National Geographic content straight to your inbox—sign up for our popular newsletters here


Inside the Controversial World of Slum Tourism
People have toured the world’s most marginalized, impoverished districts for over a century.
Hundreds of shanty towns line the riverbanks, train tracks, and garbage dumps in the Filipino capital—the most jammed-packed areas in one of the world’s most densely populated cities. Around a quarter of its 12 million people are considered “informal settlers.”
Manila is starkly representative of a global problem. According to the United Nations , about a quarter of the world’s urban population lives in slums—and this figure is rising fast.
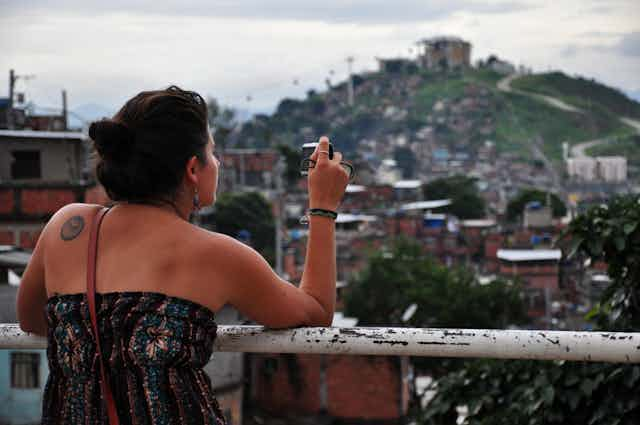
Rich cultural heritage brings visitors to Manila, but some feel compelled to leave the safety of the historic center sites to get a glimpse of the city’s inequality. Tour operators in the Philippines —as well as places like Brazil and India —have responded by offering “slum tours” that take outsiders through their most impoverished, marginalized districts.
Slum tourism sparks considerable debate around an uncomfortable moral dilemma. No matter what you call it—slum tours, reality tours, adventure tourism, poverty tourism—many consider the practice little more than slack-jawed privileged people gawking at those less fortunate. Others argue they raise awareness and provide numerous examples of giving back to the local communities. Should tourists simply keep their eyes shut?

Around a quarter of Manila's 12 million people are considered “informal settlers."

Rich cultural heritage brings visitors to Manila, but some feel compelled to leave the safety of the historic center sites to get a glimpse of the city’s inequality.
Slumming For Centuries
Slum tourism is not a new phenomenon, although much has changed since its beginning. “Slumming” was added to the Oxford English Dictionary in the 1860s, meaning “to go into, or frequent, slums for discreditable purposes; to saunter about, with a suspicion, perhaps, of immoral pursuits.” In September 1884, the New York Times published an article about the latest trend in leisure activities that arrived from across the pond, “‘Slumming’ will become a form of fashionable dissipation this winter among our Belles, as our foreign cousins will always be ready to lead the way.”
Usually under the pretense of charity and sometimes with a police escort, rich Londoners began braving the city’s ill-reputed East End beginning around 1840. This new form of amusement arrived to New York City from wealthy British tourists eager to compare slums abroad to those back home. Spreading across the coast to San Francisco, the practice creeped into city guide books. Groups wandered through neighborhoods like the Bowery or Five Points in New York to peer into brothels, saloons, and opium dens.
Visitors could hardly believe their eyes, and justifiably so. “I don’t think an opium den would have welcomed, or allowed access to, slummers to come through if they weren’t there to smoke themselves,” Chad Heap writes in his book Slumming: Sexual and Racial Encounters in American Nightlife , 1885–1940 . Recognizing the business opportunity, outsiders cashed in on the curiosity by hiring actors to play the part of addicts or gang members to stage shoot-’em-ups in the streets. After all, no one wanted the slum tourists to demand a refund or go home disappointed.

Smokey Tours does not allow participants to take photos, but this policy proves difficult to enforce.

The city of San Francisco eventually banned such mockery of the poor, the New York Times reported in 1909: “This is a heavy blow to Chinatown guides, who have collected a fee of two dollars each. The opium smokers, gamblers, blind paupers, singing children, and other curiosities were all hired.”
Tours also brought positive results, as Professor of History Seth Koven highlights in his research of slumming in Victorian London. Oxford and Cambridge Universities opened study centers in the late 19th-century to inform social policy, which was only possible by seeing the underprivileged neighborhoods firsthand.
Popularity waned after World War II with the creation of welfare and social housing—then rose again in the 1980s and 1990s as those state provisions declined and labor demands increased.
Presenting Poverty
Plastic arrives from all over India to the dark alleys and corrugated shacks of Dharavi in Mumbai —the second-largest slum on the continent of Asia (after Orangi Town in Pakistan ) and third-largest slum in the world. Ushered around by the company Reality Tour and Travel , tourists see a thriving recycling industry which employs around ten thousand to melt, reshape, and mould discarded plastic. They stop to watch the dhobiwallahs , or washermen, scrub sheets from the city’s hospitals and hotels in an open-air laundry area.
In a TripAdvisor review, one recent participant from Virginia appreciated the focus on community. “It was great to hear about the economy, education and livelihood of the residents,” she writes. “The tour group doesn't allow photography or shopping which I think is really important. It didn't feel exploitative, it felt educational.”
One traveler from London commented on the extremity of the scene. "Had to stop after about 20 minutes into it due to the overbearing nature of the surroundings. The tour is not for the faint hearted. I would've liked a few more disclaimers on the website to warn us about the nature of it." Another guest from the United Kingdom expressed disappointment over the so-called family meal. “This was in the home of one of the guides and, whilst his mum made lunch a delicious meal that we ate in her house, she didn’t eat with us so it wasn’t really what I had expected from a family lunch (or the photos promoting such on the website).”

Smokey Tours enters the Manila North Cemetery, inhabited by some of Manila's poorest people.

Children jump from grave to grave in the city’s largest cemetery.
Reality Tours hopes to challenge the stereotypical perception of slums as despairing places inhabited by hopeless people. The tour presented slum residents as productive and hardworking, but also content and happy. Analyzing more than 230 reviews of Reality Tour and Travel in her study , Dr. Melissa Nisbett of King’s College London realized that for many Dharavi visitors, poverty was practically invisible. “As the reviews show, poverty was ignored, denied, overlooked and romanticized, but moreover, it was depoliticized.” Without discussing the reason the slum existed, the tour decontextualized the plight of the poor and seemed only to empower the wrong people–the privileged, western, middle class visitors.
With good intentions, the company states that 80 percent of the profits benefit the community through the efforts of its NGO that works to provide access to healthcare, organize educational programs, and more. Co-founder Chris Way spoke to National Geographic after his company surged in popularity from the sleeper hit Slumdog Millionaire . “We do try and be as transparent as possible on our website, which does allay many people’s fears.” Way personally refuses a salary for his work.
No Two Cities Alike
The main question should be: Is poverty the central reason to visit?
Other cities take different approaches to slum tourism. In the early 1990s, when black South Africans began offering tours of their townships—the marginalized, racially-segregated areas where they were forced to live—to help raise global awareness of rampant human rights violations. Rather than exploitation inflicted by outsiders, local communities embraced slum tourism as a vehicle to take matters of their traditionally neglected neighborhoods into their own hands.
- Nat Geo Expeditions
Some free tours of favelas in Rio de Janeiro provided an accessible option to the crowds that infiltrated the city during the World Cup and Summer Olympics, while most companies continue to charge. Tour manager Eduardo Marques of Brazilian Expeditions explains how their authenticity stands out, “We work with some local guides or freelancers, and during the tour we stop in local small business plus [offer] capoeira presentations that [support] the locals in the favela. We do not hide any info from our visitors. The real life is presented to the visitors.”
Smokey Tours in Manila connected tourists with the reality facing inhabitants of a city landfill in Tondo (until 2014 when it closed) to tell their stories. Now the company tours around Baseco near the port, located in the same crowded district and known for its grassroots activism. Locally-based photographer Hannah Reyes Morales documented her experience walking with the group on assignment for National Geographic Travel. “I had permission to photograph this tour from both the operator and community officials, but the tour itself had a no photography policy for the tourists.” With the policy difficult to enforce, some guests secretly snapped photos on their phones. “I observed how differently tourists processed what they were seeing in the tour. There were those who were respectful of their surroundings, and those who were less so.”
All About Intention
Despite sincere attempts by tour operators to mitigate offense and give back to locals, the impact of slum tourism stays isolated. Ghettoized communities remain woven into the fabric of major cities around the world, each with their individual political, historical, and economic concerns that cannot be generalized. Similarly, the motivations behind the tourism inside them are as diverse as the tour participants themselves. For all participants involved, operators or guests, individual intentions matter most.

The Baseco neighborhood is located on the Pasig river near the city port, but lacks access to clean drinking water.
Better connections between cities allow more people to travel than ever before, with numbers of international tourists growing quickly every year. While prosperity and quality of life have increased in many cities, so has inequality. As travelers increasingly seek unique experiences that promise authentic experiences in previously off-limits places, access through tours helps put some areas on the map.
Travel connects people that would otherwise not meet, then provides potential to share meaningful stories with others back home. Dr. Fabian Frenzel, who studies tourism of urban poverty at the University of Leicester, points out that one of the key disadvantages of poverty is a lack of recognition and voice. “If you want to tell a story, you need an audience, and tourism provides that audience.” Frenzel argues that even taking the most commodifying tour is better than ignoring that inequality completely.
For the long-term future of these communities, the complex economic, legal, and political issues must be addressed holistically by reorganizing the distribution of resources. While illuminating the issue on a small scale, slum tourism is not a sufficient answer to a growing global problem.
Related Topics
- TRAVEL PHOTOGRAPHY
- PHOTOGRAPHY
You May Also Like

How I got the shot: Richard James Taylor on capturing Mekong sunset magic in Laos

Photo story: wild beauty in eastern Sardinia, from coast to mountains
Introducing nat geo kids book bundle.

How I got the shot: Dikpal Thapa on risking it all for one image

How to visit Grand Teton National Park

These are the best travel photos of 2022

How I got the shot: Richard James Taylor on capturing Dubrovnik's golden hour

The Masterclasses 2023: 10 practical tips to help you succeed as a travel photographer
- Environment
- Paid Content
- Photography
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved

Slumming it: how tourism is putting the world’s poorest places on the map
Lecturer in the Political Economy of Organisation, University of Leicester
Disclosure statement
From 2012-2014 Fabian Frenzel was a Marie-Curie Fellow and has received funding from the European Union to conduct his research on slum tourism.
University of Leicester provides funding as a member of The Conversation UK.
View all partners
Back in Victorian times, wealthier citizens could sometimes be found wandering among London’s poorer, informal neighbourhoods, distributing charity to the needy. “Slumming” – as it was called – was later dismissed as a morally dubious and voyeuristic pastime. Today, it’s making a comeback; wealthy Westerners are once more making forays into slums – and this time, they’re venturing right across the developing world.
According to estimates by tour operators and researchers , over one million tourists visited a township, favela or slum somewhere in the world in 2014. Most of these visits were made as part of three or four-hour tours in the hotspots of global slum tourism; major cities and towns in Johannesburg, Rio de Janeiro and Mumbai.
There is reason to think that slum tourism is even more common than these numbers suggest. Consider the thousands of international volunteers, who spend anything from a few days to several months in different slums across the world.
The gap year has become a rite of passage for young adults between school and university and, in the UK, volunteering and travel opportunities are often brokered by commercial tourism operators. In Germany and the US, state sponsored programs exist to funnel young people into volunteering jobs abroad.

