; this fare construction principle is only used internationally.
mileage surcharge
A percentage of fare increase applied to a fare because the routing exceeds the maximum permitted mileage; the percentage is in 5% increments to a maximum of 25%; this fare construction principle is only used internationally.
minimum connection time
The amount of time required to change planes; varies by airport and often varies by carrier.
minimum stay
The minimum time a travel traveler must stay at a destination (or be gone ‘away from home’ internationally) before return travel can commence.
miscellaneous charge order (MCO)
An accountable document issued by a travel agency or airline as proof of payment for a specific fee (such as pet service fee) or as residual amount of an exchange (higher priced ticket exchanged for a lower priced ticket) to be used on a future purchase.
Mountain Standard Time. A time zone in the US, also known as Mountain Time or MT.
National Business Travel Association
U.S. business travel association which is a member of IBTA. www.nbta.org
NBTA (see “National Business Travel Association”)
New distribution capability. Read more
negotiated fare/rate
This is a term used by travel agents to descibe reduced airfares that have been negotiated by their air fare specialists on behalf of clients.
neutral units of construction (NUC)
An imaginary currency established by IATA that allows fares of different currencies to be added together; this fare construction principle is only used internationally.
Non Last Room Availability. A hotel industry term for restricting availability of a negotiated rate when occupancy levels are high. Negotiated room rate is not guaranteed to be available.
Net Operating Income. A financial term for the amount by which operating revenue exceeds operating expenses in a specific accounting period.
non-endorsable
This expression often appears in the endorsements box of an airline ticket and it means that the flight coupon on which the worlds appear may be used only on the services of the airline indicated.
non-refundable(NR)
A ticket issued on a fare that does not allow for a refund; most non-refundable tickets can be changed for a fee and any difference in fare.
normal fares
The full fare established for first, business, economy or an intermediate class and any other fares published designated as normal fares.
normal open jaw (NOJ)
Travel from a country and return to the same country with a surface sector at either the origin or turnaround point (single open jaw – SOJ) or at both the origin and the turnaround point (double open jaw – DOJ).
An airline passenger or hotel guest who fails to use and/or cancel a reservation.
National Transportation Safety Board. An independent US government agency that investigates accidents including aviation, highway, marine, pipelines and railroads.
OBT and OBLT (see Online Booking Tool”)
Off-airport location.
Usually a car rental office serving an airport but physically located off the airport site (and often picking up renters at the airport in buses or taxis). When the office is located on-site, the term used is on airport location.
A destination that a carrier does not serve; see also Interline.
off-line connections
When a traveler changes airlines as well as aircraft during a journey (may also be referred to as interline connection). Changes of aircraft with the same airline are known as on-line connections.
offline transaction (traditional transaction)
A transaction that initated by an agent following a call/email request by a client.
Time of year or day of the week when travel is less common.
off-line point
Airline term to describe points (areas or cities) they do not serve.
off-loading
This occurs when an airline has over-booked: that is, it has sold more seats on a particular flight than the aircraft has to offer. The passengers to be off-loaded are usually those who have paid the lowest fares. Off-loaded passengers will normally qualify for denied boarding compensation. Passengers may also be off-loaded at the captain’s discretion if they are unfit to travel due to drink, drugs, illness or for bad behavior.
BCD Travel is a re-seller of onesto. On-esto provides an online booking platform for the confirmation of air, car, hotel and rail itineraries.
Online Booking Tool
A web-based platform allowing travelers to make self-service reservations (e.g. Cliqbook, GetThere).
operating carrier
In a codeshare, the airline providing the plane, crew and ground handling services.
online or online point
On the same carrier; TUS-UA-DEN-UA-LON is an online journey.
online adoption
An account’s use of their predetermined online booking tool.
online high touch transaction
A transaction that originates via an online booking tool, but then requires more than one agent intervention (one touch).
online low touch transaction
A transacion that originates via an online booking tool, and then requires agent intervention or manual review/processing that is initated by the customer.
online transaction fee
(E-fulfillment fee) A fulfillment fee canged per online trasaction – that excludes any ‘flow through costs’ charged by the online booking tool provider.
A BCD Travel office located at/on/in a client’s location.
Term used to describe the principle of showing a client the complete cash-flow cycle, including commissions and overrides.
open date sector
Part of a journey for which no firm reservation has been made (usually owing to changeable plans on the part of the traveler) but for which the fare has been paid.
open jaw ticket
Where passengers fly out to one destination and return from another. Open jaw arrangements save backtracking and make a trip more cost effective.
Much-used term for unrestricted air services between several countries.
open ticket
A ticket valid for transportation between two points but has no specific flight reservation.
originating carrier
The first airline of a passenger’s journey and/or portion of a trip.
Other Service Information. A GDS entry that provides information to a carrier that does not require action for traveler action such as contract discount code, record locators of additional family members traveling together (TCP), age information for children/infants, etc.
Travel from the point of origin to the farthest destination.
outplant (off-site)
Dedication operational team, based within a BTC office.
overbooking
Also known as bumping. Airlines and hotels can predict, with some accuracy, how many travelers/guests will show up for previously made reservations; when more people show up than what is expected, travelers/guests are re-accommodated; see also Denied Boarding Compensation.
Abbreviations for ‘passport and visa’ used in the U.K. Some affliates have a specialist team which advises on and acquires passports/visa on behalf of their clients.
Pacific Asia Travel Association
Association which aims to promote travel to Asia Pacific. www.pata.org
PAR (see “Passenger Account Record”)
Passenger account record.
In Galileo, the profile showing passenger information.
passenger facility charges
An airport-designated surcharge to raise funds for airport expansion, renovation, operating costs, etc.
passenger name record
Record held within a CRS/GDS which gives the personal details associated with a particular booking.
An official document issued by a government to its citizens that establishes an individual’s identity and nationality and enables travel abroad.
PATA (see “Pacific Asia Travel Association”)
Abbreviation for passengers.
Payment Card Industry. Security standards set to help protect account data information.
Time of year or day of the week when travel is most common.
A fee charged by a carrier or vendor for changing and/or canceling a reservation or ticket.
Per diem is a daily allowance given to an employee to cover business travel expenses such as lodging, meals and incidentals while traveling for the company. Learn more about per diem .
Penalty excursion fare. Public excursion fare are within minimum stay requirements, but which has no advanced purchase requirements.
PIR (see “Property Irregularity Report”)
Plate / plated.
See Validating Carrier.
PMS (see “Property Management System”)
Pnr (see “passenger name record”).
Purchase Order. A commercial document issued by a buyer to a seller that indicates the quantities and agreed upon prices for products / services.
point-to-point fares
De-regulation has led to a growing number of these on routes throughout the world. They are low fares in first, business, or economy class between two points by direct flights. Stopovers are usually, but not always, prohibited.
Point of Service or Point of Sale. The time and place in which a transaction is made.
prepaid ticket advice (PTA)
A form used when a person is buying a ticket that will be issued at the airport of the same or a different city. Example: A ticket purchased in Chicago to be picked up by the traveler in and for a departure from Buenos Aires.
pre-trip auditing
A product offered by travel management companies that allows for the review of travel itineries before departure to identify savings or prevent unnecessary expenditure.
pricing unit (PU)
A journey, or part of a journey which can be priced and ticketed as a separate entity; a round-trip, circle trip, one-way, normal open jaw or special open jaw; this fare construction principle is only used internationally.
pricing unit concept (PUC)
An alternative method of fare construction for multiple-stopover journeys that uses pricing units; this fare construction principle is only used internationally.
primary carrier
Airline flying the governing sector (prime segment).
prime segment
The first “true” international journey; often called the “over-the-water” segment; see also Gateway.
A computerized file containing company and traveler information.
promotional fare
A fare designed to attract passengers who would not otherwise travel.
proof of citizenship
Documentation that establishes nationality.
property irregularity report
Form submitted by passengers to ground handling agents at airports in the event of loss or damaged baggage.
property management system
Computer-based system for controlling hotel inventory, check-in and -out and billing.
Pacific Standard Time. A time zone in the US, also known as Pacific Time or PT.
PTA (see “Pre-paid Ticket Advice”)
Public fares (air).
Fares that anyone can obtain and is available in a regular fare display.
Quality of Service Index. An index developed by the Civil Aeronautics Board to provide a comparative rating of service offered by individual airlines.
A computer’s electronic filing system. Also a contact center term for the holding point for a number of calls or interactions that are waiting to be answered by an agent. The calls or interactions are usually assigned to available agents in a first-arrived, first-answered basis, but may also be assigned based on a company’s routing strategies.
queue group
A contact center term for a group of virtual queues. Also referred to as a DN Group or Group of Queues.
The official posted rate for each hotel room.
rate desk (see “International Rate Desk”)
Rate of exchange (roe) (see “iata rate of exchange”), rearden commerce.