International volunteering is no longer restricted to young people at specific points in their lives. Volunteers today are recruited across a wide range of age groups . Other travellers can be considered slum-tourists: from international activists seeking cross-class encounters to advance global justice, to students and researchers of slums and urban development conducting fieldwork in poor neighbourhoods.
Much modern tourism leads richer people to encounter relatively poorer people and places. But in the diverse practices of slum tourism, this is an intentional and explicit goal: poverty becomes the attraction – it is the reason to go.
Many people will instinctively think that this kind of travel is morally problematic, if not downright wrong. But is it really any better to travel to a country such as India and ignore its huge inequalities?
Mapping inequality
It goes without saying that ours is a world of deep and rigid inequalities. Despite some progress in the battles against absolute poverty, inequality is on the rise globally . Few people will openly disagree that something needs to be done about this – but the question is how? Slum tourism should be read as an attempt to address this question. So, rather than dismissing it outright, we should hold this kind of tourism to account and ask; does it help to reduce global inequality?
My investigation into slum tourism provided some surprising answers to this question. We tend to think of tourism primarily as an economic transaction. But slum tourism actually does very little to directly channel money into slums: this is because the overall numbers of slum tourists and the amount of money they end up spending when visiting slums is insignificant compared with with the resources needed to address global inequality.

But in terms of symbolic value, even small numbers of slum tourists can sometimes significantly alter the dominant perceptions of a place. In Mumbai, 20,000 tourists annually visit the informal neighbourhood of Dharavi , which was featured in Slumdog Millionaire. Visitor numbers there now rival Elephanta Island in Mumbai – a world heritage site.
Likewise, in Johannesburg, most locals consider the inner-city neighbourhood of Hillbrow to be off limits. But tourists rate walking tours of the area so highly that the neighbourhood now features as one of the top attractions of the city on platforms such as Trip Advisor . Tourists’ interest in Rio’s favelas has put them on the map; before, they used to be hidden by city authorities and local elites .
Raising visibility
Despite the global anti-poverty rhetoric, it is clear that today’s widespread poverty does benefit some people. From their perspective, the best way of dealing with poverty is to make it invisible. Invisibility means that residents of poor neighbourhoods find it difficult to make political claims for decent housing, urban infrastructure and welfare. They are available as cheap labour, but deprived of full social and political rights.

Slum tourism has the power to increase the visibility of poor neighbourhoods, which can in turn give residents more social and political recognition. Visibility can’t fix everything, of course. It can be highly selective and misleading, dark and voyeuristic or overly positive while glossing over real problems. This isn’t just true of slum tourism; it can also be seen in the domain of “virtual slumming” – the consumption of images, films and books about slums.
Yet slum tourism has a key advantage over “virtual slumming”: it can actually bring people together. If we want tourism to address global inequality, we should look for where it enables cross-class encounters; where it encourages tourists to support local struggles for recognition and build the connections that can help form global grassroots movements. To live up to this potential, we need to reconsider what is meant by tourism, and rethink what it means to be tourists.
- Volunteering
- Voluntourism

Head of School, School of Arts & Social Sciences, Monash University Malaysia

Chief Operating Officer (COO)

Clinical Teaching Fellow

Data Manager

Director, Social Policy
Slumtourism.net
Home of the slum tourism research network, virtual tourism in rio’s favelas, welcome to lockdown stories.
Lockdown Stories emerged as a response to the COVID-19 crisis. The pandemic has impacted communities all around the world and has brought unprecedented challenges. In the favelas of Rio de Janeiro this included the loss of income and visibility from tourism on which community tourism and heritage projects depend. In that context, Lockdown Stories investigated how community tourism providers responded, and what support they needed to transform their projects in the new circumstances. In these times of isolation, Lockdown Stores aims to create new digital connections between communities across the world by sharing ‘Lockdown Stories’ through online virtual tours.
We are inviting you to engage in this new virtual tourism platform and to virtually visit six favelas in Rio de Janeiro: Cantagalo, Chapéu Mangueira, Babilônia, Providência, Rocinha and Santa Marta.
The tours are free but booking is required. All live tours are in Portuguese with English translation provided.
Tours happen through November and December, every Tuesday at 7 pm (UK) / 4 pm (Brazil) Please visit lockdownstories.travel where you can find out more about the project.
This research project is based on collaboration between the University of Leicester, the University of Rio de Janeiro and Bournemouth University and is funded by the University of Leicester QR Global Challenges with Research Fund (Research England).
Touristification Impossible
Call for Papers – Research Workshop
Touristification Impossible:
Tourism development, over-tourism and anti-tourism sentiments in context.
4 th and 5 th June 2019, Leicester UK
TAPAM – Tourism and Placemaking Research Unit – University of Leicester School of Business
Keynotes by Scott McCabe, Johannes Novy, Jillian Rickly and Julie Wilson
Touristification is a curious phenomenon, feared and desired in almost equal measure by policy makers, businesses and cultural producers, residents, social movements and last but not least, tourists themselves. Much current reflection on over-tourism, particularly urban tourism in Europe, where tourism is experienced as an impossible burden on residents and cities, repeats older debates: tourism can be a blessing or blight, it brings economic benefits but costs in almost all other areas. Anti-tourism social movements, residents and some tourists declare ‘touristification impossible’, asking tourists to stay away or pushing policy makers to use their powers to stop it. Such movements have become evident in the last 10 years in cities like Barcelona and Athens and there is a growing reaction against overtourism in several metropolitan cities internationally.
This workshop sets out to re-consider (the impossibility of) touristification. Frequently, it is understood simplistically as a process in which a place, city, region, landscape, heritage or experience becomes an object of tourist consumption. This, of course, assumes an implicit or explicit transformation of a resource into a commodity and carries an inherent notion of decline of value, from ‘authentic’ in its original state to ‘commodified’ after touristification. In other words, touristification is often seen as a process of ‘selling out’. But a change of perspective reveals the complexities involved. While some may hope to make touristification possible, it is sometimes actually very difficult and seemingly impossible: When places are unattractive, repulsive, controversial, difficult and contested, how do they become tourist attractions? Arguably in such cases value is added rather than lost in the process of touristification. These situations require a rethink not just of the meaning of touristification, but the underlying processes in which it occurs. How do places become touristically attractive, how is attractiveness maintained and how is it lost? Which actors initiate, guide and manipulate the process of touristification and what resources are mobilised?
The aim of this two-day workshop is to provide an opportunity to challenge the simplistic and biased understanding of tourism as a force of good and touristification as desirable, so common among destination marketing consulting and mainstream scholarly literature. But it will equally question a simplistic but frequent criticism of touristification as ‘sell-out’ and ‘loss of authenticity’.
We invite scholars, researchers, practitioners and PhD students to submit conceptual and/or empirical work on this important theme. We welcome submissions around all aspects and manifestations of touristification (social, economic, spatial, environmental etc.) and, particularly, explorations of anti-tourism protests and the effects of over-tourism. The workshop is open to all theoretical and methodological approaches. We are delighted to confirm keynote presentations by Scott McCabe, Jillian Rickly, Johannes Novy and Julie Wilson.
The workshop is organised by the Tourism and Placemaking Research Unit (TAPAM) of the School of Business and builds on our first research workshop last year on ‘Troubled Attractions’, which brought together over 30 academics from the UK and beyond.
The workshop format
The research workshop will take place in the University of Leicester School of Business. It will combine invited presentations by established experts with panel discussions and research papers. Participants will have the chance to network and socialize during a social event in the evening of Tuesday 4 th June. There is small fee of £20 for participation. Registration includes workshop materials; lunch on 4 th and 5 th June 2019 and social event on 4 th June.
Guidelines for submissions
We invite submissions of abstracts (about 500 words) by 31 st April 2019 . Abstracts should be sent by email to: Fatos Ozkan Erciyas ( foe2 (at) le.ac.uk ).
Digital Technology, Tourism and Geographies of Inequality at AAG April 2019 in DC
Digital technology, tourism and geographies of inequality.
Tourism is undergoing major changes in the advent of social media networks and other forms of digital technology. This has affected a number of tourism related processes including marketing, destination making, travel experiences and visitor feedback but also various tourism subsectors, like hospitality, transportation and tour operators. Largely overlooked, however, are the effects of these changes on questions concerning inequality. Therefore, the aim of this session is to chart this relatively unexplored territory concerning the influence of technologically enhanced travel and tourism on development and inequality.
In the wake of the digital revolution and its emerging possibilities, early debates in tourism studies have been dominated by a belief that new technologies are able to overcome or at least reduce inequality. These technologies, arguably, have emancipatory potential, inter alia, by increasing the visibility of neglected groups, neighborhoods or areas, by lowering barriers of entry into tourism service provision for low-income groups or by democratizing the designation what is considered valuable heritage. They also, however, may have homogenizing effects, for example by subjecting formerly excluded spaces to global regimes of real estate speculation or by undermining existing labour market regimes and standards in the transport and hospitality industries. These latter effects have played a part in triggering anti-tourism protests in a range of cities across the world.
In this session we aim, specifically, to interrogate these phenomena along two vectors: mobility and inequality.
Sponsor Groups : Recreation, Tourism, and Sport Specialty Group, Digital Geographies Specialty Group, Media and Communication Geography Specialty Group Day: 03.04.2019 Start / End Time: 12:40 / 16:15 Room: Calvert Room, Omni, Lobby Level
All abstracts here:
New Paper: Tourist agency as valorisation: Making Dharavi into a tourist attraction
The full paper is available for free download until mid September 2017
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016073831730110X
Tourist agency is an area of renewed interest in tourism studies. Reflecting on existing scholarship the paper identifies, develops and critically examines three main approaches to tourism agency, namely the Service-dominant logic, the performative turn, and tourist valorisation. Tourist valorisation is proposed as a useful approach to theorise the role of tourists in the making of destinations and more broadly to conceptualise the intentions, modalities and outcomes of tourist agency. The paper contributes to the structuring of current scholarship on tourist agency. Empirically it addresses a knowledge gap concerning the role of tourists in the development of Dharavi, Mumbai into a tourist destination.