BCD Travel is a referrer for Rearden. Rearden provides an online booking platform for the confirmation of air, car, hotel and rail itineraries.
reason codes (RC)
An industry term for codes used to document and report on traveler decisions and behavior.
reconfirmation
Particularly on international flights, passengers are required to indicate their intention of using the next leg of their itinerary by contacting the appropriate carrier before departure; internationally, reconfirmation is requested 72 hours prior to departure.
record locator
A computerized number that identifies a Passenger Name Record – PNR or other reservation; when speaking to travelers, usually called a confirmation number.
red-eye flight
Usually an overnight flight that arrives early in the morning – great when you don’t want to lose precious sightseeing time at your destination.
If necessary for a passenger to change journey en route, the ticket must be reissued. The value of the original ticket will be offset against the new fare and any extra or refund, calculated. Settlement can be direct with airline or with referral to the issuing agent.
BCD Travel is a re-seller for ResX. ResX provides an online booking platform for the confirmation of air, car, hotel and rail itineraries.
return journey
A journey for which the fare is assessed as a single pricing unit using half round-trip fares.
revalidation
If the passenger’s travel date or flight needs to be changed, without affecting the route, there is not always a need to reissue the ticket. The relevant flight coupon is simply revalidated by means of a revalidation sticker.
Revenue Per Available Room. A hotel industry measure that calculates room revenue divided by rooms available (occupancy times average room rate will closely approximate RevPAR.)
Rate Loading Instructions. A hotel industry term for the instructions provided to hotel properties for loading client-specific or TMC-specific rate codes as displayed in the GDS.
room with facilities
Describes a hotel room which has a bathroom en-suite. In some smaller two-star or three-star hotels facilities may refer to toilet and washbasin only.
round-the-world (RTW) (see “Around-the-World”)
A trip that begins and ends in the same city with no un-flown portions; internationally, with the same dollar amount on both portions .
route deal / route incentive
An agreement between a corporate customer and an airline. The agreement allows for an incentive payment to be made to the cient by the airline as a reward for loyalty.
The carrier and/or cities and/or class of service and/or aircraft type via which transportation is provided between two points.
routing fare
A fare based on a specified routing.
run-of-the-house (ROH)
A flat rate for which a hotel offers any of its available rooms.
Schengen Visa
A special visa that permits holders to travel to any of the 25 Schengen member countries on a single visa (rather than obtaining a visa for each country. It is only issued to citizens of countries who are required to obtain a visa before entering Europe for leisure, tourism or business travel. Schengen Visa holders are not permitted to live permanently or work in Europe. The following countries are currently active Schengen Visa members: Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Slovak Republic, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland.
A specific time of year for a fare; High Season is the most popular time of year to travel to a specific destination and fares are more expensive at that time; Low Season is the least popular time of year to travel to a specific destination and fares are less expensive at that time; Fares affected by seasonality are usually indicated as such by fare basis coding and/or seasonality details listed in the fare’s rules.
The distance between aircraft seats, measured in inches and commonly used to show a passenger’s legroom.
security surcharge
Surcharge assessed by a carrier to cover costs of airport and in-flight security.
secondary carrier
Airline(s) flying the sectors preceding and/or succeeding the prime segment.
A journey from one point to another.
A flight; see Leg.
self-service reservations
Situation where the traveler makes his/her own reservations. A reservation generated by the customer using an online booking tool.
selling carrier
In a codeshare, the airline offering the flight for sale, under their vendor code
service fee
A fee charged by a travel agency to a company/individual for travel services.
Service Level Agreement
An agreement stating measurable performance commitments made to our customers.
Regular or schedulable bus/van transportation such as from an airport to a downtown location; regular air service on heavily-traveled routes (e.g., BOS-LGA).
A journey from and/or to an enroute point of a fare component.
Accommodations designed for one person.
SLA (see “Service Level Agreement”)
Designated take-off and landing times allocated to airlines at certain airports.
soft opening
Period when new hotel is open for business although not entirely finished – some services of facilities may not yet operate.
Standard Operating Procedure. A set of instructions that define the official standard for a specific process or situation.
Scope of Services. A document that defines the number, type, and intensity or complixity of services to be provided.
space available
Confirmation of a reservation subject to availability at the last moment.
special needs
Atypical traveler needs such as a special meal or wheelchair service.
split ticket(ing)
Issuance of two or more tickets usually for the purpose of obtaining a lower fare; usually applied to international itineraries to take advantage of fare and/or currency conversion differences.
Spouse fare
This type of are applies to selected destinations on a round-trip only basis and offers a discount of 50% to the spouse of a full first class or business class passenger. Economy passengers also qualify where there is no business fare.
SSR (see “Self Service Reservation”)
Special Service Request. A GDS request for a carrier to provide additional action for a traveler such as special meal, ticket number transmission, wheelchair, etc.
standard room
The normal hotel room type, generally with television, and en-suite bathroom.
A passenger on waitlist or one prepared to travel if space becomes available at the last moment.
Interruption of travel for more than domestic US – 4 hours; domestic US as part of an international journey – 12 hours; international – 24 hours .
stopover charge
An additional fee assessed for making a stopover.
STP (see “Satellite Ticket Printer”)
Any extra literature included with the delivery of travel documents.
sub-journey
A self-contained pricing unit that is combined end-on-end with another self-contained pricing unit on the same ticket; this fare construction principle is only used internationally.
surcharge (Q)
An airline-imposed fee included in fare calculations; see also Excess Mileage Surcharge, Fuel Surcharge, and Security Surcharge.
surface sector
Travel from one point or another not by air (ARNK – which stands for Arrival Not Known).
Travel 24. A BCD Travel department that services customers 24 hours a day when their normal business office is closed.
Ticket Fulfillment Location. An industry term for a virtual ticket printer that is shared by various BCD Travel ARC ticketing locations on the same GDS.
through fare
A fare applicable for transportation via an enroute city(ies) between the origin and destination of the fare that allows for intermediate points of travel.
A contract of carriage for an airline to transport a passenger from one point to another.
ticket on departure
Transportation ticket collected at the point of departure such as an airline ticket counter at an airport.
ticketed point
A city for which a flight coupon has been issued.
time and mileage rate
Car rental rate based on fixed charge for the rental period plus a charge for each kilometer or mile driven during the period of the rental.
TOD (see “Ticket on Departure”)
Tourist card.
A registration form required by certain countries indicating a traveler’s intended stay; used in lieu of a Visa and common in Latin America.
transaction
A Ticket issued; defined as all airline and rail tickets (electronic and paper) issued by BCD Travel or reserved by BCD Travel through a third party, regardless of whether the ticket is subsequently used, refunded, or voided in whole or in part. Cancellation of a reservation before a ticket is issued is not considered a transaction. Optional: Hotel and car booking made, regardless of whether or not the traveler uses the hotel or car reservation.
transaction – domestic air
Domestic – travel between two destinations that are within the same country. e.g. Frankfurt to Berlin
transaction – regional air
Regional – Travel within the same continent. e.g. Madrid to London
transaction – international air
International – Travel between two continents. e.g. New York to London
transaction – offline – traditional
A transaction that is initiated by an agent following a call/email request by a client
transaction – online high touch
Transaction – online low touch.
A transaction that originates via an online booking tool and then requires agent intervention or manual review/processing that is initiated by the customer.
transaction – online no touch
“Touchless E-fulfillment transaction” An electronic transaction entirely processed through an online booking tool and BCD central fulfillment service, without any agent intervention and where invoicing is provided via email.
A point at which the passenger changes aircraft; if the change is to/from the same carrier, it is an online transfer; if the change is to/from different carriers, it is an interline transfer.
transit lounge
An area within an airport for the sole purpose of international flight connections; travelers do not clear immigration or customs to enter the transit lounge as it is considered to be an international point.
transit point
Any stop at an intermediate point which does not fall into the definition of a stopover whether or not a change of planes is involved.
Travel Management Company
A travel management company (TMC) is a company that provides corporate travel services to businesses.
A BCD Travel umbrella brand name for our technology suite, which includes a variety of products listed below. read more
- TripSource:Active Itinerary A single point of access for traveler and travel arrangers for active and historical travel detail, including real time flight status, itinerary details, destination information and invoicing, billing and expense information.
- TripSource:Flight Alert Keeps travelers informed & productive while on the road by providing flight status information, including delays and real-time gate changes, for BCD Travel bookings.
- TripSource:Fulfillment Drive touch-less transactions with as little human intervention as possible while driving traveler contact behavior to minimize touches.
- TripSource:Portal (TSP) A comprehensive global solution to address traveler needs, travel program and corporation objectives. Arming travelers with rich content, productivity tools and critical safeguards for business travel, TripSource:Portal empowers travel programs as a centralized communications vehicle to deliver relevant, timely information and critical alerts to targeted audiences. The Portal expands traveler services while aligning program needs to drive savings, support business objectives and avoid corporate travel program risks.