Touristified everyday life – mundane tourism
Touristified everyday life – mundane tourism: Current perspectives on urban tourism (Berlin 11/12 May 2017) conference program announced / call for registration
Tourism and other forms of mobility have a stronger influence on the urban everyday life than ever before. Current debates indicate that this development inevitably entails conflicts between the various city users. The diverse discussions basically evolve around the intermingling of two categories traditionally treated as opposing in scientific research: ‘the everyday’ and ‘tourism’. The international conference Touristified everyday life – mundane tourism: Current perspectives on urban tourism addresses the complex and changing entanglement of the city, the everyday and tourism. It is organized by the Urban Research Group ‘New Urban Tourism’ and will be held at the Georg Simmel-Center for Metropolitan Studies in Berlin. May 11, 2017, 4:15 – 5:00pm KEYNOTE – Prof. Dr. Jonas Larsen (Roskilde University): ‚Tourism and the Everyday Practices‘ (KOSMOS-dialog series, admission is free).
May 12, 2017, 9:00am – 6:00pm PANELS – The Extraordinary Mundane, Encounters & Contact Zones, Urban (Tourism) Development (registration required).
See full conference program HERE (pdf)
REGISTRATION
If you are interested in the panels you need to register. An attendance fee of 40 € will be charged to cover the expenses for the event. For students, trainees, unemployed, and the handicapped there is a reduced fee of 20 €.
For registration please fill out the registration form (pdf) and send it back until April 20, 2017 to:
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin Georg-Simmel-Zentrum für Metropolenforschung Urban Research Group ’New Urban Tourism’ Natalie Stors & Christoph Sommer Unter den Linden 6 10099 Berlin You can also send us the form by email.
https://newurbantourism.files.wordpress.com/2017/03/conference-program.pdf
AAG Boston Programm
The slum tourism network presents two sessions at the Association of American Geographer Annual Meeting in Boston on Friday 7 April 2017 :
3230 The complex geographies of inequality in contemporary slum tourism
is scheduled on Friday, 4/7/2017, from 10:00 AM – 11:40 AM in Room 310, Hynes, Third Level
3419 The complex geographies of inequality in contemporary slum tourism
is scheduled on Friday, 4/7/2017, from 1:20 PM – 3:00 PM in Room 210, Hynes, Second Level
Stigma to Brand Conference Programme announced
From Stigma to Brand: Commodifying and Aestheticizing Urban Poverty and Violence
Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität, Munich, February 16-18, 2017
The preliminary programme has now been published and can be downloaded here .
For attendance, please register at stigma2brand (at) ethnologie.lmu.d e
Posters presenting on-going research projects related to the conference theme are welcome.
Prof. Dr. Eveline Dürr (LMU Munich, Germany) Prof. Dr. Rivke Jaffe (University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands) Prof. Dr. Gareth Jones (London School of Economics and Politics, UK)
This conference investigates the motives, processes and effects of the commodification and global representation of urban poverty and violence. Cities have often hidden from view those urban areas and populations stigmatized as poor, dirty and dangerous. However, a growing range of actors actively seek to highlight the existence and appeal of “ghettos”, “slums” and “no-go areas”, in attempts to attract visitors, investors, cultural producers, media and civil society organisations. In cities across the world, processes of place-making and place-marketing increasingly resignify urban poverty and violence to indicate authenticity and creativity. From “slum tourism” to “favela chic” parties and “ghetto fabulous” fashion, these economic and representational practices often approach urban deprivation as a viable brand rather than a mark of shame.
The conference explores how urban misery is transformed into a consumable product. It seeks to understand how the commodification and aestheticization of violent, impoverished urban spaces and their residents affects urban imaginaries, the built environment, local economies and social relations.
What are the consequences for cities and their residents when poverty and violence are turned into fashionable consumer experiences? How is urban space transformed by these processes and how are social relationships reconfigured in these encounters? Who actually benefits when social inequality becomes part of the city’s spatial perception and place promotion? We welcome papers from a range of disciplinary perspectives including anthropology, geography, sociology, and urban studies.
Key note speakers:
- Lisa Ann Richey (Roskilde University)
- Kevin Fox Gotham (Tulane University)
Touring Katutura – New Publication on township tourism in Namibia
A new study on township tourism in Namibia has been published by a team of researchers from Osnabrück University including Malte Steinbrink, Michael Buning, Martin Legant, Berenike Schauwinhold and Tore Süßenguth.
Guided sightseeing tours of the former township of Katutura have been offered in Windhoek since the mid-1990s. City tourism in the Namibian capital had thus become, at quite an early point in time, part of the trend towards utilising poor urban areas for purposes of tourism – a trend that set in at the beginning of the same decade. Frequently referred to as “slum tourism” or “poverty tourism”, the phenomenon of guided tours around places of poverty has not only been causing some media sensation and much public outrage since its emergence; in the past few years, it has developed into a vital field of scientific research, too. “Global Slumming” provides the grounds for a rethinking of the relationship between poverty and tourism in world society. This book is the outcome of a study project of the Institute of Geography at the School of Cultural Studies and Social Science of the University of Osnabrueck, Germany. It represents the first empirical case study on township tourism in Namibia.
It focuses on four aspects: 1. Emergence, development and (market) structure of township tourism in Windhoek 2. Expectations/imaginations, representations as well as perceptions of the township and its inhabitants from the tourist’s perspective 3. Perception and assessment of township tourism from the residents’ perspective 4. Local economic effects and the poverty-alleviating impact of township tourism The aim is to make an empirical contribution to the discussion around the tourism-poverty nexus and to an understanding of the global phenomenon of urban poverty tourism.
Free download of the study from here:
https://publishup.uni-potsdam.de/frontdoor/index/index/docId/9591
CfP Touristified everyday life – mundane tourism : Current perspectives on urban tourism
Touristified everyday life – mundane tourism : Current perspectives on urban tourism
11 and 12 of May 2017 in Berlin
Deadline for proposals: 1st December 2016
Find the f ull call here
Touristifizierter Alltag – Alltäglicher Tourismus: Neue Perspektiven auf das Stadttouristische
CfP AAG 2017
Cfp association of american geographers, boston 5th to 9th april 2017, the complex geographies of inequality in contemporary slum tourism.
The visitation of areas of urban poverty is a growing phenomenon in global tourism (Burgold & Rolfes, 2013; Dürr & Jaffe, 2012; Freire-Medeiros, 2013; Frenzel, Koens, Steinbrink, & Rogerson, 2015). While it can be considered a standard tourism practise in some destinations, it remains a deeply controversial form of tourism that is greeted with much suspicion and scepticism (Freire-Medeiros, 2009). In the emerging research field of slum tourism, the practices are no longer only seen as a specific niche of tourism, but as empirical phenomena that bridge a number of interdisciplinary concerns, ranging from international development, political activism, mobility studies to urban regeneration (Frenzel, 2016).
Slum tourism is sometimes cast as a laboratory where the relationships and interactions between the global North and South appear as micro-sociological encounters framed by the apparent concern over inequality. Beyond questioning the ways in which participants shape the encounters in slum tourism, structural implications and conditions come to the fore. Thus spatial inequality influences opportunities and hinders governance solutions to manage slum tourism operations (Koens and Thomas, 2016). Slum tourism is found to be embedded into post-colonial patterns of discourse, in which ‘North’ and ‘South’ are specifically reproduced in practices of ‘Othering’ (Steinbrink, 2012) . Evidence has been found for the use of slum tourism in urban development (Frenzel, 2014; Steinbrink, 2014) and more widely in the commodification of global care and humanitarian regimes (Becklake, 2014; Holst, 2015). Research has also pointed to the ethical implications of aestheticizing poverty in humanitarian aid performances and the troubles of on-the-ground political engagement in a seemingly post-ideological era (Holst 2016).
More recently a geographical shift has been observed regarding the occurrence of slum tourism. No longer a phenomenon restricted to the Global South, slum tourism now appears increasingly in the global North. Refugee camps such as Calais in the north of France have received high numbers of visitors who engage in charitable action and political interventions. Homeless tent cities have become the subject of a concerned tourist gaze in the several cities of the global north (Burgold, 2014). A broad range of stigmatised neighbourhoods in cities of the global North today show up on tourist maps as visitors venture to ‘off the beaten track’ areas. The resurfacing of slum tourism to the global North furthers reinforces the need to get a deeper, critical understanding of this global phenomena.
Mobility patterns of slum tourists also destabilise notions of what it means to be a tourist, as migrants from the Global North increasingly enter areas of urban poverty in the South beyond temporal leisurely visits, but as low level entry points into cities they intent to make their (temporal) home. Such new phenomena destabilise strict post-colonial framings of slum tourism, pointing to highly complex geographies of inequality.
In this session we aim to bring together research that casts the recent developments in slum tourism research. We aim specifically in advancing geographical research while retaining a broad interdisciplinary outlook.
Please sent your abstract or expressions of interest of now more than 300 words to Tore E.H.M Holst ( tehh (at) ruc.dk ) and Thomas Frisch ( Thomas.Frisch (at) wiso.uni-hamburg.de ) by October 15 th 2016
Becklake, S. (2014). NGOs and the making of “development tourism destinations.” Zeitschrift Für Tourismuswissenschaft , 6 (2), 223–243.
Burgold, J. (2014). Slumming in the Global North. Zeitschrift Für Tourismuswissenschaft , 6 (2), 273–280.
Burgold, J., & Rolfes, M. (2013). Of voyeuristic safari tours and responsible tourism with educational value: Observing moral communication in slum and township tourism in Cape Town and Mumbai. DIE ERDE – Journal of the Geographical Society of Berlin , 144 (2), 161–174.
Dürr, E., & Jaffe, R. (2012). Theorizing Slum Tourism: Performing, Negotiating and Transforming Inequality. European Review of Latin American and Caribbean Studies Revista Europea de Estudios Latinoamericanos Y Del Caribe , 0 (93), 113–123
Freire-Medeiros, B. (2009). The favela and its touristic transits. Geoforum , 40 (4), 580–588.
Freire-Medeiros, B. (2013). Touring Poverty . New York N.Y.: Routledge.
Frenzel, F. (2014). Slum Tourism and Urban Regeneration: Touring Inner Johannesburg. Urban Forum , 25 (4), 431–447.
Frenzel, F. (2016). Slumming it: the tourist valorization of urban poverty . London: Zed Books.
Frenzel, F., Koens, K., Steinbrink, M., & Rogerson, C. M. (2015). Slum Tourism State of the Art. Tourism Review International , 18 (2), 237–252.
Holst, T. (2015). Touring the Demolished Slum? Slum Tourism in the Face of Delhi’s Gentrification. Tourism Review International , 18 (4), 283–294.
Steinbrink, M. (2012). We did the slum! Reflections on Urban Poverty Tourism from a Historical Perspective. Tourism Geographies , 14 (2), forthcoming.
Steinbrink, M. (2014). Festifavelisation: mega-events, slums and strategic city-staging – the example of Rio de Janeiro. DIE ERDE – Journal of the Geographical Society of Berlin , 144 (2), 129–145.
Advertisement
Tourist and resident perspectives on ‘slum tourism’: the case of the Vilakazi precinct, Soweto
- Published: 06 May 2019
- Volume 85 , pages 1133–1149, ( 2020 )
Cite this article