- TripSource:Profile Manager (TSPM) Drives optimal data management by integrating profile management and online booking, and promoting secure web-based self-service maintenance of traveler-level detail.
- TripSource:Quality Measurement (TSQM) Ensures a means to track and manage supplier & transaction quality in addition to resolution of client concerns.
- TripSource:Rail Search (TSRS) BCD own rail booking tool for Deutsche Bahn only.
- TripSource:Ticket Tracker BCD manages and recovers committed travel dollars. Based on markets and supplier rules, BCD communicates with travelers to prevent loss of committed funds and when to apply unused funds toward future travel.
- TripSource:Trip Authorizer In response to growing concern for compliance, this module enables clients to implement pre-trip authorization requirements as well as post-ticketing compliance reporting.
Transportation Security Administration
twin for sole use
A twin-bedded reserved for sole occupency and charged out at a rate that falls between the single and double room price.
Two Factor Authentication
Also known as 2FA. Method of accessing a secure environment where a person proves their identity with two of three methods
User-Defined Interface Data. UDID remarks are standard and contain predefined reporting information such as lost hotel night reason codes, merchant billing codes or additional traveler data fields.
unlimited mileage rate
Car rental rate that covers all costs, other than insurance and petrol, for the duration of the rental, regardless of the distance driven.
Move to a better class of airline service, larger rental car or more luxurious hotel room.
validating carrier
Airline designated as the “owning” ticketed carrier; the carrier on whose “plate” the ticket is issued. The validating carrier is the carrier to which payment is submitted and is usually the first carrier on the itinerary (domestic) or the carrier on the first international flight (international). If a ticket is issued on multiple carriers or is validated on a carrier not on the itinerary, the validating carrier is responsible for payment to the other airlines on the ticket.
The process of stamping an air ticket or other airline document, at the time of issue, with the issue date, name and location of the issuing office and its IATA code number. Tickets not bearing such a stamp re invalid and will not be accepted by airlines.
value-added tax (VAT)
A general tax that applies, in principle, to all commercial activities involving the production and distribution of goods and the provision of services.
VAT reclaim
Value-added tax, or VAT, is included in hotel, dining and car rental bills and more when travelers go to countries that assess the tax. It can be a significant expense: VAT rates can be as high as 25%. The good news is most T&E-related VAT is eligible for reclaim. The bad news: In the past, it’s been hard to collect. But automation has made VAT reclaim for European Union transactions much easier. BCD Travel has partnered with VAT-recovery firm Taxeo to automate the process.
virtual credit card (VCC)
A VCC isn’t a physical card, but it has many of the same features as plastic corporate cards.
virtual payment
A virtual payment is a terminal-based payment method where the payment is delivered through a virtual card (VCC) instead of by check or cash.
An endorsement or stamp placed into a passport by officials of a foreign government giving a traveler permission to visit; not all countries require visas.
VCC (Virtual Call Center)
A network of call centers where the client calls one phone number, regardless of where they are based, that will be routed through to an available agent. For multi-national accounts this service would be multi-lingual as appropriate.
Virtual Multiple Purpose Document. A document issued by a travel agency or airline, working with BSP, as proof of payment for transactions and services, either related to an eticket already issued (example: rebooking fees) or for services other than flights (for items like surface transportation, transfers, and excess luggage charges).
A traffic document which has been spoiled or canceled.
Documents issued to confirm arrangements or used to be exchanged for services.
A list of people seeking a travel service that is sold out; generally, as other travelers cancel, waitlisted individuals are confirmed in the order in which their waitlist request was received – sometimes prioritized by frequent traveler membership.
When a hotel is sold out and there are no rooms available for a person who has a confirmed reservation, the hotel provide alternate accommodations at a different hotel.
an agreement to pay to use an aircraft with a crew , fuel, and insurance
wide-body aircraft
Aircraft with wide passenger cabins and seating configurations that require more than one aisle. Current models include Boeing 747, 777 or Airbus A380, A350
system that checks hand luggage at an airport, without damaging, for example, light-sensitive film material or laptops.
Yield Management
is a variable pricing strategy, based on understanding, anticipating and influencing consumer behavior in order to maximize revenue or profits from a fixed, time-limited resource (such as airline seats or hotel room reservations).
Zulu Time Zone (Z) has no offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Zulu Time Zone is often used in aviation and the military as another name for UTC +0. Zulu time, also known as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), is the time zone used by the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England. It is the basis for all other time zones in the world.
2FA, or two-factor authentication, is an extra layer of security used to protect online accounts. In addition to a password, users are also required to enter a code that is sent to their mobile device. This makes it more difficult for hackers to gain access to an account, as they would need to have both the password and the code.
Why Use a Regional Travel Specialist?
I am not telling you to use any travel agent. I’m saying there is a value in using an agent or tour operator, who specializes in planning trips to the place you are thinking of traveling, be it Africa, Southeast Asia, Latin America or even more regularly traveled places like Europe.

What Can a Travel Specialist Do for Me? Tour operators or agents who specialize in a given region are your greatest asset in getting the best possible experience. They have insights into the best deals and properties and the best ones see themselves as advocates both for you and for tourism in the countries they specialize in. A regional expert is able to take what you tell them about the experience you want on your trip, your reality based budget and uses their wealth of knowledge to make it all work in a seamless itinerary at best possible price.
Here are just a few of the advantages of using a regional travel specialist (while the examples I use here are from Africa because that is the area that Extraordinary Journeys specializes in, the principles apply to all regional travel specialist):
First Hand Knowledge An expert’s greatest value is that they have firsthand experience and opinions about hundreds of properties in the regions they specialize in and can give you insights that you cannot get online.
For example in East and Southern Africa there are camps that are great in the low season because they have great game viewing year round or because they are in areas where they actually get better in less popular seasons. Knowledge of the places where you can take advantage of low season rates without compromising game-viewing or activities is one of the huge advantages of using a regional expert. For example: We recently moved a client’s stay in Cape Town from the beginning of their trip to the end so they could take advantage of the very end of the shoulder season in the beginning of June in Botswana and saved them $3000.

Because of their first hand knowledge or properties in a specific region, travel specialists also know the value for money properties ; the hidden gems which are comparatively cheap but have great guides or a stunning location. On the flip-side they know the properties that look amazing online or get incredible TripAdvisor reviews that just don’t live up to the hype. TripAdvisor is a great tool but can benefit bigger properties because bad reviews have less of an impact on their overall rating than one bad review for a smaller property. Firsthand experience can help you sort that out.
In addition, for every country and region there are hundreds of specials out there (Stay 3 pay 2, 50% off for brides, free nights and transfers if you stay at a combination of several properties). These deals change frequently and have specific conditions and exclusions. Travel specialists are up-to-date on all the best deals in their regions and can quickly pull together an itinerary that makes the best use of them.
Long Term Relationships Travel specialists have relationships with tour operators and properties in the regions they specialize in. This means they can make sure you get the best possible experience and treatment at every property. For example just because a “bush breakfast” is an included activity at a safari camp doesn’t mean they are going to do it for 100% for their guests. But they will if your specialist (who they have a long term relationship with) reminds them that it is something you are really looking forward to. These long term relationships can also mean that sometimes when a deal crops up for properties that you have already booked, the relationship between the specialist and the property will get you that deal retroactively. They might able to get it and they might not, but you won’t get it on your own.
How Much is Your Time Worth? If you think planning a trip yourself makes it free think about how much you would charge someone else for your services. Then figure that planning your own trip by doing online research will take you about 40 hours. You have better ways to use that time and a regional specialist could get you better results.
It’s also worth noting that booking through a regional travel specialist will cost you the same as booking online. They make their commission from hotels (camps, lodges etc) not from you. Booking online won’t save you a ton and you’ll miss out on regionally specific knowledge that could make your trip better.
Finally, what happens if your flight gets cancelled, you miss your flight or the property loses your reservation? All these things can cost you money, time and cause you stress. The travel specialist always has a back up plan and it is their job to handle that situation which means less worry for you.
What it comes down to is; if you want a really a tight budget and have lots of time to do the research then you should book your trip on your own. But, if you are traveling to a country or a part of the world you know little about and want a seamless trip at a great value, then use an expert. You will save money on the trip itself and hours and hours of your time.
For more information on Why Use a Regional Travel Specialist email [email protected]

- What's Your Exit Number?
- Free Report
Selling a Business , Uncategorized
Valuation Multiples for a Travel Agency
By Jack
In the world of business, valuation multiples play a crucial role in determining the worth of a company. For travel agencies, understanding these multiples is essential for making informed decisions about their financial health and potential for growth. In this article, we will delve into the concept of valuation multiples, explore their significance for travel agencies, discuss key multiples specific to this industry, examine factors that influence multiples, and offer insights on how to calculate and interpret them.
Understanding Valuation Multiples
Valuation multiples are ratios used to evaluate the value of a business. They are calculated by dividing a financial metric by a corresponding value, such as revenue or earnings. Travel agencies, like any other company, can use these multiples to gauge their market value, compare themselves to industry peers, and attract potential investors or buyers.
When it comes to understanding valuation multiples, it is essential to delve deeper into their definition and importance in the business world. By doing so, travel agencies can gain a comprehensive understanding of how these multiples can impact their financial health and growth potential.
Definition of Valuation Multiples
Valuation multiples provide a quantitative representation of a company’s financial performance relative to its value. They allow investors and industry analysts to assess how much they are willing to pay for a share of the company’s future profits . Commonly used multiples include price-to-earnings (P/E), price-to-sales (P/S), and price-to-cash flow (P/CF).
Let’s take a closer look at each of these valuation multiples:
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: This multiple measures the price investors are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings generated by the company. A higher P/E ratio suggests that investors have high expectations for future earnings growth.
- Price-to-Sales (P/S) Ratio: The P/S ratio compares the company’s market capitalization to its annual revenue. It helps investors understand how much they are paying for each dollar of sales generated by the company.
- Price-to-Cash Flow (P/CF) Ratio: This multiple compares the company’s market value to its operating cash flow. It provides insights into the company’s ability to generate cash and its overall financial health.
By analyzing these valuation multiples, travel agencies can gain valuable insights into their financial performance and attractiveness to potential investors.
Importance of Valuation Multiples in Business
Valuation multiples serve as yardsticks for assessing a travel agency’s financial health and growth potential. By comparing multiples to industry benchmarks, business owners can gain insights into their competitive positioning, identify areas for improvement, and make informed strategic decisions.
For example, if a travel agency’s P/E ratio is significantly higher than the industry average, it may indicate that investors have high expectations for the company’s future earnings growth. This can be a positive sign for the agency, as it suggests that investors see potential in its business model and growth prospects.
On the other hand, if a travel agency’s P/S ratio is lower than the industry average, it may indicate that investors are not willing to pay a premium for the company’s sales. This could be a red flag for the agency, signaling that it needs to focus on improving its revenue generation strategies to attract investors.
Additionally, multiples help investors evaluate the risk and return potential of investing in a particular agency. By analyzing valuation multiples, investors can assess whether a travel agency is undervalued or overvalued in the market. This information can guide their investment decisions and help them identify opportunities for potential returns.
In conclusion, valuation multiples play a crucial role in evaluating the value of a travel agency. By understanding these multiples and their significance, travel agencies can make informed decisions, attract potential investors or buyers, and position themselves competitively in the industry.
Key Valuation Multiples for Travel Agencies
When it comes to travel agencies, there are specific valuation multiples that industry professionals commonly use to assess their value. Understanding these key multiples is crucial for agency owners and investors alike.
Travel agencies play a vital role in the tourism industry, connecting travelers with their dream destinations and providing a range of services to ensure a smooth and enjoyable experience. As the demand for travel continues to grow, the valuation of travel agencies becomes increasingly important.
Revenue Multiples
Revenue multiples, such as price-to-sales ratio, measure the agency’s value against its annual sales. It provides an indication of how investors value the company’s ability to generate revenue. A higher revenue multiple suggests that investors believe in the agency’s growth prospects and are willing to pay a premium for its sales.
Travel agencies generate revenue through various channels, including ticket sales, accommodation bookings, tour packages, and ancillary services. The revenue multiple takes into account the agency’s ability to attract customers, negotiate favorable deals with suppliers, and effectively market their services to a wide audience.
Furthermore, revenue multiples can be influenced by market trends and economic conditions. For instance, during periods of economic growth and increased travel demand, travel agencies may experience higher revenue multiples as investors anticipate higher sales volumes and profitability.
EBITDA Multiples
EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes , Depreciation, and Amortization) multiples are commonly used in the travel industry to assess profitability. This multiple considers the agency’s earnings before non-operating expenses, making it a useful measure of its cash flow generation potential. A higher EBITDA multiple indicates stronger profitability and cash flow.
Travel agencies incur various expenses in their operations, including employee salaries, marketing costs, technology investments, and administrative expenses. By focusing on EBITDA, investors can evaluate the agency’s ability to generate profits from its core operations, excluding non-recurring or non-operating items.
Furthermore, EBITDA multiples can provide insights into the agency’s efficiency and cost management. Agencies with higher EBITDA multiples may have streamlined operations, effective cost control measures, and strong negotiating power with suppliers, allowing them to maximize their profitability.
Cash Flow Multiples
Travel agencies often rely heavily on cash flow to fund their operations and expansion plans. Cash flow multiples, such as price-to-cash flow ratio, reflect the agency’s ability to generate cash from its business activities. A higher cash flow multiple signifies a stronger ability to generate and manage cash flow.
Cash flow is essential for travel agencies to meet their day-to-day expenses, invest in technology and infrastructure, and seize growth opportunities. By assessing the agency’s cash flow multiples, investors can gauge its financial stability and ability to weather economic downturns.
Moreover, cash flow multiples can also highlight the agency’s ability to adapt to changing market conditions and customer preferences. Agencies that consistently generate strong cash flows may have implemented effective revenue diversification strategies, developed innovative products and services, or established long-term partnerships with key industry players.
It is important to note that valuation multiples should not be considered in isolation. Other factors, such as market competition, regulatory environment, customer satisfaction, and technological advancements, also play a significant role in determining the overall value of a travel agency.
Factors Influencing Valuation Multiples
Valuation multiples are not static figures but influenced by various factors that affect a travel agency’s value in the market. Understanding these factors can help agency owners strategically position their businesses to attract higher multiples.
Market Conditions
The overall state of the travel industry, including factors like demand, competition, and economic trends, can affect valuation multiples. During prosperous times with high demand, multiples tend to be more favorable. In contrast, economic downturns and industry challenges can lead to lower multiples.
Company Size and Growth
Travel agencies come in different sizes, ranging from small boutique firms to larger-scale organizations. Generally, larger agencies with a robust track record of growth tend to command higher multiples. This is because their size and growth potential provide a sense of stability and future profitability.
Profitability and Risk
The profitability and risk profile of a travel agency also influence its valuation multiples. Agencies that consistently generate high profits and have lower perceived risks will typically receive higher multiples. Investors seek agencies with a track record of profitability and a manageable level of risk.
Calculating Valuation Multiples for a Travel Agency
Calculating valuation multiples for a travel agency involves a series of steps to ensure accuracy and reliability. Let’s explore the key steps involved in this process.
Steps in Calculation
- Identify the suitable financial metric: Determine the most relevant metric for calculating the multiple, such as revenue, earnings, or cash flow.
- Gather accurate financial data: Collect precise and up-to-date financial information from the agency’s financial statements or reliable industry sources.
- Calculate the multiple: Divide the chosen financial metric by the corresponding value, such as market capitalization or enterprise value.
- Compare with industry benchmarks: Benchmark the calculated multiple against industry averages or comparable companies to assess the agency’s relative value.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Relying solely on one multiple: Using multiple valuation methods and considering various multiples can provide a more comprehensive view of an agency’s value.
- Ignoring industry-specific dynamics: Travel agencies operate in a unique industry, and it’s crucial to factor in industry-specific variables when calculating multiples.
- Overlooking qualitative factors: While multiples provide valuable quantitative information, considering qualitative aspects like brand reputation and market positioning can round out the valuation analysis.
Interpreting Valuation Multiples
Interpreting valuation multiples involves understanding the implications they have on a travel agency’s financial standing, competitive positioning, and potential investment opportunities.
Comparing Multiples within the Industry
Comparing valuation multiples of a travel agency against industry peers can provide insights into its relative performance and value. Higher multiples suggest that the agency is perceived as stronger or more promising than its competitors, while lower multiples may indicate potential concerns or areas for improvement.
Understanding the Implications of High and Low Multiples
High multiples can indicate positive market sentiment, suggesting that investors have confidence in the travel agency’s future growth potential. However, it’s crucial to ensure that these higher multiples are supported by strong financial performance and industry trends. Conversely, low multiples could signal concerns or undervaluation, providing potential investment opportunities for astute investors.
As a travel agency owner, understanding valuation multiples is paramount for making informed strategic decisions and attracting investors. By comprehending the key multiples, factors that influence them, and their calculation and interpretation, you can strengthen your agency’s financial health and position it for long-term success in the dynamic travel industry.
Investor & Mentor

related posts:
SDE vs. EBITDA Adjustments: What Business Owners Should Know
Private sale vs. auction sale: what business owners should know, asset sale vs. share sale: what business owners should know, get in touch.
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.