- Gijsbert Hoogendoorn ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7969-7952 1 ,
- Nthabiseng Letsatsi 1 ,
- Thabisile Malleka 1 &
- Irma Booyens 2 , 3
1965 Accesses
13 Citations
Explore all metrics
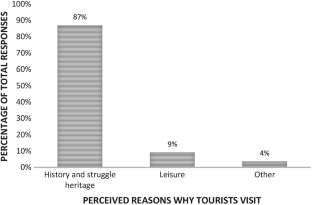
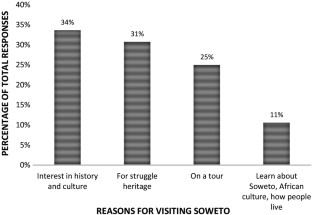
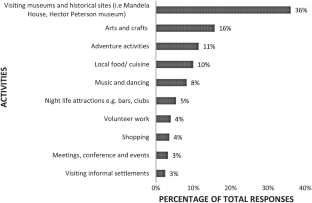
Slum tourism as a topic of investigation has seen significant growth since the beginning of this decade with increasing theoretical and empirical depth. With this growth, some inconsistencies in conceptual framing and use of terminology have emerged. The purpose of this paper is to argue for township tourism in Soweto to be regarded as a form of heritage tourism rather than slum tourism—a notion which has entered the township tourism literature in recent years. This argument is presented through two sections of analysis and debate, using Vilakazi precinct in Soweto as a case study. Firstly, the paper analyses the emergence of township tourism as an academic focus in the literature and how it came to be classified as slum tourism, considering definitional conundrums. Various South African authors emphasise the struggle heritage character of township tourism. Secondly, the historical development of townships and tourism in these areas are interrogated. The empirical data offer the perspectives on tourism in their area from: (a) residents living in and around Vilakazi Street; and (b) tourists visiting the Vilakazi precinct. The analysis reveals that neither residents nor visitors consider the Vilakazi precinct or the larger area of Orlando West as a slum; rather they perceive tourism is the area to be connected to its struggle heritage. We accordingly stress that the term ‘slum tourism’ to describe township tourism in Soweto is inaccurate and is inconsistent with the views not only of residents and visitors, but also South African authors.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
( source : authors)
( source : resident survey)

( source : visitor survey)*. *Figures subject to rounding error
( source : visitor survey)
Similar content being viewed by others

Slum Tourism and Urban Regeneration: Touring Inner Johannesburg

The Other Half of Urban Tourism: Research Directions in the Global South

The Process of Tourism Transition and the Tourism Social Contract in Indigenous Territory: The Case of the Nova Esperança Indigenous Community (Rio Cuieiras, Brazil)
This was in response to one of the authors’ presentations at the South African Cultural Observatory’s 2018 conference in Port Elizabeth, 7–8 March 2018.
Resident No. 46 (hereafter R with the questionnaire number), young female (18–30), unemployed.
Young female (18–30), relying on remittances.
Male, aged 41–50, informal income.
Female, aged 31–40, informal income.
Young male (18–30), relying on remittances.
Young female (18–30), informal income.
Visitor No. 30 (hereafter V with the questionnaire number), female, aged 30, on holiday.
Female, aged 30, on holiday.
Note that Youth Day is a National Holiday to commemorate the June 16th uprising, and it was coincidental that some of the fieldwork fell over this holiday. While the fieldwork was carried out over a three weeks in June and July 2018, 44% of the visitor responses (42 international and 17 domestic visitors) were collected on Youth Day due to the number of visitors on the day. We did not detect notable differences in the responses collected on Youth Day in comparison with the overall responses.
Male, aged 52, business owner from Germany.
Female, aged 52, on holiday.
Female, aged 18, student.
Female, aged 40, visiting family.
Male, aged 20, student from France.
Aitchison, C. (2001). Theorizing Other discourses of tourism, gender and culture: Can the subaltern speak (in tourism)? Tourist Studies, 1 (2), 133–147.
Google Scholar
BBC (British Broadcasting Cooperation). (2014). Favela life: Rio’s city within a city . https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-27635554 . Accessed January 8, 2019.
Beavon, K., & Rogerson, C. M. (1990). Temporary trading for temporary people: The making of hawking in Soweto. In D. Drakakis-Smith (Ed.), Economic growth and urbanization in developing areas (pp. 263–286). London: Routledge.
Bolay, J. C. (2006). Slums and urban development: Questions on society and globalisation. The European Journal of Development Research, 18 (2), 284–298.
Booyens, I. (2010). Rethinking township tourism: Towards responsible tourism development in South African townships. Development Southern Africa, 27 (2), 273–287.
Booyens, I., & Rogerson, C. M. (2018). Creative tourism: South African township explorations. Tourism Review, 74 (2), 256–267. https://doi.org/10.1108/TR-12-2017-0200 .
Article Google Scholar
Booyens, I., & Rogerson, C. M. (2019). Recreating slum tourism: Perspectives from South Africa. Urbani izziv, 30, S52–S63.
Bourdieu, P. (1971). Systems of education and systems of thought. In M. Young (Ed.), Knowledge and control: New directions for the sociology of education (pp. 189–207). London: Collier-Macmillan.
Briedenhann, J., & Ramchander, P. (2006). Township tourism: Blessing or blight? The case of Soweto in South Africa. In M. K. Smith & M. Robinson (Eds.), Cultural tourism in a changing world: Politics, participation (re)presentation (pp. 124–142). Clevedon: Channel View.
Butler, R. W. (1980). The concept of a tourist area cycle of evolution: Implications for management of resources. The Canadian Geographer, 24 (1), 5–12.
Butler, S. R. (2010). Should I stay or should I go? Negotiating township tours in post-apartheid South Africa. Journal of Tourism and Cultural Change, 8 (1/2), 15–30.
Census. (2011). Orlando West. Statistics South Africa. https://census2011.adrianfrith.com/place/798026032 . Accessed January 7, 2019.
Choplin, A. (2016). Rethinking precarious neighborhoods, rethinking the future city. In A. Deboulet (Ed.), Rethinking precarious neighbourhoods (pp. 245–250). Paris: Agence Française De Développement.
Cirolia, L. R., & Scheba, S. (2019). Towards a multi-scalar reading of informality in Delft South Africa: Weaving the ‘everyday’ with wider structural tracings. Urban Studies, 56 (3), 594–611.
City of Johannesburg. (2004). Soweto tourism plan . Johannesburg: Site Solutions, Tourism Intelligence and Open Transcommunication.
Deboulet, A. (2016). Introduction, Rethinking precarious neighbourhoods. Knowledge and recognition. In A. Deboulet (Ed.), Rethinking precarious neighbourhoods (pp. 9–35). Paris: Agence Française De Développement.
Department of Environmental Affairs and Tourism. (2005). Vilakazi Precinct Project . Johannesburg: Interfaith Community Development Association and Holicki and Associates JV.
Dürr, E. (2012). Urban poverty, spatial representation and mobility: Touring a slum in Mexico. International Journal of Urban and Regional Research, 36 (4), 706–724.
Dyson, P. (2012). Slum tourism: Representing and interpreting ‘reality’ in Dharavi. Mumbai. Tourism Geographies, 14 (2), 254–274.
Freire-Medeiros, B. (2009). The favela and touristic transits. Geoforum, 40 (4), 580–588.
Freire-Medeiros, B. (2014). Touring poverty . Abingdon: Routledge.
Frenzel, F. (2013). Slum tourism in the context of the tourism and poverty (relief) debate. Die Erde, 144 (2), 117–128.
Frenzel, F. (2014). Slum tourism and urban regeneration: Touring inner Johannesburg. Urban Forum, 25 (4), 431–447.
Frenzel, F. (2016). Slumming it: The tourist valorization of urban poverty . London: Zed.
Frenzel, F. (2018). On the question of using the concept ‘slum tourism’ for urban tourism in stigmatised neighbourhoods in inner city Johannesburg. Urban Forum, 21 (1), 51–62.
Frenzel, F., & Koens, K. (2012). Slum tourism: Developments in a young field of interdisciplinary tourism research. Tourism Geographies, 14 (2), 195–212.
Frenzel, F., Koens, K., Steinbrink, M., & Rogerson, C. M. (2015). Slum tourism: State of the art. Tourism Review International, 18 (4), 237–252.
Frisch, T. (2012). Glimpses of another world: The Favela as a tourist attraction. Tourism Geographies, 14 (2), 320–338.
Gastrow, C. (2015). Thinking futures through the slum. The Avery Review, 9 . http://www.averyreview.com/issues/9/thinking-futures .
Gauteng Province. (2014). Gauteng township economy revitalisation strategy 2014–2019 . Johannesburg: Gauteng Province.
George, R., & Booyens, I. (2014). Township tourism demand: Tourists’ perceptions of safety and security. Urban Forum, 25 (4), 449–467.
Giddy, J. K., & Hoogendoorn, G. (2018). Ethical concerns around inner city walking tours. Urban Geography, 39 (9), 1293–1299. https://doi.org/10.1080/02723638.2018.1446884 .
Giliomee, H. B., & Mbenga, B. (2007). New history of South Africa . Cape Town: Tafelberg.
Hernandez-Garcia, J. (2013). Slum tourism, city branding and social urbanism: The case of Medellin, Colombia. Journal of Place Management and Development, 6 (1), 43–51.
Hlongwane, A. K. (2007). The mapping of June 16 1976 Soweto student uprising routes: Past recollections and present reconstruction(s). Journal of African Cultural Studies, 19 (1), 7–36.
Holst, T. (2018). The affective negotiation of slum tourism: City walks in Delhi . London: Routledge.
Hoogendoorn, G., & Giddy, J. K. (2017). “Does this look like a slum?” Walking tours in the inner city of Johannesburg. Urban Forum, 28 (3), 315–328.
Jones, G. A., & Sanyal, R. (2015). Spectacle and suffering: The Mumbai slum as a worlded space. Geoforum, 65, 431–439.
Koens, K., & Thomas, R. (2016). “You know that’s a rip off”: Policies and practices surrounding micro-enterprises and poverty alleviation in South African township tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 24 (12), 1641–1654.
Lejano, R. P., & Del Bianco, C. (2018). The logic of informality: Pattern and process in a São Paulo favela. Geoforum, 91, 195–205.
Linke, U. (2012). Mobile imaginaries, portable signs: Global consumption and representations of slum life. Tourism Geographies, 14 (2), 294–319.
Lombard, M. (2014). Constructing ordinary places: Place-making in urban informal settlements in Mexico. Progress in Planning, 94, 1–53.
Ma, M., & Hassink, R. (2013). An evolutionary perspective on tourism area development. Annals of Tourism Research, 41, 89–109.
Magubane, P., & Lee, M. (1979). Soweto . Cape Town: Don Nelson.
Marschall, S. (2006). Visualizing memories: The Hector Pieterson Memorial in Soweto. Visual Anthropology, 19 (2), 145–169.
Masilo, H., & van der Merwe, C. D. (2016). Heritage tourist’s experiences of ‘Struggle Heritage’ at Liliesleaf Farm Museum and Hector Pieterson Memorial & Museum South Africa. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure, 5 (3), 1–20.
Mekawy, M. A. (2012). Responsible slum tourism: Egyptian experience. Annals of Tourism Research, 39 (4), 2092–2113.
Meschkank, J. (2011). Investigations into slum tourism in Mumbai: Poverty tourism and the tensions between different constructions of reality. GeoJournal, 76 (1), 47–62.
Mkono, M. (2016). The reflexive tourist. Annals of Tourism Research, 57, 206–209.
Muldoon, M. (2018). Gazing back: A feminist postcolonial lens on tourism in the townships of South Africa . Unpublished PhD, University of Waterloo, Canada.
Ndlovu, S. (2006). Mapping the Soweto uprising routes . Johannesburg: Emba Project Management on behalf to the Gauteng Department of Public Works.
Nisbett, M. (2017). Empowering the empowered? Slum tourism and the depoliticization of poverty. Geoforum, 85, 37–45.
Pieterse, E. (2011). Grasping the unknowable: Coming to grips with African urbanisms. Social Dynamics, 37 (1), 5–23.
Poria, Y., Butler, R., & Airey, D. (2003). The core of heritage tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 30 (1), 238–254.
Poria, Y., Butler, R., & Airey, D. (2004). Links between tourists, heritage and reasons for visiting heritage sites. Journal of Travel Research, 43 (1), 20–28.
Pott, A., & Steinbrink, M. (2009). Die kultur des Slum(ming)s. Zur historischen Rekonstruktion eines globalen Phänomens. In H. Wöhler, A. Pott, & V. Denzer (Eds.), Tourismusräume. Zur soziokulturellen Konstruktion eines globalen Phänomens . Bielefeld: Springer.
Pratt, A. (2019). Formality as exception. Urban Studies, 56 (3), 612–615.
Ramchander, P. (2003). Towards the responsible management of socio-cultural impact of township tourism. In P. M. Burns & M. Novelli (Eds.), Tourism and politics: Global frameworks and local realities (pp. 149–172). Oxford: Elsevier.
Ramchander, P. (2004). Towards the responsible management of the social - cultural impact of township tourism. Unpublished PhD thesis, Department of Tourism Management, University of Pretoria.
Rogerson, C. M. (2004). Urban tourism and small tourism enterprise development in Johannesburg: The case of township tourism. GeoJournal, 60 (3), 249–257.
Rogerson, C. M. (2013). Urban tourism, economic regeneration and inclusion: Evidence from South Africa. Local Economy, 28 (2), 188–202.
Rogerson, C. M. (2014). Rethinking slum tourism: Tourism in South Africa’s rural slumlands. Bulletin of Geography: Socio-Economic Series, 26 (26), 19–34.
Rogerson, C. M. (2015). Revisiting VFR tourism in South Africa. South African Geographical Journal, 97 (2), 139–157.
Rogerson, C. M. (2019). The economic development of South Africa’s townships. In J. Knight & C. M. Rogerson (Eds.), The geography of South Africa—Contemporary changes and new directions (pp. 187–194). Cham: Springer.
Rogerson, C. M., & Hoogendoorn, G. (2014). VFR travel and second home tourism: The missing link? The case of South Africa. Tourism Review International, 18 (3), 167–178.
Rolfes, M. (2010). Poverty tourism: Theoretical reflections and empirical findings regarding an extraordinary form of tourism. GeoJournal, 75 (5), 421–442.
Scheyvens, R. (2001). Poverty tourism. Development Bulletin, 55, 18–21.
Selinger, E., & Outterson, K. (2010). The ethics of poverty tourism. Environmental Philosophy, 7 (2), 93–114.
Silberg, T. (1995). Cultural tourism and business opportunity for museums and heritage sites. Tourism Management, 16 (5), 361–365.
Slikker, N., & Koens, K. (2015). “Breaking the silence”: Local perceptions of slum tourism in Dharavi. Tourism Review International, 19 (1–2), 75–86.
South Africa. (1999). National Heritage Resources Act 25 of 1999 . Pretoria: Government Printer.
Spivak, G. C. (1994). Can the subaltern speak? In P. Williams & L. Chrisman (Eds.), Colonial discourse and post-colonial theory (pp. 66–111). New York: Columbia University Press.
Steinbrink, M. (2012). ‘We did the slum!’—Urban poverty tourism in historical perspective. Tourism Geographies, 14 (2), 213–234.
Torres, I. (2012). Branding slums: A community-driven strategy for urban inclusion in Rio de Janeiro. Journal of Place Management and Development, 5 (3), 198–211.
Turok, I., & Visagie J. (2018). Inclusive urban development in South Africa: What does it mean and how can it be measured? IDS Working Paper, 512.
Turok, I., Budlender, J., & Visagie, J. (2017). Urban ‘slums’ and social mobility. Development Policy Review, 36 (6), 703–725. https://doi.org/10.1111/dpr.12325 .
Tzanelli, R. (2018). Slum tourism: A review of state-of-the-art scholarship. Tourism, Culture & Communication, 18 (2), 149–155.
Urry, J., & Larsen, J. (2011). The tourist gaze 3.0 . London: Sage.
United Nations Habitat. (2003). Housing and slum upgrading . http://unhabitat.org/urban-themes/housing-slum-upgrading/ . Accessed July 16, 2018.
Vecco, M. (2010). A definition of cultural heritage: From the tangible to the intangible. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 11 (3), 321–324.
Waterton, E., & Smith, L. (2010). The recognition and misrecognition of community heritage. International Journal of Heritage Studies, 16 (1–2), 4–15.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the helpful comments of the reviewers.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Geography, Environmental Management and Energy Studies, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Gijsbert Hoogendoorn, Nthabiseng Letsatsi & Thabisile Malleka
Economic Performance and Development, Human Sciences Research Council, Cape Town, South Africa
Irma Booyens
School of Tourism and Hospitality, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gijsbert Hoogendoorn .
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement.
All ethical requirements as expected by the University of Johannesburg were followed. No under aged individuals were interviewed, no people that may be considered vulnerable because of economic or social reasons were interviewed. All respondents are kept completely confidential and due diligence was followed.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Hoogendoorn, G., Letsatsi, N., Malleka, T. et al. Tourist and resident perspectives on ‘slum tourism’: the case of the Vilakazi precinct, Soweto. GeoJournal 85 , 1133–1149 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-019-10016-2
Download citation
Published : 06 May 2019
Issue Date : August 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-019-10016-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Slum tourism
- Township tourism
- Vilakazi Street
- Representation
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Print this article
Explorations | Exploraciones
Theorizing slum tourism: performing, negotiating and transforming inequality.
- Rivke Jaffe
- Rivke Jaffe , Assistant Professor at the Centre for Urban Studies at the Universityof Amsterdam, the Netherlands Rivke Jaffe is an Assistant Professor at the Centre for Urban Studies at the Universityof Amsterdam, the Netherlands. She previously held teaching and research positions at Leiden University, the University of the West Indies, and the Royal Netherlands Institute of Southeast Asian and Caribbean Studies (KITLV). She has conducted fieldwork in Jamaica, Curaçao and Suriname on topics ranging from the urban environment to the political economy of multiculturalism. Her current research, in Jamaica, studies how criminal organizations and the state share control over urban spaces and populations, and the formulations of governance and citizenship that result from this. She is the author of several peer-reviewed articles in journals such as Anthropological Quarterly, Ethnic and Racial Studies, and Social and Cultural Geography. In addition, she is the editor of The Caribbean City (Ian Randle, 2008) and the co-editor of Urban Pollution (with Eveline Dürr, Berghahn, 2010).
This Exploration focuses on the emerging field of slum tourism research, which has the potential to connect Latin American and Caribbean studies on tourism and urban inequality. Slum tourism involves transforming poverty, squalor and violence into a tourism product. Drawing on both altruism and voyeurism, this form of tourism is a complex phenomenon that raises various questions concerning power, inequality and subjectivity. This essay seeks to advance the theoretical debate on slum tourism research and to stimulate comparative studies. Introducing brief examples of slum tourism in Mexico and Jamaica, this contribution moves towards an initial theorization of the performance, negotiation and transformation of inequality in a framework of tourism and global mobilities.
Resumen: Teorizar el Turismo en las zonas marginadas: Construcción, negociación y transformación de la desigualdad
Esta Exploración se centra en el campo emergente del turismo en zonas marginadas, que tiene como potencial conectar a América Latina y el Caribe en los estudios sobre el turismo y la desigualdad urbana. Turismo 'Slum' implica la transformación de la pobreza, la miseria y la violencia en un producto turístico. Basándose tanto en el altruismo como en el voyerismo, esta forma de turismo es un fenómeno complejo que plantea diversas cuestiones relativas al poder, la desigualdad y la subjetividad. Con este ensayo se pretende avanzar en el debate teórico sobre la investigación de turismo en zonas marginadas y estimular estudios comparativos. Presentando ejemplos breves de turismo en barrios pobres en la ciudad de México y de Jamaica, esta contribución se mueve hacia una teorización inicial de la construcción, la negociación y la transformación de la desigualdad en el marco del turismo y la movilidad global.
- Page/Article: 113-123
- DOI: 10.18352/erlacs.8367
- Peer Reviewed