All of cycling information sources
Home » Travel » Question: What Is The Role Of A Multiple Travel Agent
Question: What Is The Role Of A Multiple Travel Agent
Multiple – Multiple travel agencies are travel agencies that are part of a national chain of retail outlets. Call centers – Miniples and multiples all have call centres, this means that they can have retail travel agencies in high streets but also people can book holidays via the phone.
What does a multiple travel agent do?
There are two main types of travel agents; independent and multiple. Independent agents – such as ourselves can tailor make deals to suit customers’ needs. Multiples are vertically integrated, who can only sell the products that they provide.
What are the roles of travel agents?
Travel agents help their clients make travel plans. In addition to booking reservations, they assist customers in choosing their destination, transportation, and lodging and inform travellers of passport and visa requirements, rates of currency exchange, and import duties.
What are multiples in tourism?
A multiple travel agent is one which has a chain of branches. They are typically large organisations with a strong high street presence. Multiple travel agents did have a monopoly of the market for many years.
What different types of travel agents are there?
Travel agencies in the UK are either independent, multiple and miniple travel agents: Independent travel agents:are companies that cater for the needs of residents in small towns and villages. Multiple travel agents: Are companies which operate a chain of retail outlets through out the UK.
What do Hays travel sell?
Hays Travel Trade name Hays Travel Products Charter and scheduled passenger airlines, package holidays, cruise lines, hotels and resorts Brands Hays Cruise Hays Faraway Owner Estate of John Hays (56.42%) Dame Irene Hays (43.58%) Website www.haystravel.co.uk.
Why are travel agents important in tourism?
Intermediaries such as tour operators, wholesalers, travel agents and online retailers play a significant role in attracting international visitors to Britain. The travel trade can help open up new markets, attract more visitors to your destination and encourage them to spend more time exploring what you have to offer.
What is the most important role of a travel agency?
Travel agencies provide conveyance, accommodation, and admission to entertainment activities to individuals and groups scheduling trips. They offer advice on destinations, plan trip itineraries, and make travel arrangements for clients. They play a crucial role in the development and flourishment of tourism industry.
What is the most important job for a travel agent?
A travel agent’s role is to help people plan, choose and arrange their holiday. They will usually work to a budget set out by whoever is planning the holiday. They also offer advice and opinions on where to go and local tourist attractions, events and customs.
How do travel agents work?
A traveler works with a travel agent and finalizes their itinerary. The travel agent makes the booking and is credited with the booking via their accreditation number. The commission is paid to the travel agent. For most trips, the vendor pays commission to the travel agent after the client has traveled.
What are Miniple travel agents?
A ‘miniple’ travel agent is a company with a small. number of branches, often in a particular geographical. area. independent advice on holiday choices and a personal. service to their clients. miniples the chance to negotiate more favourable. terms with principals. Barrhead Travel in Scotland and Althams Travel in the.
What are the five functions of the operations department of a travel agency?
The most important functions of a travel agency are described below: Travel Information: A retail travel agency provides necessary travel information to the general public. Preparation of Itineraries: Liaison with Providers of Service: Ticketing: Provision of Foreign Currencies: Insurance:.
Are Hays Travel in trouble?
The firm which bought Thomas Cook shops has said up to 878 employees out of 4,500 may lose their jobs because of new coronavirus travel restrictions. Hays Travel took on more than 2,000 former Thomas Cook employees when it went bust in October last year.
How do Hays Travel make money?
Hays makes its money from the commission it receives as a travel agent, as well as from selling currency and its work as a tour operator.
Are Hays Travel still in business?
Hays Travel currently operates 535 shops and employs 7,700 people. Last September the company launched a consultation on 878 redundancies in its Foreign Exchange and Travel Academy. Following the consultation 261 permanent and temporary jobs were saved.
What is the important role of a travel agent and tour operator?
Travel agents are private retailers that provide their customers with services on behalf of hotels, airlines, car rental companies, and tour companies. A tour operator is a company that provides customers with activities and travel to and from these activities.
How does a travel agent get paid?
Travel agents get paid on commission by hotels, airlines and resorts, but many more are charging fees on top of that because of their time. Some agencies charge fees up front and then drop the fees when the client actually books.
What is the role of travel agencies in hospitality and tourism industry?
Travel agencies are private or public sector hospitality businesses that sell travel- and tourism-related services, as well as products, to customers. The travel agency will first talk to the customer to better understand what he or she wants.
What are the 3 departments of a travel agency?
The role of most agencies has been diversified into a series of services that can be divided into six main areas: 1) Travel Management. 2) Passenger assistance. 3) Consulting. 4) Marketing and internal communication. 5) Technology. 6) Leisure Services.
What are the 5 A’s of tourism?
These key elements are known as the 5 A’s: Access, Accommodation, Attractions, Activities, and Amenities.
What skills do you need to be a travel agent?
Travel Agent Qualifications/Skills: Strong sales and interpersonal skills. Excellent verbal and written communications skills. Ability to negotiate effectively. Excellent knowledge of computer reservation computer programs. Strong problem-solving skills. Detail oriented and highly organized.
How much do travel agents make annually?
Host Agency Reviews and the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) found some common ground in regard to the average salary of a travel agent. The BLS currently lists the average travel agent salary in 2019 as $44,690 with a range of $23,360 and $69,420 dividing the lower to upper 10% of travel agents.
Can you become a travel agent without experience?
Do You Need Qualification to Be a Travel Agent? Work from home travel agents must obtain a travel agent certification before starting their business. Dream Vacations franchise owners need only a computer, internet, and phone to run their business and become a travel agent without experience.
Do travel agents travel a lot?
Some travel agents do still travel for fun, but most will do at least one hotel site inspection or other work-related task while they’re there. Regardless of connections, you’re not traveling for free. With discounts come expectations, aka receiving business from your clients in return.
How much do travel agents make per trip?
Some offer a meager $2 per reservation (regardless of value), while others based on incentives and productivity will pay commissions as high as 20%. Across the board the average commissions are 3% for Internet bookings, 3-5% on promotional rental rates and 10% on leisure rates booked through GDS distribution channels.
Do travel agents let you make payments?
When you use a travel agent, you can book by putting down a deposit. Yup, you can reserve your spot for as little as $100 per person 1 . When you book your vacation online, you pay in full. When you use a travel agent, you can book by putting down a deposit.
Related Posts
- How Has The Role Of Travel Agents Changed
- Question: What Is A Multiple Travel Agent
- How Do Travel Agents Get Paid Multiple Ways
- Question: How To Make A Travel Role
- Where Can Travel Agents Buy Vouchers Travel Agent Incentive
- Question: How Do Independent Travel Agents Get Agent Number
- Quick Answer: How To Travel Multiple Countries
- Quick Answer: Can I Travel Abroad Multiple Times
- Can I Travel With Multiple Laptops
- Quick Answer: Can Teleporters Travel To Multiple Locations
- How To Travel With Multiple Passports
- Question: Do Travel Nurses Need Multiple Licenses
Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution, update may 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Mexico Travel Advisory
Travel advisory august 22, 2023, mexico - see state summaries.
Reissued after periodic review with general security updates, and the removal of obsolete COVID-19 page links.
Country Summary: Violent crime – such as homicide, kidnapping, carjacking, and robbery – is widespread and common in Mexico. The U.S. government has limited ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in many areas of Mexico, as travel by U.S. government employees to certain areas is prohibited or restricted. In many states, local emergency services are limited outside the state capital or major cities.
U.S. citizens are advised to adhere to restrictions on U.S. government employee travel. State-specific restrictions are included in the individual state advisories below. U.S. government employees may not travel between cities after dark, may not hail taxis on the street, and must rely on dispatched vehicles, including app-based services like Uber, and regulated taxi stands. U.S. government employees should avoid traveling alone, especially in remote areas. U.S. government employees may not drive from the U.S.-Mexico border to or from the interior parts of Mexico, except daytime travel within Baja California and between Nogales and Hermosillo on Mexican Federal Highway 15D, and between Nuevo Laredo and Monterrey on Highway 85D.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Mexico.
Do Not Travel To:
- Colima state due to crime and kidnapping .
- Guerrero state due to crime .
- Michoacan state due to crime and kidnapping .
- Sinaloa state due to crime and kidnapping
- Tamaulipas state due to crime and kidnapping.
- Zacatecas state due to crime and kidnapping .
Reconsider Travel To:
- Baja California state due to crime and kidnapping .
- Chihuahua state due to crime and kidnapping .
- Durango state due to crime .
- Guanajuato state due to crime and kidnapping .
- Jalisco state due to crime and kidnapping .
- Morelos state due to crime .
- Sonora state due to crime and kidnapping .
Exercise Increased Caution When Traveling To:
- Aguascalientes state due to crime .
- Baja California Sur state due to crime .
- Chiapas state due to crime .
- Coahuila state due to crime .
- Hidalgo state due to crime .
- Mexico City due to crime .
- Mexico State due to crime .
- Nayarit state due to crime.
- Nuevo Leon state due to crime and kidnapping .
- Oaxaca state due to crime .
- Puebla state due to crime and kidnapping .
- Queretaro state due to crime .
- Quintana Roo state due to crime .
- San Luis Potosi state due to crime and kidnapping .
- Tabasco state due to crime .
- Tlaxcala state due to crime .
- Veracruz state due to crime .
Exercise Normal Precautions When Traveling To:
- Campeche state
- Yucatan state
Visit our website for Travel to High-Risk Areas .
If you decide to travel to Mexico:
- Keep traveling companions and family back home informed of your travel plans. If separating from your travel group, send a friend your GPS location. If taking a taxi alone, take a photo of the taxi number and/or license plate and text it to a friend.
- Use toll roads when possible and avoid driving alone or at night. In many states, police presence and emergency services are extremely limited outside the state capital or major cities.
- Exercise increased caution when visiting local bars, nightclubs, and casinos.
- Do not display signs of wealth, such as wearing expensive watches or jewelry.
- Be extra vigilant when visiting banks or ATMs.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Follow the U.S. Embassy on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Mexico.
- Mariners planning travel to Mexico should check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts , which include instructions on reporting suspicious activities and attacks to Mexican naval authorities.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
- Visit the CDC page for the latest travel health information related to your travel.
Aguascalientes state – Exercise Increased Caution
Exercise increased caution due to crime.
Criminal activity and violence may occur throughout the state.
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Aguascalientes state.
Baja California state – Reconsider Travel
Reconsider travel due to crime and kidnapping.
Transnational criminal organizations compete in the border area to establish narco-trafficking and human smuggling routes. Violent crime and gang activity are common. Travelers should remain on main highways and avoid remote locations. Of particular concern is the high number of homicides in the non-tourist areas of Tijuana. Most homicides appeared to be targeted; however, criminal organization assassinations and territorial disputes can result in bystanders being injured or killed. U.S. citizens and LPRs have been victims of kidnapping.
U.S. government employees must adhere to the noted restrictions:
- Mexicali Valley: U.S. government employees should avoid the Mexicali Valley due to the heightened possibility of violence between rival cartel factions. The boundaries of the restricted area are: to the east, the Baja California/Arizona and Baja California/Sonora borders; to the south, from La Ventana (on Highway 5) due east to the Colorado River; to the west, Highway 5; and to the north, Boulevard Lazaro Cardenas/Highway 92/Highway 1 to Carretera Aeropuerto, from the intersection of Highway 1 and Carretera Aeropuerto due north to the Baja California/California border, and from that point eastward along the Baja California/California border.
- Travelers may use Highways 2 and 2D to transit between Mexicali, Los Algodones, and San Luis Rio Colorado during daylight hours. Travelers may also use Highways 1 and 8 to transit to and from the Mexicali Airport during daylight hours. Travel on Highway 5 is permissible during daylight hours.
There are no other travel restrictions for U.S. government employees in Baja California state. These include high-traffic tourism areas of border and coastal communities, such as Tijuana , Ensenada , and Rosarito .
Baja California Sur state – Exercise Increased Caution
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Baja California Sur state.
Campeche state – Exercise Normal Precautions
Exercise normal precautions.
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Campeche state.
Chiapas state – Exercise Increased Caution
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Chiapas state.
Chihuahua state – Reconsider Travel
Violent crime and gang activity are common. Most homicides are targeted assassinations against members of criminal organizations. Battles for territory between criminal groups have resulted in violent crime in areas frequented by U.S. citizens and U.S. government employees, including restaurants and malls during daylight hours. Bystanders have been injured or killed in shooting incidents. U.S. citizens and LPRs have been victims of kidnapping.
U.S. government employee travel is limited to the following areas with the noted restrictions:
- Ciudad Juarez: U.S. government employees may travel to the area of Ciudad Juarez bounded to the east by Bulevar Independencia; to the south by De los Montes Urales/Avenida Manuel J Clouthier/Carretera de Juárez; to the west by Via Juan Gabriel/Avenida de los Insurgentes/Calle Miguel Ahumada/Francisco Javier Mina/Melchor Ocampo; and to the north by the U.S.-Mexico border. Direct travel to the Ciudad Juarez airport (officially called the Abraham González International Airport) and the factories located along Bulevar Independencia and Las Torres is permitted. Travel to San Jerónimo is permitted only through the United States via the Santa Teresa U.S. Port of Entry; travel via Anapra is prohibited.
U.S. government employees may only travel from Ciudad Juarez to the city of Chihuahua during daylight hours via Federal Highway 45, with stops permitted only at the Guardia Nacional División Caminos station, the Umbral del Milenio overlook area, the border inspection station at KM 35, and the shops and restaurants on Federal Highway 45 in the city of Ahumada.
- U.S. government employees may travel between Ciudad Juarez and Ascension via Highway 2.
- Nuevo Casas Grandes Area (including Nuevo Casas Grandes, Casas Grandes, Mata Ortiz, Colonia Juárez, Colonia LeBaron, Paquimé and San Buenaventura): U.S. government employees may travel to the Nuevo Casas Grandes area during daylight hours via Mexico Federal Highway 2, and subsequently Federal Highway 10, to Nuevo Casas Grandes. Employees are permitted to stay overnight in the cities of Nuevo Casas Grandes and Casas Grandes only.
- City of Chihuahua: U.S. government employees may travel at any time to the area of the city of Chihuahua bounded to the north by Avenida Transformación; to the east by Avenida Tecnológico/Manuel Gómez Morín/Highway 16/Blvd.José Fuentes Mares; to the west by the city boundary; and to the south by Periférico Francisco R. Almada.
- U.S. government employees may travel on Highways 45, 16, and 45D through the city of Chihuahua and to the Chihuahua airport (officially called the General Roberto Fierro Villalobos International Airport).
- U.S. government employees may travel to Santa Eulalia to the east of the city of Chihuahua, as well as to Juan Aldama via Highway 16 to the northeast.
- U.S. government employees may travel south of the city of Chihuahua on Highway 45 to the southern boundary of Parral, including each town directly connected to Highway 45, including Lázaro Cárdenas, Pedro Meoqui, Santa Cruz de Rosales, Delicias, Camargo, Ciudad Jiménez, and Parral itself.
- U.S. government employees may only travel on official business from the city of Chihuahua on Highway 16 to Ciudad Cuauhtémoc bounded by Highway 21 to the north and east, Highway 5 to the west, and Bulevar Jorge Castillo Cabrera to the south.
- Ojinaga: U.S. government employees must travel to Ojinaga via U.S. Highway 67 and enter through the U.S. Port of Entry in Presidio, Texas.
- Palomas: U.S. government employees may travel to Palomas via U.S. highways through the U.S. Port of Entry in Columbus, New Mexico, or via Highway 2 in Mexico.
U.S. government employees may not travel to other areas of Chihuahua, including Copper Canyon .
Coahuila state – Exercise Increased Caution
Violent crime and gang activity occur in parts of Coahuila state.
U.S. government employees must adhere to the following travel restrictions:
- Zaragoza, Morelos, Allende, Nava, Jimenez, Villa Union, Guerrero, and Hidalgo municipalities : U.S. government employees may not travel to these municipalities.
- Piedras Negras and Ciudad Acuña: U.S. government employees must travel directly from the United States and observe a curfew from midnight to 6:00 a.m. in both cities.
There are no other restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Coahuila state.
Colima state – Do Not Travel
Do not travel due to crime and kidnapping.
Violent crime and gang activity are widespread. Most homicides are targeted assassinations against members of criminal organizations. Shooting incidents between criminal groups have injured or killed bystanders. U.S. citizens and LPRs have been victims of kidnapping.
Travel for U.S. government employees is limited to the following areas with noted restrictions:
- Manzanillo: U.S. government employee travel is limited to the tourist and port areas of Manzanillo.
- Employees traveling to Manzanillo from Guadalajara must use Federal Toll Road 54D during daylight hours.
U.S. government employees may not travel to other areas of Colima state.
Durango state – Reconsider Travel
Reconsider travel due to crime.
Violent crime and gang activity are common in parts of Durango state.
- West and south of Federal Highway 45: U.S. government employees may not travel to this region of Durango state.
There are no other restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Durango state.
Guanajuato state – Reconsider Travel
Gang violence, often associated with the theft of petroleum and natural gas from the state oil company and other suppliers, occurs in Guanajuato, primarily in the south and central areas of the state. Of particular concern is the high number of murders in the southern region of the state associated with cartel-related violence. U.S. citizens and LPRs have been victims of kidnapping.
- Areas south of Federal Highway 45D: U.S. government employees may not travel to the area south of and including Federal Highway 45D, Celaya, Salamanca, and Irapuato.
There are no other restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Guanajuato state, which includes tourist areas in: San Miguel de Allende , Guanajuato City , and surrounding areas.