Slum tourism: What is it and how does it work?
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Slum tourism is, believe it or not, a real type of tourism . Yep, you got that right- people go to slums whilst on holiday. But, why? In this article I will introduce you to the concept of slum tourism and tell you what it’s all about. Interested to learn more? Read on…
What is slum tourism?
Slum tourism definitions, what is white saviour syndrome, what does a slum tour involve, positive impacts of slum tourism, negative impacts of slum tourism, the ethics of slum tourism, slum tourism in south africa, slum tourism in brazil, slum tourism in india, slum tourism in indonesia, slum tourism in africa, slum tourism: conclusion, further reading.

Slum tourism is essentially when people visit slums – or, more widely, poverty stricken areas – as a form of tourism. This will generally be in a foreign country, one they are visiting as a tourist on holiday or on a business trip. It has also been referred to as ghetto tourism and poverty tourism.
In ‘ Theorizing Slum Tourism ’, researchers Eveline Dürr and Rivke Jaffe described slum tourism as follows:
‘ Slum tourism involves transforming poverty, squalor and violence into a tourism product. Drawing on both altruism and voyeurism, this form of tourism is a complex phenomenon that raises various questions concerning power, inequality and subjectivity. ‘
While this describes slum tourism, it doesn’t necessarily define what it actually is. Bob Ma of the University of Pennsylvania says this:
‘ Slum tourism is one of the fastest-growing niche tourism segments in the world, but it is also one of the most controversial. The United Nations defines a slum as, “a run-down area of a city characterized by substandard housing and squalor and lacking in tenure security” (UN, 2007). Slum tourism is the organization of tours in these areas. As a niche segment, slum tourism is distinguished from developmental tourism, which is a broader term that includes tourism in any region that is undergoing development. ‘
Slum tourism as charity tourism
Some people engage in charity tourism – visiting slums or areas of high poverty with the intention of ‘making things better’. This is also sometimes called volunteer tourism . You can see this on Children In Need in the UK, for example, where we see videos of people heading to various underdeveloped areas of Africa to build schools or install wells for fresh water access etc. You can pay (a lot of) money to do this yourself through various organisations.

People do this as it is within human nature to want to help people who have less than we do. But it is also, of course, a chance to see somewhere new and explore a different culture . It can also be a great way to boost your CV. This means that taking part in slum tourism isn’t a purely selfless act, and this is why it can sometimes be frowned upon.
Studies show that slum tourism can have negative impacts on local communities – the use of unskilled labour, for example, and the taking of jobs that could ultimately have gone to local people. There is also usually no long term commitment involved, and of course there is the concept of white saviour syndrome.
The following extract comes from De-constructing the ‘White Saviour Syndrome’: A Manifestation of Neo-Imperialism by Felix Willuweit:
‘With the recent widespread of protests for black civil rights and against racism across the Western world, the topic of white prejudice has risen to the centre of public attention, of which one manifestation is the so-called ‘White Saviour Syndrome’. Whether it is Ed Sheeran posing for ‘Comic Relief’ with a number of black children (Hinsliff, 2019), Madonna adopting children from Malawi (Hinsliff, 2019), or students going on adventures advertised for ‘young philanthropists’ within a multi-million dollar gap-year industry (Bandyopadhyay, 2019), numerous cases of altruistic acts of ‘White Saviours’ can be found throughout popular culture in the global North.’
Whereas these practices follow an altruistic narrative, they are commonly criticised as serving to satisfy a ‘White Saviour Syndrome’, the phenomenon in which a white person “guides people of colour from the margins to the mainstream with his or her own initiative and benevolence” which tends to render the people of colour “incapable of helping themselves” and disposes them of historical agency (Cammarota, 2011: 243-244).
So what does slum tourism involve? Many tour operators offer literal ‘slum tours’ as part of their packages, and of course you can visit slum areas alone as they are just parts of various areas. AfricanTrails.co.uk, for example, have a page discussing slum tours and they state that some of their packages do offer slum visits in Kenya, Uganda, Namibia and more.