Guerrero state – Do Not Travel
Do not travel due to crime.
Crime and violence are widespread. Armed groups operate independently of the government in many areas of Guerrero. Members of these groups frequently maintain roadblocks and may use violence towards travelers. U.S. citizens and LPRs have been victims of kidnapping in previous years.
Travel for U.S. government employees is limited to the following area with the noted restrictions:
- Taxco: U.S. government employees must use Federal Highway 95D, which passes through Cuernavaca, Morelos, and stay within downtown tourist areas of Taxco. Employees may visit Grutas de Cacahuamilpa National Park during the day with a licensed tour operator.
U.S. government employees may not travel to other areas of the state of Guerrero, including to tourist areas in Acapulco , Zihuatanejo , and Ixtapa .
Hidalgo state – Exercise Increased Caution
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Hidalgo state.
Jalisco state – Reconsider Travel
Violent crime and gang activity are common in parts of Jalisco state. In Guadalajara, territorial battles between criminal groups take place in tourist areas. Shooting incidents between criminal groups have injured or killed innocent bystanders. U.S. citizens and LPRs have been victims of kidnapping.
- Jalisco-Michoacan border and Federal Highway 110: U.S. government employees may not travel to the area between Federal Highway 110 and the Jalisco-Michoacan border, nor travel on Federal Highway 110 between Tuxpan, Jalisco, and the Michoacan border.
- Federal Highway 80: U.S. government employees may not travel on Federal Highway 80 south of Cocula.
There are no other restrictions on travel for U.S government employees in Jalisco state which includes tourist areas in: Guadalajara Metropolitan Area , Puerto Vallarta (including neighboring Riviera Nayarit) , Chapala , and Ajijic .
Mexico City (Ciudad de Mexico) – Exercise Increased Caution
Both violent and non-violent crime occur throughout Mexico City. Use additional caution, particularly at night, outside of the frequented tourist areas where police and security patrol more routinely. Petty crime occurs frequently in both tourist and non-tourist areas.
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Mexico City.
Mexico State (Estado de Mexico) – Exercise Increased Caution
Both violent and non-violent crime occur throughout Mexico State. Use additional caution in areas outside of the frequented tourist areas, although petty crime occurs frequently in tourist areas as well.
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Mexico State.
Michoacan state – Do Not Travel
Do not travel due to crime and kidnapping.
Crime and violence are widespread in Michoacan state. U.S. citizens and LPRs have been victims of kidnapping.
Travel for U.S. government employees is limited to the following areas with the noted restrictions:
- Federal Highway 15D: U.S. government employees may travel on Federal Highway 15D to transit the state between Mexico City and Guadalajara.
- Morelia: U.S. government employees may travel by air and by land using Federal Highways 43 or 48D from Federal Highway 15D.
- Lazaro Cardenas: U.S. government employees must travel by air only and limit activities to the city center or port areas.
U.S. government employees may not travel to other areas of the state of Michoacan, including the portions of the Monarch Butterfly Reserve located in Michoacan.
Morelos state – Reconsider Travel
Violent crime and gang activity are common in parts of Morelos state.
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Morelos state.
Nayarit state – Exercise Increased Caution
Criminal activity and violence may occur throughout Nayarit state.
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S government employees in Nayarit state.
Nuevo Leon state – Exercise Increased Caution
Exercise increased caution due to crime and kidnapping.
Criminal activity and violence may occur throughout the state. U.S. citizens and LPRs have been victims of kidnapping.
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Nuevo Leon state.
Oaxaca state – Exercise Increased Caution
Criminal activity and violence occur throughout the state.
U.S. travelers are reminded that U.S. government employees must adhere to the following travel restrictions:
- Isthmus region: U.S. government employees may not travel to the area of Oaxaca bounded by Federal Highway 185D to the west, Federal Highway 190 to the north, and the Oaxaca-Chiapas border to the east. This includes the cities of Juchitan de Zaragoza, Salina Cruz, and San Blas Atempa.
- Federal Highway 200 northwest of Pinotepa: U.S. government employees may not use Federal Highway 200 between Pinotepa and the Oaxaca-Guerrero border.
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees to other parts of Oaxaca state, which include tourist areas in: Oaxaca City , Monte Alban , Puerto Escondido, and Huatulco .
Puebla state – Exercise Increased Caution
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Puebla state.
Queretaro state – Exercise Increased Caution
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Queretaro state.
Quintana Roo state – Exercise Increased Caution
Criminal activity and violence may occur in any location, at any time, including in popular tourist destinations. Travelers should maintain a high level of situational awareness, avoid areas where illicit activities occur, and promptly depart from potentially dangerous situations.
While not directed at tourists, shootings between rival gangs have injured innocent bystanders. Additionally, U.S. citizens have been the victims of both non-violent and violent crimes in tourist and non-tourist areas.
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Quintana Roo state. However, personnel are advised to exercise increased situational awareness after dark in downtown areas of Cancun, Tulum, and Playa del Carmen, and to remain in well-lit pedestrian streets and tourist zones.
San Luis Potosi state – Exercise Increased Caution
Criminal activity and violence may occur throughout the state. U.S. citizens and LPRs have been victims of kidnapping.
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in San Luis Potosi state.
Sinaloa state – Do Not Travel
Violent crime is widespread. Criminal organizations are based in and operating in Sinaloa. U.S. citizens and LPRs have been victims of kidnapping.
- Mazatlan: U.S. government employees may travel to Mazatlan by air or sea only, are limited to the Zona Dorada and historic town center, and must travel via direct routes between these destinations and the airport and sea terminal.
- Los Mochis and Topolobampo: U.S. government employees may travel to Los Mochis and Topolobampo by air or sea only, are restricted to the city and the port, and must travel via direct routes between these destinations and the airport.
U.S. government employees may not travel to other areas of Sinaloa state.
Sonora state – Reconsider Travel
Sonora is a key location used by the international drug trade and human trafficking networks. Violent crime is widespread. U.S. citizens and LPRs have been victims of kidnapping. Travelers should maintain a heightened level of awareness of their surroundings in all their travels in Sonora. Security incidents may occur in any area of Sonora.
- Travel between Hermosillo and Nogales: U.S. government employees may travel between the U.S. Ports of Entry in Nogales and Hermosillo during daylight hours via Federal Highway 15 only. U.S. government employees may not use ANY taxi services, public buses, nor ride-share applications due to a lack of secure vetting and/or dispatching procedures. Travelers should exercise caution and avoid unnecessary stops as security incidents, including sporadic, armed carjackings, and shootings have been reported along this highway during daylight hours. Travelers should have a full tank of gas and inform friends or family members of their planned travel.
- Nogales: U.S. government employees may not travel in the triangular area north of Avenida Tecnologico, west of Bulevar Luis Donaldo Colosio (Periferico), nor east of Federal Highway 15D (Corredor Fiscal). U.S. government employees also may not travel in the residential and business areas to east of the railroad tracks along Plutarco Elias Calle (HWY 15) and Calle Ruiz Cortino, including the business area around the Morley pedestrian gate port-of-entry. U.S. government employees may not use ANY taxi services, public buses, nor ride-share applications in Nogales due to a lack of secure vetting and/or dispatching procedures and the danger of kidnapping and other violent crimes.
- Puerto Peñasco: U.S. government employees may travel between Puerto Peñasco and the Lukeville-Sonoyta U.S. Port of Entry during daylight hours via Federal Highway 8 only. They may not travel on any other route to Puerto Peñasco. U.S. government employees may not use ANY taxi services, public buses, nor ride-share applications in Puerto Peñasco. due to a lack of secure vetting and/or dispatching procedures and the danger of kidnapping and other violent crimes.
- Triangular region near Mariposa U.S. Port of Entry: U.S. government employees may not travel into or through the triangular region west of the Mariposa U.S. Port of Entry, east of Sonoyta, and north of Altar municipality.
- San Luis Rio Colorado, Cananea, and Agua Prieta : U.S. government employees may travel directly from the nearest U.S. Port of Entry to San Luis Rio Colorado, Cananea (via Douglas Port of Entry), and Agua Prieta, but may not go beyond the city limits. Travel is limited to daylight hours only. Travel between Nogales and Cananea via Imuris is not permitted. U.S. government employees may not use ANY taxi services, public buses, nor ride-share applications in these cities due to a lack of secure vetting and/or dispatching procedures and the danger of kidnapping and other violent crimes.
- Eastern and southern Sonora (including San Carlos Nuevo Guaymas and Alamos): U.S. government employees may not travel to areas of Sonora east of Federal Highway 17, the road between Moctezuma and Sahuaripa, and State Highway 20 between Sahuaripa and the intersection with Federal Highway 16. U.S. government employees may travel to San Carlos Nuevo Guaymas and Alamos; travel to Alamos is only permitted by air and within city limits. U.S. government employees may not travel to areas of Sonora south of Federal Highway 16 and east of Federal Highway 15 (south of Hermosillo), as well as all points south of Guaymas, including Empalme, Guaymas, Obregon, and Navojoa. U.S. government employees may not use ANY taxi services, public buses, nor ride-share applications in these areas due to a lack of secure vetting and/or dispatching procedures and the danger of kidnapping and other violent crimes.