Reality Tours and Travel are another company offering slum tours. As the company name suggests, they hope to offer a ‘realistic’ side to the places tourists visit. Based in India , a country with a lot of poverty, their slogan is ‘USING TOURISM TO CHANGE LIVES’. They say: Our ethical and educational Dharavi slum tours give visitors a unique glimpse into everyday life for many Mumbaikars while breaking down the negative stereotypes associated with slums. 80% of the profits from every tour are invested back into the community through the programs of our NGO, Reality Gives , and most of our guides are from the community.
Slum tourism has some positives to it. It gives people an insight into how poverty can affect people – humans are curious by nature, and if you are not living in poverty yourself, or never have, then it can be hard to imagine what it is really like. Visiting a slum whilst on holiday is like opening a window to another life, however briefly.
It is also a chance to provide an income to people living in slums, if the tour involves some sort of opportunity to purchase goods or donate money. And with some tours, as you can see from Reality Tours and Travel above, the booking cost goes into improving the community.
Of course, there are negatives impacts associated with slum tourism too. The main one is that it treats those who live in slums as though they are in a zoo, dehumanising them so tourists can see what it’s like before swanning off back to their hotel and other luxuries. Some would go so far as to argue that they are a form of ‘ human zoo ‘. These tours portray poverty as something exotic, rather than a very real danger to the lives of the people impacted by it. It is also questionable how far the money trickles down. With people paying for organised tours, how sure can we be that real people are accessing the money?

Looking at the pros and cons it is clear that there is an ethical question surrounding slum tourism . People who live in poverty and live in slums are real people. We need to ask ourselves whether it is fair for them to be paraded around in front of us as part of an organised tour that we are paying a company to go on.
Some questions we should ask ourselves when looking to engage in slum tourism, courtesy of slumtourism.net, are:
- To what extent does slum tourism provide an income and positive visibility for people in deprived areas?
- Which stakeholders are involved in slum tourism and who profits most?
- How are guided tours organised or composed?
- What are the geographical scopes of slum-tourism and which place does it occupy in the new mobility system?
- Where does slum tourism fit in a globalised world of tourist consumption?
It is similar to visiting remote tribes, in a way, just as I explain in my article about the long neck tribe in Thailand . Tourists coming in from outside to view life in a slum through a western lens for a few minutes… does this paint a fair picture of slums?
Slum tourism destinations
There are various places around the world where slum tourism is prevalent. Here are some examples-
Slum tourism exists across South Africa . Here it is also known as township tourism – in SA, townships are the underdeveloped urban areas, generally populated by people of colour as a fall out from the Apartheid era. Apparently, around 25% of visitors to Cape Town engage in township tours. This city alone has around 40-50 township tour operators.
Slum tourism in Brazil equates to ‘favela tours’. Favelas are slums or shanty towns built on the outskirts of major cities across Brazil, and many people visit them for tourist purposes while on holiday in this beautiful country. Favelas are known to be dangerous areas. They are rife with crime, violence and drug dealing, but thousands of tourists every month visit these areas with curiosity.
As mentioned above when I spoke about Reality Tours and Travel, India is a prime spot for slum tourism due to the high levels of poverty here. The film Slumdog Millionaire put Indian slums onto the screens of millions of people, many of whom became keen to see it for themselves on a trip to India. There are around 15,000 people visiting the Dharavi slum each year alone.
Jakarta is home to a slum where families of 5 squeeze into ‘houses’ no bigger than the average western bathroom. They survive on pennies, and welcome tourists into their homes to see what it is like. Jakarta Hidden Tours is run by Ronnie. He’s a charity worker who donates half of his profits to the local community in an attempt to improve their lives.
Across Africa there are poor and underdeveloped communities. Slums tend to exist in Kenya and Uganda, for the most part. AfricanTrails say:
Going on an Africa slum tour is a great way to see what life is like for the majority of residents in a specific African town or city. Visitors can see how people live and the work they carry out in order to provide for their families. Slum tours are not purely filled with misery, the towns often have vibrant communities with shops, schools and market stalls.
I t is easy to forget that there are people living in these conditions, as it is not something you see every day, so for many, Africa slum tours are a real eye-opening experience. Visitors leave the area with the intention of donating to charities, helping those living in these places. Slum tours give the chance for tourists to interact with others from different backgrounds and see the true beauty of Africa and its people.
To conclude, slum tourism occurs around the world, and has done since Victorian times in England. Back then, the aristocracy would visit the capital’s poorest areas for voyeuristic and/or philanthropic purposes. And still it continues. People are, of course, eager to see another way of life. Often they believe that they are helping, and visiting people at their lowest can be a great way to remind you that really, you don’t have it all that bad. The ethics are questionable, but there are definitely ways you can visit a slum without it being a negative thing.
Top 10 dark tourism destinations (including WUHAN!)
Dark tourism explained: What, why and where
What is suicide tourism?
Medical tourism: What where and why
Liked this article? Click to share!
- Share full article

Stephen Hiltner/The New York Times
The sculpted facade of a 2,000-year-old tomb glows in the late-afternoon sun at Hegra, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
Crowds of Muslim pilgrims gather outside the Prophet’s Mosque in Medina.
Camels march through the desert on the outskirts of the Empty Quarter, the world’s largest sand sea.
For many years these Saudi Arabian scenes, including the lively open-air markets in Jeddah, were off limits to most travelers.
But not anymore. As it undergoes a profound transformation, Saudi Arabia is spending lavishly to lure tourists with its luxe new resorts ...
... its rich cultural heritage ...
... and its sublime natural beauty.
Can the Saudi government persuade would-be visitors to look past — or reconsider — its longstanding associations with religious extremism, ultraconservatism and human rights abuses?
Will the kingdom’s $800 billion bet on tourism pay off?
Supported by
Surprising, Unsettling, Surreal: Roaming Through Saudi Arabia
To witness the kingdom’s profound transformation and assess its ambitious tourism projects, a Times journalist spent a month on the road there. Here’s what he saw.

By Stephen Hiltner
An editor and photojournalist for the Travel section, Stephen Hiltner drove 5,200 miles and visited all 13 of Saudi Arabia’s provinces while reporting and shooting this story.
Wandering alone along the southern fringes of Saudi Arabia’s mountainous Asir Province, some eight miles from the Yemeni border, in a nondescript town with a prominent sculpture of a rifle balanced on an ornately painted plinth, I met a man, Nawab Khan, who was building a palace out of mud.
Actually, he was rebuilding the structure, restoring it. And when I came across him, he hadn’t yet begun his work for the day; he was seated on the side of the road beneath its red-and-white windows — cross-legged, on a rug, leaning over a pot of tea and a bowl of dates.
Two weeks earlier, on the far side of the country, a fellow traveler had pointed at a map and described the crumbling buildings here, in Dhahran al-Janub, arranged in a colorful open-air museum. Finding myself nearby, I’d detoured to have a look — and there was Mr. Khan, at first looking at me curiously and then waving me over to join him. Sensing my interest in the cluster of irregular towers, he stood up, produced a large key ring and began opening a series of padlocks. When he vanished through a doorway, I followed him into a shadowy stairwell.
This, of course, was my mother’s worst nightmare: Traveling solo, I’d been coaxed by a stranger into an unlit building in a remote Saudi village, within a volatile border area that the U.S. Department of State advises Americans to stay away from .
By now, though, more than halfway through a 5,200-mile road trip, I trusted Mr. Khan’s enthusiasm as a genuine expression of pride, not a ploy. All across Saudi Arabia, I’d seen countless projects being built, from simple museums to high-end resorts. These were the early fruits of an $800 billion investment in the travel sector, itself part of a much larger effort, Vision 2030 , to remake the kingdom and reduce its economic dependence on oil.
But I’d begun to see the building projects as something else, too: the striving of a country — long shrouded to most Westerners — to be seen, reconsidered, accepted. And with its doors suddenly flung open and the pandemic behind us, visitors like me were finally beginning to witness this new Saudi Arabia, much to Mr. Khan’s and all the other builders’ delight.

Few countries present as complicated a prospect for travelers as Saudi Arabia.
Long associated with Islamic extremism, human rights abuses and the oppression of women, the kingdom has made strides in recent years to refashion its society and its reputation abroad.
The infamous religious police, which upheld codes of conduct based on an ultraconservative interpretation of Islam, were stripped of their power. Public concerts, once banned, are now ubiquitous. Women have been granted new rights — including the freedom to drive and to travel without permission from a male guardian — and are no longer required to wear floor-length robes in public or to cover their hair.
These changes are part of a broad set of strategies to diversify the kingdom’s economy, elevate its status in the world and soften its image — the last of which is a tall order for a government that has killed a newspaper columnist , kidnapped and tortured dissidents , precipitated a humanitarian crisis in Yemen and imprisoned people for supporting gay rights , among a number of other recent abuses .
Central to the transformations led by 38-year-old Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, the kingdom’s de facto ruler, is a major push for international visitors. It represents a sea change in a country that, until 2019, issued no nonreligious tourist visas and instead catered almost exclusively to Muslim pilgrims visiting Mecca and Medina, Islam’s two holiest cities. In February, by contrast, my tourist e-visa was approved online in minutes.
Saudi Arabia has already transformed one of its premier destinations — Al-Ula, with its UNESCO-listed Nabatean tombs — from a neglected collection of archaeological sites into a lavish retreat with a bevy of activities on offer, including guided tours, wellness festivals, design exhibitions and hot air balloon rides.
Another project will create a vast array of luxury resorts on or near the Red Sea.
Still more projects include the development of Diriyah , the birthplace of the first Saudi state; the preservation and development of the coastal city of Jeddah ; an offshore theme park called the Rig ; and Neom , the futuristic city that has garnered the lion’s share of attention.
All told, the country is hoping to draw 70 million international tourists per year by 2030, with tourism contributing 10 percent of its gross domestic product. (In 2023, the country logged 27 million international tourists, according to government figures , with tourism contributing about 4 percent of G.D.P.)

At-Turaif, a UNESCO World Heritage site, was the birthplace of the kingdom of Saudi Arabia. It is now the centerpiece of the $63 billion Diriyah project, a new center of culture just outside Riyadh.
Nujuma, a Ritz-Carlton Reserve on a remote island in the Red Sea, opened in late May. (A one-bedroom villa costs about $2,500 per night, excluding taxes and fees.) It is one of 50 properties scheduled to open in the area by 2030.
The preservation and development of Jeddah, a coastal city famous for its historic district built largely from blocks of coral, comes with a price tag of some $20 billion.
Al-Ula is a cornerstone of Saudi Arabia’s tourism ambitions. Part of the city’s Old Town, long crumbling in neglect, has now been painstakingly restored.
To get a sense of these projects and the changes unfolding in Saudi society, I spent a month exploring the kingdom by car. I traveled alone, without a fixer, driver or translator. Per New York Times ethics guidelines, I declined the government’s many offers of discounts and complimentary services.
Much of the time I felt I’d been tossed the keys to the kingdom. But there were moments, too, when I faced a more complicated reality, one epitomized by a road sign that forced me to abruptly exit the highway some 15 miles from the center of Mecca. “Obligatory for Non Muslims,” it read, pointing to the offramp.
To me, the sign broadcast the lines being drawn to compartmentalize the country, which is now marketing itself to two sets of travelers with increasingly divergent — and sometimes contradictory — expectations: luxury tourists at ease with bikinis and cocktails, and pilgrims prepared for modesty and strict religious adherence. It’s hard to know whether the kingdom can satisfy both without antagonizing either.
My trip began in Jeddah, where, after spending two days exploring its historic district, I rented a car and drove eight hours north to Al-Ula, a benchmark for the new Saudi tourism initiatives.

Saudi Arabia
Reporter’s route
Dhahran al-Janub

Wadi al-Disah
Red Sea Resort
The name Al-Ula refers to both a small city and a broader region packed with attractions: Hegra , the kingdom’s first UNESCO World Heritage site and its biggest archaeological draw, is a 30-minute drive north of Old Town, a maze of crumbling mud-brick buildings now partly restored. Between the two, and fanning out to the east and west, are several other archaeological sites, as well as a smattering of resorts, event spaces and adventure outfitters. Farther northeast, beyond Hegra, is the Sharaan Nature Reserve , a vast protected zone used for conservation efforts.
My first priority during my five-day stay in Al-Ula was a visit to Hegra.
Like Petra , its better-known counterpart in Jordan, Hegra was built by the Nabateans, an ancient people who flourished 2,000 years ago. The site contains more than 100 tombs that were carved from solid rock, their entrances adorned with embellishments. Most impressive among them, set apart and standing some 70 feet tall, is a tomb colloquially called the Lonely Castle.
Not long ago, visitors could hire private guides and wander the area on foot, climbing in and out of — and no doubt damaging — the many tombs. Not anymore: I boarded an air-conditioned tour bus and zipped past most of them, stopping at just four locations.
At the penultimate stop, we exited the bus and trudged several hundred feet along a sandy path to the front of the Lonely Castle. Even in the late afternoon, the heat was stifling. I craned my neck to take in the details of the sculpted facade, which emerged like a mirage from one side of a massive boulder: its four pilasters, the rough chisel marks near the bottom, its characteristic five-stepped crown. Ten minutes evaporated, and I turned to find my group being shepherded back onto the bus. I jogged through the sand to catch up.
A few miles north of Hegra, I hopped in the back of a Toyota Land Cruiser — accompanied by an Italian graduate student and his mother — for a drive through the sandy expanse of the Sharaan Nature Reserve.
The scenery was sublime: Slipping through a narrow slot canyon, we emerged into a vast, open desert plain, then settled into a wide valley enclosed by an amphitheater of cliffs. Occasionally our guide stopped and led us on short hikes to petroglyphs, some pockmarked by bullet holes, or to lush fields of wildflowers, where he plucked edible greens and invited us to sample their lemony tang.
Gabriele Morelli, the graduate student, had first come to Al-Ula a few years ago — a different era, he said, given how quickly the place had transformed. He described a version that no longer exists, rife with cheap accommodation, lax rules and a free-for-all sensibility.
Some of the changes, of course, have been necessary to protect delicate ecosystems and archaeological sites from ever-growing crowds. But several people I met in Al-Ula — Saudis and foreigners alike — quietly lamented the extent of the high-end development and the steady erosion of affordability. Many of the new offerings, like the Banyan Tree resort, they pointed out, are luxury destinations that cater to wealthy travelers.
These hushed criticisms were among my early lessons on how difficult it can be to gauge the way Saudis feel about the pace and the pervasiveness of the transformations reshaping their society.
I got a taste of Al-Ula’s exclusivity — and of the uncanniness that occasionally surfaced throughout my trip — at a Lauryn Hill concert in an event space called Maraya . To reach the hall, I passed through a security gate, where an attendant scanned my e-ticket and directed me two miles up a winding road into the heart of the Ashar Valley, home to several high-end restaurants and resorts.
Rounding the final bend, I felt as if I’d stumbled into a computer-generated image: Ant-size humans were dwarfed by a reflective structure that both asserted itself and blended into the landscape. Inside, waiters served hors d’oeuvres and brightly colored mocktails to a chic young crowd.
The surreality peaked when, midway through the show, I left my plush seat to join some concertgoers near the stage — only to turn and see John Bolton, former President Donald J. Trump’s national security adviser, seated in the front row.
Where else, I wondered, could I attend a rap concert in the middle of the desert with a longtime fixture of the Republican Party — amid a crowd that cheered when Ms. Hill mentioned Palestine — but this strange new corner of Saudi Arabia?

The mirrored facade at Maraya, a vast event space in Al-Ula, warps and reflects the surrounding desert landscape.
The building is in some ways a precursor to the kingdom’s most ambitious architectural design: the project at Neom called the Line, a 106-mile linear city that will also feature a mirrored surface.
Lauryn Hill performing in front of a large crowd at Maraya.
After Al-Ula, I drove to another of the kingdom’s extravagant schemes: the Red Sea project, billed as the “world’s most ambitious regenerative tourism destination.” After weaving through a morass of construction-related traffic, I boarded a yacht — alongside a merry band of Saudi influencers — and was piloted some 15 miles to a remote island, where I disembarked in a world of unqualified opulence at the St. Regis Red Sea Resort .
I was chauffeured around in an electric golf cart — past 43 beachside “dune” villas and onto two long boardwalks that connect the rest of the resort to 47 “coral” villas, built on stilts over shallow turquoise water. Along the way, I listened to Lucas Julien-Vauzelle, an executive assistant manager, wax poetic about sustainability. “We take it to the next level,” he said, before rattling off a list of facts and figures: 100 percent renewable energy, a solar-powered 5G network , plans to enhance biologically diverse habitats.
By 2030, he said, the Red Sea project will offer 50 hotels across its island and inland sites. Citing the Maldives, he mentioned the kingdom’s plans to claim a share of the same high-end market.
Another prediction came by way of Keith Thornton, the director of restaurants, who said he expects the resort to legally serve alcohol by the end of the year. (While a liquor store for non-Muslim diplomats recently opened in Riyadh, the Saudi government has made no indication that it plans to reconsider its broader prohibition of alcohol.)
The hotel was undeniably impressive. But there’s an inescapable irony to a lavish resort built at unfathomable expense in the middle of the sea — with guests ferried out by chartered boat and seaplane — that flaunts its aspirations for sustainability.
Toward the end of my several-hour visit, I learned that every piece of vegetation, including 646 palm trees, had been transplanted from an off-site nursery. Later, reviewing historical satellite images, I found visual evidence that the island — described to me as pristine — had been dramatically fortified and, in the process, largely remade. Its footprint had also been significantly altered. It was, in a sense, an artificial island built where a smaller natural island once stood.
Something else struck me, too: The place was nearly empty, save for the staff and the Saudi influencers. Granted, the resort had just opened the month before — but the same was true at the nearby Six Senses Southern Dunes , an inland Red Sea resort that opened in November. Fredrik Blomqvist, the general manager there, told me that its isolated location in a serene expanse of desert — part of its appeal — also presented a challenge in drawing customers. “The biggest thing,” he said, “is to get the message out that the country is open.”
Since the country began issuing tourist visas, influencers have been documenting their experiences in places like Jeddah and Al-Ula, their trips often paid for by the Saudi government. Their breezy content contributes to the impression that the kingdom is awaiting discovery by foreign visitors with out-of-date prejudices. To an extent, for a certain segment of tourists, that’s true.
For many travelers, though, the depiction of the kingdom as an uncomplicated getaway could be dangerously misleading.
Speech in Saudi Arabia is strictly limited; dissent is not tolerated — nor is the open practice of any religion other than the government’s interpretation of Islam. In its travel advisory , the U.S. Department of State warns that “social media commentary — including past comments — which Saudi authorities may deem critical, offensive, or disruptive to public order, could lead to arrest.” Punishment for Saudi nationals has been far worse: In 2023, a retired teacher was sentenced to death after he criticized the ruling family via anonymous accounts. As of late 2023, he remained in prison.
Other restrictions are harder to parse. L.G.B.T.Q. travelers are officially welcome in the kingdom but face a conundrum: They might face arrest or other criminal penalties for openly expressing their sexual orientation or gender identity. As recently as 2021, an independent U.S. federal agency included Saudi Arabia on a list of countries where same-sex relationships are punishable by death , noting that “the government has not sought this penalty in recent years.”
When asked how he would convince a same-sex couple that it was safe to visit, Jerry Inzerillo, a native New Yorker and the group chief executive of Diriyah, said: “We don’t ask you any questions when you come into the country or when you leave.”
“Maybe that’s not conclusive enough,” he added, “but a lot of people have come.”
Female travelers might also face difficulties, since advancements in women’s rights are not equally distributed throughout the kingdom.
The changes were more visible in big cities and tourist centers. Ghydda Tariq, an assistant marketing manager in Al-Ula, described how new professional opportunities had emerged for her in recent years. Maysoon, a young woman I met in Jeddah, made extra money by occasionally driving for Uber. Haneen Alqadi, an employee at the St. Regis Red Sea, described how women there are free to wear bikinis without fear of repercussions.
Outside such places, though, I sometimes went for days without seeing more than a handful of women, invariably wearing niqabs, let alone seeing them engaged in public life or tourism. My photographs reflect that imbalance.
As an easily identifiable Western man, I moved through the country with an array of advantages: the kindness and cheery curiosity of strangers, the ease of passage at military checkpoints, and the freedom to interact with a male-dominated society at markets, museums, parks, restaurants, cafes. Not all travelers could expect the same treatment.
Roaming in the far north and south, I often found the earlier version of the kingdom — with lax rules and less development — that had been described to me in Al-Ula.
I trekked to the northern city of Sakaka to see an archaeological site promoted as the Stonehenge of Saudi Arabia: a set of monoliths called the Rajajil Columns thought to have been erected some 6,000 years ago but about which little is definitively known.
My heart sank when I pulled into the parking lot after a five-hour drive and found the columns blocked by a tall fence. Approaching on foot, though, I noticed that a section of the fence had been peeled back and that visitors were wandering freely among the stones, which protruded from the earth like isolated clusters of crooked teeth. I joined the small crowd, if hesitatingly, and was surprised to find no footpaths, nor anything to keep us a safe distance from the columns. In the end I wondered if our access had been officially approved or informally arranged.
My travel experiences were sometimes awkward in other ways, too.
Standing just outside the grounds of the central mosque in Medina, where the Prophet Muhammad is buried, I was detained by a stern member of the Special Forces. (Even after 2019, non-Muslim tourists remained barred from Mecca and Medina, Islam’s two holiest cities. The ban was relaxed in parts of Medina in 2021.)
The guard interrogated me and, after calling a colleague to confer, demanded that I leave the area. “Go,” he said threateningly. Another traveler who witnessed the encounter scurried away to avoid a similar fate.
The unsettling exchange cast a pall over my time in the city, which few non-Muslims have seen. As far as I knew, I’d abided by the rules by staying outside the grounds of the Prophet’s Mosque — a boundary line that I’d confirmed with tourism officials beforehand.