U.S. government employees may travel to other parts of Sonora state in compliance with the above restrictions, including tourist areas in: Hermosillo , Bahia de Kino , and Puerto Penasco .
Tabasco state – Exercise Increased Caution
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Tabasco state.
Tamaulipas state – Do Not Travel
Organized crime activity – including gun battles, murder, armed robbery, carjacking, kidnapping, forced disappearances, extortion, and sexual assault – is common along the northern border and in Ciudad Victoria. Criminal groups target public and private passenger buses, as well as private automobiles traveling through Tamaulipas, often taking passengers and demanding ransom payments.
Heavily armed members of criminal groups often patrol areas of the state and operate with impunity particularly along the border region from Reynosa to Nuevo Laredo. In these areas, local law enforcement has limited capacity to respond to incidents of crime. Law enforcement capacity is greater in the tri-city area of Tampico, Ciudad Madero, and Altamira, which has a lower rate of violent criminal activity compared to the rest of the state.
U.S. citizens and LPRs have been victims of kidnapping.
- Matamoros and Nuevo Laredo: U.S. government employees may only travel within a limited radius around and between the U.S. Consulates in Nuevo Laredo and Matamoros, their homes, the respective U.S. Ports of Entry, and limited downtown sites, subject to an overnight curfew.
- Overland travel in Tamaulipas: U.S. government employees may not travel between cities in Tamaulipas using interior Mexican highways. Travel between Nuevo Laredo and Monterrey is limited to Federal Highway 85D during daylight hours with prior authorization.
U.S. government employees may not travel to other parts of Tamaulipas state.
Tlaxcala state – Exercise Increased Caution
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Tlaxcala state.
Veracruz state – Exercise Increased Caution
Violent crime and gang activity occur with increasing frequency in Veracruz, particularly in the center and south near Cordoba and Coatzacoalcos. While most gang-related violence is targeted, violence perpetrated by criminal organizations can affect bystanders. Impromptu roadblocks requiring payment to pass are common.
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Veracruz state.
Yucatan state – Exercise Normal Precautions
There are no restrictions on travel for U.S. government employees in Yucatan state, which include tourist areas in: Chichen Itza , Merida , Uxmal , and Valladolid .
Zacatecas state – Do Not Travel
Violent crime, extortion, and gang activity are widespread in Zacatecas state. U.S. citizens and LPRs have been victims of kidnapping.
- Zacatecas City : U.S. government employee travel is limited to Zacatecas City proper, and employees may not travel overland to Zacatecas City.
- U.S. government employees may not travel to other areas of Zacatecas state.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, search for travel advisories, external link.
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A multiple travel agent is one which has a chain of branches. They are typically large organisations with a strong high street presence. Multiple travel agents did have a monopoly of the market for many years. However, they have struggled to compete with the Internet travel agents, who have fewer overheads and are more conveniently located- on ...
Multiple Travel Agents operate as part of a large chain or group that has multiple branches or outlets across different locations. They can offer a wide range of products and services, such as the following: They can also benefit from economies of scale, bulk buying, and brand recognition. Some examples of multiple Travel Agents are TUI, Thomas ...
A travel agency is a business that helps people and groups choose, plan, and book travel-related services. Flights, hotels, rides, trips, sports, and other things can be a part of these services. Most travel companies know about a lot of different trips that their clients can take that fit their wants and budgets.
Travel agents include customization of itineraries and personalized service. - Itineraries tailored to your preferences, interests, and budget. - Suggestions based on their travel experiences or client feedback. - Access to hidden gems and unique experiences that may not be easily found online.
Travel. There are three main categories of travel agents: business, special interest, and leisure, and they fall into six types. These are: Global distribution systems. Online travel agents. Guest information centers. Hotel and concierge agents. Inbound tour operators. Independent travel agents.
Travel agencies can be categories on the basis of business or leisure such as: Leisure Travel Agency: These types of travel agencies manly serve holidaymakers with package tours. Business Travel agency: Today, business travel has become core area for many travel agencies. Business travel agency arrange travel for business travelers and ...
A travel agent assists individuals or groups in planning, organizing, and booking various aspects of their travel arrangements. They act as intermediaries between travelers and travel suppliers, such as airlines, hotels, car rental companies, and tour operators. Travel agents have in-depth knowledge of different destinations, travel options, and industry trends, which they leverage to provide ...
Definition of a. Travel Agent. A travel agent is a professional advisor who specializes in planning and booking travel experiences for individuals, groups, and businesses. They serve as a bridge between travelers and various travel service providers, such as airlines, hotels, and tour companies. Utilizing their extensive knowledge of travel ...
A travel agency is essentially the 'middle man' between travel companies and the general public i.e consumers. They book all sorts of travel-related experiences for customers on behalf of larger companies. The main aim of a travel agency is to make the booking process simpler for the public, who might lack the time or confidence to book ...
Travel Agencies. Figure 7.2 A travel agency in the United Kingdom. A travel agency is a business that operates as the intermediary between the travel industry (supplier) and the traveller (purchaser). Part of the role of the travel agency is to market prepackaged travel tours and holidays to potential travellers.
travel agent: [noun] a person engaged in selling and arranging transportation, accommodations, tours, or trips for travelers.
A travel agency is a business that operates as the intermediary between the travel industry (supplier) and the traveller (purchaser). Part of the role of the travel agency is to market prepackaged travel tours and holidays to potential travellers. The agency can further function as a broker between the traveller and hotels, car rentals, and ...
Both host agencies and consortia are powerful allies for independent travel advisors, according to Susan Ferrell, owner and president of Travel Experts, a host agency based in Raleigh, N.C. "Each provides a different set of resources, so of course it's beneficial to be part of both," she said. "This is most easily accomplished by ...
Travel agency in Taiwan. A travel agency is a private retailer or public service that provides travel and tourism -related services to the general public on behalf of accommodation or travel suppliers to offer different kinds of travelling packages for each destination. Travel agencies can provide outdoor recreation, arranging logistics for ...
Here are the 6 types of travel agents tour operators can work with in building mutually beneficial relationships. 1. Independent travel agents. Most travelers prefer independent travel agents as their go-to type of retail travel agent. Both offline and online travel agents want to customize the travel itineraries for their clients in order to ...
Air Travel - air travel is the action or process of making a journey by aircraft. Air/sea - a term referring to tickets, trips, fares, etc. that include both air and land-based travel arrangements, such as a cruise package with air included. Aircraft - Generally speaking, any machine capable of flight.
Discuss arrangements and costs with customers. Once they have found travel options that meet the specified requirements, they calculate costs and discuss arrangements with customers. Travel agents often use sales skills to help customers make decisions about their travel plans. Advise clients about itineraries and plans.
lessen the risk that something will be forgotten and that things will go wrong. remove obstacles that get in the way of what the client wants to do. add convenience by relieving the client from doing all the work. provide travel options that are good, better, and best. rescue the client from difficult situations.
An online travel agency, or OTA, is a website or mobile app that allows users to search for and book travel services such as flights, hotels, car rentals, cruises, and activities. The booking is made directly with the online travel agency but confirmed by the service provider, such as an airline or a hotel. As a customer, your relationship is ...
Multiple reservations, often subject to deposit forfeiture, which wholesalers or travel agents make with a supplier in anticipation of resale. boarding pass. A permit to board a ship, plane, or other form of transportation. In the case of air travel, the card indicates boarding gate and aircraft seat number. booking code
Serian Camp emphasizes great guiding. Because of their first hand knowledge or properties in a specific region, travel specialists also know the value for money properties; the hidden gems which are comparatively cheap but have great guides or a stunning location.On the flip-side they know the properties that look amazing online or get incredible TripAdvisor reviews that just don't live up ...
Travel agencies generate revenue through various channels, including ticket sales, accommodation bookings, tour packages, and ancillary services. The revenue multiple takes into account the agency's ability to attract customers, negotiate favorable deals with suppliers, and effectively market their services to a wide audience.
A 'miniple' travel agent is a company with a small. number of branches, often in a particular geographical. area. independent advice on holiday choices and a personal. service to their clients. miniples the chance to negotiate more favourable. terms with principals. Barrhead Travel in Scotland and Althams Travel in the.
Reissued after periodic review with general security updates, and the removal of obsolete COVID-19 page links. Country Summary: Violent crime - such as homicide, kidnapping, carjacking, and robbery - is widespread and common in Mexico.The U.S. government has limited ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in many areas of Mexico, as travel by U.S. government employees to ...