Peering through the perimeter fence — the boundary line for non-Muslims — at the Prophet’s Mosque in Medina.
The Mosque of Al-Ghamamah, one of the oldest in the holy city.
A sprawling maze of ramshackle residential buildings sits less than a mile from the Prophet’s Mosque.
A guide speaking to a group of visitors near the Hejaz Railway Museum, visible in the distance. (The museum was closed for renovations at the time.)
A group of young men, most of whose families emigrated from Sudan, playing soccer in a field just outside the center of Medina.
More than anything, family and friends wanted to know if I felt safe on my trip — and I did, almost without exception. Petty crime in Saudi Arabia is exceedingly rare. And while parts of the country are under a Level 4 “Do Not Travel” advisory , even my rambling itinerary was approved by a security expert.
Instead of fearing for my safety, I was often preoccupied with how I’d fairly portray a place that elicited such a range of conflicting emotions: joy and distress, excitement and apprehension, sincerity and doubt. So much lay hidden from public view — like the collective anguish over the war raging in Gaza . And so little was easy to categorize, in part because the warmth of everyday Saudis was strikingly at odds with the ruthlessness of their authoritarian government.
In Riyadh, a young man warned me not to speak openly with strangers. “People get arrested here for a tweet ,” he said. “Can you imagine?”
I could, actually. The Saudi columnist Jamal Khashoggi had chronicled his government’s increasingly draconian responses to criticism. “Repression and intimidation are not — and never should be — the acceptable companions of reform,” he wrote in The Washington Post in 2018, just months before he was killed and dismembered at his country’s consulate in Istanbul.

Were we to travel only where we feel comfortable and unchallenged, we’d all be poorer for it. But the question of whether to travel to Saudi Arabia is thornier than that.
It’s easy to see one response, “No,” as yielding to closed-mindedness at the expense of ordinary people — like the kindly vendor Abdullah, who served me local honey at his shop in the southern mountains.
But it’s easy, too, to see “Yes” as an affirmation that might makes right, that amusement outweighs morality, that princely wealth can wipe a stained slate clean.

Sunrise over the mountainous village of Fayfa, some six miles from the Yemeni border.
Abdullah Ghaleb Zaid, a honey vendor, at his shop atop a mountain pass near the southern city of Abha.
Sunset near Jabal Soudah, the kingdom’s highest peak.
Ten days into my trip, I ventured to Wadi al-Disah, a steep-walled valley where I’d booked a tent at a campsite I found on Airbnb. For an additional 300 riyals ($80), my host, Faisal, led me on a four-wheel-drive tour, departing the paved road and weaving through a path along the bed of an ephemeral river. Continually jolted by the uneven terrain, we eased past thick reeds, lofty palms and small bands of visitors who’d nestled into clearings.
As we left, I met a group of young men gathered for a picnic, their sandals scattered around a carpet on which they were preparing their dinner. Delighted to meet an American with a camera, they asked if I’d take a group portrait, then exchanged information with me so I could send them a copy — a scenario by then so familiar that I hardly thought anything of it.
A full day later, some 200 miles away, I was cruising along a lonely highway near the Jordanian border when a Land Cruiser blew past me at an astonishing speed. I felt my compact car rock from its turbulence — and then I watched with a twinge of dread as the car abruptly braked, slowing hard in the left lane until our front ends were aligned. It held steady there.
For a moment I stared straight ahead, hoping to avoid a confrontation. When I finally turned to look, I saw a group of boys grinning wildly and waving through an open window. Then I realized: Improbably, it was three of the young men I’d met the day before. Somehow we’d all followed the same route. And somehow, in the split second it took them to fly past, they’d recognized me. I lifted my camera from the passenger seat and snapped a photograph.
The picture shows three young Saudis on a precipice: endearing, erratic, captivating. I have a sense of where they came from but no certainty about where they’re going. Two are flashing peace signs, and none appears to be wearing a seatbelt. No one is watching the road as their car drifts out of its lane, careening a little recklessly into a hopeful and uncertain future.
Stephen Hiltner’s recent work includes a photo essay about his childhood in Budapest , an examination of A.I.-generated guidebooks and an investigation into the deaths of Russian soldiers in Ukraine . You can follow his travels on Instagram .
Got a question about this story? Drop a note in the comments section. Got a tip? Send him an email .
Stephen Hiltner is an editor, writer and photographer for the Travel section of The Times. More about Stephen Hiltner
Open Up Your World
Considering a trip, or just some armchair traveling here are some ideas..
52 Places: Why do we travel? For food, culture, adventure, natural beauty? Our 2024 list has all those elements, and more .
The Alaska Highway: On an epic road trip, a family plots a course from Alaska to the Lower 48, passing through some of Canada’s most spectacular scenery .
Minorca: Spend 36 hours on this slow-paced Spanish island , which offers a quieter and wilder retreat than its more touristy neighbors.
Japan: A new high-speed train stop unlocks Kaga, a destination for hot springs, nourishing food and traditional crafts , as an easy-to-reach getaway from Tokyo.
London: The Victoria and Albert Museum is a treasure trove of art and design. Here’s one besotted visitor’s plan for taking it all in .
Advertisement

COMMENTS
Slum tourism sparks considerable debate around an uncomfortable moral dilemma. No matter what you call it—slum tours, reality tours, adventure tourism, poverty tourism—many consider the ...
A brief history of slum tourism. Whether called a township, a favela, a barrio, a slum, a shantytown, or a ghetto, outsiders recreationally visiting these typically impoverished places is nothing new.
Witness this. Sarah.Ahearn/Flickr, CC BY-ND. Slum tourism has the power to increase the visibility of poor neighbourhoods, which can in turn give residents more social and political recognition ...
In central Bangkok, Thai researchers found that residents of a 100-year-old slum used tourism as a means of staving off governmental plans for their eviction. And contrary to the common accusation ...
The slum tourism network presents two sessions at the Association of American Geographer Annual Meeting in Boston on Friday 7 April 2017 : 3230 The complex geographies of inequality in contemporary slum tourism. is scheduled on Friday, 4/7/2017, from 10:00 AM - 11:40 AM in Room 310, Hynes, Third Level.
Slum 1 tourism can be broadly defined as a variety of "activities undertaken by people of wealth, social standing, or education in urban spaces inhabited by the poor" (Koven, 2004, p. 9).The breadth of this definition stresses the variety of ways in which it is possible to cross into "other" spaces, without a priori distinguishing between more or less moral activities.
Our research offers stakeholders in slum tourism, including travel agencies and policymakers, valuable insights into operating slum tours in a more ethical way. Get full access to this article View all access and purchase options for this article.
This article provides a view on the state-of-the-art literature on slum tourism. It points to the rapid growth of slum tourism research in recent years and highlights the main avenues that ...
Mumbai's Dharavi slum occupies a plot half the size of Central Park. It is home to one million people, with almost half of residents living in spaces under 10 m 2, making it over six times as dense as daytime Manhattan.Using ethnographic fieldwork and online analysis, this article examines slum tourism and the perceptions and experiences of western visitors.
1. Introduction. Slum tourism (varyingly characterized as poverty, township, favela, reality, or cultural tourism) has been defined as tourism that involves visiting impoverished or deprived areas (Frenzel, 2016; Mekawy, 2012).This form of tourism was first formally enacted in South Africa and Brazil in the early 1990s, under the auspices of the social justice movements (Freire-Medeiros, 2013 ...
This article was an in-depth study of the situation of slum tourism in Dharavi, Mumbai's, and Asia's, largest slum area, based on the inquiries conducted via questionnaires given to city residents, in order to understand their opinion about this kind of niche tourism.
tial to connect Latin American and Caribbean studies on tourism and urban inequality. Slum tourism. involves transforming poverty, squalor and violence into a tourism product. Drawing on both altruism and voyeurism, this form of tourism is a complex phenomenon that raises various questions concerning. power, inequality and subjectivity.
Slum tourism as a topic of investigation has seen significant growth since the beginning of this decade with increasing theoretical and empirical depth. With this growth, some inconsistencies in conceptual framing and use of terminology have emerged. The purpose of this paper is to argue for township tourism in Soweto to be regarded as a form of heritage tourism rather than slum tourism—a ...
Fourthly, the history of slum tourism is shown to have implications for understanding present-day slum tourism in the Global South, using South Africa as an example. The article is designed to be a first step towards understanding the conditions, forms and consequences of globalization of slum tourism and the process of constructing the global ...
The widening scope and diversity of slum tourism is clearly reflected in the variety of papers presented at the conference and in this Special Issue. Whilst academic discussion on the theme is evolving rapidly, slum tourism is still a relatively young area of research. Most papers at the conference and, indeed, most slum tourism research as a ...
Mr. Cronin was briefly shaken when a man, "obviously drunk," rifled through his pockets, but the two-and-a-half-hour tour changed his image of India. "Everybody in the slum wants to work ...
122. Nairobi, Kenya. SLUM tourism has a long history during the late 1800s, lines of wealthy New Yorkers snaked along the Bowery and through the Lower East Side to see "how the other half lives ...
Slum tourism in Five Points, Manhattan in 1885. Slum tourism, poverty tourism, ghetto tourism or trauma tourism is a type of tourism that involves visiting impoverished areas, or in some cases, areas that were affected by disasters, such as nuclear fallout zones like Chernobyl or Fukushima (hence the term "trauma tourism"). Originally focused on the slums and ghettos of London and Manhattan in ...
Abstract:This Exploration focuses on the emerging field of slum tourism research, which has the potential to connect Latin American and Caribbean studies on tourism and urban inequality. Slum tourism involves transforming poverty, squalor and violence into a tourism product. Drawing on both altruism and voyeurism, this form of tourism is a complex phenomenon that raises various questions ...
Slum tourism is related to a number of cultural and social forms that also address the poor-nonpoor relationship, including literature, film, and art. The economic impact of slum tourism has been discussed mainly with regard to the narrow definition of slum tourism as commoditized tours of poor neighborhoods. More recent approaches to slum ...
Slum tourism, referring to trips, leisure, and other activities conducted by wealthy people in spaces inhabited by disadvantaged populations, is highly controversial. On the one hand, there is the risk of exploitation and dehumanization of slum dwellers; on the other hand, it can help fighting stereotypes and stigmatization. We explore the ...
An article published in India Outlook in July 2019 announced to its readers that Dharavi, the biggest slum of Mumbai, and one of the largest slums in the world (Monroe & Bishop, Citation 2016), has now beaten the Taj Mahal as the most popular tourist destination in India.While acknowledging the long history of slum tourism, the article claimed that both Hollywood and Indian films had played a ...
Reality Tours and Travel are another company offering slum tours. As the company name suggests, they hope to offer a 'realistic' side to the places tourists visit. Based in India, a country with a lot of poverty, their slogan is 'USING TOURISM TO CHANGE LIVES'.They say: Our ethical and educational Dharavi slum tours give visitors a unique glimpse into everyday life for many Mumbaikars ...
An editor and photojournalist for the Travel section, Stephen Hiltner drove 5,200 miles and visited all 13 of Saudi Arabia's provinces while reporting and shooting this story. June 5, 2024 ...